epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
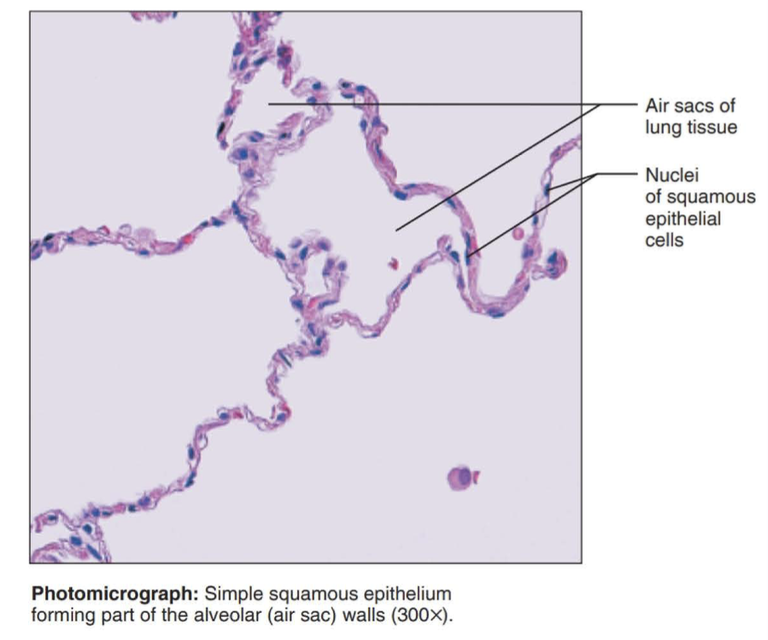
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells
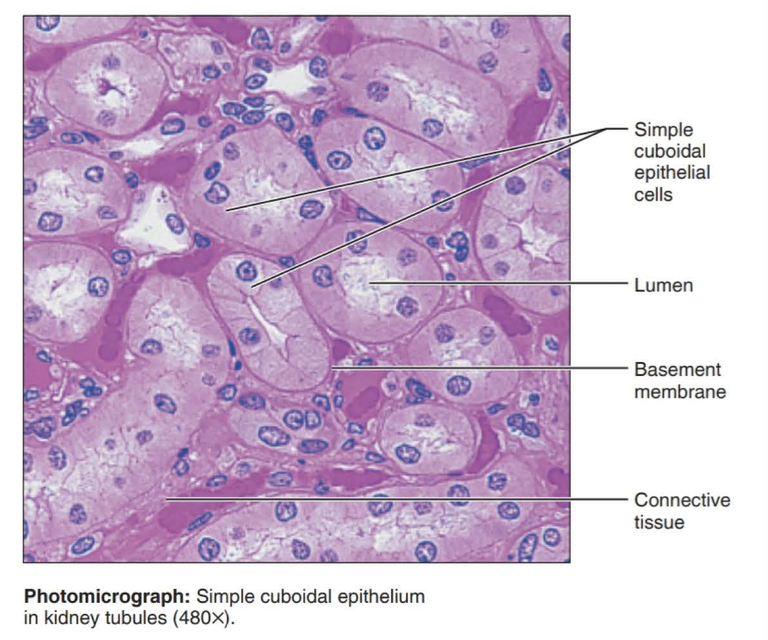
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped cells
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells bear cilia; layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells)

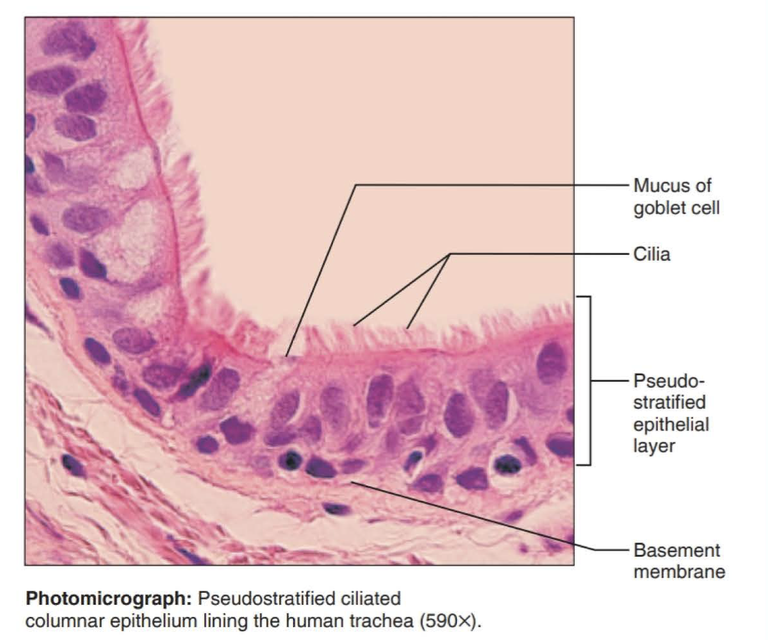
