Geology Chapter 10: Deep Time: How Old is Old?
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Uniformitarianism is succinctly summarized by which phrase?
a. the future is the key to the present
b. the present is the key to the past
c. the past is the key to the present
d. the present is the key to the future
B
As understood by modern geologists, the principle of uniformitarianism implies that
a. the Earth has always had the same basic appearance that it has today
b. physical processes observed today (such as erosion and volcanic eruptions) have been active in the past at approximately the same rates
B
In the area immediately surrounding an igneous intrusion, a host limestone is locally metamorphosed to produce marble. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. the intrusive igneous rock must be younger than the limestone
b. the limestone must be younger than the igneous rock
A
Within the world's sedimentary rocks, fossils
a. are rarely, if ever, found
b. are randomly distributed
c. occur in limited intervals of strata
d. are found only in igneous rocks
C
Based on the figure, what is the age of Layer 7 relative to Layer 3?
a. Layer 7 is younger than Layer 3
b. Layer 7 is older than Layer 3
c. Layer 7 and Layer 3 are the same rock type, so they are the same age
d. their relative ages cannot be determined
A
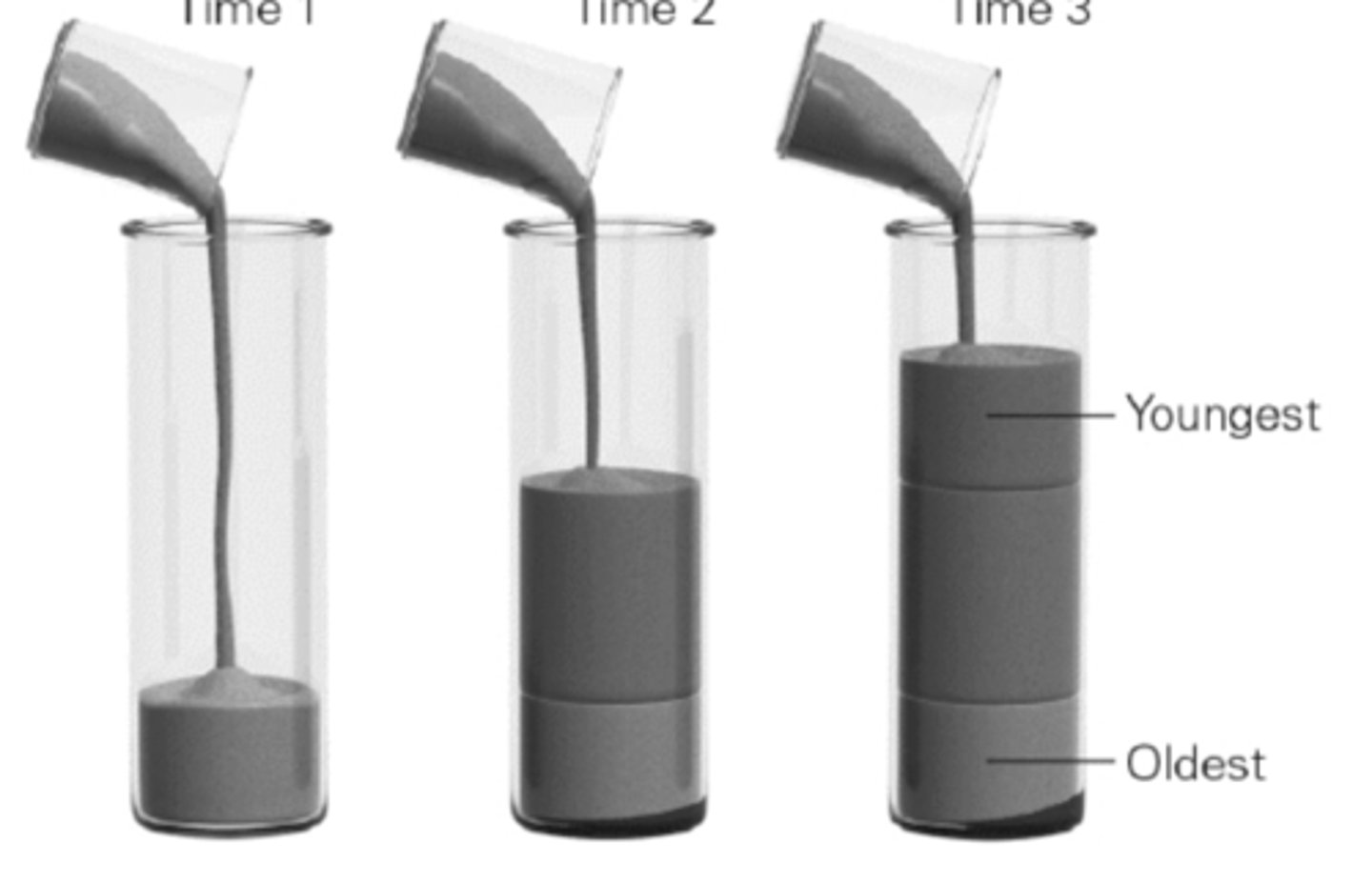
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, younger layers overlay older layers, according to the principle of ____________.
a. superposition
b. original continuity
c. original horizontality
d. uniformitarianism
A

Which of the following geologic principles is a direct result of gravity?
a. baked contacts
b. crosscutting relationships
c. original horizontality
d. inclusions
C
What type of age are the geologic principles described by Charles Lyell used to determine?
a. absolute age
b. numerical age
c. relative age
d. fossil age
C
If an igneous dike cuts across a sequence of sedimentary beds, then ________.
a. the beds must be older
b. the dike must be older
c. the beds and the dike must have formed at the same time
d. their relative ages cannot be determined from the information given
A
If a basalt body cuts across a fault, what are the relative ages of the basalt and the fault?
a. the fault must be older, according to the principle of crosscutting relationships
b. the basalt must be older, according to the principle of crosscutting relationships
A
Magma has intruded into a limestone and a marble rind formed surrounding the granite pluton. The marble rind must be younger than the limestone according to the principle of
a. superposition
b. baked contacts
c. original horizontality
d. lateral continuity
B
If the lithology and fossil content of two bodies of rock on opposite sides of a canyon are identical, then these remaining outcrops were likely physically connected at one time and formed part of an extensive, sheet-like layer of rock. This idea summarizes the principle of ____________.
