FHA exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Information sent along a myelinated axon track can move either up or down the CNS within the same track
False
Cross-bridging is the repeated cycle of the myosin heads moving further away from the active sites on actin during a muscle contraction.
False
All synovial joints have the same basic components, including a joint capsule, articular cartilages, synovial fluid, a synovial membrane, sensory nerves, blood vessels, and accessory structures.
True
The hyoid bone articulates with which bone?
No bones
The following is true regarding joints:
The more mobile the joint, the less stable it is; limited mobility reduces the chance of injury
Abduction/adduction and flexion/extension are considered which type of movements for synovial joints?
angular
If the CNS were susceptible to a drug that should normally not affect it, this might indicate damage to the blood-brain barrier and a problem with which of the following cells?
astrocytes
_____ is a type of tissue that has a gelatinous matrix and is avascular
cartilage
Myelin in the PNS is produced by _____ cells
Schwann
In the region of L1-L2, the spinal cord…
tapers to form the conus medullaris, then separates inferiorly into the cauda equina
Tilting the chin toward the chest and then returning the head to anatomical position is an example of cervical
flexion and extension
The elbow is _____ to the wrist, The wrist is _____ to the shoulder.
proximal; distal
When a person is standing upright in the anatomical position, the palms of the hands face____, and the ____ plane separates the body into____ sections
anteriorly; frontal; anterior and posterior
A _____ is a painful displacement of articulating bones that temporarily deforms and immobilizes the joint
dislocation
The tension of a muscle when it is relaxed is called ____
muscle tone
These are needed for muscle contraction to occur:
interactions between thick and thin filaments, presence of calcium ions, presence of ATP (all of the above)
_____ is the failure to maintain homeostatic conditions
disease
All of the following are caused by muscle atrophy except ____
increase in muscle tone
each skeletal muscle in the body begins at a(n) _____, ends at a(n) _____, and contracts to produce a specific _____.
origin, insertion, action
When lifting something heavy it is recommended to keep a straight back, let your legs do the work, and engage the muscles of the _____ region to act as antagonist muscles and decrease the risk of injury to the back.
abdominal
The cells which secrete acid that breaks down bone during osteolysis are called _____
osteoblasts
The following bone(s) is/are paired.
maxilla
The entire spinal cord is divided into__segments.
31
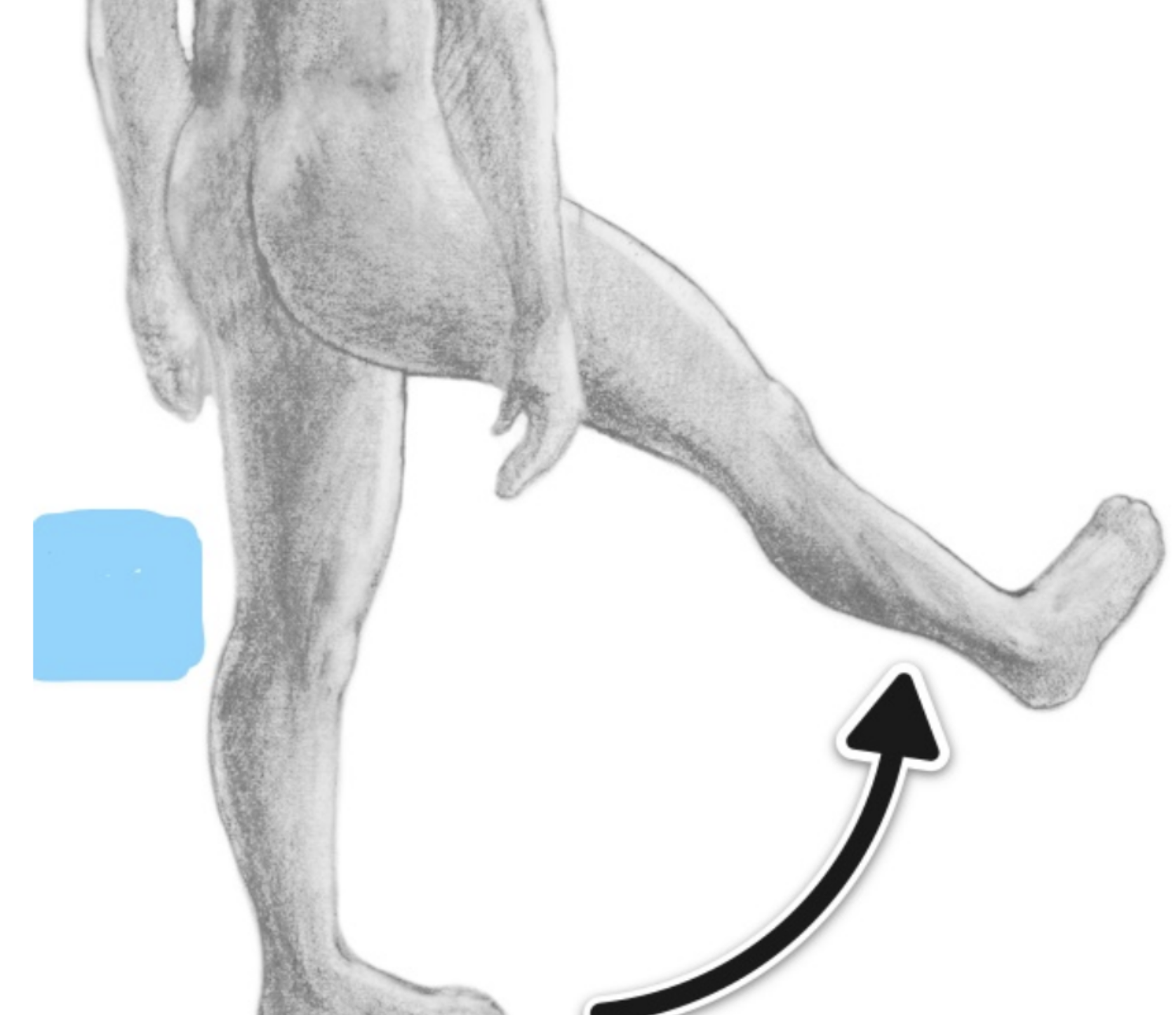
flexion
All of the paranasal sinuses are located either above, in between, or below the optic orbits and in the same frontal plane as the optic orbits
false
muscles that perform an action opposite to that of the prime movers are considered
antagonists
These neurons are part of the afferent division of the PNS
somatic and visceral sensory neurons
