Small Animal Wounds
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
where does a wound often get stuck
at granulating
how do you describe the stage a wound is at
Describe the stage of wound healing by the colour

what colour is necrotic
back
what colour is sloughy
yellow
what colour is granulating
red
what colour is epithelialisation
light pink
at sloughing
dry out as overly wet
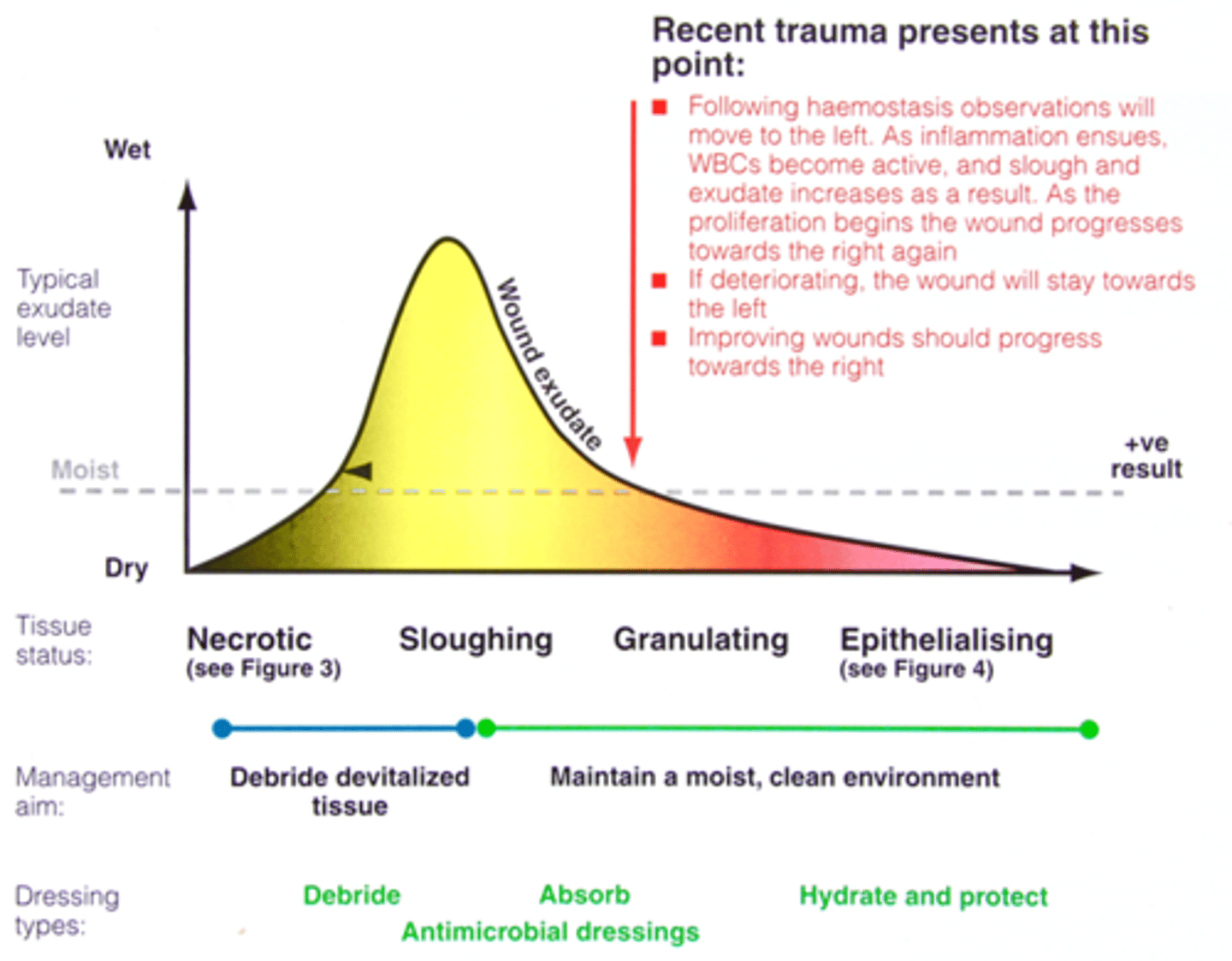
at granulating and epithelialising
add dressing with moisture as dry
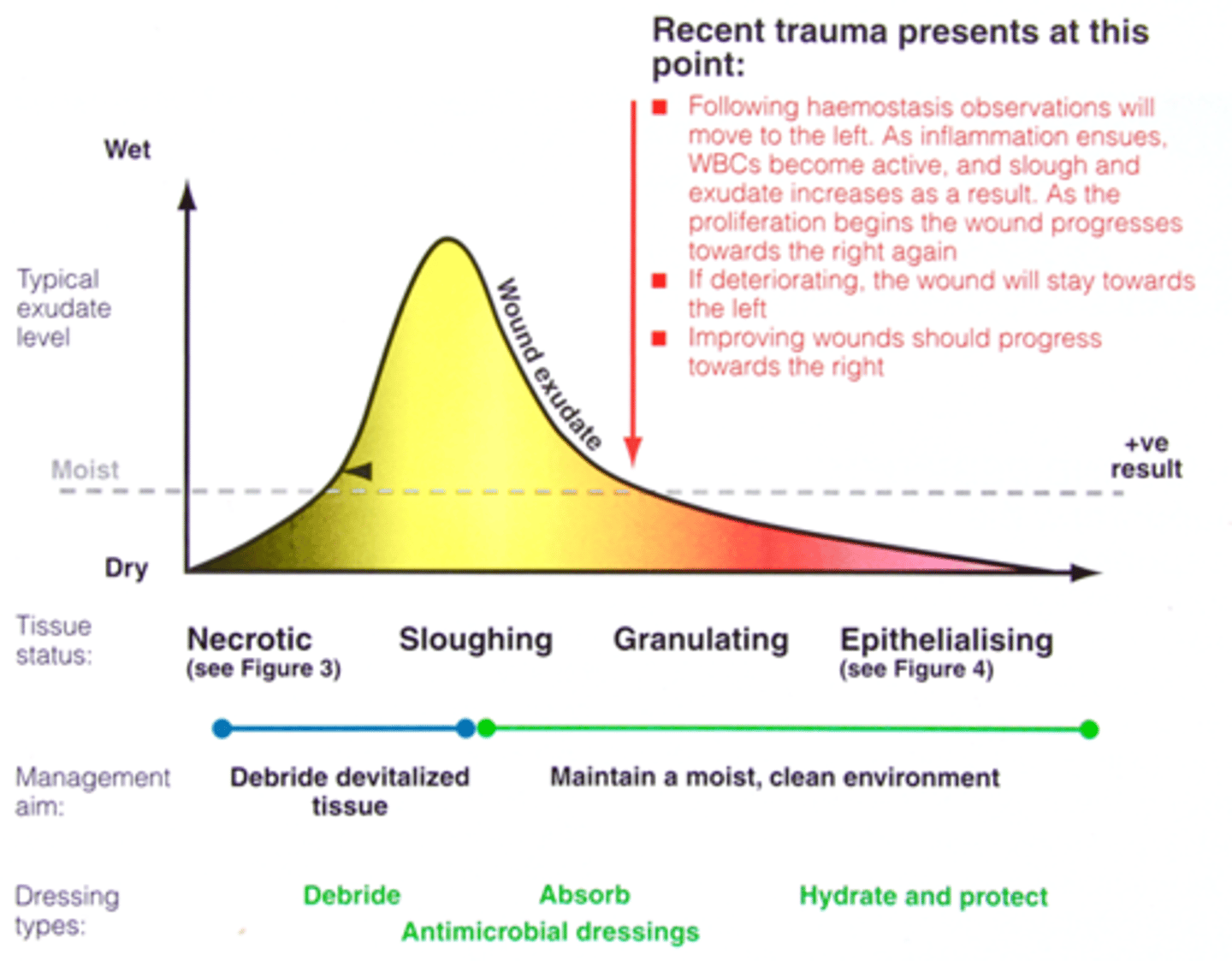
recent trauma presents as
-between granulating and sloughing
-following haemostasis observations will move to left. as inflam ensues, WBCs become active and slough and exudate increase as result. as proliferation begins, wound progresses towards right again
-if deteriorating, wound will stay towards left
-improving wounds should progress to right
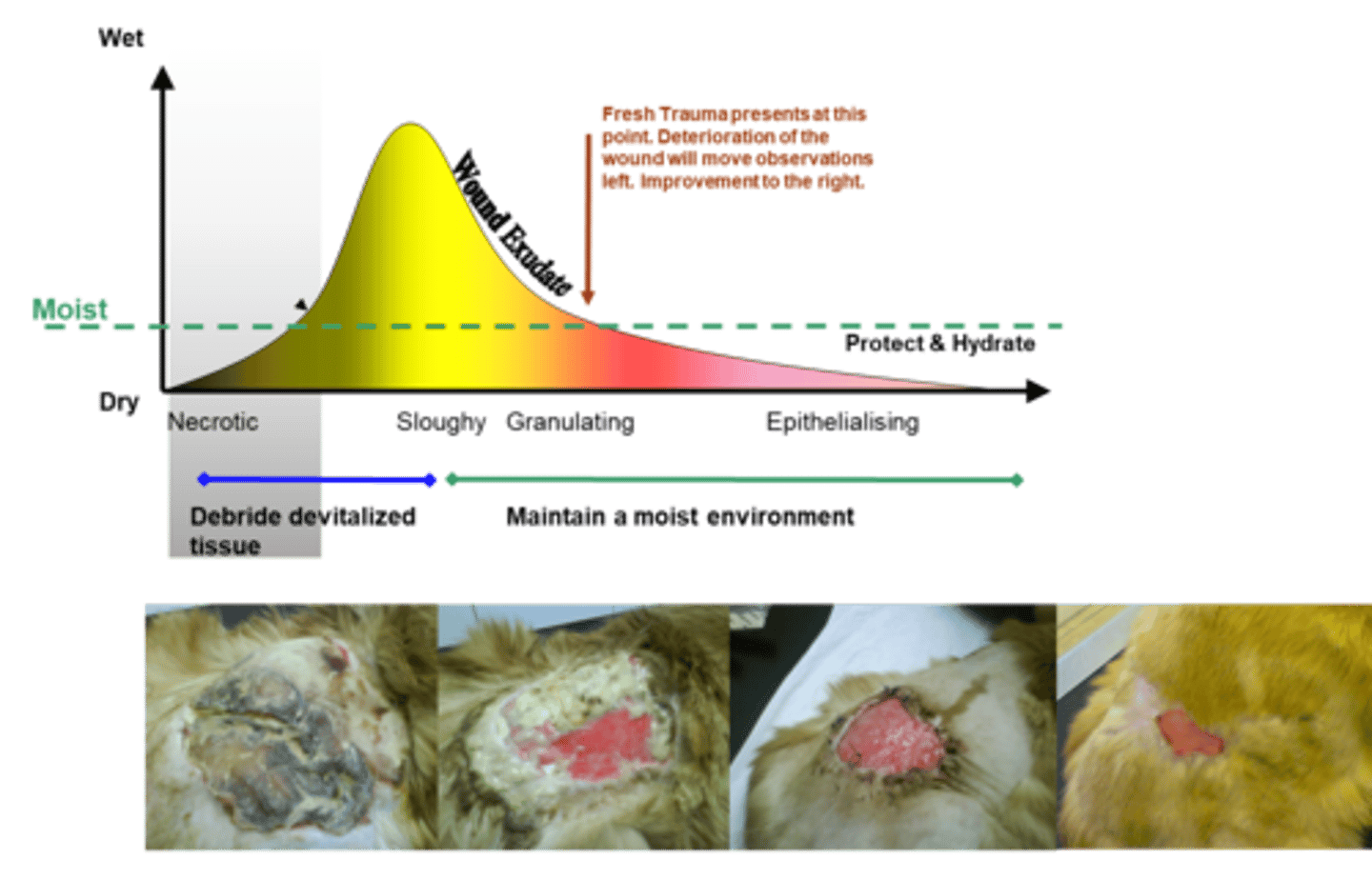
