firestine ocular and pulmonary pharmacology
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
3 divisions of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteric
in the sympathetic response,
bp and heart rate __________
glycogenolysis __________
GI peristalsis __________
bp and heart rate __increase___
glycogenolysis _increases__
GI peristalsis _decreases__
in the parasympathetic system,
preganglionic neuron releases _______ onto _______,
postganglionic neuron releases _______ onto _______, leading to ___(constrict/dilate?)__
pre: ACh onto nicotinic
post: ACh onto muscarinic
= constriction
in the sympathetic system,
preganglionic neuron releases _______ onto _______,
postganglionic neuron releases _______ onto _______, leading to ___(constrict/dilate?)__
pre: ACh onto nicotinic
post: NE onto
alpha-> constriction
beta-> dilation
identify whether stimulation of the receptor leads to constriction or dilation
muscarinic:
alpha:
beta:
muscarinic: constriction
alpha: constriction
beta: dilation
t/f: acetylcholine acts at ALL junctions of the parasympathetic system
true
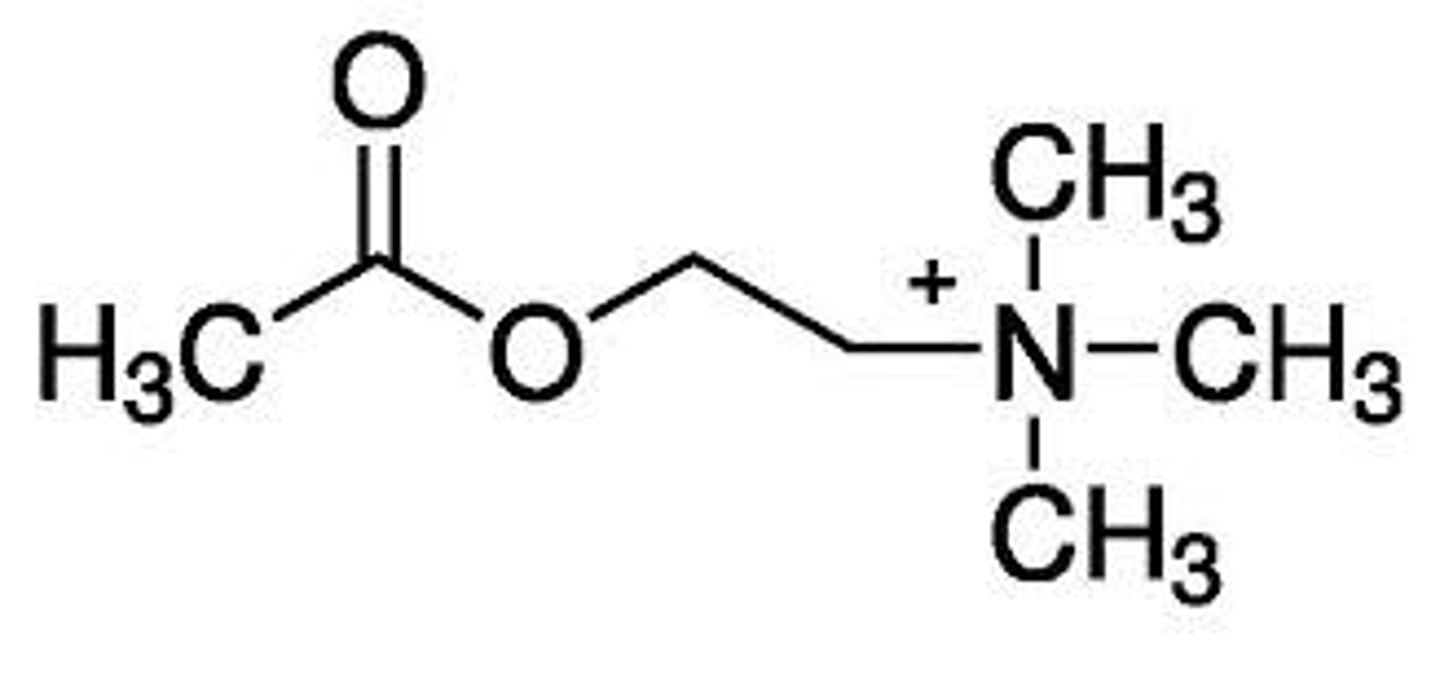
which nt do sympathetic neuroeffector junctions use primarily
norepinephrine
which nt does the adrenal medulla predominantly release
epinephrine
what allows for systemic activation of sympathetic sites even if there is no direct innervation
adrenal medulla-> releases epi/ne into blood
which receptors are activated and what is the response in symp/para stimulation of:
eye (iris)
symp: alpha1-> contraction of dilator/mydriasis
para: M->contraction of sphincter/ miosis
which receptors are activated and what is the response in symp/para stimulation of:
eye (ciliary muscle)
symp: beta2= relaxation, distant vision
[FFS: far, flat lens, symp]
para: M= contraction, near vision, increased aqueous humor OUTflow into canal of Schlemm
[PRN: para, round lens, near] / pronto: to canal
what kind of stimulation results in increased aqueous humor OUTflow into canal of Schlemm
parasympathetic stimulation of M receptors on ciliary muscle
what kind of stimulation results in increased aqueous humor production
sympathetic stimulation of B1
which receptors are activated and what is the response in symp/para stimulation of:
eye (ciliary body epithelium)
only sympathetic!
