ap psych review
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Scientific method
A self-correcting process for asking questions and observing natural answers.
Hypothesis
A theory that can be tested.
Theory
Explains behaviors or events by offering ideas that organize observations.
Operational definitions
A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study.
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study to see whether the basic finding can be reproduced.
Naturalistic observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without manipulation.
Case study
A descriptive technique studying one individual or group in depth to reveal universal principles.
Survey
A technique for obtaining self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a group through questioning.
Sampling bias
A flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample.
Population
All those in a group being studied from which samples may be drawn.
Random sample
A sample that fairly represents a population with each member having an equal chance of inclusion.
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together and predict each other.
Correlation coefficient
A statistical index of the relationship between two things, ranging from -1.00 to 1.00.
Variable
Anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure.
Scatterplot
A graph of dots representing values of two variables, indicating the direction and strength of their relationship.
Illusory correlation
Perceiving a relationship where none exists or a stronger relationship than actual.
Regression toward the mean
The tendency for extreme scores to fall back toward the average.
Experiment
A research method where an investigator manipulates factors to observe effects on behavior or mental processes.
Experimental group
The group exposed to the treatment in an experiment.
Control group
The group not exposed to the treatment, serving as a comparison for evaluating effects.
Random assignment
Assigning participants to groups by chance to minimize preexisting differences.
Double-blind procedure
An experimental procedure where both participants and staff are unaware of treatment assignments.
Placebo
Experimental results caused by expectations alone, involving an inert substance assumed to be active.
Independent variable
The factor manipulated in an experiment to study its effect.
Confounding variable
A factor other than the one being studied that might influence study results.
Dependent variable
The outcome measured in an experiment that may change when the independent variable is manipulated.
Validity
The extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
Informed consent
Providing potential participants with enough information to choose whether to participate.
Debriefing
The post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions.
Descriptive statistics
Numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups.
Histogram
A bar graph depicting a frequency distribution.
Mode
The most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution.
Mean
The arithmetic average of a distribution.
Median
The middle score in a distribution.
Skewed distribution
A representation of scores lacking symmetry around their average value.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution.
Standard deviation
A measure of how much scores vary around the mean.
Normal curve
A symmetrical bell-shaped curve describing the distribution of many types of data.
Inferential statistics
Numerical data that allow generalizations from sample data to a population.
Statistical significance
A statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance.
Neuron
A nerve cell, the basic building block of the nervous system.
Cell body
The part of a neuron containing the nucleus and life support center.
Dendrites
Branching extensions of a neuron that receive and integrate messages.
Axon
The neuron extension that passes messages to other neurons or muscles.
Myelin sheath
A fatty tissue layer encasing axons, enabling faster transmission of impulses.
Glial cells
Cells that support, nourish, and protect neurons, playing a role in learning and memory.
Action potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse.
Refractory period
A brief resting pause after a neuron has fired, during which subsequent action potentials cannot occur.
All-or-none response
A neuron's reaction of either firing or not firing.
Synapse
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the receiving neuron.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross synaptic gaps between neurons.
Reuptake
The reabsorption of neurotransmitters by the sending neuron.
End
Lesion
Tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
MEG (magnetoencephalography)
A brain imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity.
CT scan (computed tomography)
A series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure.
PET (position emission tomography) scan
A visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue, showing brain anatomy.
fMRI (functional MRI)
A technique for revealing blood flow and brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans, showing brain function as well as structure.
Brain stem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, responsible for automatic survival functions.
Medulla
The base of the brainstem that controls heartbeat and breathing.
The Thalamus
The brain’s sensory control center, directing messages to sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmitting replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
Reticular formation
A nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus, playing an important role in controlling arousal.
Cerebellum
The little brain at the rear of the brainstem, responsible for processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory.
Limbic system
A neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres, associated with emotions and drives, including the amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus.
Amygdala
Two lima bean neural clusters in the limbic system linked to emotion.
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus that directs several maintenance activities, governs the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
The hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process the storage of explicit memories of facts and events.
Cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres, responsible for control and information processing.
Frontal lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex located just behind the forehead, involved in speaking, muscle movements, planning, and judgment.
Parietal lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex at the top of the head and toward the rear, responsible for receiving sensory input for touch and position.
Occipital lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex at the back of the head, which includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
Temporal lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex located roughly above the ears, containing auditory areas that receive information primarily from the opposite ear.
Motor cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
Somatosensory cortex
An area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes sensations of body touch and movement.
Association areas
Areas of the cerebral cortex not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
Plasticity
The brain's ability to change, particularly during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or forming new pathways based on experience.
Neurogenesis
The formation of new neurons.
brocas area
responsible for speaking (forming words or sentences) damage : broca’s aphasia
wernickes area
comprehending written and spoken language damage: wernickes aphasia
pons
above the brain stem, attentions, death
corpus callosum
connect left and right hemispheres
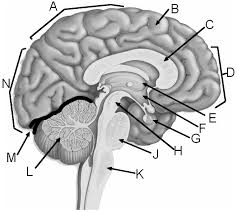
a
parietal lobe
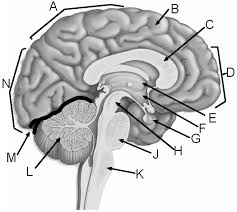
b
gyrus of cerebrum
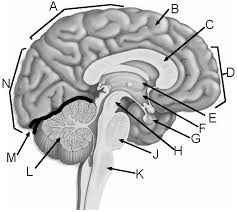
c
corpus callosum
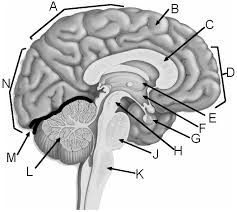
d
frontal lobe
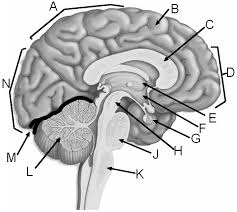
e
thalamus
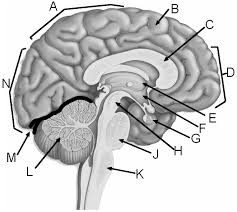
f
hypothalamus
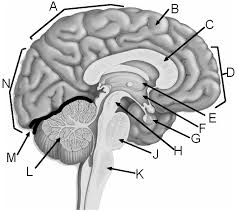
g
pituitary gland
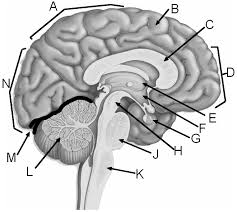
h
midbrain
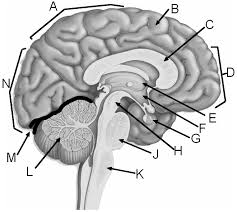
j
pons
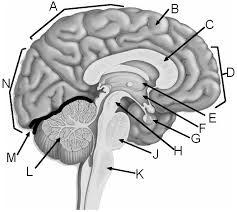
k
medulla
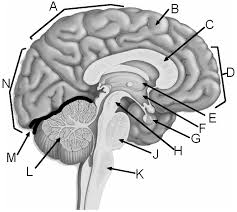
l
cerebellum
Corpus Callosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
Split brain
A condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain’s two hemispheres by cutting the fibers connecting them.
Consciousness
Our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment.
Cognitive neuroscience
The interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition.
Dual processing
The principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks.