Human Bio - Exam 3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Digestive System Functions
Absorbs nutrients, electrolytes, and water
Converts food to ATP and products for new and existing tissues
Digestive Processes
Motility - Muscles move contents (via mixing and propulsion) in digestive tract. Longer tract (typically 4.5 m or 15 ft long) allows more digestion and absorption
Secretion - Includes endocrine (for integrated function), paracrine (local changes), neurocrine (nerve endings), and juxtacrine (for pathological circumstances)
Digestion - Breaking complex molecules to simple absorbable ones
Absorption - Absorbable units transferred from lumen of tract to blood/lymph
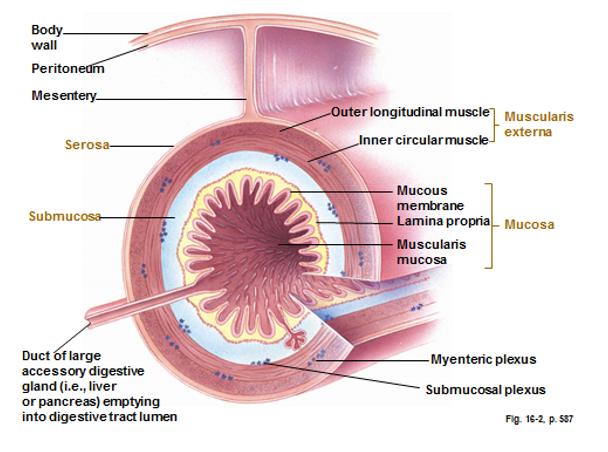
Digestive Tract Wall Layers (outer to inner)
(Ducts of accessory glands like liver and pancreas empty into tract lumen)
Body wall
Peritoneum
Mesentery
Serosa
Muscularis externa
Outer longitudinal muscles
Myenteric Plexus
Inner circular muscles
Submucosa
Submucosal plexus
Mucosa
Mucus Membrane
Lamin Propria
Muscularis Mucosa
Neurohumoral System
Nutrients trigger two paths:
Special senses → Dorsal Vagal Complex → Vagus Nerve
Chemo/mechanosensitive nerve endings → ENS
These paths trigger stomach, intestines, pancreas, gallbladder, and sphincter to change secretion and motility
Intrinsic Nerves (Enteric Nervous System)
Consists of sensory neurons, interneurons, and efferent neurons (to smooth muscle, exocrine, and endocrine cells)
Myenteric Plexus
Control muscularis externa along tract
Stimulatory neurons - ACh
Inhibitory neurons - Nitric oxide
Ascending/descending interneurons - Ach and Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine)
Sensory neurons - Substance P
Submucosal Plexus
Regulate secretion of fluids/electrolytes and muscularis mucosa
Promotes vasodilation
Noncholinergic neurons - VIP
Cholinergic neurons - ACh
Sensory neurons - Substance P
Extrinsic Nerves
Sympathetic Innervation (slows contraction/secretion)
Postganglionic adrenergic nerves (prevertebral ganglion)
Synapse enteric nervous system, glands and smooth muscles
Parasympathetic Innervation (enhances digestion)
Preganglionic CN X fibers
Synapse myenteric plexus of stomach, small intestine, cecum, ascending, and transverse colon
Rest of colon innervated by pelvic nerve
Autonomous Smooth Muscle Function
Pacemaker cells (Cajal) and gap junctions of muscularis externa
Slow waves (cyclic membrane potential fluctuations) do not trigger action potential normally
Presence of food moves starting point of slow waves near threshold and causes rhythmic cycles of contraction
GI Hormones
Gastrin (G cells) target CCK-B receptors (G-protein receptor → calcium release)
CCK (I cells) target CCK-A and CCK-B receptors (G-protein receptor → calcium release)
Secretin (S cells) target secretin receptors (Gs-protein receptor → cAMP release)
GIP (K cells) target GIP receptors (Gs-protein receptor → cAMP release)
Motilin (M cells) controls motor complex in tract
Other hormones include enteroglucagon, pancreatic peptide, and pYY
Only gastrin produced in antrum; all hormones made in duodenum and jejunum; only CCK and secretin produced in ileum
Paracrine and Immune Mediators of GI Tract
Made from non-excitable cells in lamina propria to fine-tune humoral and neural regulation
Histamine (ECL and mast cells) secretes gastric acid and intestinal chloride
Serotonin (enterochromaffin cells) responds to nutrients
Somatostatin (D cells) is stored in nerve cells and has inhibitory effects in tract
Prostaglandins (subepithelial myofibroblasts) and adenosine (various cells) regulates vascularity and causes intestinal secretion
Short vs Long Reflex
Short Reflex
Influences motility and secretion in response to change
In digestive tract walls
In stomach, stretch receptors trigger ENS for acid secretion
Long Reflex
Extrinsic nerve system superimposes local controls
Modifies smooth muscle and glandular activity
Stomach uses vagovagal reflex
Oral Cavity Components
Lips - Tactile sensation, guides food to mouth, speech
Palate - Breathing, chewing, sucking occur simultaneously
Uvula - Seals off nasal passage when swallowing
Tongue - Taste and tactile sensation, guides food, speech
Teeth - Grind/break down food, stimulate taste buds
Saliva
1-2 liters produced per day (0.5-5 mL/min)
Components:
Water - Helps with dissolving food, speech, and swallowing
Bicarbonate - Neutralizes gastric acid reflux
Mucins - Lubrication
Amylase - Starch Digestion
Lipase - Lipid Digestion
Lysozyme, lactoferrin, IgA - Innate and acquired immune protection
Epidermal and nerve growth factors - Mucosal growth and protection
Salivary Gland Cells
Acinar Cells - Produces saliva, chloride, and sodium ions
Parotid glands - Serous (and protein content of saliva)
Submandibular glands - Serous and mucous mix
Sublingual glands - Mucous (and a small amount of serous)
Ductular Cells - Sends saliva out of acini, modifies ionic composition (slow rates is hypotonic with plasma; high rates resemble plasma) and prevents backflow
