Biology - Diversity of Organisms
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
whole chapter summarised into active recall type questions!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
List the 5 kingdoms of living things
Monera
protista
fungus
plant
animal
What are the key features of living things from the Monera kingdom? (3)
they are simple and unicellular. they are fed by many methods and are prokaryotic (do not contain membrane bound organelle)
What are the features of living things from the Protista Kingdom? (3)
they are complex and unicellular . they are fed by many methods. they are eukaryotic
what is the main difference between organisms from the protista kingdom and the monera kingdom .
organisms from the monera kingdom are prokaryotic while organisms from the protista kingdom are eurokaryotic.
What are the features of living things from the fungus kingdom (3)
heterotrophic , multicellular (except for yeast which is unicellular), eukaryotic.
What are the features of living things from the plant kingdom (3)
autotrophic , eukaryotic , multicellular organisms
What are the features of living things from the Animal Kingdom (3)
heterotrophic , multicelluar organisms , eukaryotic
give an example of an organism from the Monera Kingdom
Bacteria
give an example of an organism from the protista kingdom
amoeba
the type of bacteria is based on its shaped. list the 3 types of bacteria
spherical
rod
spiral
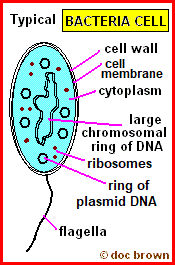
Describe the structure of Bacteria (6)
simple cellular structure
contain flagella for movement
contain capsule , cell wall and cell membrane
prokaryotic
contain DNA and plasmids
contain ribosomes
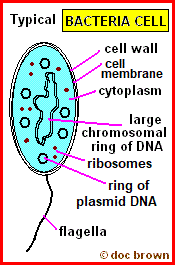
what is the function of the plasmid in the bacteria cell
remembers information about antibiotics
what is an endospore?
an endospore is a tough outer coat on a bacteria produced by spores in unfavourable conditions/
what is the function of endospores
endospores resist high temperatures and lack of water helping the bacteria survive in unfavourable conditions
what is the process called in which bacteria reproduces asexually
Binary Fission
autotrophic bacteria can make there own food . name the two ways in which bacteria can make its own food
photosynthetically
chemosynthetically
some bacteria are heterophic meaning the can’t make there own food. they are known as saprophytes what does this mean
it means they feed of dead and decaying material
explain the term symbiotes
2 organisms live together and atleast 1 benefits
parasitism
a living organism living of another living organism causing it harm
explain the term mutualism in relation to bacteria
when both the host and the bacteria benefit
explain the term commensalism in relation to bacteria
the bacteria benefits with no harm to the host
List the 5 limiting factors for bacteria (factors that effect reproduction/growth)
temperature
space
PH
food
oxygen
what is an obligate anaerobe
bacteria that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen e.g. botulinum
what is a facultative Anaerobe
bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen
what is an obligate aerobe
bacteria that can only survive in the presence of oxygen
what is the name for disease causing bacteria (they are mostly parasites)
pathogenic bacteria
name two types of fungi
rhizopous
yeast
rhizopus is a saprophyte true or false
true
what is the function of the spore in the Rhizopus
reproduction
what is the function of the sporangium in the rhizopus
holds the spores
what is the function of the sporangeophore in the rhizopus
holds up the sporangium
what is the function of the Stolon in the Rhizopus
spreads the fungus across the food surfaces
what is the function of the Rhizoids in the rhizopus
anchors the fungus
how does rhizopus get its nutrition
by releasing enzymes into bread breaking it into a simpler substance which can be absorbed by the fungus where it is used for respiration and growth
explain how fungus reproduce asexually
this occurs in favourable conditions and is the common method of reproduction for fungi. the sporangium produce spores by mitosis . when the spores are released by bursting through the sporangium , they land on the bread where they germinate into hyphae which develop into mycelium (a group of hyphae is known as mycelium)
explain how sexual reproduction of fungus happens (5steps)
hyphae from opposite strains grow closer together producing gametes
the two strains touch breaking down the walls between them
fertilisation occurs between the gametes forming a diploid zygote
the zygote produce a thick outer coat on the outside to protect it from unfavourable conditions and help it to survive
when conditions are favourable the zygospore germinates by meiosis and a hyphae grows out of the zygote . it produces a sporangium at the top. the sporangium by mitosis
what is the function of the contractile vacuole in the ameoba
the contractile vacuole regulates the amount of water let into the amoeba preventing the cell from bursting