B1= increased aqueous humor production
which receptors are activated and what is the response in symp/para stimulation of:
lungs
symp: B2= dilates bronchioles
para: M= constrict bronchioles
summarize how ANS process affect aqueous humor
sympathetic: ciliary body epithelium B1= increases aqueous humor PRODUCTION
parasympathetic: ciliary muscle M= increases aqueous humor OUTFLOW
what explains why side effects may be seen in drugs meant for only one target area
receptors are found in multiple sites so even if you target a beta receptor in the eye, it may affect a beta receptor in the lungs, causing an undesired effect
what can minimize side effects
1. route of administration (topical eye drops, inhalation)
2. receptor subtype selectivity
muscarinic receptors are stimulated by _____ and blocked by _______
ACh; atropine
which ANS system controls pupillary constriction and how? whats another term for constriction?
parasympathetic control of sphincter pupillae- M; miosis
carbachol
moa
effect
-muscarinic agonist (like acetylcholine)
-Constricts pupils (miosis)
- used in lens replacement surgery
pupil dilation, or ________, can be caused by which drug classes
mydriasis
-muscarinic antagonists (relax circular/sphincter pupillae)
-alpha1 agonist (contract radial muscle)
alpha1 agonist effect on pupil
mydriasis (dilation)
- forces contraction of radial muscle
muscarinic agonists work to produce
a. miosis
b. mydriasis
c. miosis and aqueous humour drainage
d. mydriasis and aqueous humour drainage
e. none
c
pupil contraction and fluid drainage via parasymp stimulation
pilocarpine
brand
moa
effect
- Carpine
-muscarinic agonist
- drains fluid in eye; ocular hypertension and glaucoma