a. superposition
b. lateral continuity
c. original horizontality
d. uniformitarianism
B
What is the term for boundary surface in a sequence of rock strata indicating lack of deposition, where erosion and deformation may have occurred?
a. an unconformity
b. a fault
c. a fossil succession
d. an inclusion
A
The surface below sedimentary rocks that overlie igneous or metamorphic rocks is termed a(n)
a. disconformity
b. angular unconformity
c. nonconformity
d. marker bed
C
If horizontal sedimentary strata overlie tilted strata (and no fault is present), the surface between the horizontal and tilted strata must be a(n) ____________.
a. conformable sedimentary contact
b. angular conformity
c. disconformity
d. nonconformity
B
Look at the figure below. The contact between the Unkar Group and the Tapeats Sandstone is a(n) ____.
a. conformable contact
b. disconformity
c. nonconformity
d. angular unconformity
D
Look at the figure below. The contact between the Vishnu Schist and the Tapeats Sandstone is a(n)
a. conformable contact
b. disconformity
c. nonconformity
d. angular unconformity
C
Can the age of Earth be reliably estimated from sediment thicknesses?
a. Yes, sedimentation rates remain constant at any one locality throughout Earth's history
b. No, most of the Earth's history is represented by unconformities between strata rather than the strata themselves
B
Which method of correlation is most reliable for determining age equivalence among bodies of rock that are physically separated by vast distances
a. lithologic correlation
b. fossil correlation
c. inclusion correlation
d. unconformity correlation
B
Relative ages expressed on the geologic time scale primarily resulted from the study of
a. fossil content and spatial relationships among igneous rocks
b. fossil content and spatial relationships among sedimentary rocks
c. radiometric dating of igneous rocks
d. radiometric dating of sedimentary rocks
B
Which of the following is true of the geologic column?
a. Is is the complete record of the Earth's history that is preserved in the rocks at any given location
b. It portrays the spatial distribution of rock units at the Earth's surface
c. It is a composite stratigraphic column created by correlating strata from millions of locations around the world
d. It is an interval of strata composed of specific rock type or group of rock types that together can be traced over a broad region
C
What type of spatial representation of geologic information shows the distribution of rock units at the Earth's surface, their contacts, and the structures that affect them?
a. a block diagram
b. a geologic cross section
c. a geologic map
d. a digital elevation model
C
What type of age does the measurement of parent and daughter isotopes in a mineral determine?
a. relative age
b. numerical age
c. seasonal age
d. fossil age
B
Basaltic clasts within a conglomerate have been radiometrically dated to 50 million years ago. Is this a reliable age for the conglomerate?
a. Yes
b. No, this age is likely too old
c. No, this age is likely too young
d. No, basalt never contains minerals bearing radioactive isotopes
B
In an unweathered sample of igneous rock, the ratio of an unstable isotope to its stable daughter isotope is 1:15. If no daughters were present at the time the rock cooled below closure temperature, and the half-life of the isotope is 50 million years, how old is the rock?
a. 200 million years
b. 400 million years
c. 750 million years
d. 1 billion years
A
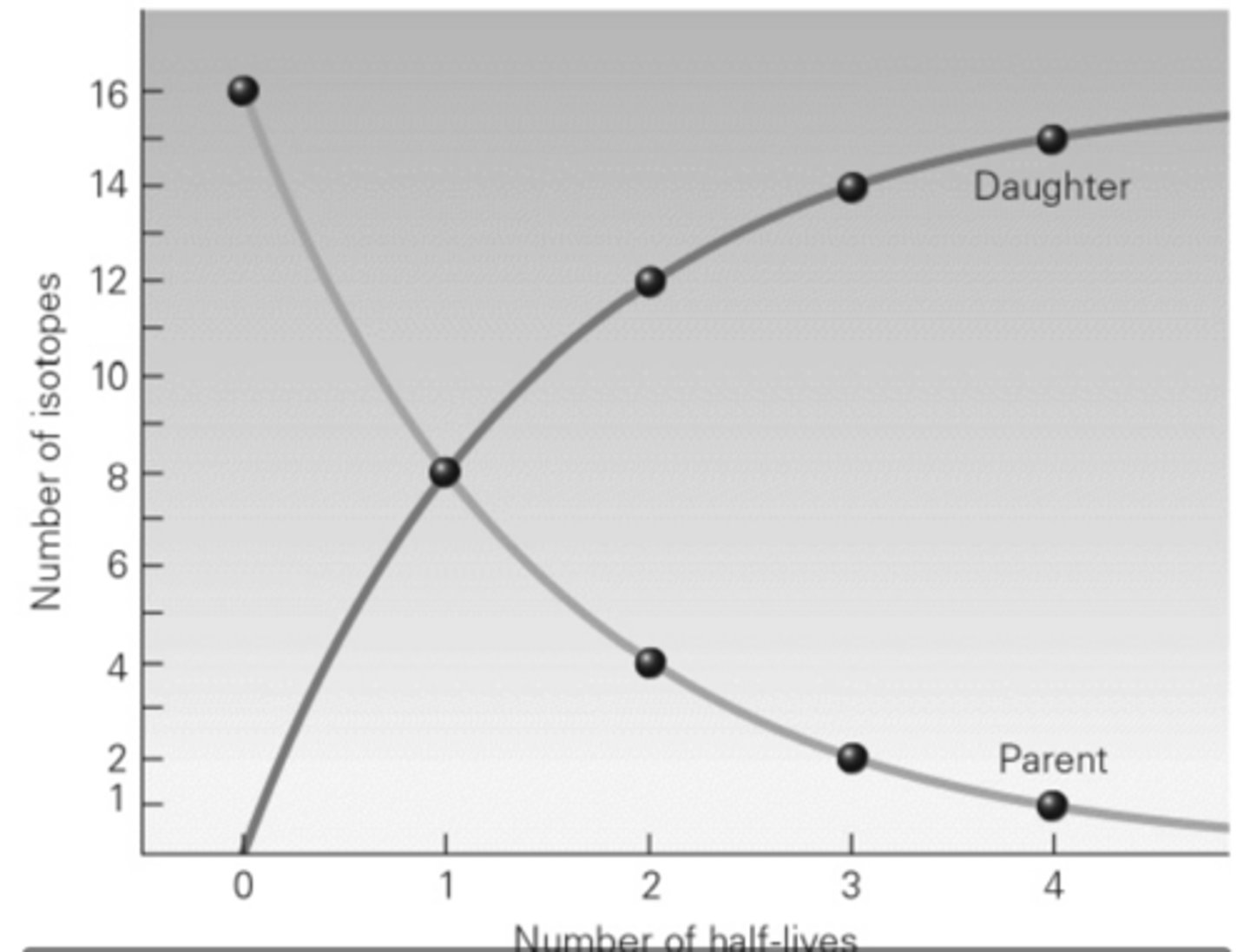
Referring to the graph below, after one half-life has passed, what is the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes?