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and sized cells that give the appearance of multiple layers; found in ducts of certain glands and the upper respiratory tract
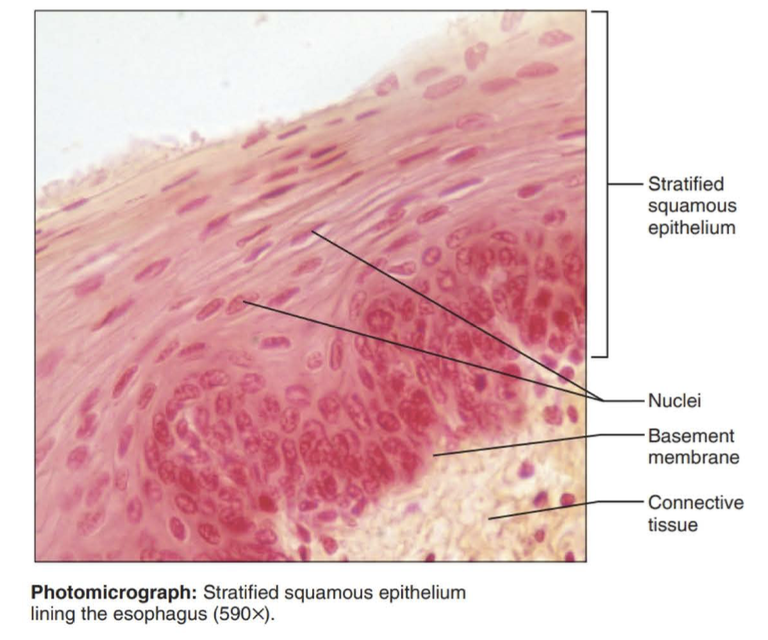
stratified squamous epithelium
Function: protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
Location: nonkeratinized type forms the moist lining of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized type forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane.
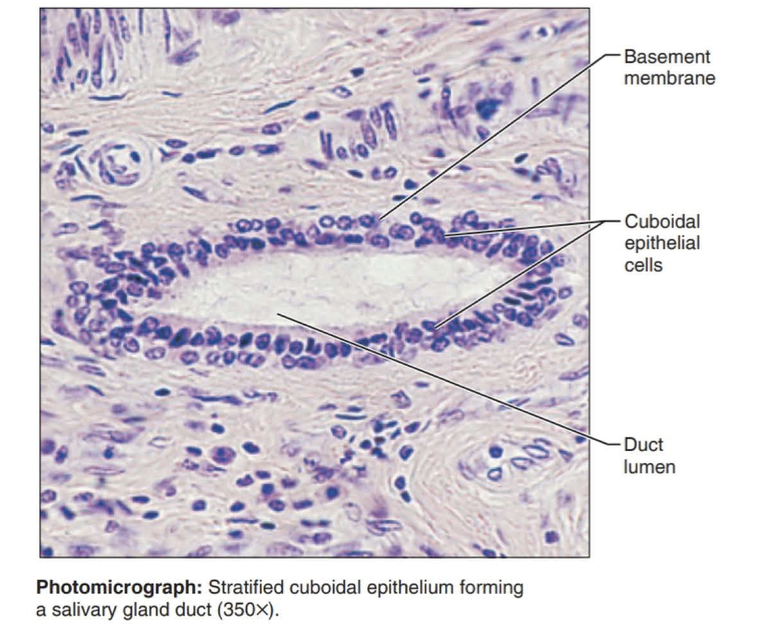