options with healthy granulation bed
-secondary intention healing
-tertiary intention healing
-bring in new epithelium with pinch/punch graft or free skin graft
key to wound healing
healthy granulation bed
where does epithelisation come from
epithelium
what is the main aim in chronic wound
get to state of healthy granulation bed in chronic wound
Bc then have options
what must be done to necrotic tissue
debride to remove it
what happens to the wound at epithelialisation
wound contracts and gets smaller
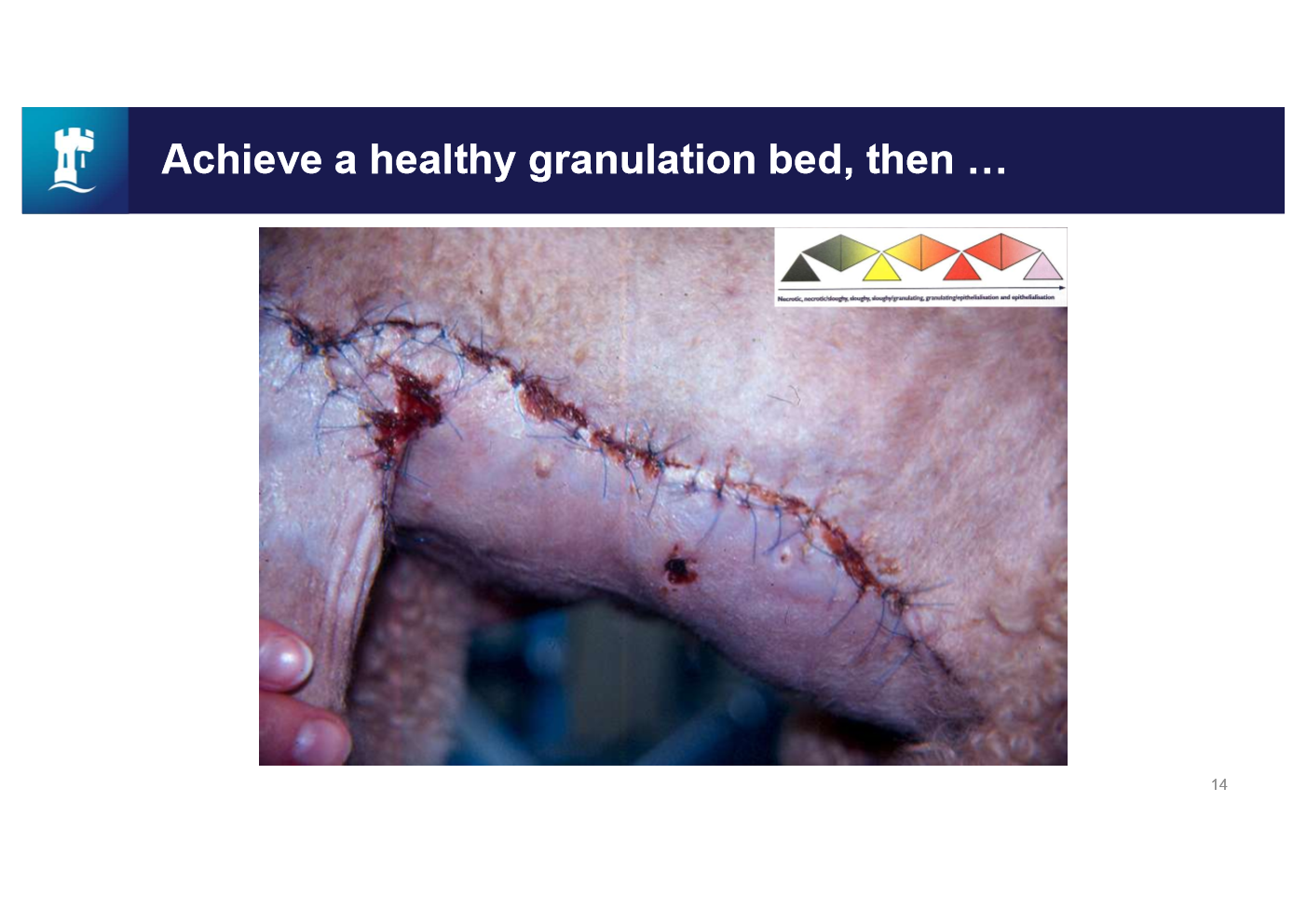
what has happened here
Has been undermined and placed over
So will heal quicker than leaving for secondary intention
The costs might be less
why might we choose not to dress wounds
can be costly and means lots of trips to vet so stress
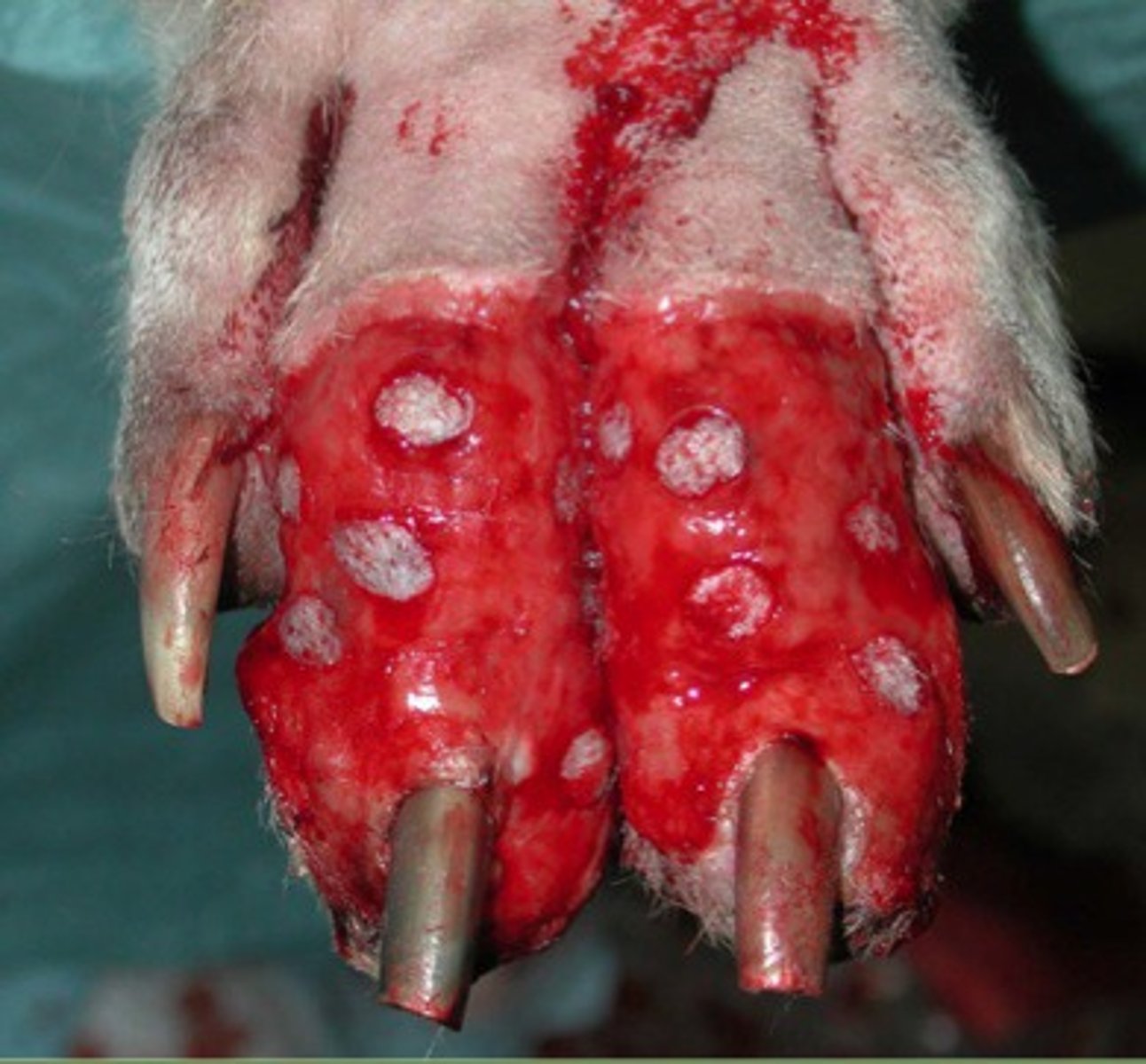
what are pinch/ punch grafts and why
use tool