a. 16:0
b. 1:1
c. 1:3
d. 1:7
B
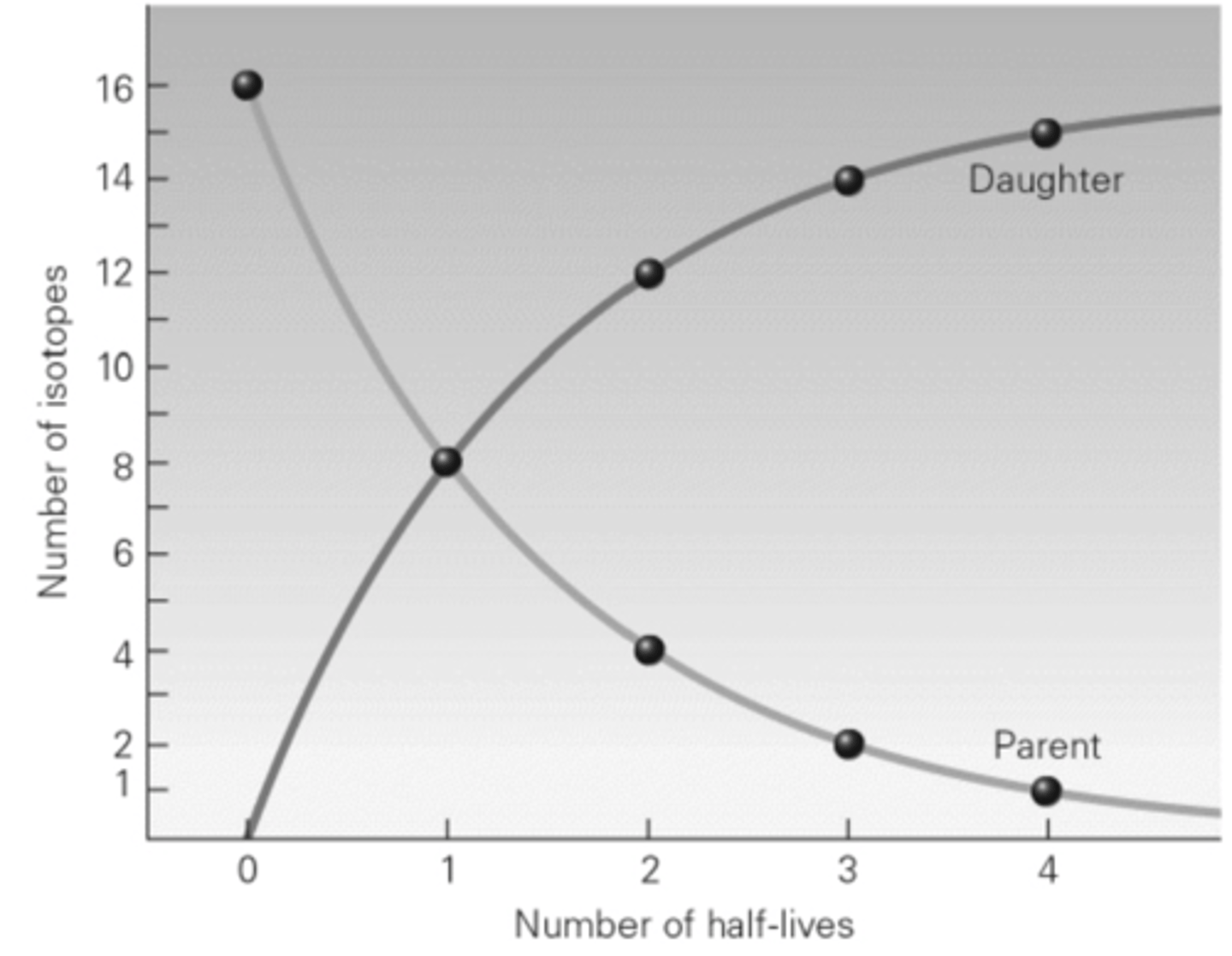
Two atoms of a single element that differ in number of neutrons are said to represent two distinct ________ of that element.
a. isomers
b. isotopes
c. isotherms
d. atomic species
B
Which of the following is ALWAYS the same for different isotopes of a single element?
a. atomic number
b. atomic mass
c. the number of neutrons
d. half-life
A
A radiometric age for a mineral crystal within an igneous rock measures the amount of time that has passed since the
a. atoms within the crystal were part of a body of molten magma
b. crystal solidified
c. temperature of the crystal became equal to the surface temperatures
d. temperature of the crystal became equal to the closure temperature for the mineral
D
How has the half-life of a radioactive parent isotope defined?
a. the time it takes for half of the parent isotope to decay
b. half the time it takes for the amount of parent isotopes to reach zero
c. the time it takes the parent isotope to go through half the decay steps necessary to produce a stable daughter isotope
d. half of the average rate of decay of the parent isotope
A
Accurate radiometric dating typically requires that a rock contains a measurable amount of
a. parent isotope atoms
b. daughter isotope atoms
c. either parent or daughter atoms
d. both parent and daughter atoms
D
The closure temperature represents the point when ________.
a. a magma cools to the point where minerals begin to crystallize
b. radioactive isotopes begin to decay
c. atoms are no longer free to move out of a crystal lattice
d. the last remaining magma crystallizes
C
Why is radiocarbon dating rarely applied in geological work?
a. No substances on the Earth contain significant amounts of carbon-14
b. The half-life of carbon-14 is so long that it is effectively a stable isotope
c. The half-life of carbon-14 is so short that it can only be used to date materials that are less than 70,000 years old
d. Carbon-14 is destroyed by the heat of magma
C
Dendrochronology involves dating of historic and geologic events through the study of
a. growth layers in shells
b. oxygen isotope profiles in glacial ice
c. remnant magnetism in iron-rich minerals
d. annual growth rings in trees
D
How long are the half-lives of radioisotopes commonly used to date igneous and metamorphic rocks?