stratified cuboidal epithelium
Function: protection
Location: Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
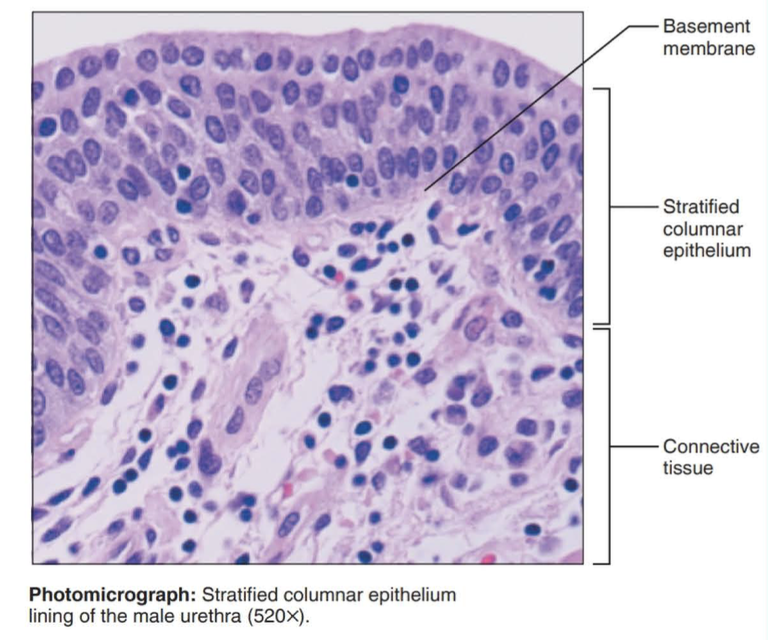
stratified columnar epithelium
Function: protection and secretion
Location: rare in the body; small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
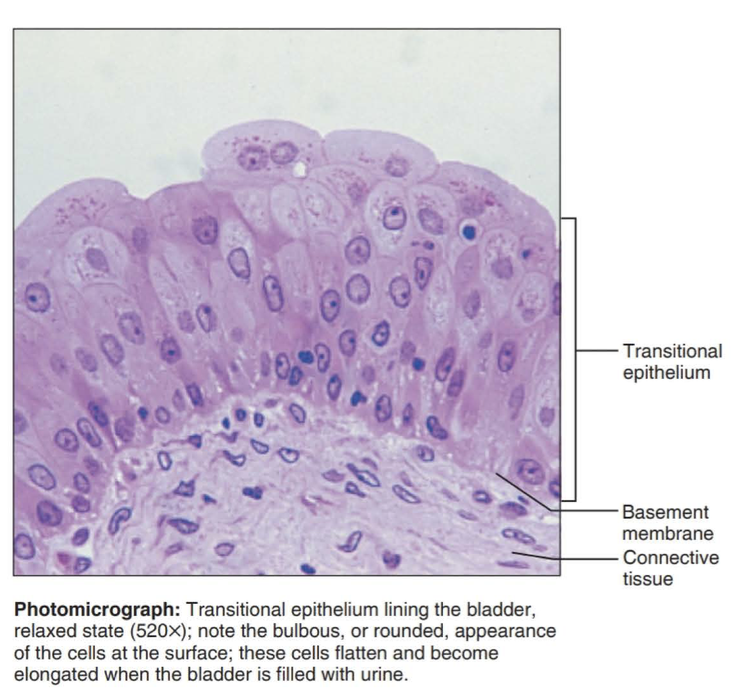
transitional epithelium
function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
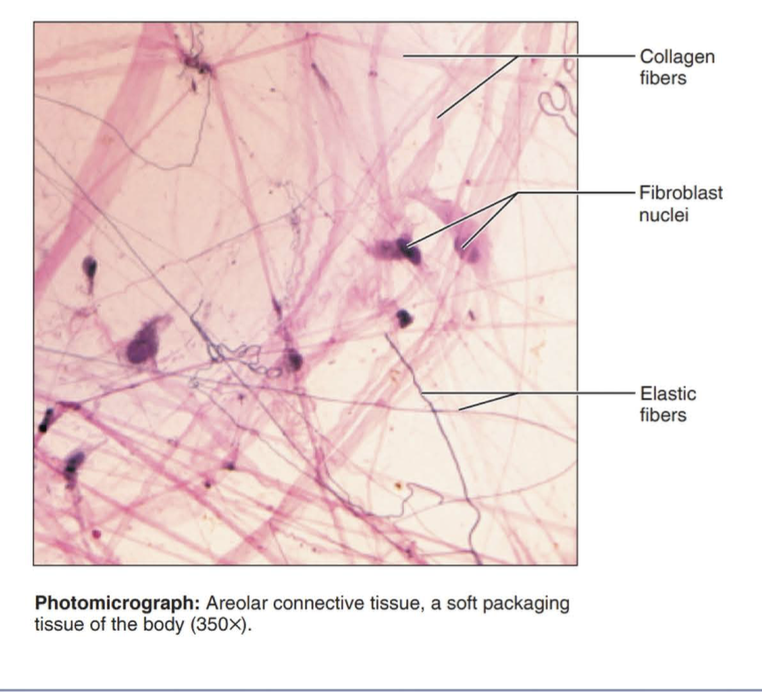
areolar connective tissue