Take subcut fat off it and place into granulation tissue
Bringing more epithelium-> epithelisation is quicker bc epithelium edge is bigger
pinch/punch grafts indications
Indications:
- granulating wounds
- small wounds
- contaminated wounds or low grade infection
- wounds over areas not requiring durability
- irregular contour
-Bed pockets: 2-4 mm deep, 5-7 mm apart with scalpel blade
- Pockets for punch: 1-2 cm apart, 4mm bx punch
- change first bandage 3-4 days post-op
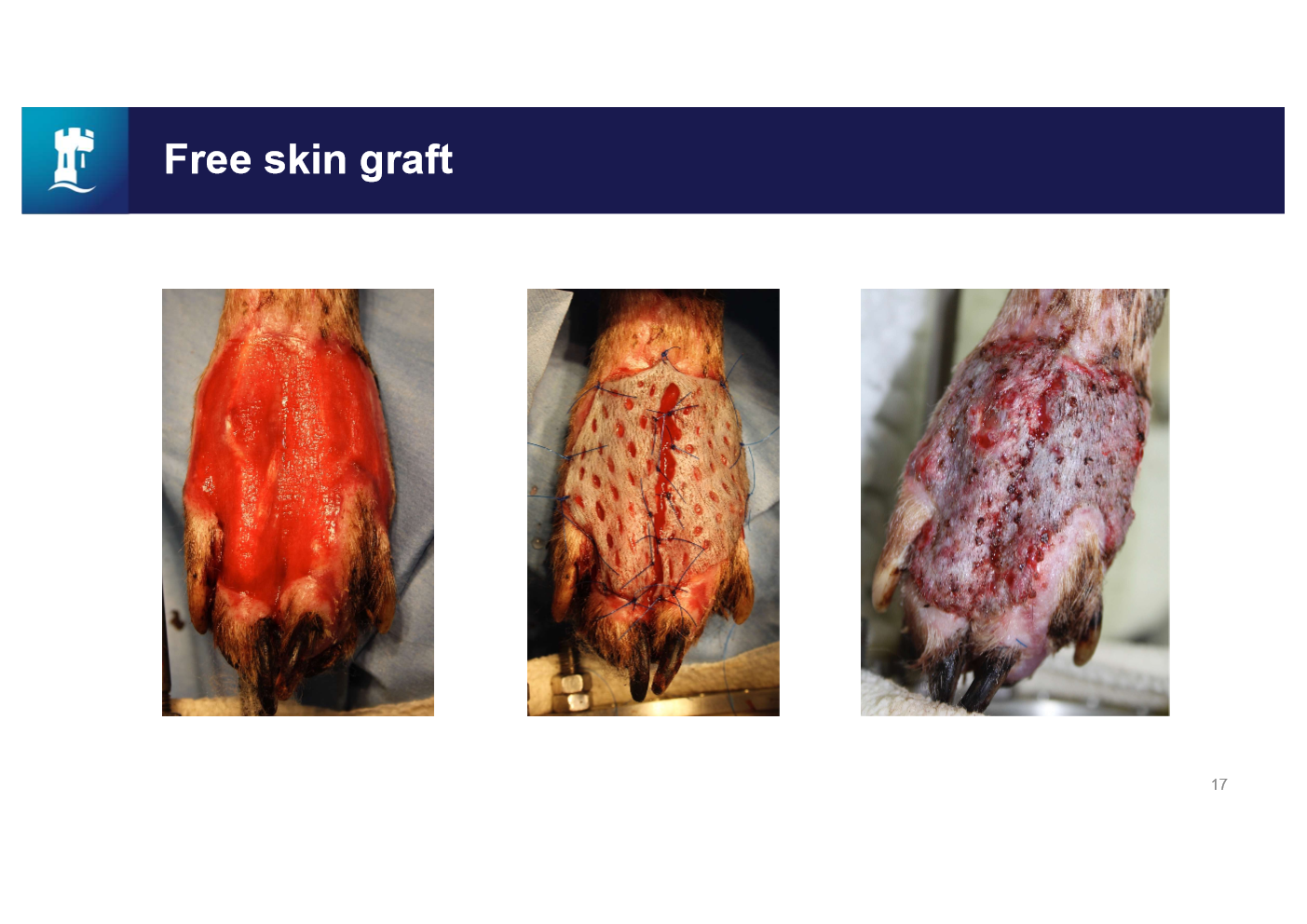
why make small holes in free skin grafts
Holes to drain excess fluid out
pinch/punch grafts advantages
- quick, easy
- take easy and reliable
- less invasive
- easy wound drainage
- irregular surface
pinch/punch grafts disadvantages
Disadvantages:
- XS bleeding may float graft out or delay revascularization
- poor cosmetic appearance
- remainder of recipient bed covered with neoepithelium from keratinocyte proliferation and migration -> delicate epithelium
