Digestion Key Terms
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Absorption
Uptake of a substance
Desiccation
Removing water
Secretion
Release of a substance
Mechanical Digestion
Breakdown of food into smaller bits of the same food with no molecular alteration
Ingestion
Consumption via mouth
Mastication
Chewing
Deglutition
Swallowing
Propulsion
Pushing/moving forward
Peristalsis
Waves of SM contraction that cause propulsion
Defecation
Expelling feces (anything not absorbed/broken down) from the GI tract
Churning
Method of mechanical breakdown
Segmentation
Mechanical breakdown in intestines, breaking food into "segments and mixing (moving in both directions)
Bolus
rounded mushy lump of food (esophagus)
Chyme
Liquefied food (stomach/small intestines)
Feces
Found in colon
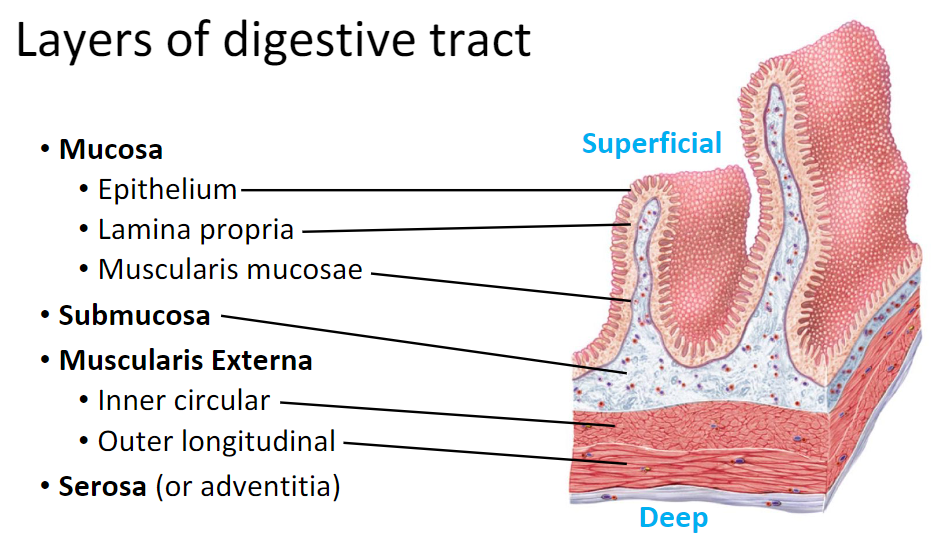
Layers of the Digestive Tract
Mucosa- Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae
Submucosa
Muscularis Externa- Inner circular, Outer Longitudinal
Serosa
Enteric Nerves of the GI tract
Myenteric Plexus - controls peristalsis and other contractions of muscularis externa
Submucosal Plexus- controls muscularis mucosae and glandular excretions of the mucosa
Peritoneum Layers?
Visceral and Parietal
Retroperitoneal organs?
Duodenum, part of the pancreas, part of the large intestines
Mesentery
holds SI to posterior abdominal wall
Mesocolon
Holds LI to posterior abdominal wall
Falciform ligament
Holds liver to anterior abdominal wall
Greater Omentum
Fat layer over transverse colon and SI
Lesser Omenteum
Connects stomach (medial curve) to liver
Esophageal Sphincters? Function?
Upper Esophageal Sphincter- regulates swallowing and keeps excess air out of the esophagus
Lower Esophageal Sphincter- prevents reflux of stomach contents
Layers of the stomach- muscularis
Oblique (inner)
Circular muscle
Longitudinal muscle (outer)
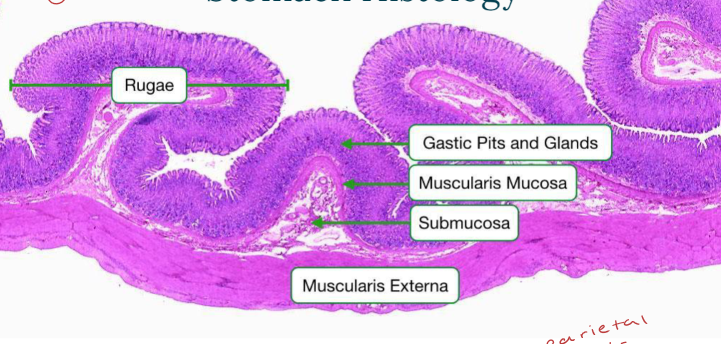
Secretions of the Stomach? Functions? What is the rugae?