which enzyme terminates ACh activity
acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
physostigmine moa
inhibits AChE (INDIRECT M agonist since less ACh depleted)
= for glaucoma
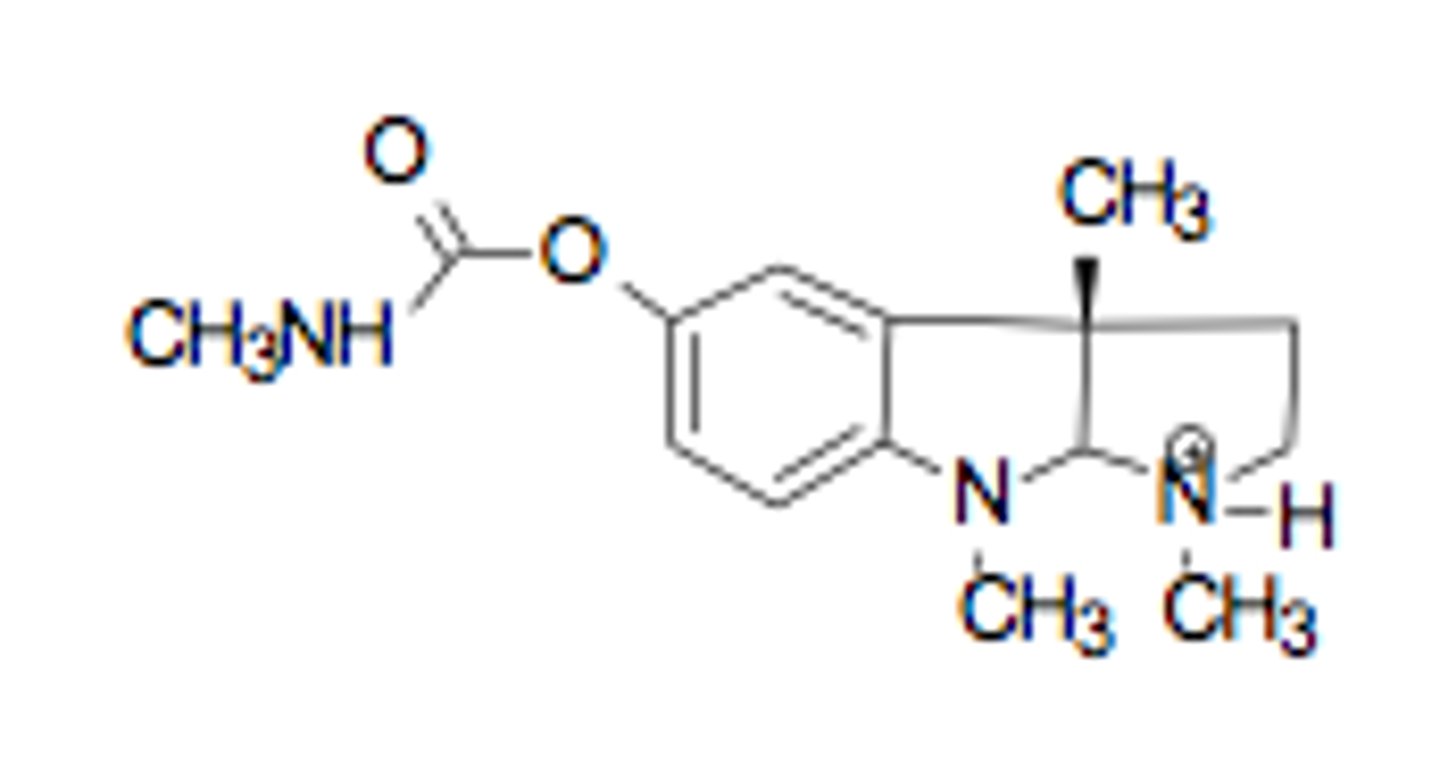
tropicamide
moa
effect
-muscarinic antagonist eye drops
- mydriasis (pupil dilation), vasoconstriction
phenylephrine
moa
effect
-alpha1 receptor agonist
- mydriasis, reduce red eyes via vasoconstriction, nasal decongestion
tetrahydrozoline
brand
moa
effect
Visine
-alpha-1 receptor agonist
-local vasoconstriction= reduce red eye
naphazoline
brand
moa
effect
Clear Eyes Redness Relief
-alpha-1 receptor agonist
-local vasoconstriction= reduce red eye
what contraindication do mydriatic drugs have?
individuals with glaucoma
what are the 3 anatomical pathways that control aqueous humour in the eye
(targets for glaucoma and intraocular pressure)
1. ciliary body receptors
-alpha decreases production [alpha2 agonist]
-beta increases production [beta1 blocker]
2. carbonic anhydrase [inhibitor] regulates bicarb (ion)- osmosis
3. prostaglandins [analog] increase uveoscleral outflow of fluid
brimonidine
brand
moa
effect
Alphagan P, Mirvaso
alpha-2 agonist
decrease aqueous humor (glaucoma)
timolol
brand
moa
effect
Betimol, Istalol, Timoptic
beta-1 blocker
decrease aqueous humor (glaucoma)
brimonidine/timolol
brand
moa
effect
Combigan
brimonidine (alpha2-agonist) and timolol (beta1 blocker)
decrease aqueous humor (glaucoma)
_______ is a prodrug of epinephrine, often used for ocular use
dipivefrin
what is the first line agent for glaucoma treatment?
topical prostaglandin analogs
- latanoprost, bimatoprost, travoprost
what are the brand names and moa for the following drugs?