Function: wraps and cushions organs
Location: widely distributed under epithelia of body
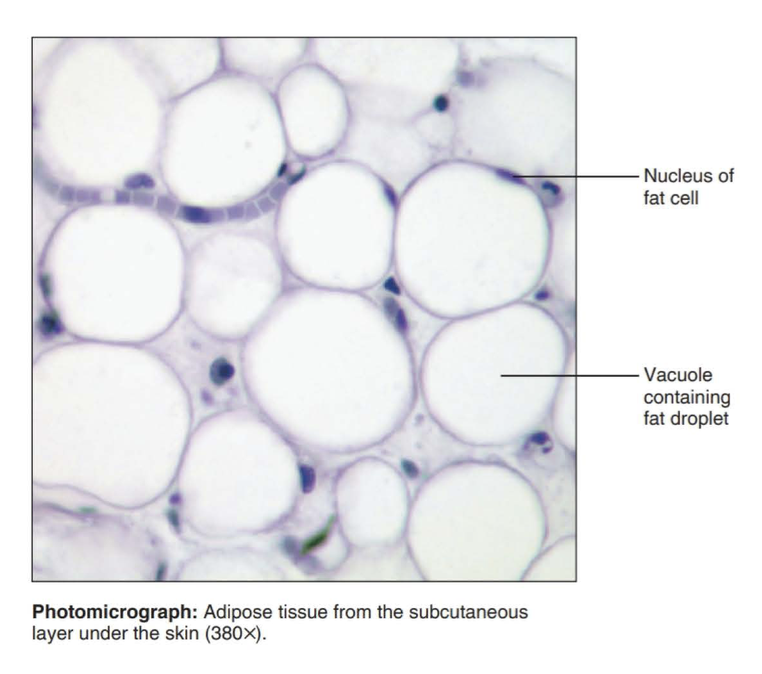
adipose connective tissue
acts as a storage depot for fat
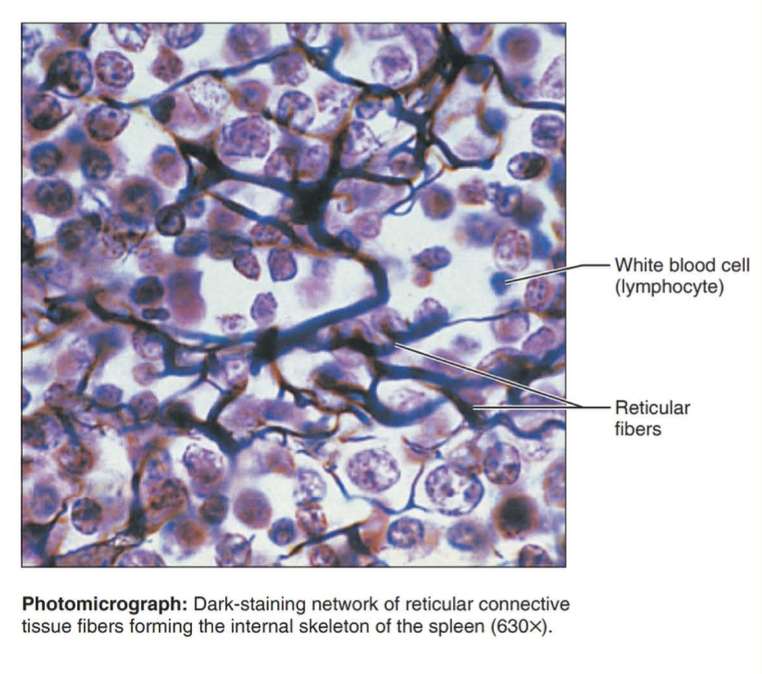
reticular connective tissue
fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
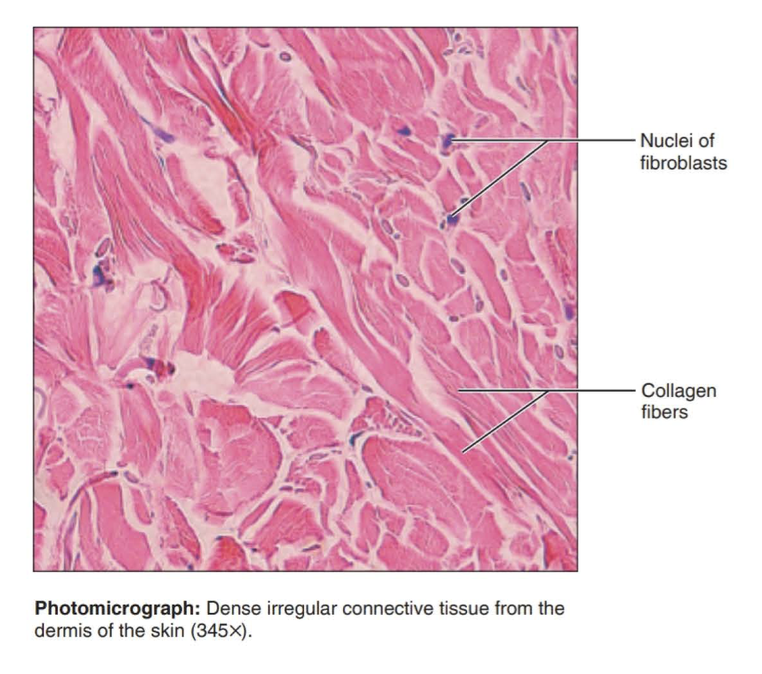
dense irregular connective tissue
Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