wound care product selection
-topical therapy
-continually reassess patient and wound
-remain up to date with products so informed decisions made
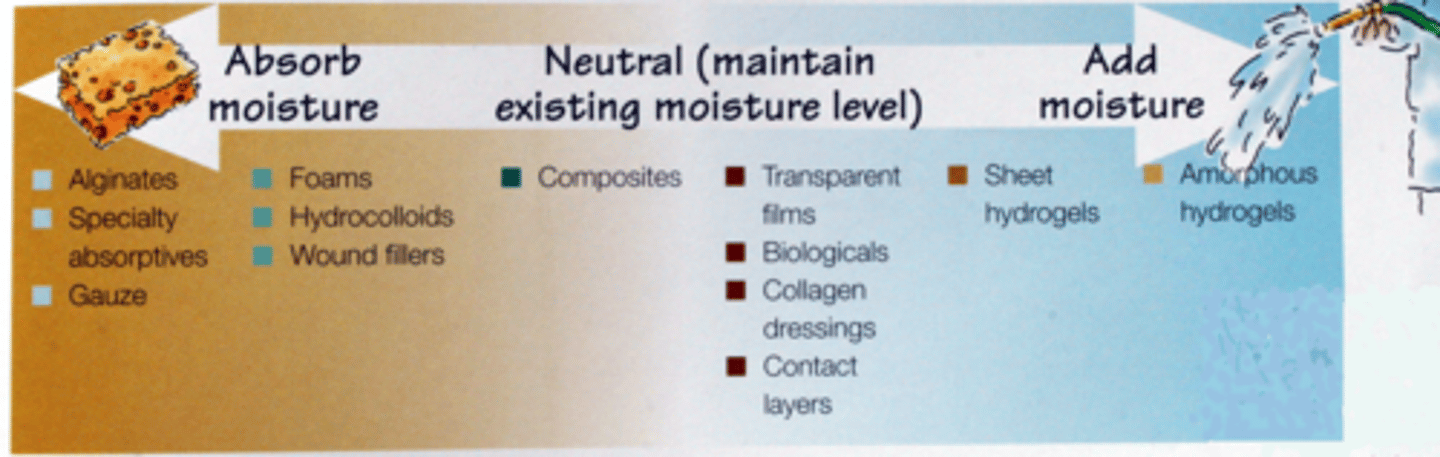
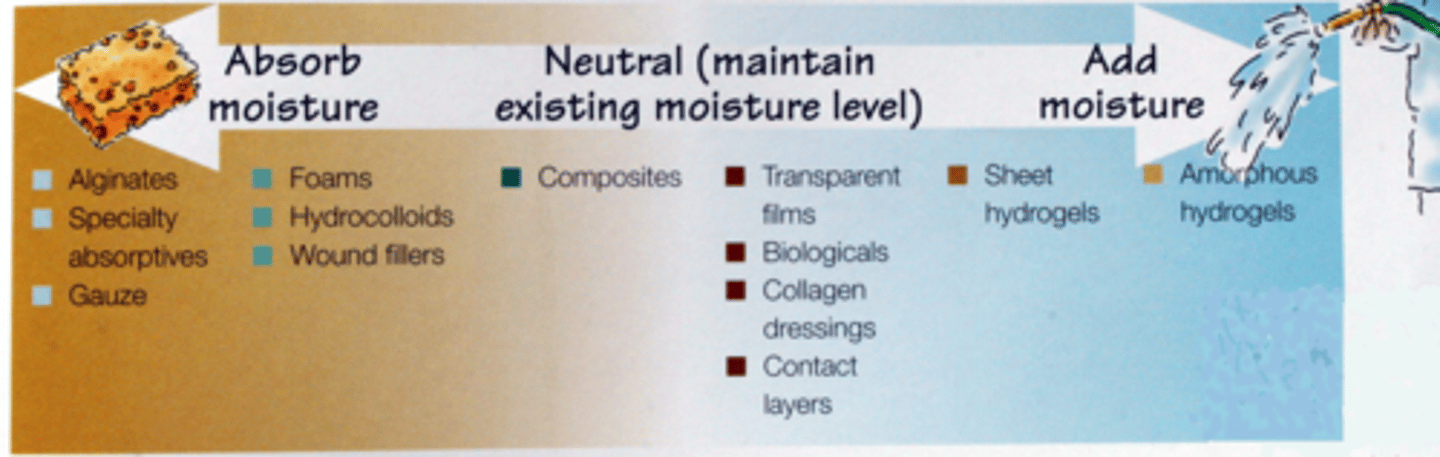
wound dressings that absorb moisture
-alginates
-specialty absorptives
-gauze
-foams
-hydrocolloids
-wound fillers
-honey
wound dressings that maintain existing moisture levels
-composites
-transparent films
-biologicals
-collagen dressing
-contact layers
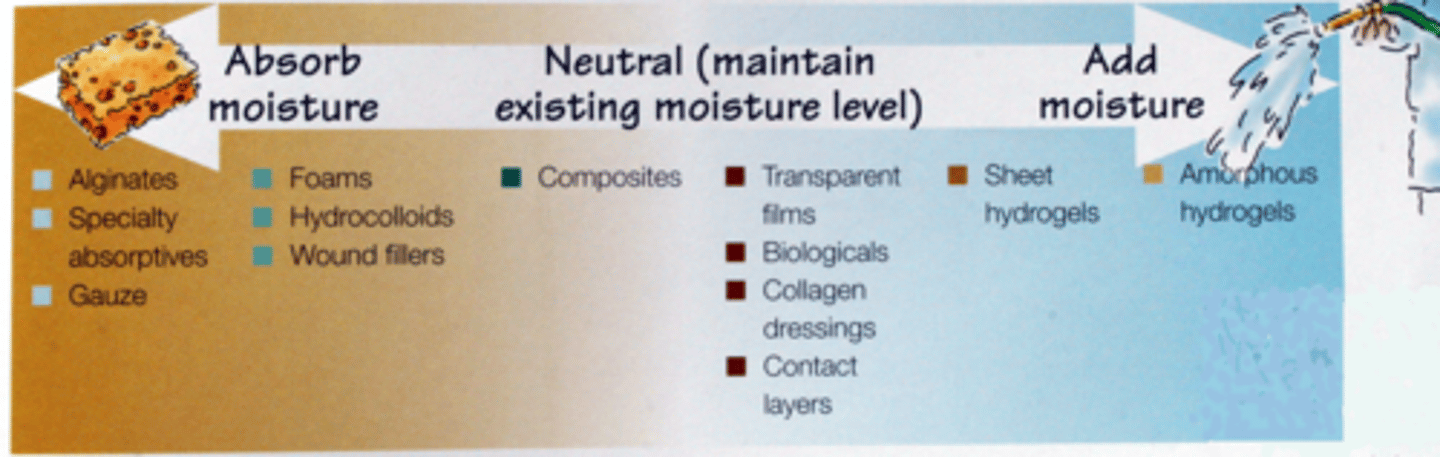
wound dressings that add moisture
-sheet hydrogels
-amorphous hydrogels
criteria for product selection of wound dressings
-frequency of change
-ease or difficulty of dressing change procedure
-availability of products
-cost of products
-requirement for hospitalisation
-requirement for topical antimicrobial agent
