Enzyme-substrate interactions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Name the factors that affect enzyme activity:
pH
Denaturing reagents
Temperature
Enzyme concentration
Substrate concentration
Inhibitors
pH
Affects ionisation of side chains and active site; extreme pH causes denaturation.
Denaturing reagents disrupt protein structure. Name some denaturing reagents:
Detergents
Urea
Guanidinium hydrochloride
Temperature
Increases kinetic energy and collision rate; high temperatures cause protein unfolding.
Enzyme concentration
More enzyme → more active sites → higher maximum rate.
Substrate concentration
Rate increases with substrate until enzymes are saturated.
Inhibitors
Reduce enzyme activity by blocking or altering the active site.
What 4 things do simple models assume?
Only one molecule of one substrate binds to the enzyme
Enzyme and substrate form a [ES] complex
Enzyme converts substrate to product and product release is fast
Products bind weakly to enzymes
What does the Michaelis–Menten curve show?
The relationship between reaction rate (v) and substrate concentration [S], showing saturation at high [S].
![<p>The relationship between reaction rate (v) and substrate concentration [S], showing saturation at high [S].</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e73e3e54-9a4b-4785-964a-a17ba4aada42.png)
What’s the Michaelis-Menten equation?
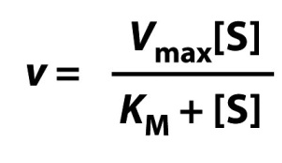
What is v?
v = rate
What is [S]?
[S] = substrate concentration
What is Vmax?
Vmax = rate when all enzyme active sites are occupied
What is Km?
Km = [S] at which v = ½ Vmax.
The substrate concentration when half of all enzyme active sites are occupied.
What does it mean for “enzyme reactions to saturate”?
All enzyme active sites are occupied, the rate has reached Vmax, and increasing substrate concentration no longer increases the reaction rate.
Why do enzyme reactions saturate at high substrate concentrations?
Because all enzyme active sites become occupied, so adding more substrate cannot increase the rate further.
How can Km and Vmax be measured directly?
By plotting v against [S] (Michaelis–Menten plot).
![<p>By plotting v against [S] (Michaelis–Menten plot).</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/80280cd8-ff33-4ca9-8c6d-e43224faa89b.png)
Michaelis-Menten Plot
Plots v against [S]
Can be difficult to decide when Vmax is reached
Usually requires a computer programme
![<ul><li><p>Plots v against [S]</p></li><li><p>Can be difficult to decide when V<sub>max</sub> is reached</p></li><li><p>Usually requires a computer programme</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f6bec42e-14f1-45d8-a7f1-25ab572782fb.png)
Lineweaver-Burk Plot
Plots 1/v against 1/[S]
Y-intercept = 1/Vmax
X-intercept = -1/Km
Higher precision;
Lower accuracy;
Errors are not equal at all points (least squares regression is not appropriate).
![<ul><li><p>Plots 1/v against 1/[S]</p></li><li><p><span><span>Y-intercept = 1/</span><em><span>V</span></em><sub><span>max</span></sub></span></p></li><li><p><span><span>X-intercept = -1/</span><em><span>K</span></em><sub><span>m</span></sub></span></p></li><li><p><span><span>Higher precision;</span></span></p></li><li><p><span><span>Lower accuracy;</span></span></p></li><li><p><span><span>Errors are not equal at all points (least squares regression is </span><strong><span>not </span></strong><span>appropriate).</span></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1d614257-b351-4fde-8f94-a94d4cc565c9.png)
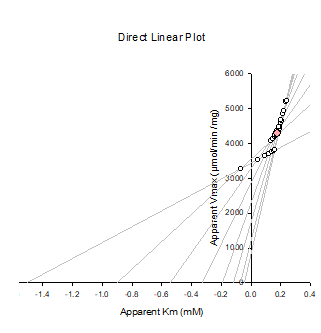
Direct Linear Plot
x axis = Km
y axis = Vmax
Each data point gives a straight line; all lines intersect near true Km and Vmax
Gives median value
Makes no assumptions about the errors
Accurate
What is kcat?
kcat = Vmax ÷ amount of enzyme.
It is the first-order rate constant for conversion of substrate to product.
What does kcat/Km represent?
A measure of enzyme efficiency (specificity constant) that allows comparison between different enzymes.
What are 6 assumptions of the steady state model (Michealis-Menten)?
Substrate is in large excess over enzyme ([E] « [S])
[S] remains constant
Measured rate is initial rate (linear start of curve)
[ES] remains constant
The product binds weakly to enzyme
The backwards reaction is neglible
If Vmax = 0.5 what does that mean?
The maximum rate of the enzyme catalysed reaction is 0.5 units per second.
When the enzyme is working as fast as it possibly can (all enzyme active sites are full of substrate), it can make 0.5 units of product per unit time.
What does Km tell us?
It tells us how strongly an enzyme binds to its substrate.
What does a low Km mean?
A low Km means the enzyme binds tightly (it works well even at low substrate levels).
What does a high Km mean?
A high Km means the enzyme binds weakly (it needs more substrate to work efficiently).
What does Kcat show?
Kcat shows how fast the enzyme can convert substrate to product once the substrate is bound.
Exam Question:
In an enzyme kinetic experiment, the value for 1/Vmax was 0.102 min/nmol and -1/Km was -3.45 mM-1 from a Lineweaver-Burk (double reciprocal) plot.
Each assay contained 0.14 mg of enzyme with a molecular weight (MW) of 47 146 Da.
Showing your workings, calculate values for Vmax, Km, kcat, kcat/Km, assuming one active site per monomer (hint: kcat = Vmax divided by amount of enzyme) [10 marks].
1/Vmax = 0.102 min/nmol
-1/Km = -3.45 mM-1
Lineweaver-Burk Plot
Each assay contained 0.14 mg of enzyme with a molecular weight (MW) of 47 146 Da.
Calculate values for Vmax, Km, kcat, kcat/Km