a. seconds to minutes
b. a few years
c. hundreds of millions to billions of years
d. hundreds to thousands of years
C
In the 1800s, Lord Kelvin estimated the age of the Earth, utilizing a number of assumptions. Which wrong assumption was the primary reason why his estimate (approx. 20 million years) was so wildly inaccurate?
a. that the Earth was once hotter than it presently is today
b. that the Earth may have been molten when first formed
c. that no new heat has been added to the Earth since its initial formation
d. that the Earth would lose heat over time through radiation into outer space
C
Which statement best summarizes the development of the geologic time scale?
a. Relative ages for sedimentary strata were known before accurate numerical dates for these rocks were measured
b. Numerical ages for rocks were known before the relative sequence of sedimentary layers was established
A
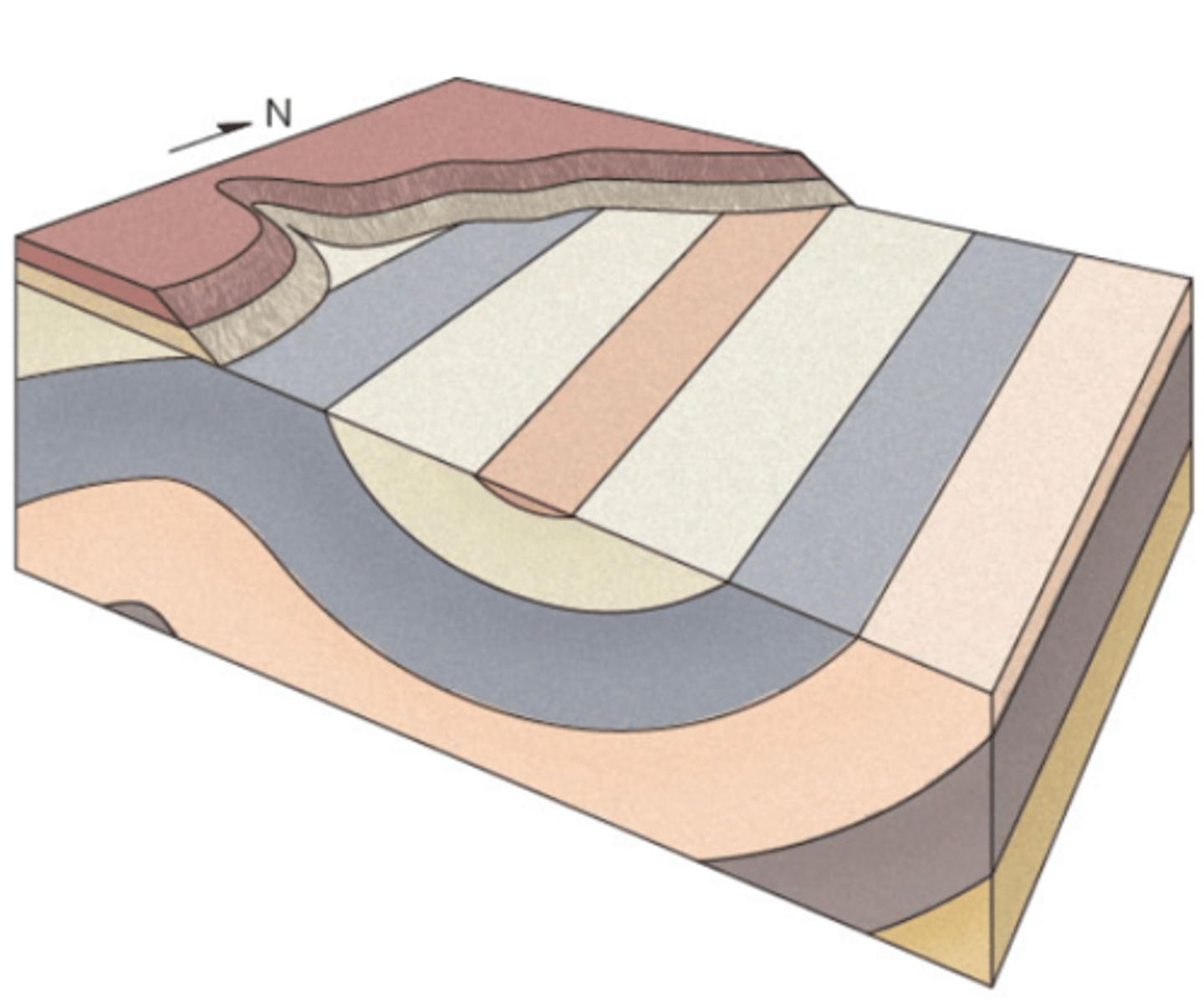
Block diagrams allow for geologists to render rock units in three dimensions. Features such as unconformities and folds will look different from different angles. What features are shown in the block diagram below?