what are the most likely reasons for things to go wrong when dressing wounds
-frequency of change
-requirement for hospitalisation
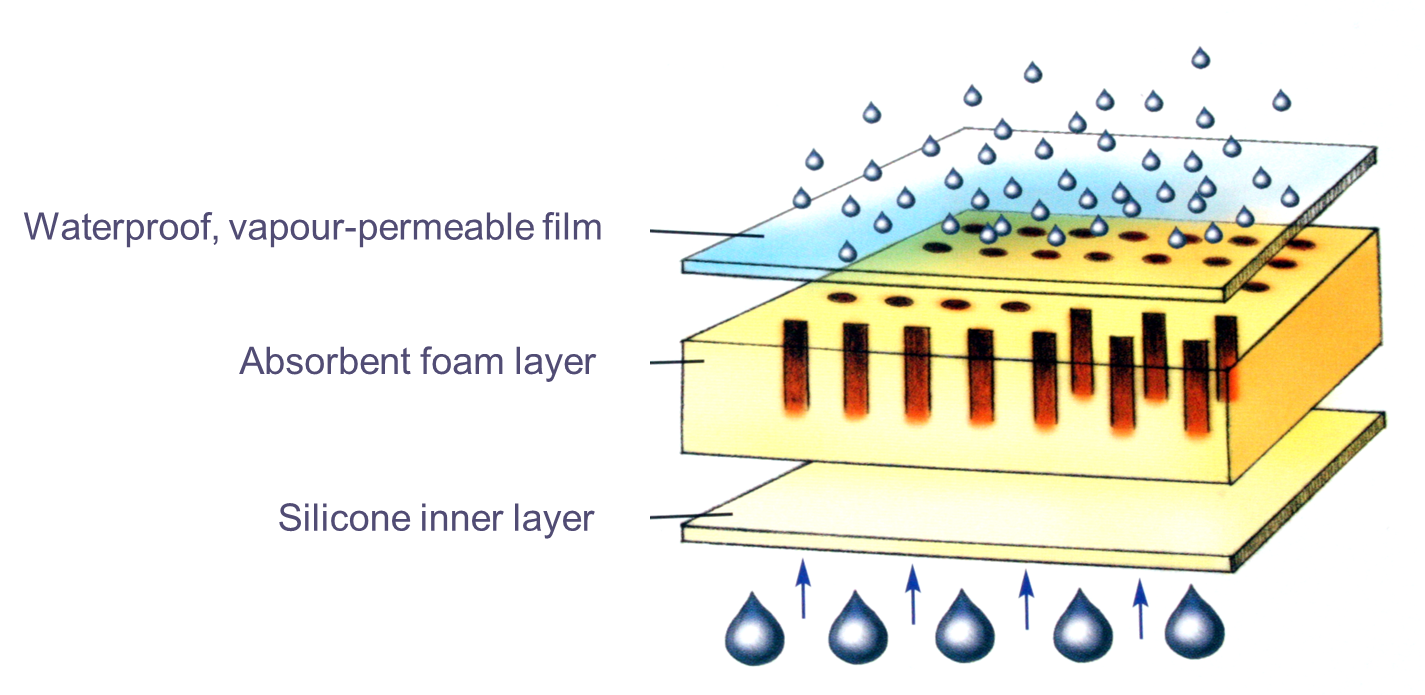
foam dressings
-absorbent, sponge like polymer dressings (hydrophilic polyurethane)
-provide thermal insulation
-help create moist wound environment
-allow gas exchange
-impermeable to bacteria and water
can be adhesive
Rely from moisture coming from the wound and trap it
Can evaporate but is delayed
So remains moist
foam dressings suitable for
-all types of exuding wounds but NOT DRY
-some have moisture sensitive film backing with variable permeability dependent on level of exudate
foam dressings vary in ability to absorb exudate
-some suitable only for lightly to moderately exudating wounds
-others have greater fluid handling capacity and suitable for heavily exuding wounds
foam dressings under compression bandaging
-fluid handling capacity of foam reduced
