a/p
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:37 AM on 7/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy vs. Physiology
Anatomy: structure Physiology: function
thoracic cavity
thoracic cavity
2
New cards
Oblique Sections
cuts made diagonally between the horizontal and the vertical planes
3
New cards
Pleural Cavities
lateral subdivision of Thoracic Cavity, enveloping a lung, and the Medial Mediastinum
4
New cards
Abdominopelvic Cavity
seperated from thoracic cavity by the diaphram, a dome shaped muscle important in breathing. Has abdominal and pelvic cavities
5
New cards
Abdominopelvic Regions
Nine divisions used primarily by anatomists
6
New cards
What are the 3 different subdivisions of gross or macroscopic anatomy?
regional, systemic, and surface anatomy
7
New cards
What are 2 subdivisions of study for microscopic anatomy?
cytology (cells) and histology (tissues)
8
New cards
What are some subdivisions of physiology?
renal physiology (operation of kidney), neurophysiology, and cardiovascular physiology
9
New cards
main parts of lymphatic system/ immunity
red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, and lymph nodes
10
New cards
What are the survival needs?
Nutrients, oxygen, water, normal body temp. and atmospheric pressure
11
New cards
Ventral (anterior)
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
12
New cards
Axial
fundamental division of our body. Makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk.
13
New cards
Posterior/Dorsal Body
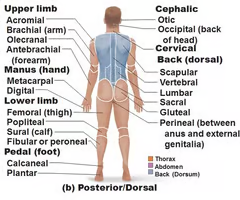
14
New cards
Sagittal
a vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts
15
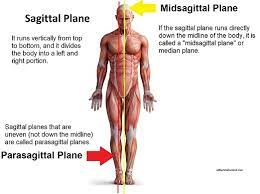
New cards
Median Plane (midsagittal plane)
sagittal plane that lies exactly in the midline
16
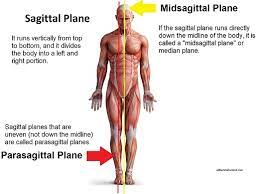
New cards
Parasagittal Planes
all other sagittal planes offset from the midline
17
New cards
Frontal Planes (Coronal Plane)
like sagittal plane lie vertically, divide body into anterior and posterior parts
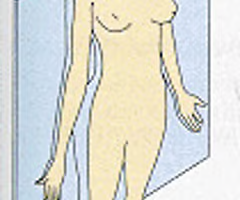
18
New cards
Transverse/Horizontal Plane
runs horizontally from right to left, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts. (Transverse is perpendicular to long axis of an organ, horizontal is from front to back)
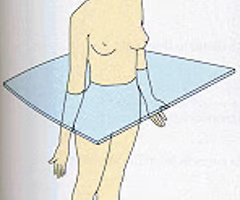
19
New cards
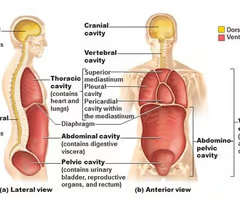
Dorsal Body Cavity
protects the fragile nervous system organs, has 2 subdivisions
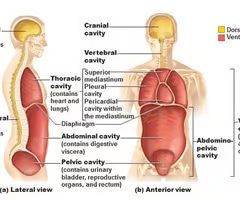
20
New cards
Cranial Cavity
in the skull, encases the brain
21
New cards
Vertebral Cavity (Spinal Cavity)
runs within the bony vertebral column, encloses the delicate spinal cord
22
New cards
Ventral Body Cavity
the more anterior and larger of the closed body cavities, has 2 major subdivisions, houses internal organs called Viscera
23
New cards
Thoracic Cavity
surrounded by the ribs and muscles of the chest
24
New cards
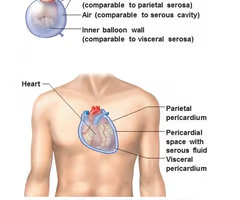
Pericardial Cavity
encloses the heart and also surrounds the the remaining thoracic organs (esophagus, trachea, and others)
25
New cards
Abdominal Cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
26
New cards
Pelvic Cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
27
New cards
Serosa (Serous Membrane)
the walls of the ventral body cavity and the outer surfaces of the organs it contains are covered by this thin double layered membrane
28
New cards
Parietal Serosa
lines internal body walls
29
New cards
Visceral Serosa
covers the internal organs
30
New cards
What is anatomy?
the study of structure
31
New cards
What is physiology?
the study of function at many levels
32
New cards
What is gross or macroscopic anatomy?
the study of large body parts, visible to the naked eye
33
New cards
What is regional anatomy?
the study of all the structures in a particular region of the body.ex: abdomen or legs
34
New cards
What is systemic anatomy?
the study of body systems such as the cardiovascular system
35
New cards
What is surface anatomy?
the study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface
36
New cards
What can be studied within developemental anatomy?
embryology (changes occurring before birth)
37
New cards
What is the principle of complementarity?
anatomy and physiology are inseparable, the function always refects structure and what a structure can do depends on its specific form.
38
New cards
In what way does physiology depend of anatomy?
the operation or function of a structure is dictated by its anatomy
39
New cards
Would you be studying anatomy or physiology if you investigated how muscles shorten? If you explored the location of the lungs in the body?
