20. Investigation and management of nystagmus in optometric practice
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is nystagmus?
constant, involuntary, oscillation of the eyes
3 categories of nystagmus?
Physiological nystagmus, Early-onset nystagmus, Acquired nystagmus
describe the 2 components of nystagmus
slow phase drift away from the assumed position of gaze
fast phase that returns the eyes to the position of gaze
What is Optokinetic nystagmus (OKN)
an oculomotor response to minimise retinal slip provoked by large moving stimuli or the entire visual field
What is end point nystagmus?
End-point nystagmus is seen when looking at extreme positions of gaze
3 types of early-onset nystagmus
latent
spasmus nutans
infantile
Features of Early-onset nystagmus
Nystagmus that presents within the first few months of life • Unless it results from a condition that has caused an acquired nystagmus such as a head trauma or brain injury
define Latent nystagmus (early-onset nystagmus)
Form of nystagmus that appears when one eye is occluded (latent-latent nystagmus) or worsens upon occlusion (manifest-latent nystagmus)
what is the beat direction in latent nystagmus
• In latent nystagmus the beat direction of the nystagmus is always towards the fixating eye
For instance, if the right eye is occluded both eyes will beat to the left (fixating eye; left-beating nystagmus)
Switching the occlusion to the other eye will reverse the beat direction
What is latent nystagmus also known as?
fusion maldevelopment nystagmus syndrome
define Spasmus nutants (early-onset nystagmus)
a high frequency, low amplitude nystagmus of disconjugate nature with irregular head nodding and abnormal head posture
Onset of spasmus nutants
Onset during the first year of life
does spasmus nutants resolve?
the condition tends to resolve spontaneously usually within two years of onset•
define infantile nystagmus (early-onset nystagmus)
a constant nystagmus, usually predominantly in the horizontal axis, of similar amplitude in each eye, and at an average frequency of 2-3Hz (Vertical and torsional (rotary) components may also be present)
How does infatile nystagmus prsent?
Develops in the first 6 months of age and persists throughout life
What is the waveform
the pattern of eye movements (eye position change between beat-to-beat) seen in each individual
How does the waveform vary?
between individuals, and often, within the same individual at different times of gaze angles
Classification pf nystagmus waveform?
jerk or pendular
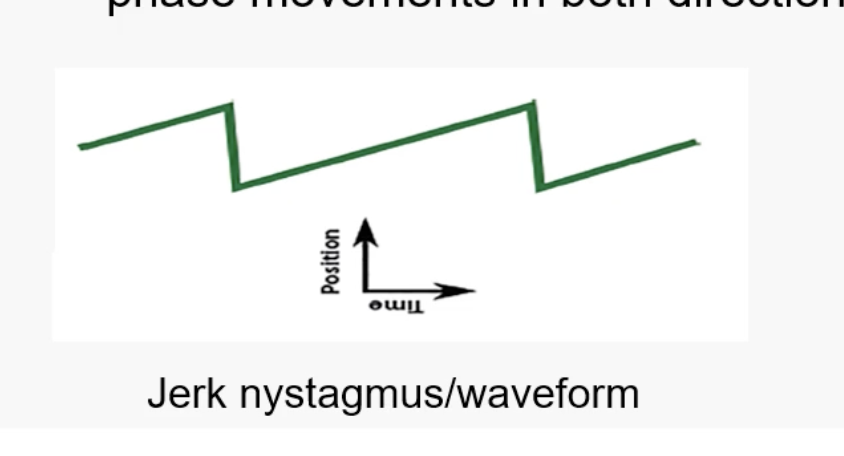
What is Jerk nystagmus?