-takes same volume as dressing but when compressed then less
If not allowed to evaporate -> become a wet wound
why do you need to make sure the foam dressing is on the right way round
otherwise wont work
what can saturated foam dressings cause
cause maceration of healthy skin
bc is over moist
now prone to infection
hydrogel dressings
-made up of water in polymer to maintain moist wound base
-available in amorphous or sheet formulations
-take shape of wound
-secondary, non absorbent dressing needed
hydrogel dressings used for
donate liquid to dry wound
when to avoid hydrogel dressings
in presence of infection and heavily exuding wounds
what phase best to use amorphous gels on
granulating and epithelialising
provide moisture in controlled manner
-use with foam dressing
what do you need to work out with hydrogel
Will say how much is in the tube
Eg 15g= 15ml
So need to work out how much of it you need to get the foam dressing to work efficiently
hydrocolloid paste
manage dermal wounds with light drainage
hydrocolloid gel
-used on partial and full thickness wounds
-fills dry wound cavities
-promotes autolytic debridement
clingfilm as dressing
-water vapour impermeable
-very likely to macerate
but Best way to know if things are working is to have a look b
silver ions dressing
--exudating wounds
-infectious wound
-proportional release
silver nitrates swab ointment
-easy application
-cauterise infected tissue
silver sulfadiazine cream
-serious burns
-infected wound
silver zirconium phosphate sheet like crystals
-early wound management
-kills bacteria
why use silver
has broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity
honey
-antibacterial
-healing stimulating properties (reduce wound size, healing time, complete healing, stim of granulation tissue, epithelialisation)
-debriding effect
-anti inflam effect