An athlete whose MRI shows a stress fracture of the leg has damage to the outermost covering of the bone and should refrain from their activity. If they do not, they would put themselves at risk of fracturing the next layer of bone called ____
compact bone
_____ is a dense regular connective tissue that connects bone to bone
ligament
this vertebra is part of the cervical spine and articulates with the axis
atlas
The zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone form the zygomatic arch which is commonly called the _____
cheekbones
Which of the following divisions of the nervous system carries motor commands directly to muscles and glands?
efferent division of the peripheral nervous system
Joints are junctions between two or more bones which may be in direct contact or separated by fibrous tissue, cartilage, or fluid
true
of the three layers that comprise the spinal meninges, the _____ is the tough, fibrous outermost layer that stabilizes the spinal cord within the vertebral canal?
dura mater
The appendicular skeleton consists of the skull, ribcage, and vertebral column
false
Which sequence is correct regarding the levels of anatomical organization from higher to lower complexity?
organism, organ systems, organs, tissues, cells, and chemical
the eye is _____ to the ear
medial
if a body is cut along a plane that is not frontal, sagittal, or transverse, the plane would be _____
oblique
in the adult, most red bone marrow is found in the___ bones.
flat
_____ give bone tensile strength
collagen fibers
this type of muscular tissue pulls on skeletal bones and is voluntarily contracted.
skeletal
A transverse view of the spinal cord reveals the horns of the gray matter. The anterior horns contain
somatic motor nuclei
Which division of the nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the control centers responsible for processing?
central nervous system
the three main categories of connective tissue are connective tissue prosper, fluid connective tissue, and ______
supporting connective tissue
Angular motion and rotation are movements of which type of joint?
a diarthrotic joint
The muscular system plays an important role in many physiological processes including
eating, circulation, maintaining body temperature, and elimination
The optic orbit is made of the following bones
frontal, maximal, lacrimal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and zygomatic
The bone formation known as the “Turkish saddle” on the _____ bone is where the ____ is found
sphenoid, pituitary gland
Functions of the nervous system include which of the following?
all of the above: seat of higher functions, such as intelligence, memory, learning, and emotions; receives sensory input, coordinates sensory input and motor output; integrating anf processing data
The deepest meningeal layer, known as the ____, is bound directly to the underlying neural tissue
pia mater
The protein molecule is the most predominant molecule found in the human body
false
All nervous system controlled functions of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands are controlled by the _____
automatic nervous system
The following are features of spongy bone, except….