the waveform has a slow phase or drift away from fixation, which is the abnormal movement, and a fast corrective movement (saccade) in the opposite direction
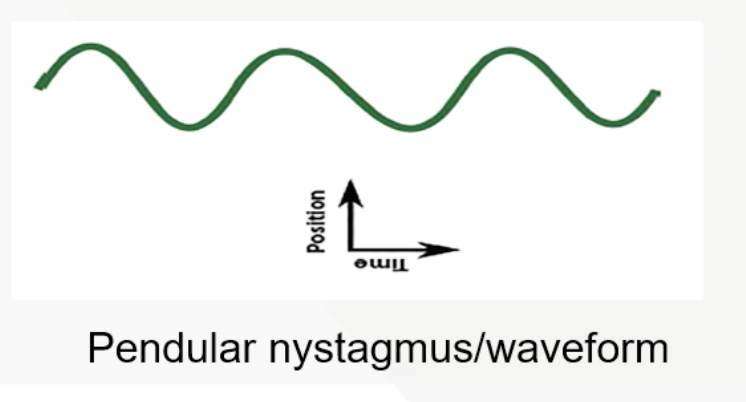
What is Pendular nystagmus
the waveform is characterised by equal velocity slow phase movements in both directions similar to the motion of a pendulum
3 ways to describe a waveform
amplitude
frequency
foveation period
What does the amplitude of a nystagmus waveform represent
Amplitude: measured in degrees, represents the extent of the movement between the start of the drift away from the fixation and the start of the corrective fast movement (saccade) in the opposite direction
What does the frequency of a nystagmus waveform represent?
Frequency: number of beats that occur in a given time. The greater the number of beats, the higher the frequency (i.e. low, moderate or high)-
What does the foveation period of a nystagums waveorm represent?
Foveation period: area in the waveform where the eye velocity is at a minimum and VA is maximal (where the image has returned to the fovea before it drifts off again)
What is used to describe typical nystagmus waveform?
Amplitude, Frequency, Foveation period
What is the null zone
The null zone is the gaze angle at which the nystagmus is minimised
Infantile nystagmus null zone
73% of individuals with IN have a null zone within the 10 of primary gaze position • Most of these individuals use a precise head posture to facilitate this, particularly if the null point is more than 20 outside of the primary position• In around 44% of individuals with IN, convergence also reduces the nystagmus•
How is the nystagmus null zone and VA related?
Although there is controversy in relation to the null zone and an improvement of VA, patients with nystagmus often report that vision is at least 'most comfortable' in this position
What is Oscillopsia
the perception of the world as moving back and forth
Who is more likely to experience oscillopsia
Patients with acquired nystagmus are much more likely to experience oscillopsia
head shaking of infantile nystagmus
Some individuals with IN also exhibit regular head oscillations that increase in intensity with effort to see
Infantile nystagmus and refractive error and astig
High refractive error is common in IN
A broad range of refractive errors may be found
Tendency towards myopia
High incidence of corneal with-the-rule astigmatism
Astigmatism seems to increase with age
define Idiopathic infantile nystagmus and what testing is used
Idiopathic IN is a diagnosis by exclusion where all other possible causes and associated conditions have been ruled out
Electrophysiological testing is essential to rule out some of the conditions known to be associated with IN
What is Acquired nystagmus
Pathological nystagmus may develop as a result of disease, injury often to the vestibular or central nervous system
Common causes of acquired nystagmus?
multiple sclerosis and stroke
When should nystagmus be reffered?
Any suspicion of acquired nystagmus should result in a prompt referral • Every patient with any form of pathological nystagmus should have (or have had) a thorough neuro-ophthalmological examination • Any patient presenting for the first time with nystagmus requires urgent referral to rule out life-threatening causes
Features that should raise the suspicion of acquired nystagmus
Asymmetry, that is disconjugacy of the nystagmus eye movements
Significant vertical component
Reports of oscillopsia
Key Qs for H&S with nystagmus
How long has nystagmus been present?
Is oscillopsia perceived?
Is there a history of strabismus?
Is there a family history of nystagmus?
What should be assessed with nystagmus during optometric exam?
Whether the nystagmus intensity increases with occlusion
Whether the eye movement is symmetrical
Whether the beat direction changes depending on which eye is covered
Whether head shaking is present
Whether convergence reduces the nystagmus
Whether there is a null zone and whether a head posture is used
What modifications can allow an accurate refraction for px with nystagmus?