Location: fibrous capsules of organs and joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract
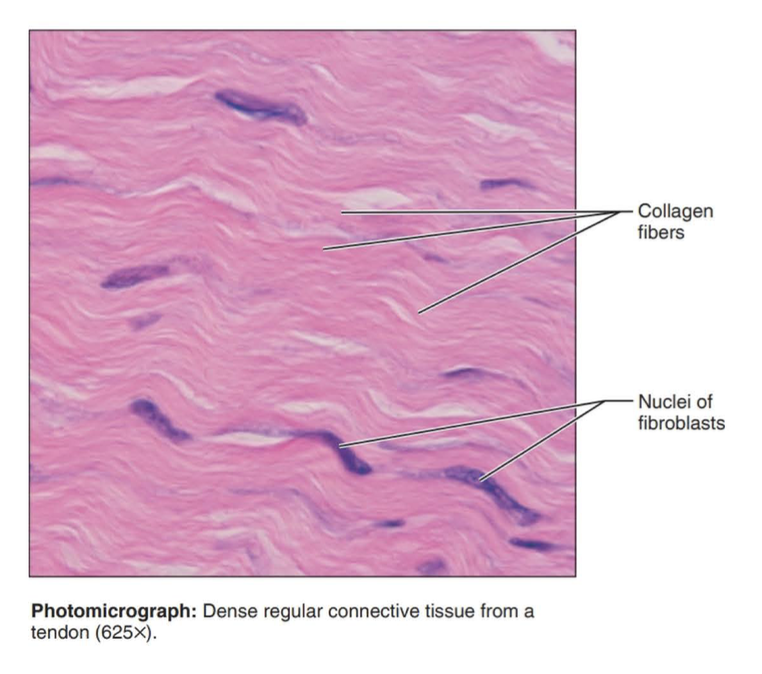
dense regular connective tissue
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
Location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
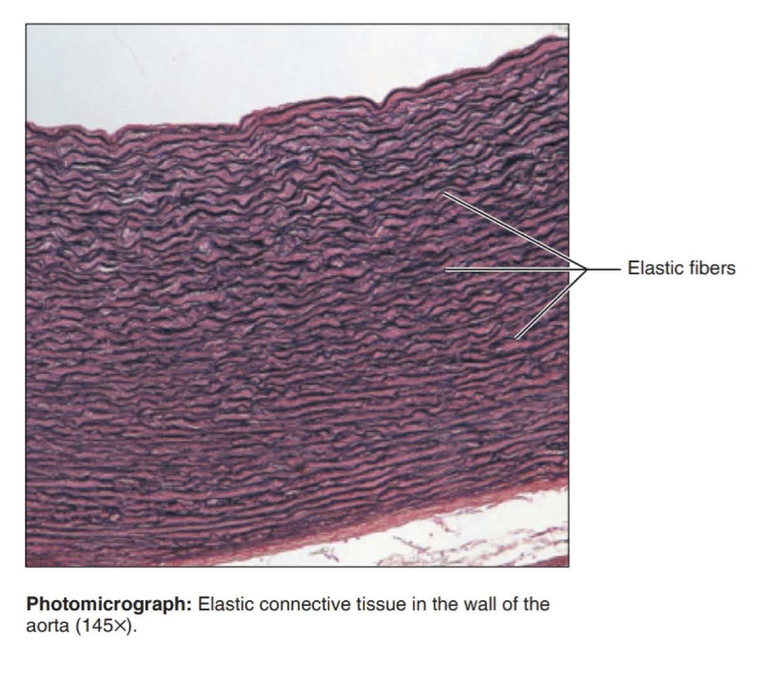
elastic connective tissue
Function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
Location: walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with vertebral column, within the walls of the bronchial tubes