latanoprost
bimatoprost
travoprost
moa: topical prostaglandin analogs (increase humour outflow)
latanoprost= Xalatan
bimatoprost= Lumigan
travoprost= Travatan Z
dorzolamide
moa
effect
carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
decreases bicarb production which reduces fluid into eye (glaucoma)
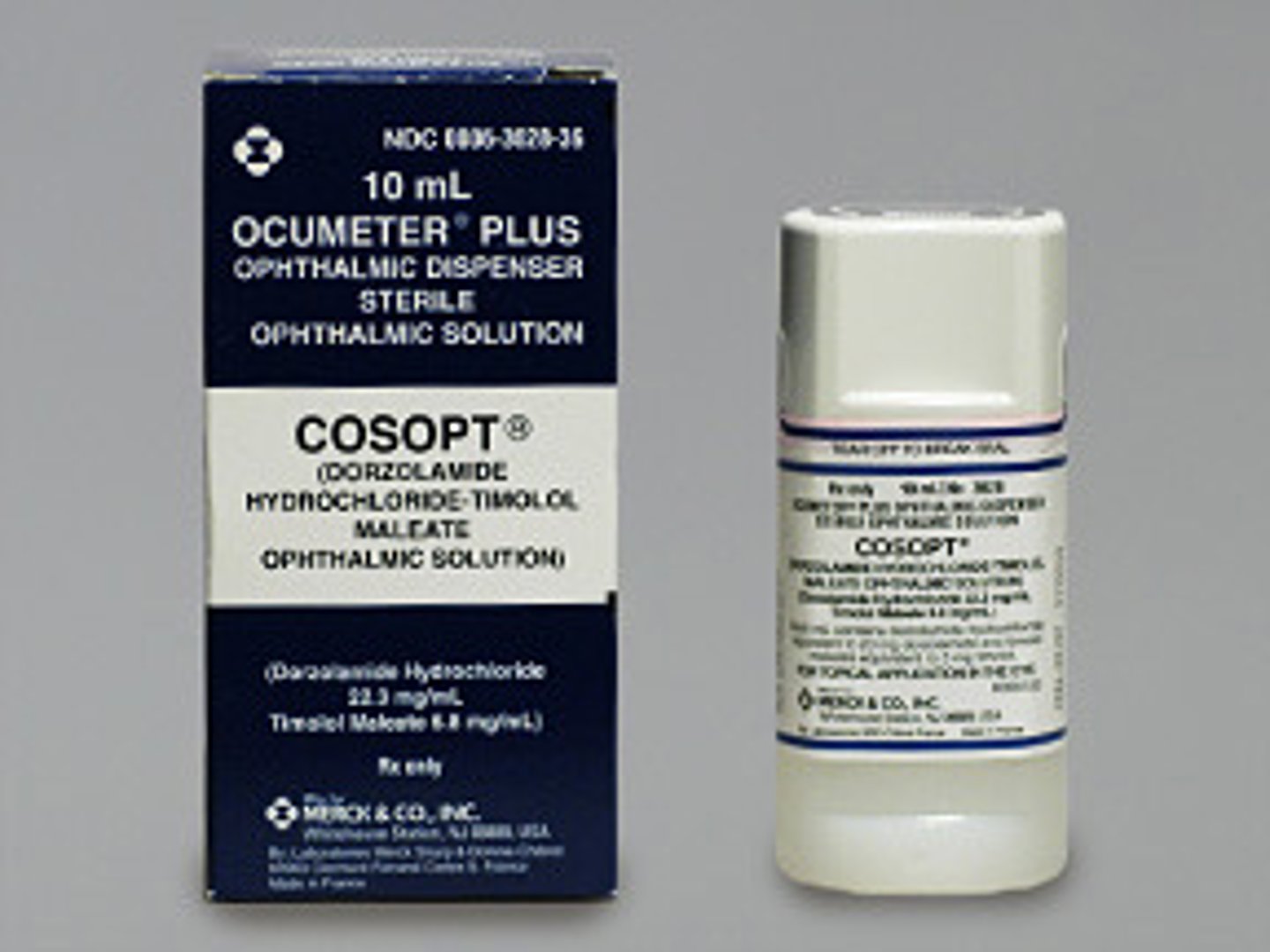
Cosopt
Generic: Dorzolamide (carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) and Timolol (beta1 blocker)
Drug Class: Ophthalmic glaucoma agents
muscarinic agonists favor ________ vision
near
muscarinic antagonists __(relax/contract?)___ the ciliary muscle, to produce a resting lens that ___(can/cant?)___ focus on near objects
muscarinic ANTAGONISTS
relax
cannot
strabismus
cross-eyed/ misalignment of the eye
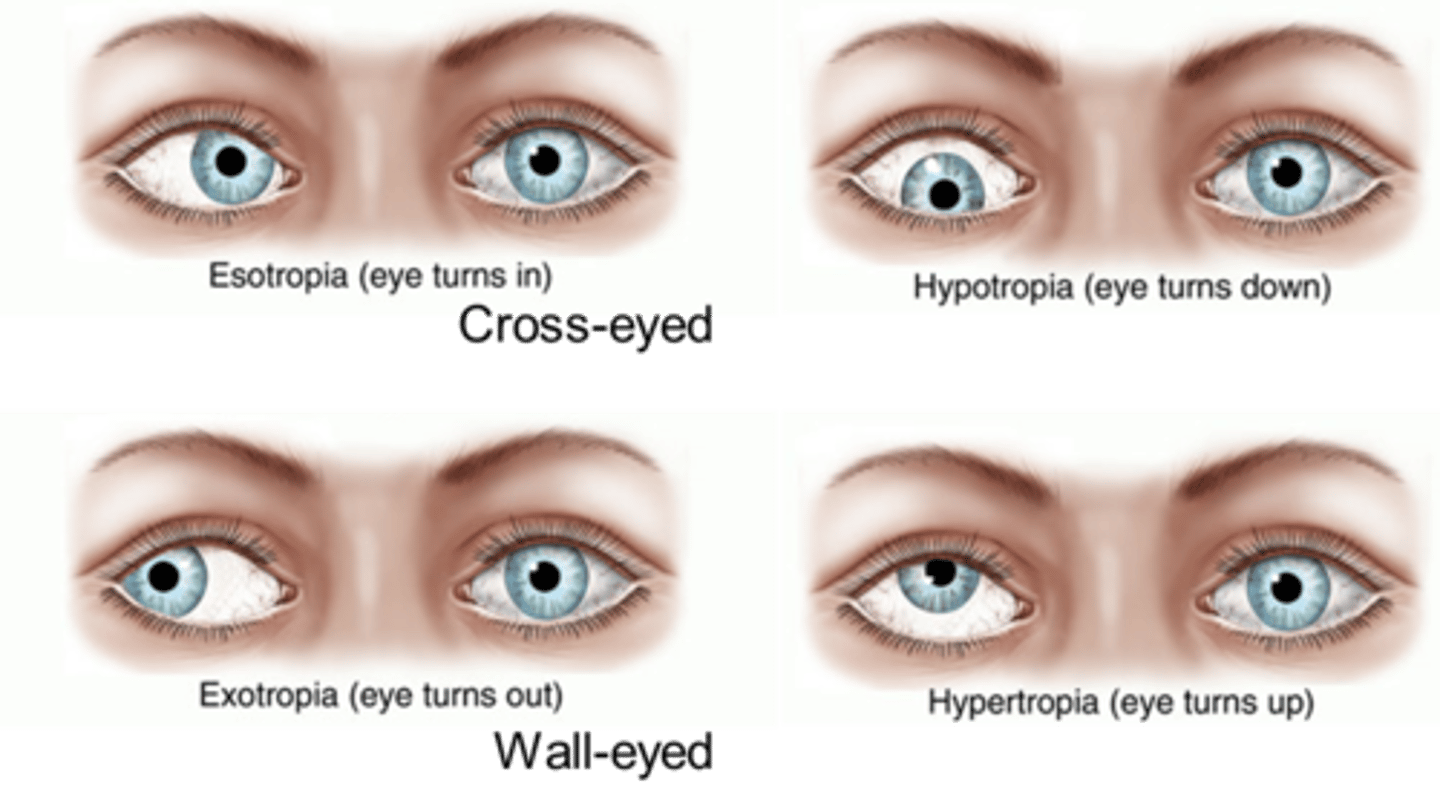
what are 2 drug therapies for strabismus
1. atropine for underactive eye (forces eye to focus)
2. botox for overactive eye (paralyzes it)
pheniramine
moa/effect
ophthalmic H1 receptor antagonists
lowers eye inflammation

antazoline
moa/effect
ophthalmic H1 receptor antagonists
lowers eye inflammation
naphazoline
alpha 1 agonist= vasoconstriction
for eye redness; often added with antihistamines

cromolyn sodium
brand
moa
Opticrom
decreases histamine release from mast cells (for inflammation)

dexamethasone
moa
effect
glucocorticoid-> anti-inflammatory
- local and systemic side effects
prednisolone
moa
effect
glucocorticoid-> anti-inflammatory
- local and systemic side effects
diclofenac
brand
moa
Voltaren
NSAID (inflammation)
flurbiprofen
brand
moa
Ocufen
NSAID (inflammation)
cyclosporin ophthalmic
brand
moa
effect
Restasis
immunosuppressive that inhibits t lymphocyte activation->
decreases cytokines and inflammation in lacrimal gland
= for dry eyes; increases tear production
lifitegrast
brand
moa
effect
Xiidra
immunosuppressive that inhibits t lymphocyte activation->
decreases cytokines and inflammation in lacrimal gland
= for dry eyes; increases tear production
What did the AREDS study find?
