QC Lab - Experiment 1: Preparation Test Solutions and Indicator
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
test solutions
TS
•A solution of a reagent in a specified strength, used in chemical analysis or testing
pH
- power of hydrogen
-developed by Soren Sorensen (danish scientist) = easier system for indicating the concentration of hydrogen ions
pH scale
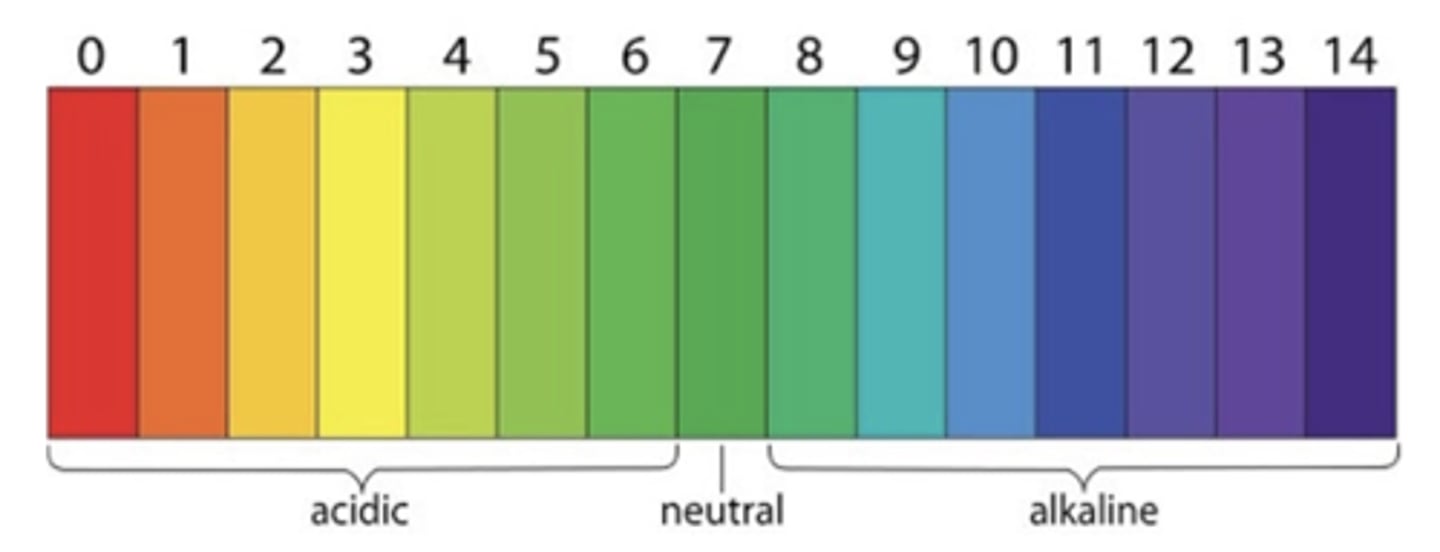
acidic
0-6 = high concentration of H ions
- bronsted-lowry theory: proton donor
neutral
7 = equal concentration of H and Hydroxyl ions
basic/alkaline
7-14 = low concentration of H but high concentration of OH (hydroxyl ions)
- bronsted-lowry theory: proton acceptor
indicator
•A substance that changes color in response to a chemical change.
•complex organic compounds used:
✔️_ To determine the end points in neutralization process
ü_ To determine the hydrogen ion concentration
ü_ To indicate that the desired change in pH has been effected
•A drop of ? solution is added to titration in the beginning and the change of color signifies that the reaction is completed.
•The ? changes color when the reaction has reached the equivalence point or stoichiometric point
- will change color if pH is within pH scale
rules for indicators
•Use 3 drops of indicator test solution for a titration unless otherwise directed
•When a strong acid is titrated with a strong alkali, or a strong alkali with a strong acid, Methyl Orange, Methyl Red, or Phenolphthalein may be used
•When a weak acid is titrated with a strong alkali, use phenolphthalein
•When a weak alkali is titrated with a strong acid, use methyl red
•A weak alkali should never be titrated with a weak acid and vice versa, since there will not be a sharp end point.
•Presence of a color is more easily observable compared to a disappearance of a color, titrate to a color.
strong acid + strong base (vv)
(titrate) methy red, methyl orange, phenolphthalein
weak acid + strong base
Phenolphthalein
strong acid + weak base
methyl red
weak acid + weak base (vv)
never titrate because endpoint will not be sharp
colorless = colored (always)
malachite green
0.0-2.0
acid: yellow
base: green
methyl yellow
2.9-4.0
acid: red
base: yellow
bromophenol blue
3.0-4.6
acid: yellow
base: blue
methyl orange
3.2-4.4
acid: pink
base: yellow
bromocresol green
4.0-5.4
acid: yellow
base: blue
methyl red
4.2-6.2
acid: red
base: yellow
bromocresol purple
5.2-6.8
acid: yellow
base: purple
bromothymol blue
6.0-7.6
acid: yellow
base: blue
phenol red
6.8-8.2
acid: yellow
base: red
cresol red
7.2-8.8
acid: yellow
base: red
thymol blue
8.0-9.2
acid: yellow
base: blue
phenolphthalein
8.0-10 (basic medium)
acid: colorless
base: pink
thymolphthalein
9.3-10.5
acid: colorless
base: blue