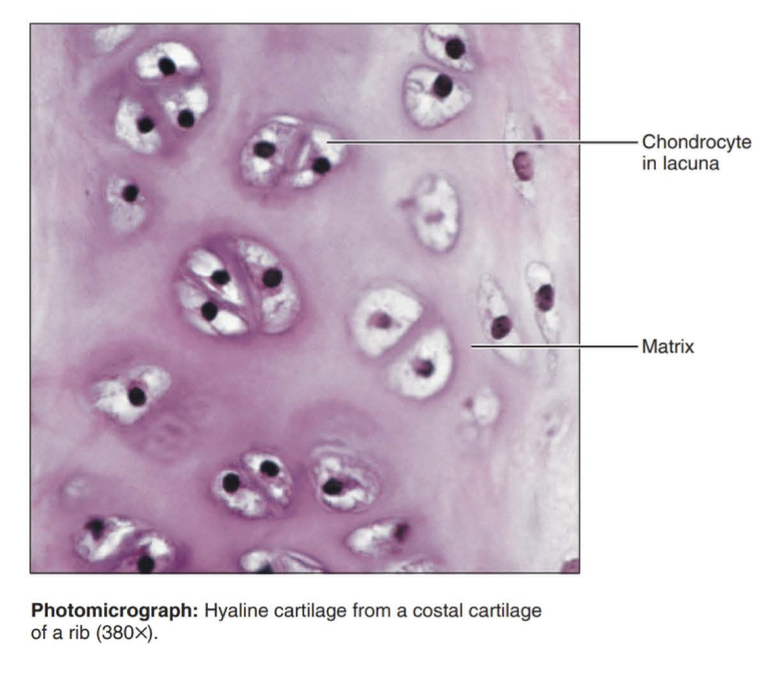
hyaline cartilage
Amorphous but firm matrix; collagen fibers form an imperceptible network; chondroblasts produce the matrix and when mature (chondrocytes) lie in lacunae
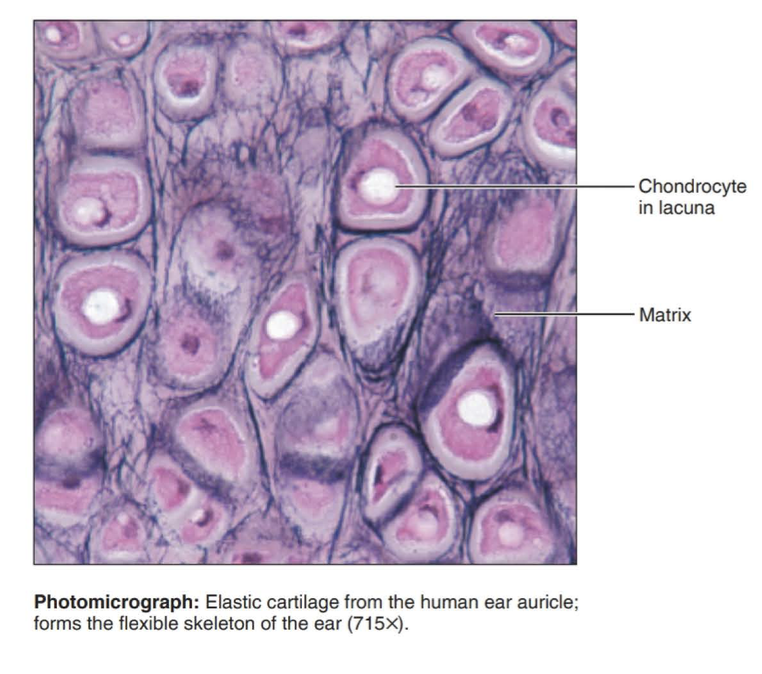
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
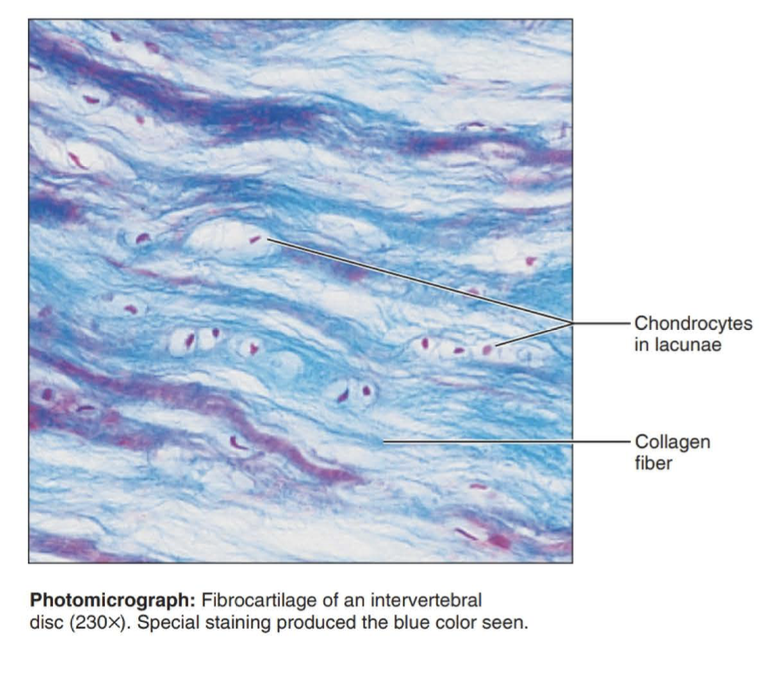
Fibrocartilage
cartilage that contains fibrous bundles of collagen, such as that of the intervertebral disks in the spinal cord.