a. a fault and a nonconformity
b. an anticline, syncline and an angular unconformity
c. a disconformity and a reverse fault
d. a syncline and a nonconformity
B
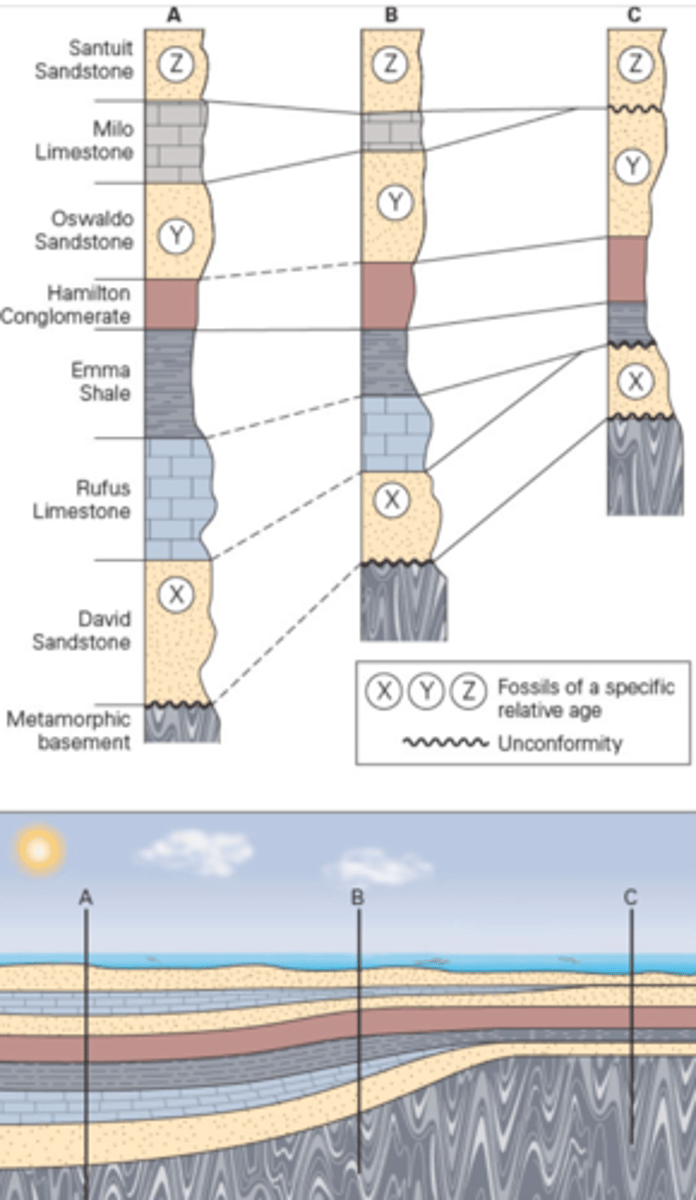
Examining stratigraphic sections from several different locations can determine, through stratigraphic correlation, the lateral extent of units. Which unit(s) are present in sections A and B, but not in section C?
a. the Oswaldo Sandstone
b. The Rufus and Milo Limestones
c. The Emma Shale and the Hamilton Conglomerate
d. The Santuit Sandstone
B
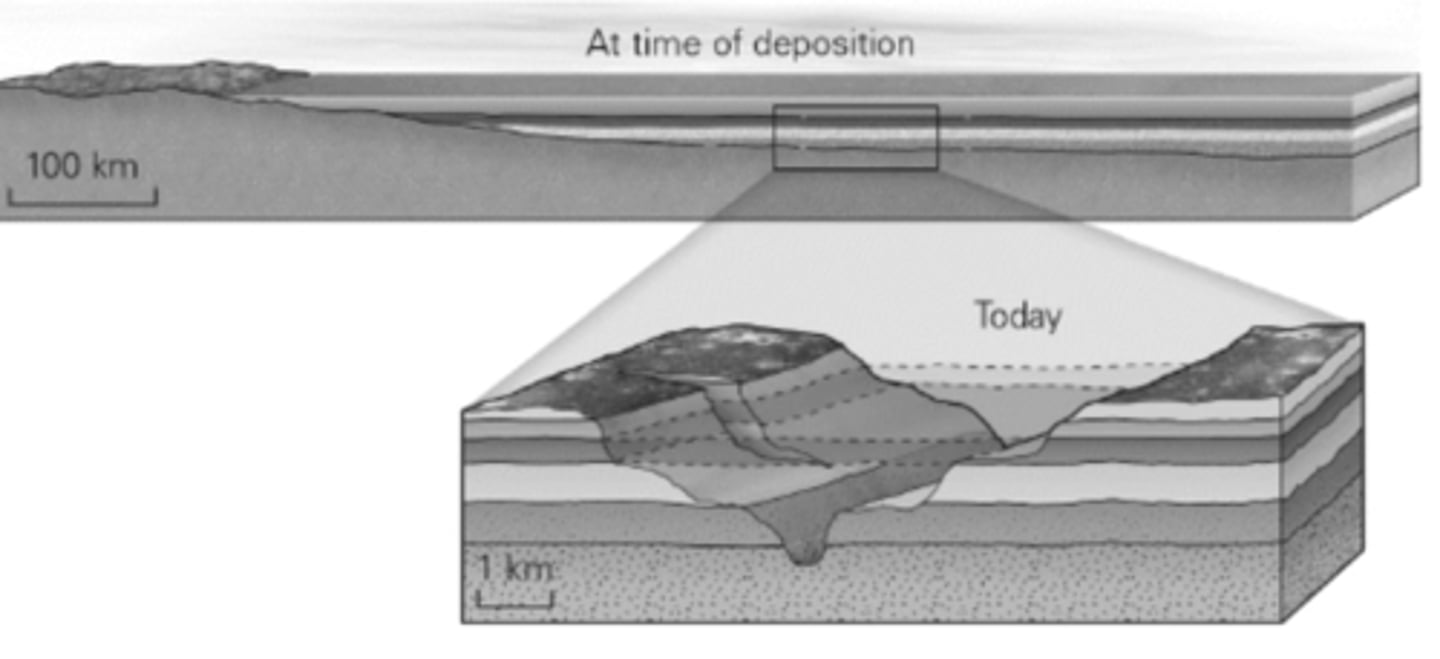
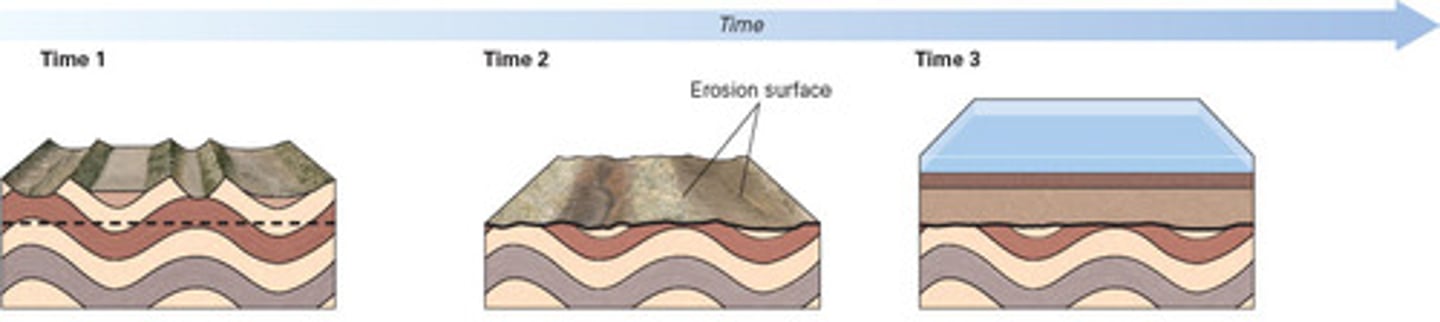
Geologists refer to the contact between two units as an unconformity when it represents a period of no deposition, or possibly erosion. What type of unconformity is illustrated by the time sequence illustrated below?