HCl (acid), enzymes, and mucous
Churns and liquifies foods
Rugae- layer of mucosa = wrinkly, most superficial (holds more food and + size)
Regions of the stomach?
Cardia, Fundus, Pyloric antrum, Pyloric canal, body, Pylorus, Pyloric Sphincter
Stomach Histology- Gastric Pits & Glands: Cell types?
Chief cells (pepsinogen/gastric lipase), mucous cells, parietal cells (HCl), regenerative SC, enteroendocrine cells (G cells, gastrin…)
Small Intestines functions? Regions? Sphincter?
Absorption, secretion, mixing, propulsion, segmentation, and chemical/mechanical digestion
Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum → Ileocecal Sphincter (small/large)
Small Intestines Circular Folds has…. and function?
Villi and microvilli to increase the SA for absorption.
Small Intestines histology anatomy? A Villus has…
Brush border of microvilli, Goblet cell, Lacteal, blood capillary, chylomicrons, & intestinal crypts
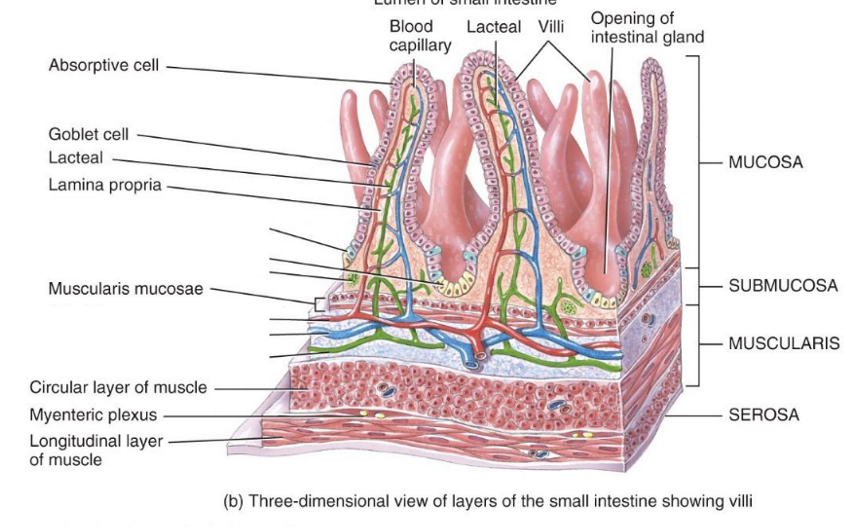
Chylomicrons is…
lymph containing triglycerides, coming from the lacteal. Travels to Thoracic duct (lymph flow) and the venous blood goes to the hepatic portal vein to be cleaned in sinusoids
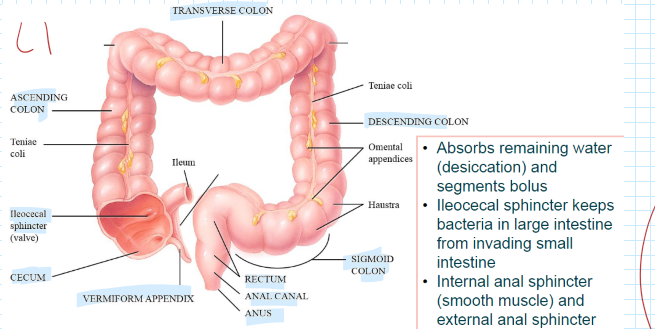
Large Intestines: Functions, regions, and Sphincters?