Muscle shortening is a topic of physiology. The body location of the lungs is an anatomy topic.
40
New cards
What are the levels of structural organization?
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system and organismal level
41
New cards
What does the digestive system do?
takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and eliminates unabsorbed matter (feces)
42
New cards
What does the respiratory system do?
takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide
43
New cards
What does the urinary system do?
eliminates nitrogenous wastes and excess ions
44
New cards
What does the cardiovascular system do?
via the blood, distributes oxygen and nutrients to all body cells and delivers wastes and carbon dioxide to deposal organs
45
New cards
What does the integumentary system do?
protects the body as a whole from the external environment
46
New cards
all ____ depend on organ systems to meet their survival needs
cells
47
New cards
_____ ____ work cooperatively to perform necessary life functions
organ systems
48
New cards
What are the main parts of the integumentary system?
hair, nails and skin
49
New cards
What are the main parts of the Skeletal System?
bones and joints
50
New cards
What is the main part of the muscular system?
skeletal muscles
51
New cards
What are the main parts of the nervous system?
the brain, nerves and spinal cord
52
New cards
What are the main parts of the endocrine system?
pineal, pituitary, thyroid and adrenal gland, thymus, pancreas, ovaries and testis
53
New cards
What are the main parts of the cardiovascular system?
blood vessels and heart
54
New cards
main parts of respiratory system
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs and bronchus
55
New cards
main parts of digestive system
oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum , and anus
56
New cards
main parts of urinary system
kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra
57
New cards
main parts of male and female reproductive systems
male: prostate gland, penis, testis, scrotum, ductus deferens. female: mammary glands, ovary, uterine tube, uterus, and vagina
58
New cards
What are some functions of the lymphatic system?
it picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood; disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream; houses white blood cells involved in immunity;
59
New cards
What are the necessary life functions?
maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction and growth
60
New cards
What is metabolism?
a broad term that includes all chemical reactions that occur within the body
61
New cards
What is homeostasis?
the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in an ever-changing outside world
62
New cards
What are control mechanisms for homeostasis?
receptor is a sensor that monitors the environment and responds to changes, called stimuli and then sends info to the control center where it is analyzed and determines the appropriate response or course of action and then to the effector which provides the means for the control centers output
63
New cards
What is negative feedback within homeostasis? and example
the response reduces or shuts off the original stimulus regulation of body temp (nervous mechanism) regulation of blood volume by ADH (endocrine mechanism)
64
New cards
What separates living beings from nonliving objects?
Living organisms are able to maintain their boundaries, move, respond to environmental change, digest nutrients, carry out metabolism, dispose of wastes, reproduce and grow. while inanimate objects do not exhibit all of these
65
New cards
what name is given to all chemical reactions that occur within body cells
metabolism
66
New cards
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
because the atmosphere is thinner at high altitudes and the amount of oxygen entering the blood under such conditions may be insufficient to maintain life
67
New cards
What's the process of negative back for regulation of blood volume by ADH
Receptors sense decreased blood volume, control center in hypothalamus stimulates pituitary gland to release antidiuretic hormone ADH, ADH causes the kidneys (effectors) to return more water to the blood.
68
New cards
What is positive feedback examples
the response enhances or exaggerates the original stimulus; exhibits an amplifying effect; usually controls infrequent events ex: enhancement of labor contractions by oxytocin, platelet plug formation and blood clotting
69
New cards
Homeostatic imbalance is the ...what does this cause?
disturbance of homeostasis increases risk of disease, contributes to changes associated with aging, may allow destructive positive feedback mechanisms to take over (heart failure)
70
New cards
What process allows us to adjust to either extreme heat or extreme cold?
Negative feedback mechanisms allow us to adjust to conditions outside the normal temperature range by causing heat to be lost from the body and retained or generated by the body.
71
New cards
When we begin to get dehydrated, we usually get thirsty, which causes us to drink fluids. Is thirst part of a negative or a positive feedback control system?
thirst is part of a neg. feedback control system because it prods us to drink which ends the thirst stimulus and returns body fluid volume to the normal range
72
New cards
the walls of the ____ body cavity are covered by a thin, double layered membrane
Ventral
73
New cards
what cavity in the thoracic cavity contains the heart and esophagus and trachea
pericardial cavity
74
New cards
what cavity in the thoracic cavity contains the lungs
pleural cavities
75
New cards
what does the ventral body cavity contain
thoracic and abdominal pelvic cavities
76
New cards
the double layered membrane covering the the outer surfaces of the organs
serosa or serous membrane
77
New cards
The part of the membrane lining the cavity walls is called the
parietal serosa
78
New cards
When the parietal serosa folds in on itself it forms the
visceral serosa
79
New cards
in the body the serous membranes are separated by a thin layer of lubricating fluid called
serous fluid
80
New cards
81
New cards
82
New cards
83
New cards
84
New cards
85
New cards
86
New cards
87
New cards
88
New cards
89
New cards
90
New cards
91
New cards
92
New cards
93
New cards
94
New cards
95
New cards
96
New cards
97
New cards
98
New cards
99
New cards
100
New cards