a. nonconformity
b. disconformity
c. lateral conformity
d. angular conformity
D
Geologists refer to the contact between two units as an unconformity when it represents a period of no deposition, or possibly erosion. What type of unconformity is illustrated by the time sequence illustrated below?
a. nonconformity
b. disconformity
c. lateral conformity
d. angular conformity
A
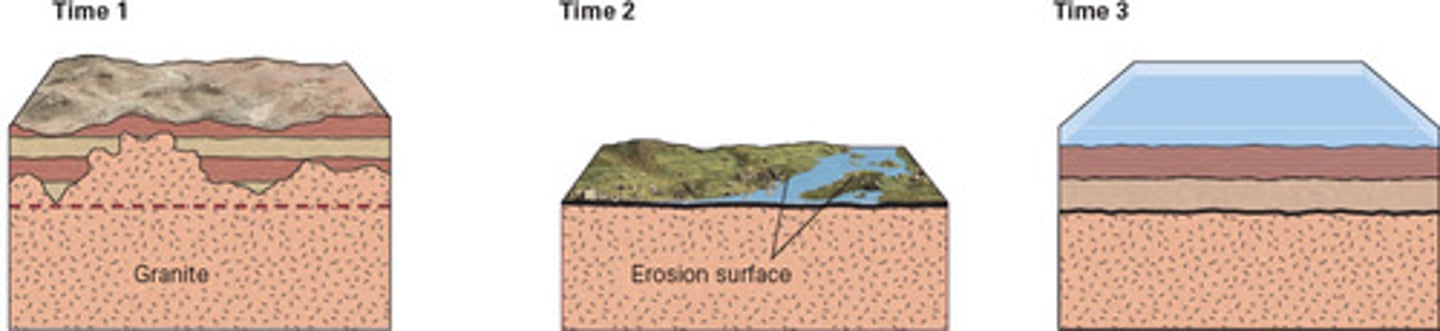
The following image shows a stratigraphic section of the Grand Canyon. Between which two groups is there an angular unconformity?