Absorbs remaining water (desiccation) and segments bolus
R: Cecum, Vermiform appendix, ascending/transverse/descending colon/sigmoid colon, rectum, anal canal, and anus
Sphincters: Internal (SM) and External (Skel. M)
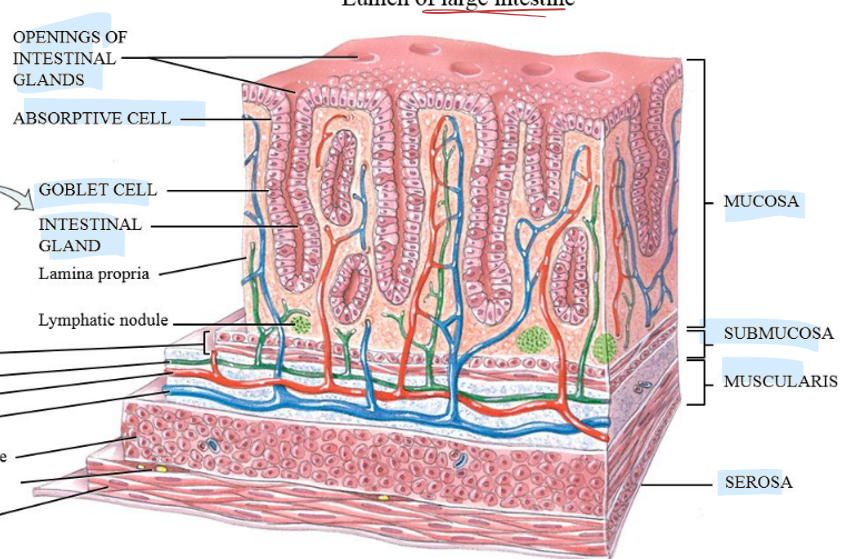
Large Intestines hisology?
Microvilli, absorptive cell (water), goblet cell (mucus secretion), intestinal gland, and openings
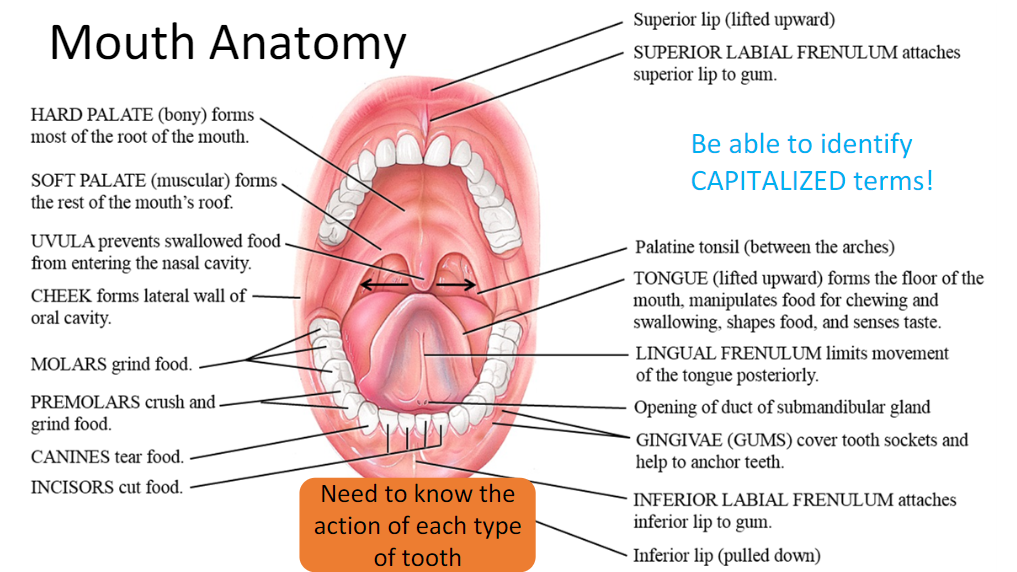
Mouth Anatomy:
Hard palate, soft palate, uvula, gingivae, superior labial frenulum, inferior labial frenulum, lingual frenulum, molar (grind), premolars (grind + crush), canines (tear), and incisors (Cut)
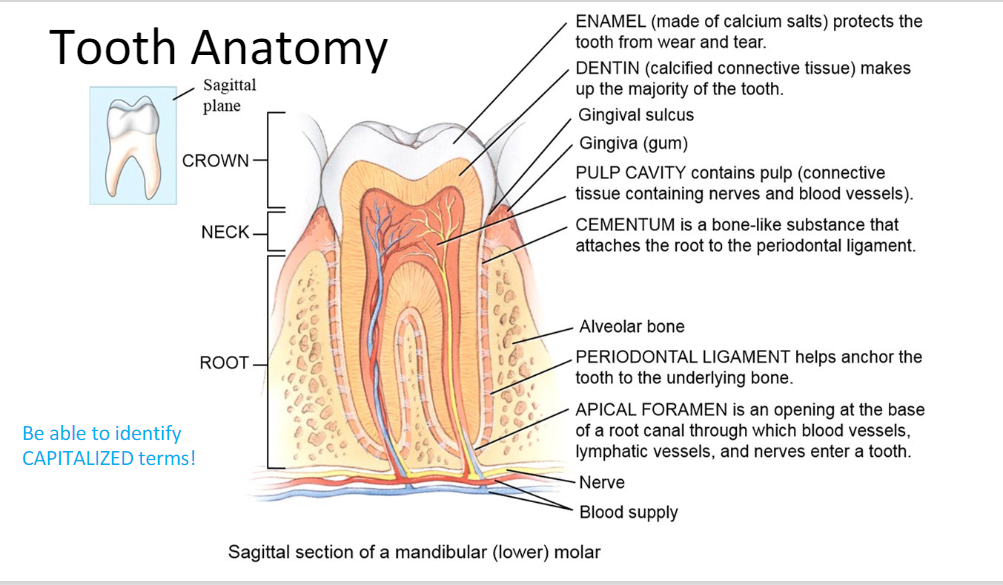
Tooth Anatomy
Enamel (protection), Dentin (calcified CT), Pulp cavity (BVs and nerves), Cementum (root to periodontal ligament), Periodontal ligament (anchor tooth to bone), Apical Foramen (opening for nerves, LVs, and BVs)