Vit C and E, zinc, copper, and beta carotene slowed progression of age-related macular degeneration
What did AREDS2 find?
did not use beta carotene in study= less cancers but no improvement in eye
t/f: the FDA does not regulate whether supplements are beneficial, but they do regulate composition
false. they regulate neither
how is verteporfin used for age-related macular degeneration
-photodynamic therapy with verteporfin
-combats neo-vascularization (overgrowth of blood vessels)
-shining a light on cells treated with verteporfin makes free radicals= cell death
which drugs are given via intravitreal injection and target VEGF to treat age-related macular degeneration
-tanibizumab
-aflibercept
-pegaptanib
(TAP)
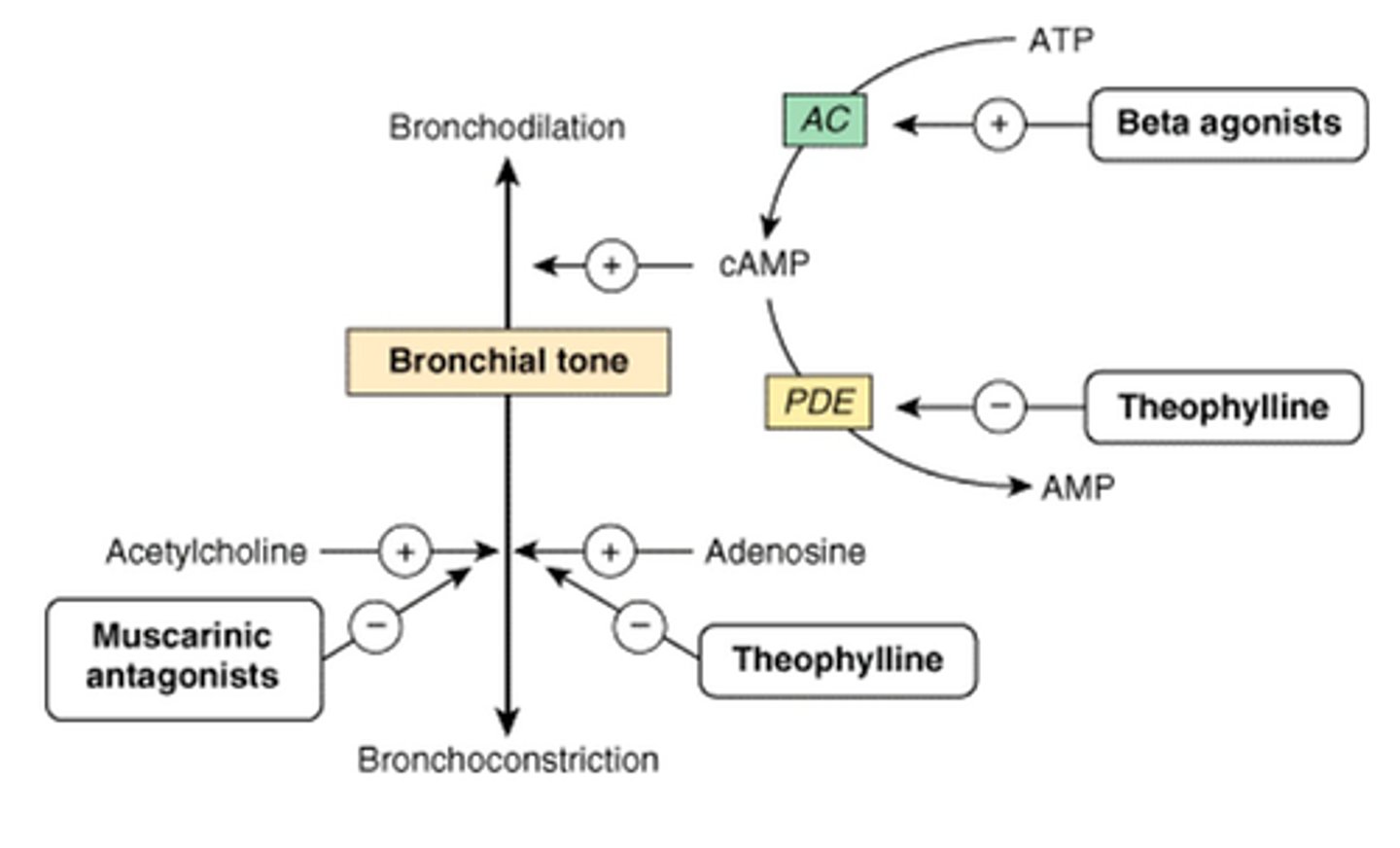
in the normal ANS system, what cause bronchodilation? constriction?