-odour reducing
-reduction in wound pain
honey has good debridement properties because
-low pH
-osmotic effect
-help draw up fluid from wound area
honey has antimicrobial properties due to
-hydrogen peroxide (glucose oxidase)
-anti oxidants
-high sugar content (osmotic)
-acidic (pH 3.2-4.5)
how does honey debride
Pulls fluid towards the honey -> helps debride
what is methylgloxal in manuka honey
-potency as antimicrobial can be measured by unique manuka factor
-+15 ensures potent antimicrobial properties over and above those of standard honey
High conc of methylglyoxal= better antimicrobial effect
tie over dressing
A dressing placed over a skin graft and tied on by sutures that have been left long enough for that purpose
put dressings over the top and use the loops to tie in the dressing
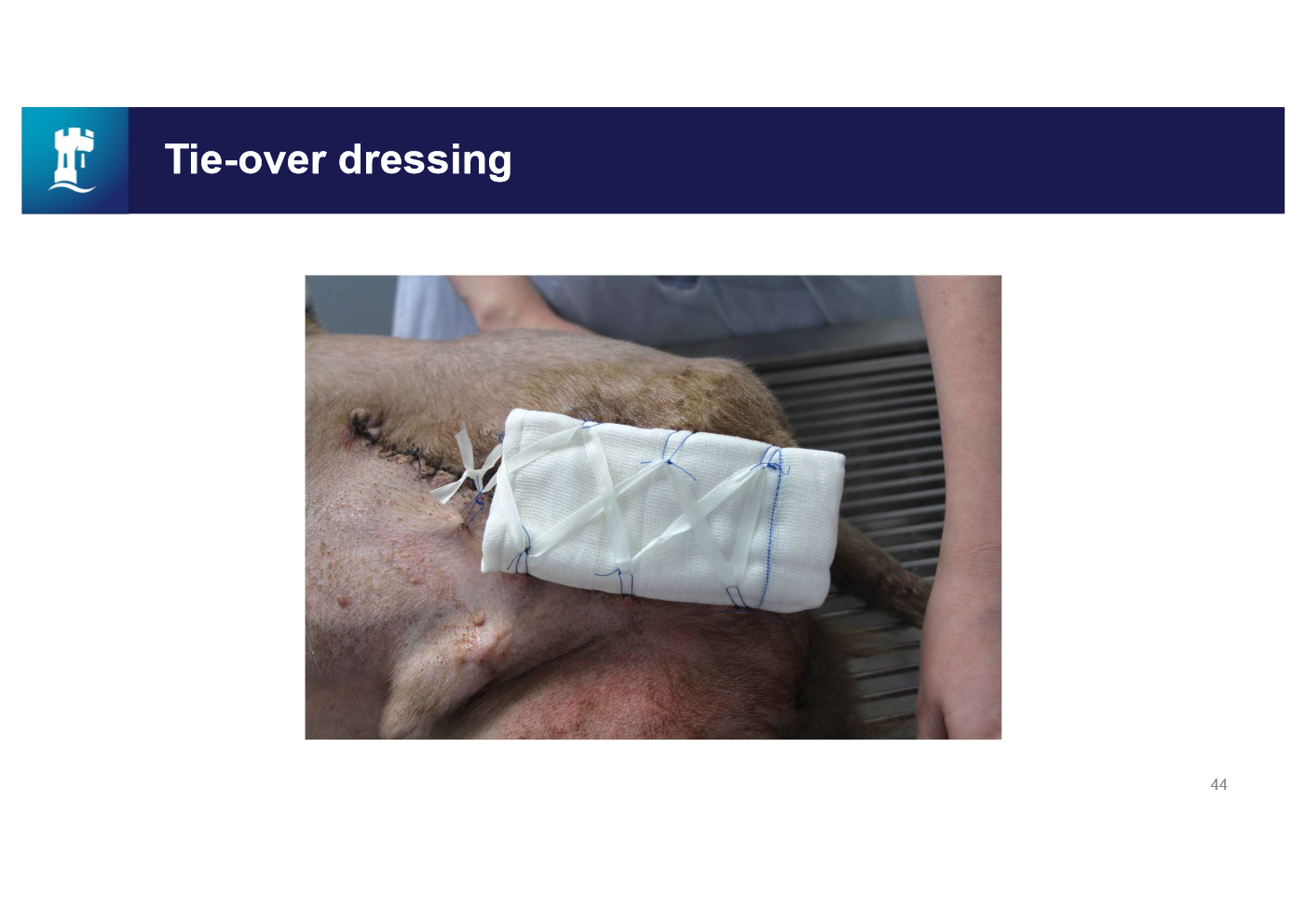
what can be placed over tie over dressing
nappy
is absorbent layer