Crown, Neck, Root
Salivary Glands: Minor/Major
Intrinsic: scattered = saliva to moisten
Extrinsic: 3 pairs, outside of oral mucosa (Parotid, submandibular, and sublingual)
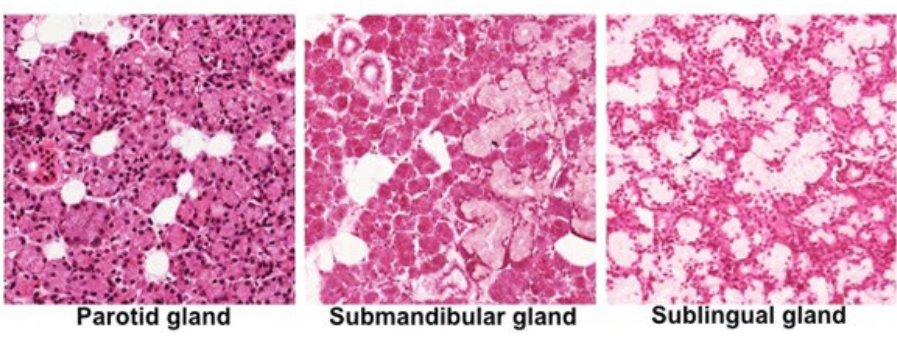
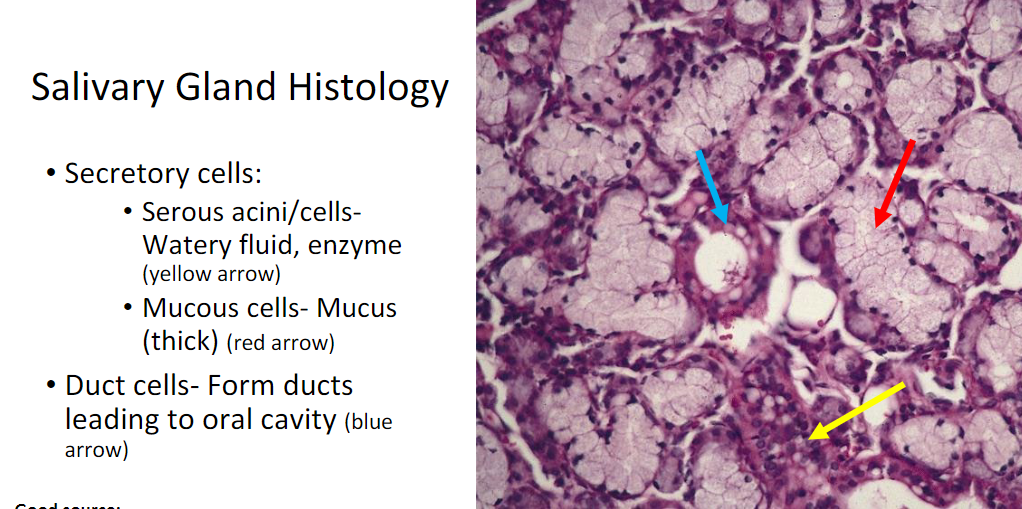
Salivary Glands Histology
Secretory cells: acini and mucous cells
Duct cells: form ducts → oral cavity
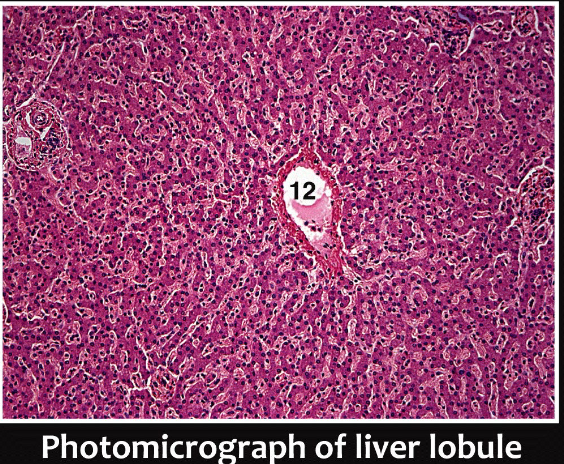
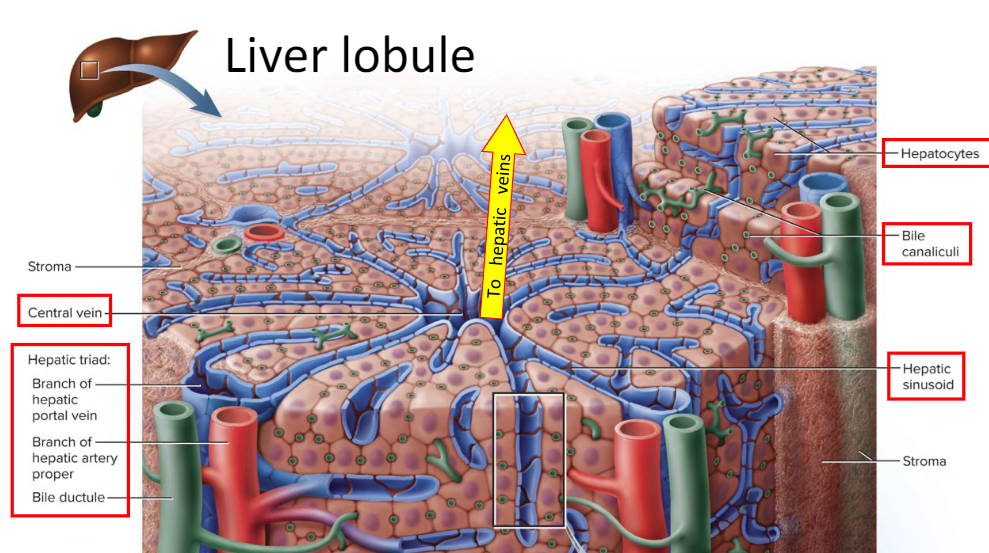
Liver Lobule Components:
Central vein, Hepatic triad (Branch of Hepatic vein/artery and bile ductule), Hepatocytes, Bile canaliculi, and hepatic sinusoid
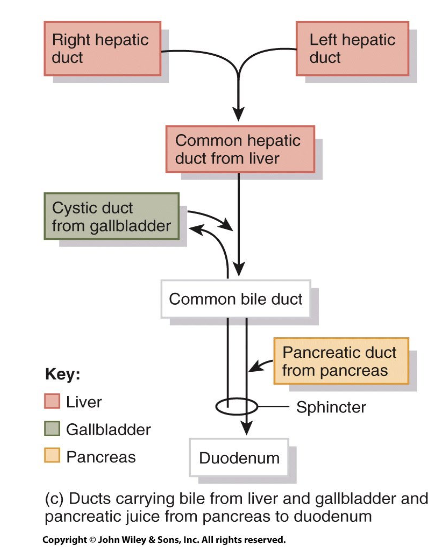
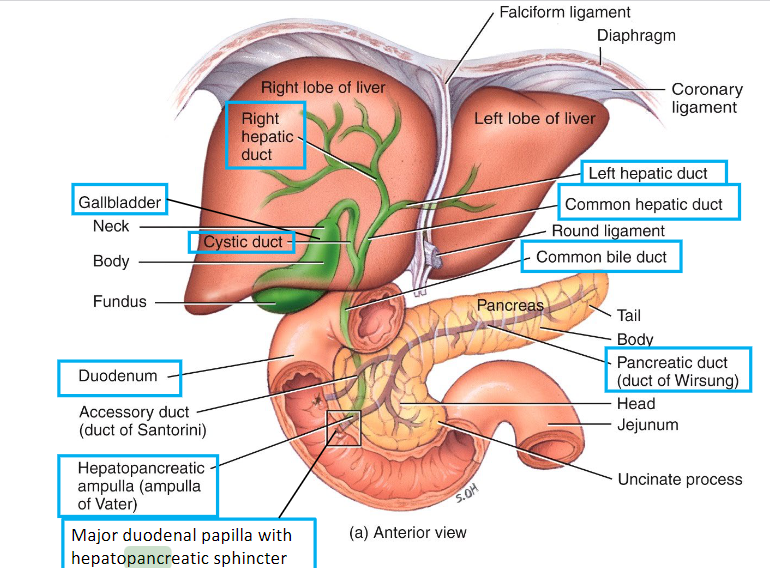
Liver & Gallbladder Flow
Right/Left hepatic duct → Common Hepatic duct from the liver (Cystic Duct from Gallbladder) → Common Bile Duct (Pancreatic duct from pancreas) → Duodenum
Pancreas: Functions and anatomy
F: Secrete digestive enzymes & bicarbonate into the duodenum through the main pancreatic duct, hepatopancreatic ampulla, and Major Duodenal papilla w/ Hepatopancreatic Sphincter
Pancreas Histology:
Islets of Langerhans (endocrine- alpha = glucagon and beta- insulin) and acini (exocrine)
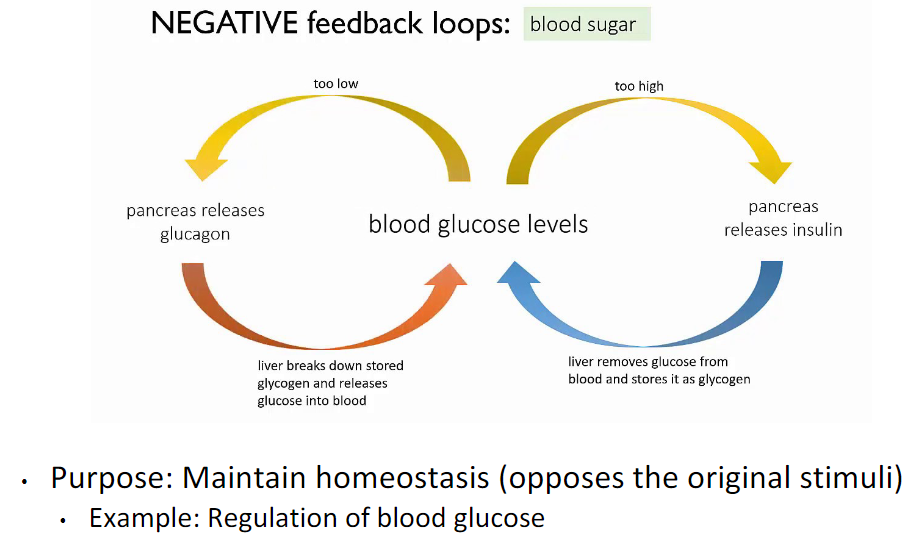
Negative Feedback: Blood sugar (practice
Insulin from beta cells decrease blood sugar by making glucose into glycogen. Glucagon from alpha cells bring blood sugar up by breaking glycogen into glucose.
Protein Digestion
Stomach: Chief cells release pepsin and HCl by parietal cells (Polypeptides → smaller)
SI: Pancreas- trypsin (smaller → dipeptides and aas), Brush Border: Aminopeptidase (smaller peptides → aas + smaller polypeptide) & Dipeptidase (dipeptides → aas)
Carb Digestion
Mouth:
polysaccharides → smaller by salivary amylase by salivary glands
SI:
smaller → disaccharides & monosaccharides, by pancreatic amylase by pancreas
By Brush Border:
alpha-dextrins → monosaccharides by alpha-dextrinase
Sucrose → glucose & fructose, by sucrase
Lactose → glucose & galactose, by lactase
Maltose → 2 glucose, by maltase
Lipid Digestion
Stomach:
lipids → glycerol & fatty acids, by lingual lipase by salivary glands
by gastric lipase by chief cells
SI:
Pancreatic lipase, by pancreas
Parietal cells: Secretions and Their Functions
HCl (kill bacteria, denature protein, activate pepsin) and Intrinsic factor (absorb vitamin B12)
Experiment 1: Enzymes and pH/temp- What was the point? What effect digestion more?
Decrease in pH seems to affect digestion more than decreases in temperature.