dilation= epi-> beta 2
constriction= vagus releasing ACh-> M3
dyspnea
difficulty breathing/ shortness of breath
t/f: emphysema is reversible with bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory therapy
false. lung parenchyma is destroyed; never reversible
methacholine
-Muscarinic receptor (M3) agonist.
-Used in bronchial challenge test to help diagnose asthma. (constricts bronchioles even more)
t/f: cromolyn sodium can be used for both eye inflammation and asthma
true. it is a mast cell stabilizer
muscarinic _____ are used for bronchodilation in COPD
antagonists
which functional group is present in SAMAs and LAMAs to treat asthma
quaternary amine (permanent positive charge)
ipratropium
SAMA= short acting muscarinic antagonist used for bronchodilation
Combivent
Generic: Albuterol (SABA) and Ipratropium (SAMA)
Drug Class: Bronchodilator Combo
tiotropium
Spiriva
LAMA= long acting muscarinic antagonist used for bronchodilation
first line bronchodilator agents
beta 2 agonists (albuterol, salmeterol)
what is the principal endogenous ligand that causes bronchodilation
epinephrine; also used for anaphylaxis
albuterol
brand
moa
ProAir, Ventolin, Proventil
SABA= short acting beta agonist
for bronchodilation
salmeterol, formoterol
moas
effect
both are LABAs
long acting beta agonists
for bronchodilation
rank the following according to length of activity (short acting to longest acting). which drug class are these?
epinephrine, formoterol, albuterol, salmeterol
= beta 2 agonist
(shortest) epi, albuterol, salmeterol, formoterol (longest)
frequent use of a beta 2 inhaler often requires an additional drug class. which one? what does it do?
corticosteroid (ICS)
for inflammation
salmeterol + fluticasone
brand?
moa?
Advair
salmeterol is LABA, fluticasone is ICS
formoterol + budesonide
brand?
moa?
Symbicort
formoterol is LABA, budesonide is ICS

vilanterol + fluticasone + umeclidinium
brand?
moas?
Trelegy
vilanterol= LABA
fluticasone= ICS
umeclidinium= LAMA
theophylline
brand?
moa?
effect?
Elixophyllin
PDE inhibitor-> decreases cAMP-> bronchodilation
- available orally, but narrow therapeutic range
budesonide
Pulmicort
inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) for inflammation
most prominent endogenous glucocorticoid? 3 effects?
cortisol (hydrocortisone)
1. metabolic
2. anti-inflammatory
3. sodium-retentive
corticosteroids
systemic side effects?
local side effects?
systemic= cataracts, osteoporosis, growth suppression, adrenal suppression, metabolism
local= cough, oral thrush
t/f: corticosteroids work to both decrease the immune response and inflammatory responses
true
ciclesonide
brand?
moa?
Alvesco
an ICS PRODRUG!, less systemic side effects from steroid
which drug class is sometimes used to prevent newborn respiratory diseases and how? which drug and why?
-corticosteroids= produces surfactant
-betamethasone= best penetration into fetal circulation
omalizumab
-humanized monoclonal anti-IgE antibody
- for allergen-mediated asthma
meplizumab and reslizumab
-humanized mAbs against IL-5
- for eosinophilic asthma
benralizumab
-humanized mAB against IL-5 receptor
- for severe eosinophilic asthma
zileuton
5-lipoxygenase inhibitor
-blocks leukotriene synthesis, used for asthma
montelukast
Singulair
leukotriene receptor antagonist
for asthma and seasonal allergic rhinitis
t/f: opiates may suppress cough through central action
true
dextromethorphan
Robitussin
anti-tussive (cough)

benzonatate
Tessalon Perles
local anesthetic for cough suppression

driving cells of pulmonary fibrosis
activated myofibroblasts
pirfenidone
brand
moa
effect
Esbriet
- blocks TGF-beta stimulated collagen production
- for pulmonary fibrosis

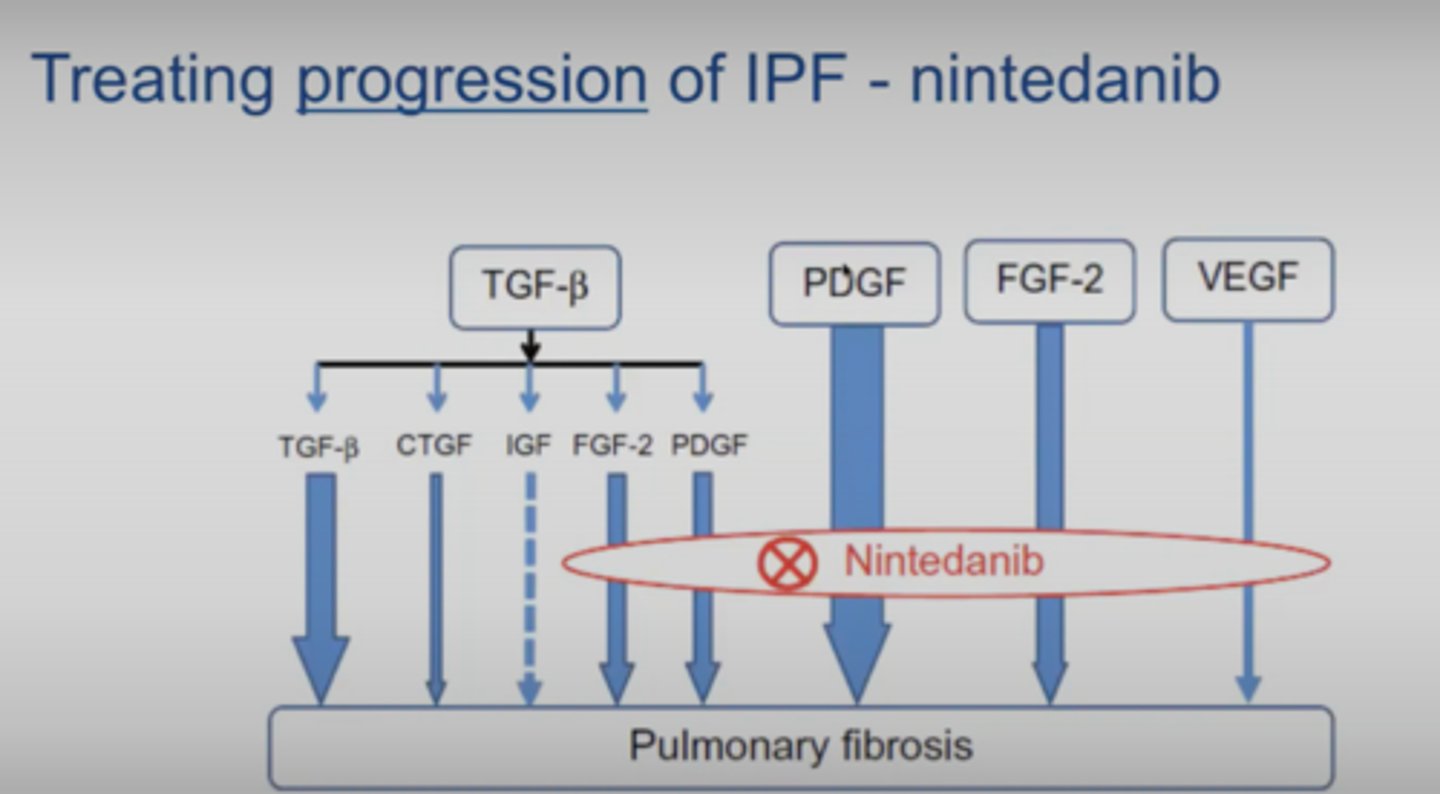
nintedanib
brand
moa
effect
Ofev
ATP-competitive inhibitor of tyrosine kinase receptors
- lowers FGF
- for pulmonary fibrosis