Na/K ATPase in basolateral membrane for sodium secretion
HCO3- for bicarbonate secretion
No water reabsorption makes hypotonic saliva
Myofibroblasts (contractile cells) - Hydrostatic force expels saliva from salivary glands
Salivary Secretion Mechanism Pathway
Pressure and chemoreceptors (simple reflex; pressure in mouth) or cerebral cortex (conditioned reflex; thinking, seeing, smelling food) →
Salivary centers in medulla* →
Autonomic parasympathetic nerves →
Otic ganglion → parotid gland (via ACh and VIP on muscarinic receptors)
Submandibular ganglion → submandibular gland (via ACh and VIP on muscarinic receptors)
*Inhibited by fatigue, sleep, fear, and dehydration
Sympathetic innervation from superior cervical ganglion causes more protein release
Pharynx
Cavity at rear end of throat
Common passageway for digestive and respiratory tract separating air and food
Tonsils - Lymphoid tissue in oropharynx walls
Anatomy and Innervation of Esophagus
Information from pharynx and esophagus relayed via vagus nerve to medulla (nucleus tractus solitarius and dorsal vagal complex)
Skeletal muscle (upper half) and smooth muscle (lower half) innervated by vagus nerves
UES (innervated by nucleus retrofacialis and ambiguus of medulla) and LES
Prevents backflow into esophagus
Mucosa has stratified squamous epithelium. Lubricates and protects tract
Retrograde movement (belching and vomiting) can occur because air presence opens UES
Swallowing Proces
Food is chewed till suitable to swallow
Tongue pushes bolus to back of tongue
Soft palate elevates and epiglottis covers glottis
Cricopharyngeus muscle relaxes to open UES and let bolus descend in esophagus
Pressure gradient of tongue and muscles of pharynx push bolus down UES
Longitudinal contractions bring UES to tongue
Transverse contractions of pharynx sweep remaining food
Peristalsis
Primary Peristalsis
Moves bolus along esophagus with help of gravity
Each wave is ~ 10 seconds long
Contraction varies along esophagus
Vagovagal reflex (vagus nerve to dorsal vagal complex) activates enteric neurons above bolus to release ACh and contract muscle and enteric neurons below bolus to release NO and relax muscle
Secondary Peristalsis
For smooth muscles to clear bolus not expelled from primary wave or to clear acid
Also uses vagovagal reflex
LES Relaxation
Normally contracted
Tone is increased by neurohumoral agents (ACh and gastrin)
Relaxation occurs by vagus nerve through release of NO and VIP
GERD
Caused by retrograde flow from inappropriate relaxation of LES or gastroparesis
Obesity (high BMI) also relaxes LES
Barrett’s esophagus (damage from acid reflux) can cause cancer
Manifestations include heartburn, regurgitation, and dysphagia
Symptoms are damage to mucosal lining of esophagus, water brash, a globus, odynophagia, and nausea
Treated with diet changes, no lying down after eating, antacid to neutralize acids, histamin-2 receptor agonists and proton pump inhibitors
Surgically can narrow LES diameter or alter gastroesophageal junction
GERD can cause erosion of enamel and dentin lingual surfaces and incisal edges of maxillary anterior teeth; can be fixed by placing lots of crowns
Esophageal Varices
Caused by cirrhosis and portal hypertension (high blood resistance)
Variceal hemorrhage can occur
Blood diversion due to resistance of collateral vessels (thin walled and supported by connective tissue)
Pressure dilates collateral vessels causing mucosa protrusion
Swallowing and acid reflux causes trauma
Treatments
Insert balloon device in esophagus
Rubber rings around dilated vessels
Surgical bypass
Stomach Functions
Stores food and empties into intestine for digestion and absorption
Secretes HCl and digestion proteins
Food is pulverized to liquid as chyme
Gastric Cells
Fundus Region (Parietal Glands)
Parietal cells - HCl and intrinsic factor (binds to Vitamin B12 allowing it to be absorbed; lack of it causes pernicious anemia). HCl cleaves pepsinogen to pepsin (pepsin also converts pepsinogen to pepsin; auto-catalytic), denatures proteins, and kills microorganisms
Chief cells - Inactive pepsinogen (exocytosis of zymogen granules)
Enterochromaffin (ECL) - Histamine
Surface mucous cells - Mucous (alkaline lubricant protecting stomach lining from mechanical harm, pepsin, and acid)
Anchored stem cells - Parietal, chief, ECL, and mucous cells
Antral Region (Pyloric Gland)
G cells - Gastrin (released from peptide in diet with help of Gastrin Releasing Peptide or GRP)
D cells - Somatostatin (released when pH is below 3 to stop acid secretion)
Mucous secreting cells - Mucous
Stomach Innervation
Vagovagal Reflex - Afferent sent through vagus nerve to dorsal vagal complex
Processed in hypothalamus and sent back through vagus nerve
Visceral input from nucleus tractus solitarius
ENS controls secretion activity
Postprandial Secretion
Cephalic
Preparation for receiving food from sight, smell, and taste
Vagovagal reflex releases GRP and ACh to activate gastrin, which activates parietal and chief cells
Gastric
Vagal activity
Intestinal