it contains osteons
blood and lymph are examples of connective tissue proper
false
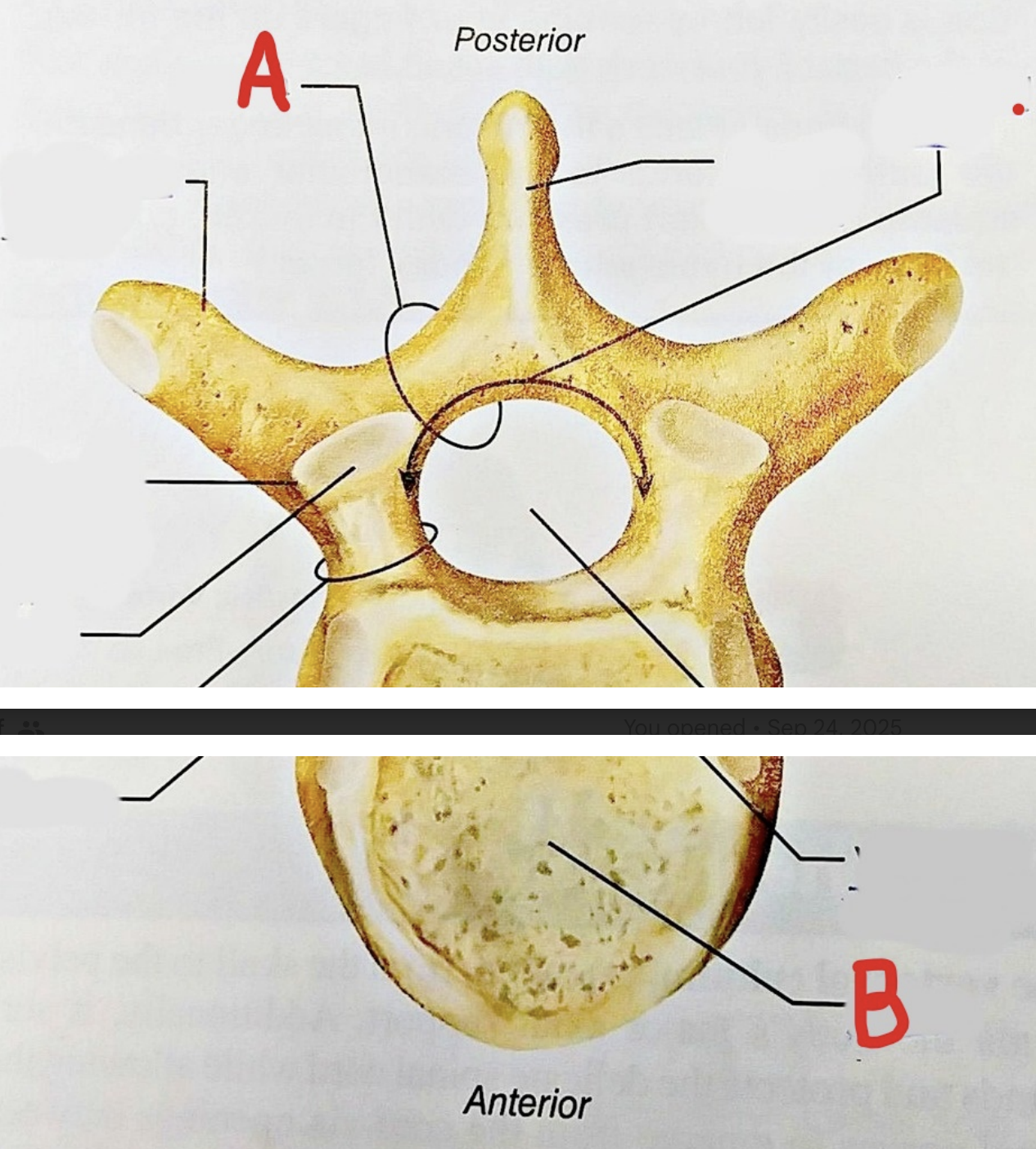
A is ___, B is ____
lamina; vertebral body
The _____ is the main functioning unit of muscle fibers and where the “action” takes place. It is bordered at each end by ___
sarcomere; Z lines
In the long bone, the ___ refers to the shaft, which contains yellow marrow, and the ____ refers to the areas at the distal ends.