a. between the Kiabab Limestone and the Toroweap Formation
b. between the Unkar Group and the Tapeats Sandstone
B
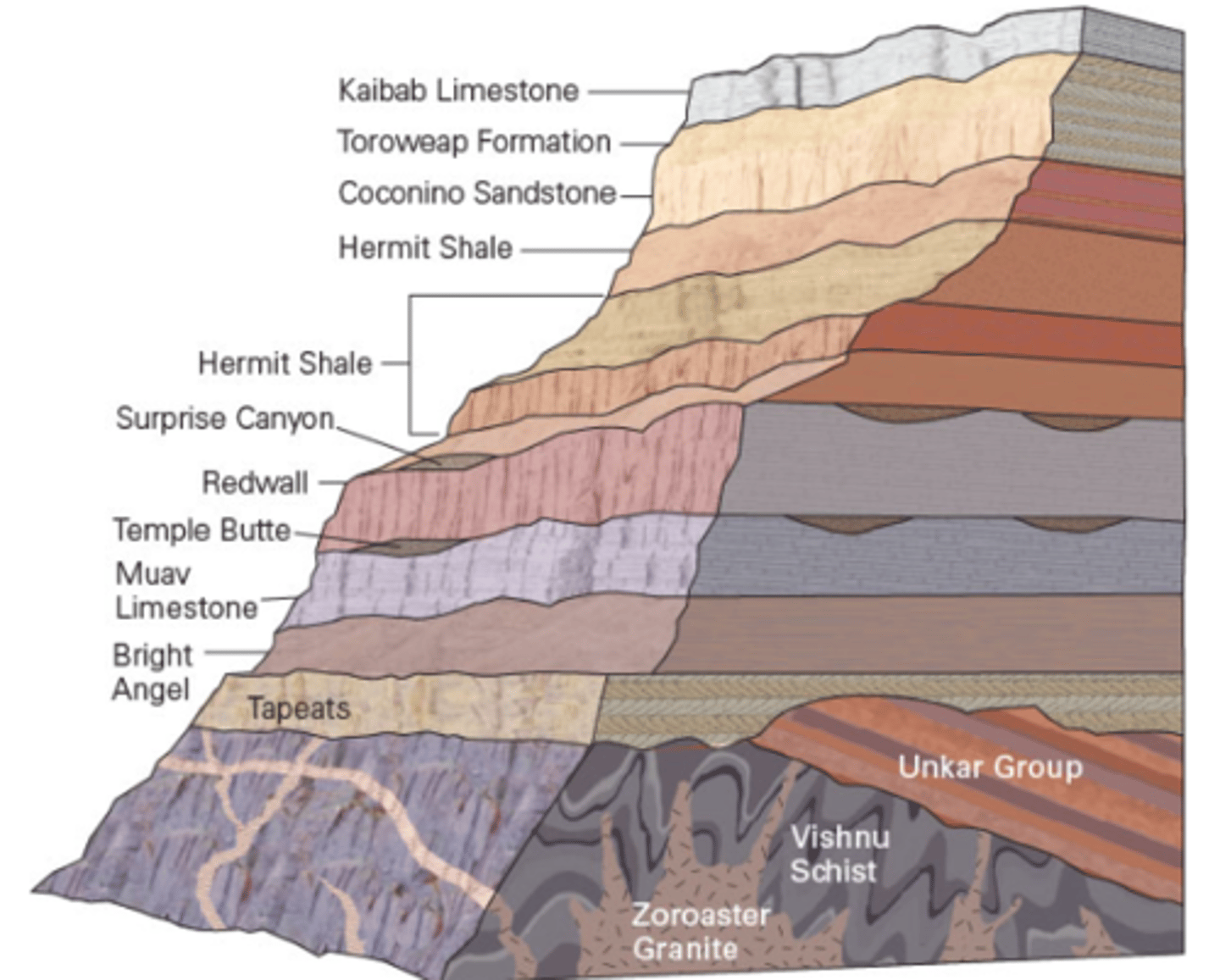
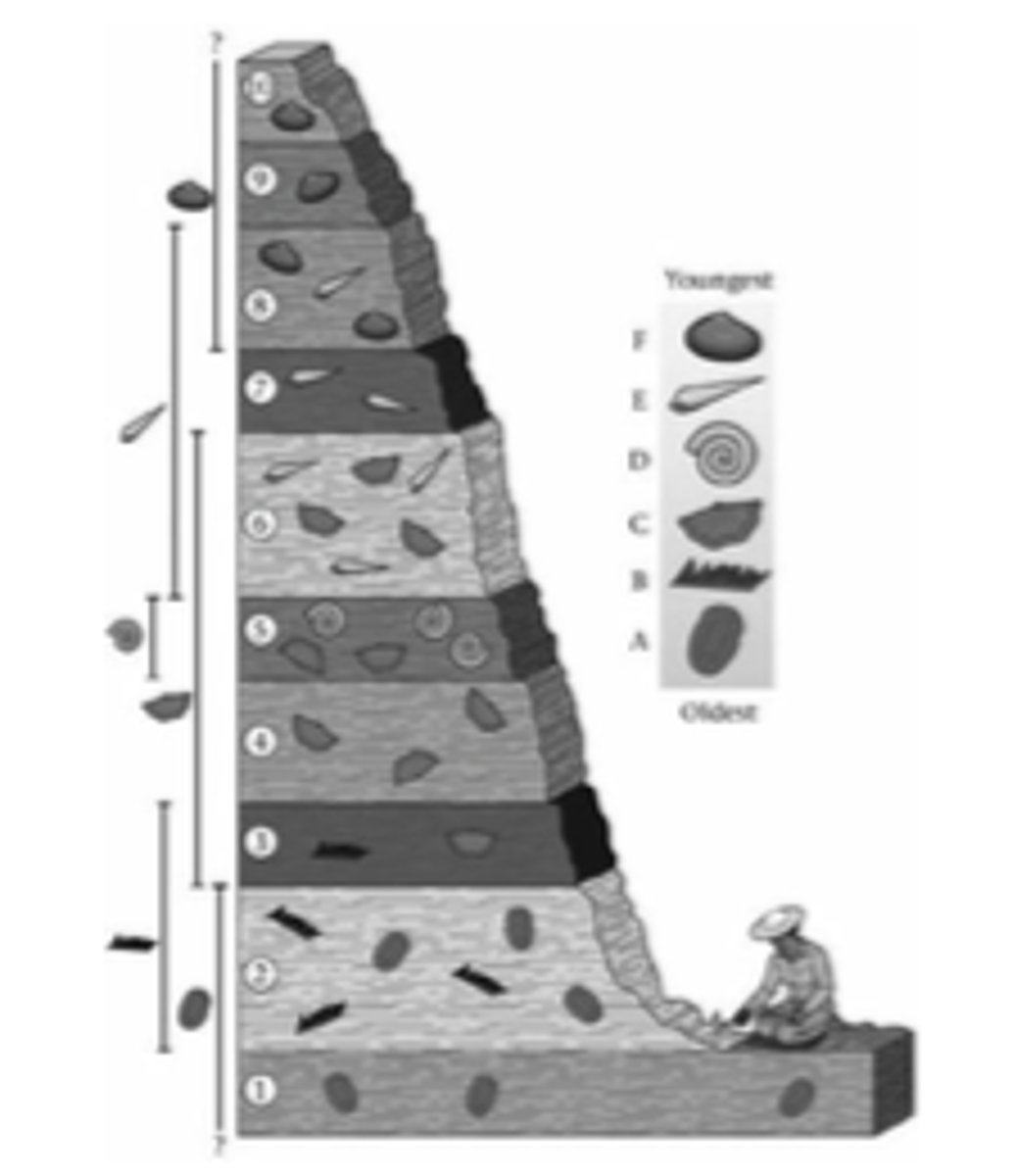
The principle of fossil succession states that each fossil species has a distinct range, an interval of time when it lived. According to the image below, what is the range for fossil E?
a. unit 6
b. units 1-10
c. units 6-8
d. units 3-6
C
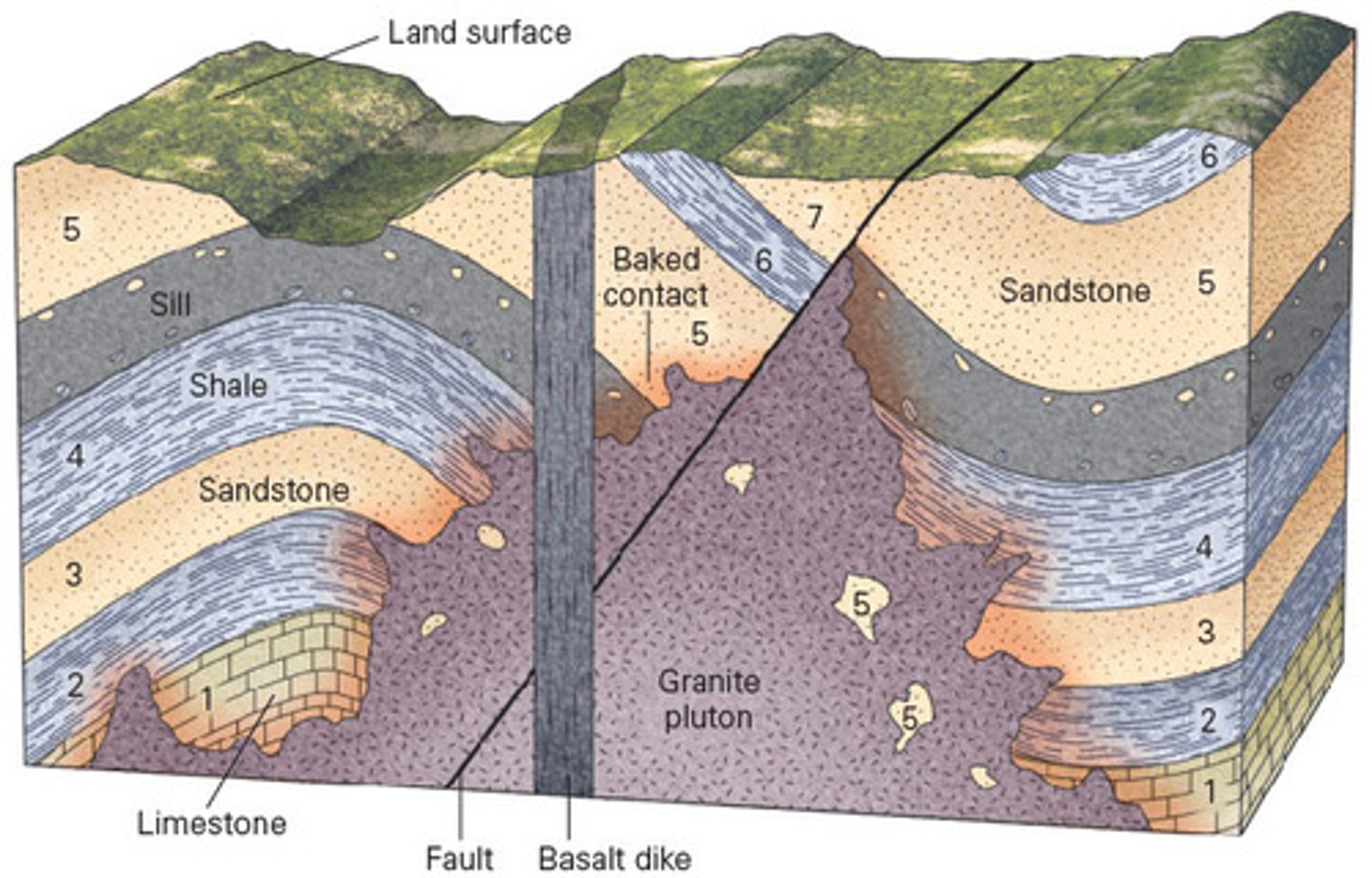
Using the geologic principles of relative dating, it is possible to tease apart rock outcrops and determine which are the oldest and the youngest beds in a sequence. In the cross-section below, identify oldest bed in the sequence.
a. 1
b. granite pluton
c. 5
d. basalt dike
A
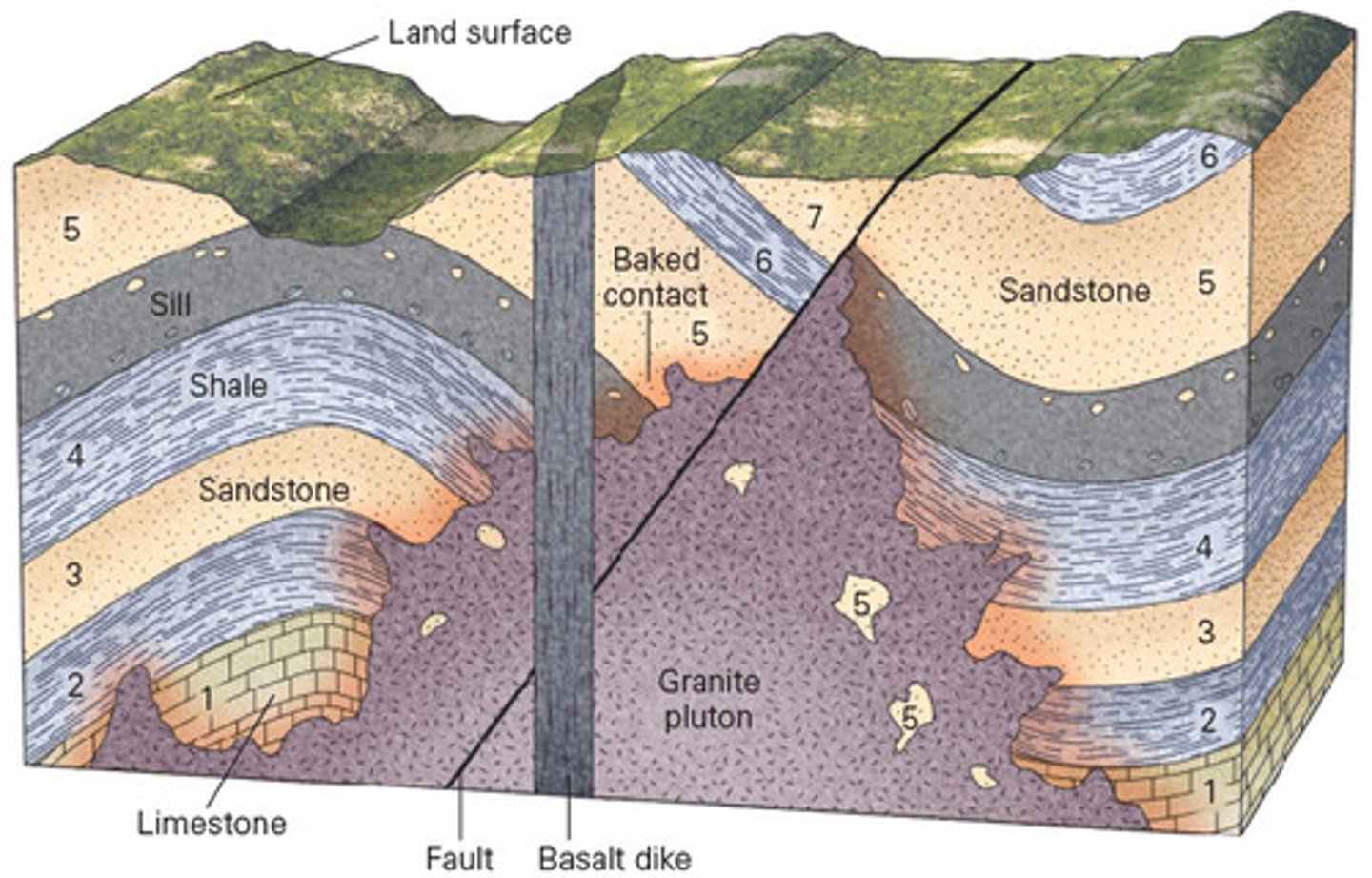
Using the geologic principles of relative dating, it is possible to tease apart rock outcrops and determine which are the oldest and the youngest beds in a sequence. In the cross-section below, identify youngest event in the sequence.
a. erosion of the land surface
b. the basalt dike
c. the granite pluton
d. folding
A