Experiment 2: Role of saliva in CARB digestion-
The cracker softens → becomes sweet with time
With time, complex carbs → smaller polysaccharides with salivary amylase
Digestion of carbs begins in the mouth
Experiment 3: Saliva in gustation
Takes longer to taste sweetness on a dry tongue
Sugar from packets (sucrose) can easily dissolve → glucose and fructose ONLY in presence of saliva where receptors can detect it on the tongue
Experiment 4: Influence of Smell on Gustation
Olfactory neurons respond thousands of times more strongly to smell than gustatory receptors do to “taste”
Experiment 5: Role of Bile in Lipid Digestion
Bile emulsifies lipids- mechanically separating oil → smaller droplets
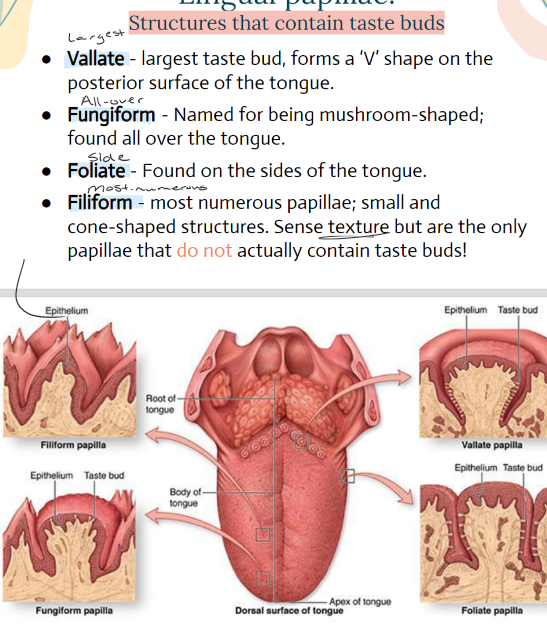
Lingual Papillae: Structures containing tastebuds- Name the 4 and their functions/where they’re found
Vallate- LARGEST, = V shape on posterior surface of the tongue
Fungiform- ALL OVER, mushroom shaped
Foliate- SIDES of tongue,
Filiform- MOST NUMEROUS, small/cone shaped. Sense texture BUT are the ONLY papillae that do not contain taste buds.
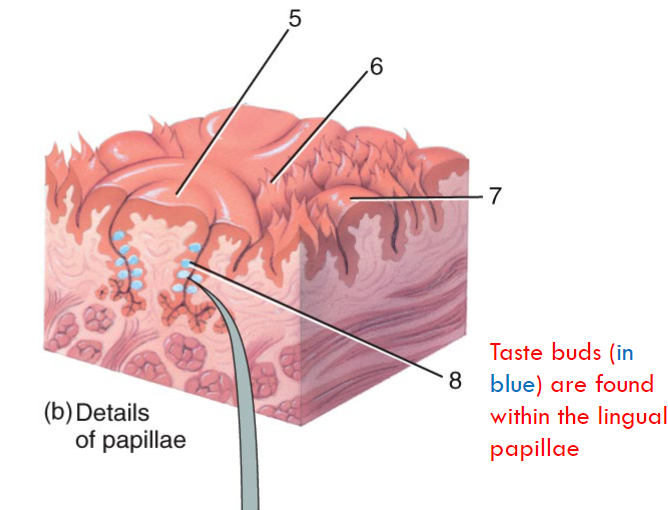
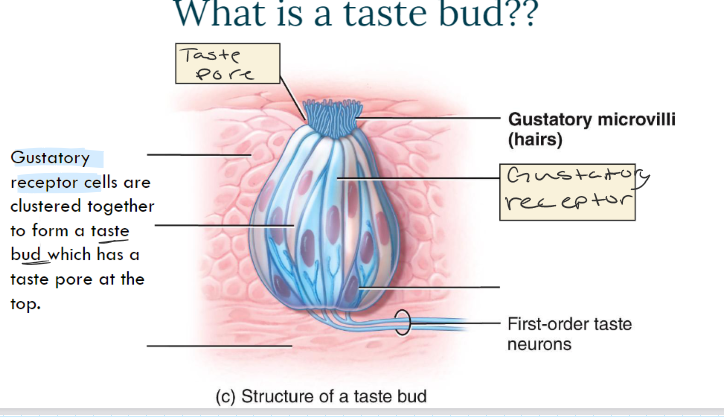
What is a taste bud? Anatomy?
Taste pore, gustatory microvilli, gustatory receptors (form taste bud…)
What are the 5 taste sensations?
Umami, sweet, savory, bitter, and sour (SSUSB)