diaphysis, epiphysis
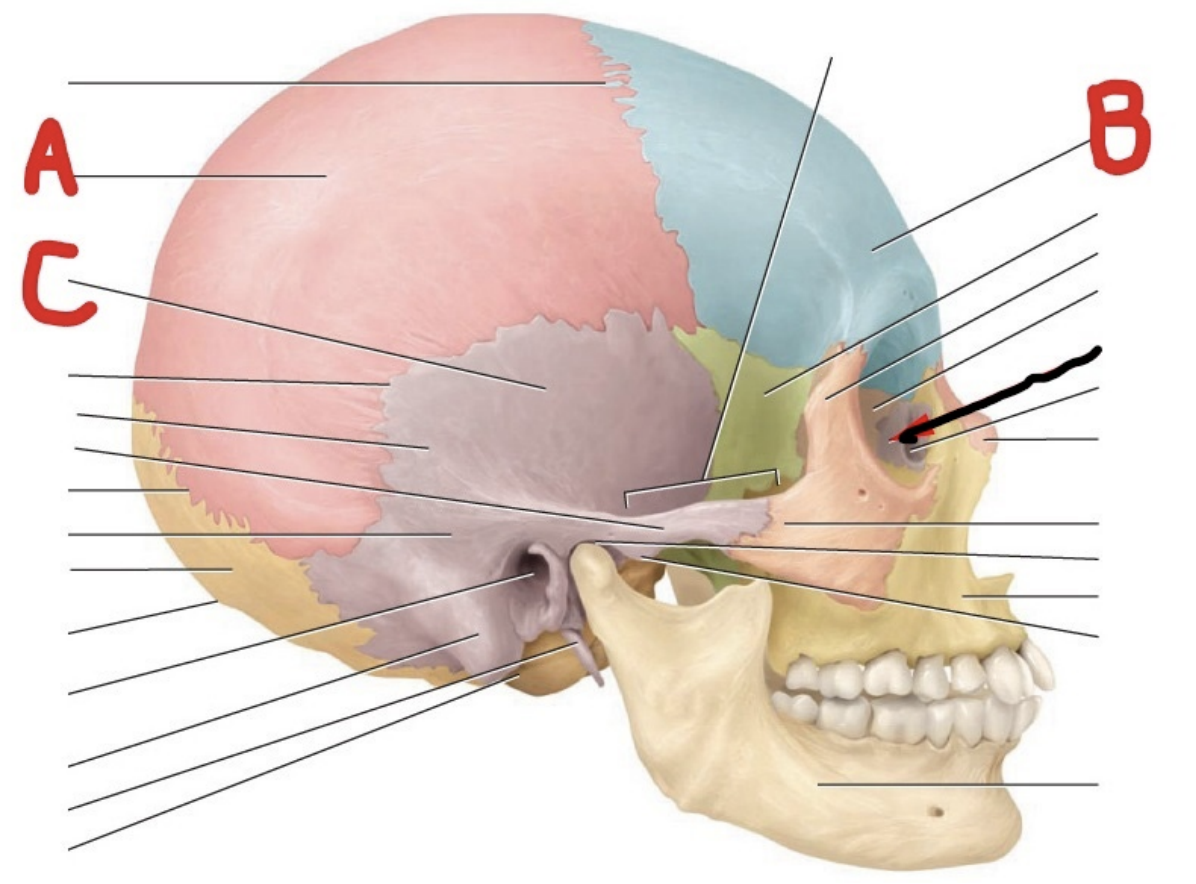
A ___, B ___, C___
parietal; frontal; temporal
The lumbar spine curves ___ to counterbalance the ___ curve of the ___ spines
anteriorly; posterior; thoracic and sacral
Histologically, neural tissue dominated by myelinated axons is defined as:
white matter
fibrous cartilage tissue, as found in the pads within the knee joints, in the intervertebral discs, and in the pubic symphysis resists
true
If you bit chicken and bone punctured the soft tissue at the anterior aspect of the roof of your mouth, eventually, it would hit the ___ bone.
maxilla
Flexion/extension, lateral flexion, and rotation are movements available throughout the spine. This segment has the most movement.
C3-C7
one function of neuroglia in the nervous system is to ___
act as phagocytes
The neuronal cell body usually has several branching _____, which are specialized to response to specific stimuli in the extracellular environment.
dendrites
The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and the vomer make up the ___
bony nasal septum
The ____ suture is located between left and right parietal bones
sagittal
As a person ages, if they do not engage in regular exercise, skeletal muscle fibers become less elastic and develop fibrosis, and the ability to tolerate increased exercise improves.
false