Avoid phoropters
Allow patients to use their preferred head position to use their null zone
Use wide aperture trial lenses
Give patients plenty of time to respond to letters when reading the chart
Use fogging lenses and conduct a binocular refraction instead of occlusion
VF may be performed in patients with nystagmus nut the results may not be very sensitive to small field defects
CT may be more difficult due to the constant movement of the eyes
3 steps in an 'ideal' management plan for patients with nystagmus
Treat the underlying condition (if any)
Fully correct the refractive error
Minimise the nystagmus intensity
What is Nystagmus Network
a national charity an support group that can provide individuals with nystagmus and their families with practical information
Management of latent nystagmus
Refractive error correction for accommodative SOT and/or surgical management alignment of the deviation can reduce the nystagmus intensity
These interventions can convert the manifest-latent nystagmus to latent-latent nystagmus and improve binocular VA
what special considerations should be taken when managing an amblyopia associated or combined with a latent nystagmus
The nystagmus will worsen with traditional occlusion (patching) so use penalisation or atropine therapy should be used instead
Management of infantile nystagmus
At present there is no effective treatment for IN but there are a number of interventions
Optical management
Recommendations regarding the use of the null zone
Surgical management
Pharmacological management
management of infantile nystagmus
Full refractive error correction should be given
CL
Prism therapy to modify the null zone
why are Contact lenses good for infantile nystagmus?
CL provide superior refractive error correction over spectacles in nystagmus due to the reduction in peripheral lens aberrations and lack of prismatic effect when the eye moves away from primary position
Some studies report that CL provide at least a line of VA improvement compared to spectacles
What is Prism therapy to modify the null zone for IN
Prisms may be used to allow patients to adopt their null zone of gaze while keeping the head straight • For example, a patient with a null zone right-gaze will turn the head to the left and would benefit from 'base left' prisms in front of each eye (BOUT in LE and BIN in RE)
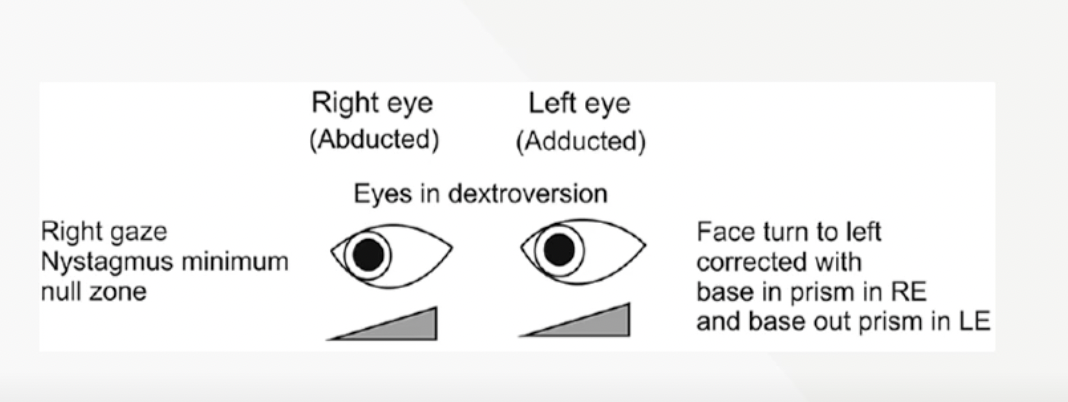
Prism therapy options to modify the null zone
An alternative is to use Fresnel stick-on prisms, although neither option may be cosmetically acceptable to the patient
Many nystagmus have a convergence null zone and therefore it is possible to reduce the nystagmus intensity by inducing convergence with prisms BOUT
Rarely the null zone is in divergent position, in which case BIN prism to induce divergence can reduce the nystagmus intensity
Recommendations regarding the use of the null zone in infantile nystagmus
Using the null zone of gaze usually improves visual function in IN
Individuals with nystagmus often adopt an abnormal head posture to achieve the required gaze position
While such head posture should not be dissuaded, long-term use of such head posture may lead to a restriction of neck movement
Besides using prisms, adjustment to the surroundings, such as changing the seating position during viewing, can be made to place the eyes into the null zone while keeping the head straight
how to manage aquired nystagmus
same as IN
retrobulbar injections of botox