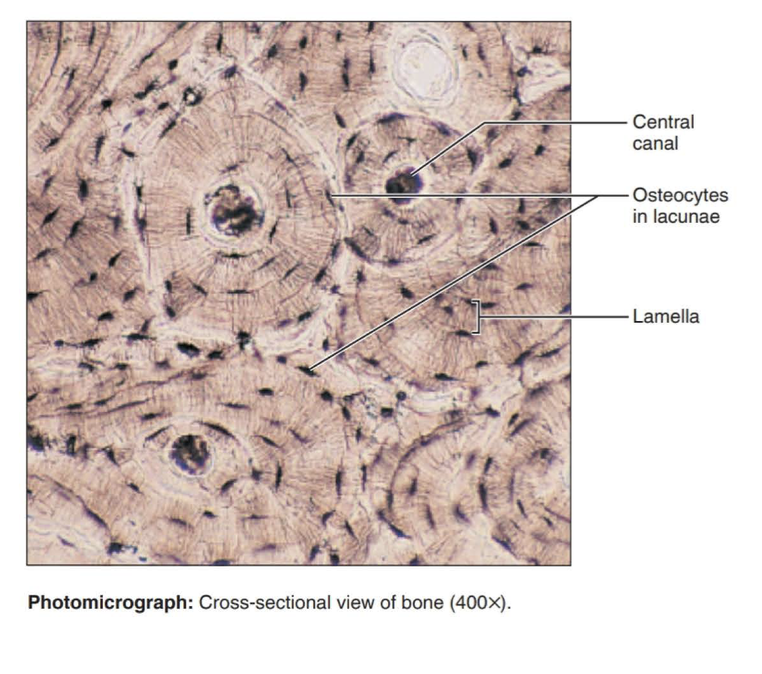
Bone (osseous tissue)
Hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in lacunae. Very well vascularized.
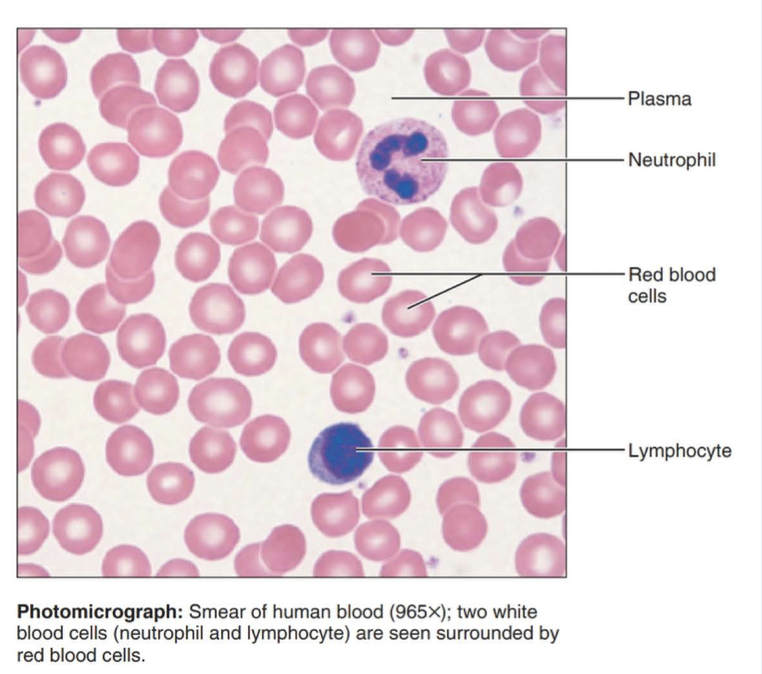
blood
A connective tissue with a fluid matrix called plasma in which red blood cells, white blood cells, and cell fragments called platelets are suspended.
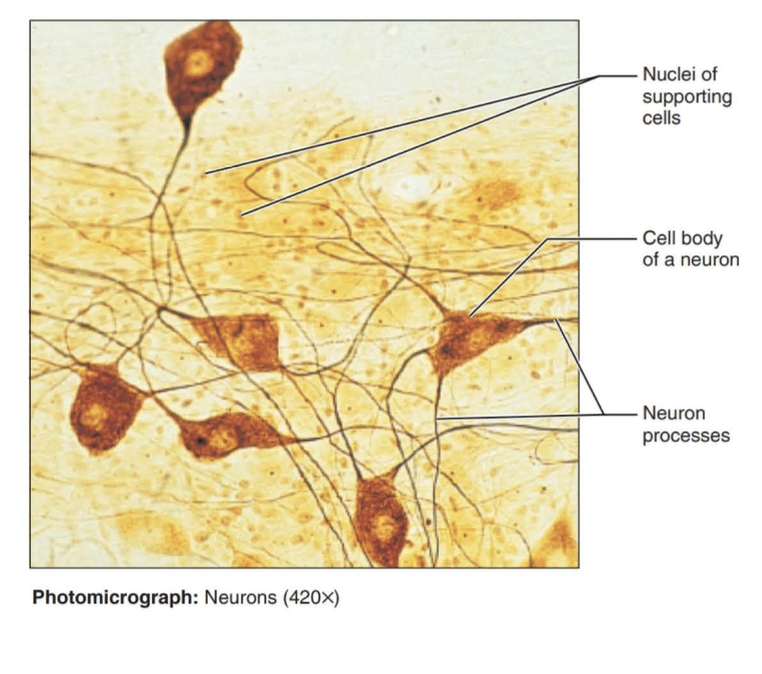
nervous tissue
A body tissue that carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body.
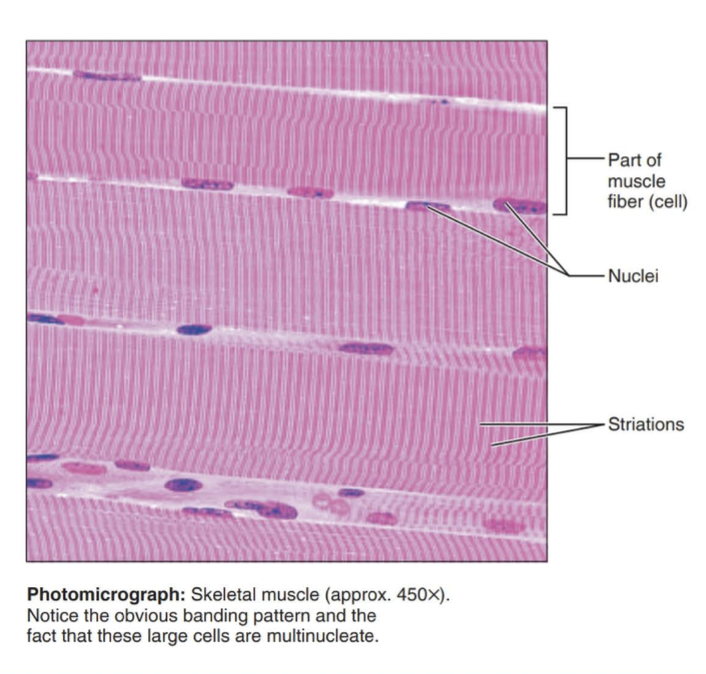
skeletal muscle
Long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells; obvious striations.
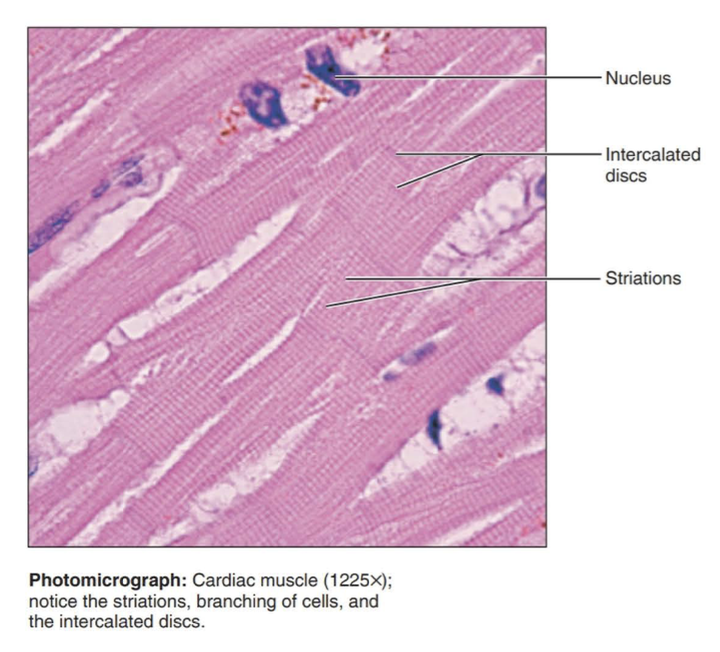
cardiac muscle
Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate at specialized junctions called intercalated discs.
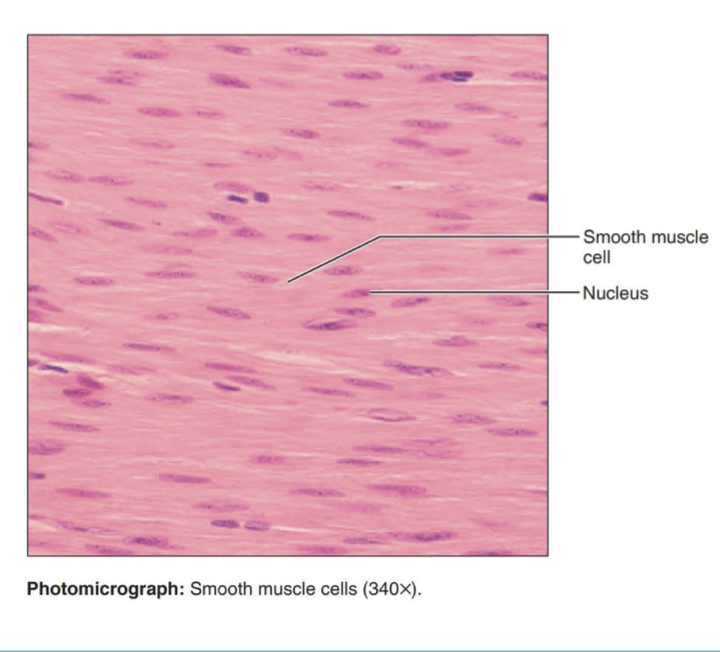
smooth muscle
Spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets.