Variation from Meiosis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Variation
Produced during meiosis, it is important for the daughter cells (and potentially offspring) to differ genetically.
Variation causes
Crossing over
Independent assortment
Non-disjunction
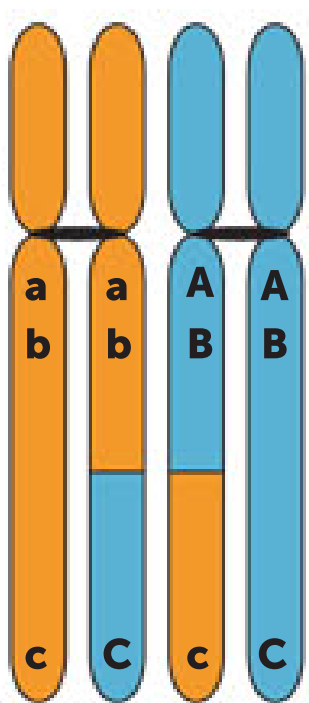
Crossing over
Occurs = During prophase 1.
Homologous chromosomes form tetrads consisting of 4 chromatids.
Can occur between non-sister chromatids.
Part of the chromatid breaks off and reattaches to the non-sister chromatid.
Chromosomes passed onto offspring are not identical to the parents.
Chiasma
The point where two chromatids cross during crossing over.
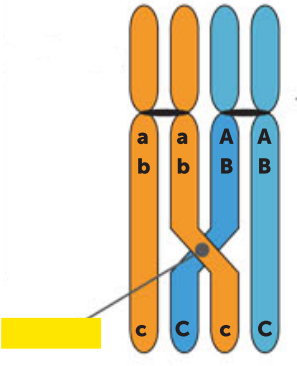
Recombination
After crossing over - occurs as there is a new combination of alleles on the chromosomes.
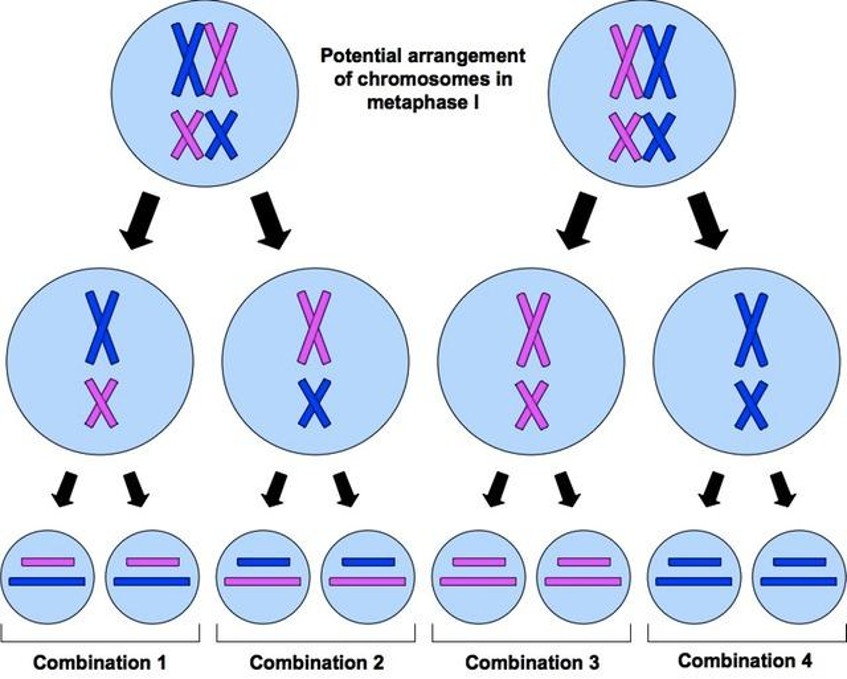
Independent assortment
Occurs = During metaphase 1.
Tetrads can align at the equator of the cell in a number of different combinations. The maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes can be on the left or the right of each other.
Number of possible combinations can be calculated by 2n (where n = haploid number of chromosomes) → 223 = 8.4 million.
Process is random and the way one chromosome pair separates is independent of how all the other pairs of chromosomes separate.
The zygote produced from fertilisation contains a set of genes arranged in an order that has never occurred before and will probably never occur again.
Non-Disjunction
Occurs = During anaphase 1 and anaphase 2
Sometimes homologous chromosomes do not pull apart during anaphase 1. Both homologous chromosomes are pulled to the same pole of the cell.
Alternatively, sister chromatids may not pull apart in anaphase 2. Both sister chromatids are pulled to the same pole of the cell.
Non-disjunction results in gametes that have an abnormal number of chromosomes.
one has an extra chromosome (24 in humans)
The other is missing one (22 in humans)
Non-disjunction results
After fertilisation with a normal gamete of the opposite sex, the zygote will have either 45 or 47 chromosomes.
Often causes miscarriage or birth defects.
Trisomy = occurs when an individual inherits an extra copy of a chromosome:
Trisomy-21 occurs quite frequently (Down Syndrome)
Trisomy-13 (Patau syndrome)
Trisomy-18 (Edwards Syndrome)
Monosomy = occurs when an individual is missing a chromosome.
Partial monosomy/trisomy = chromosome is missing a part/has an extra part.