1.2.3 Price, income and cross elasticities of demand
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Definition of price elasticity of demand (PED)
The responsiveness in the demand for a good due to change in its price
Formula for PED

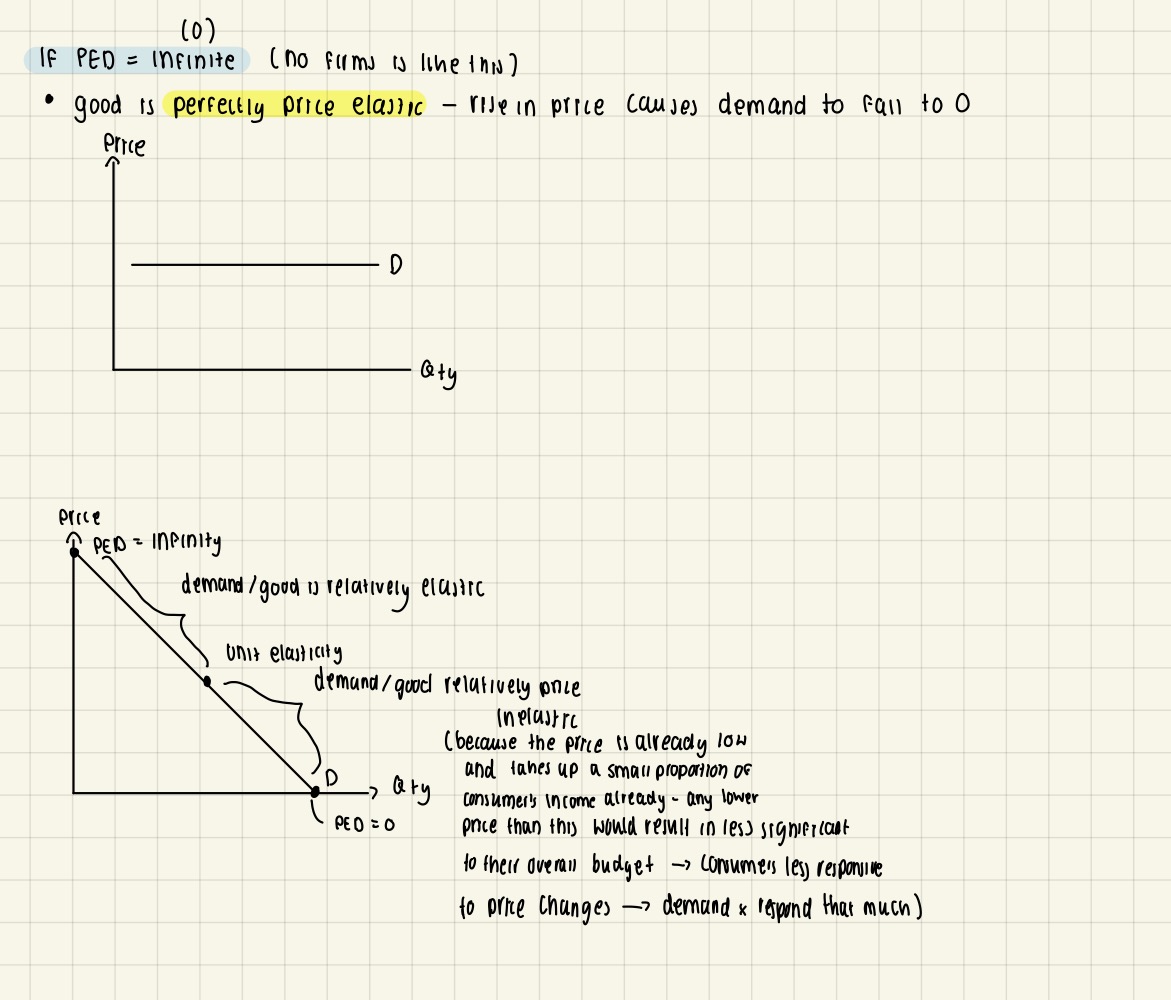
Interpret numerical values of price elasticity of demand
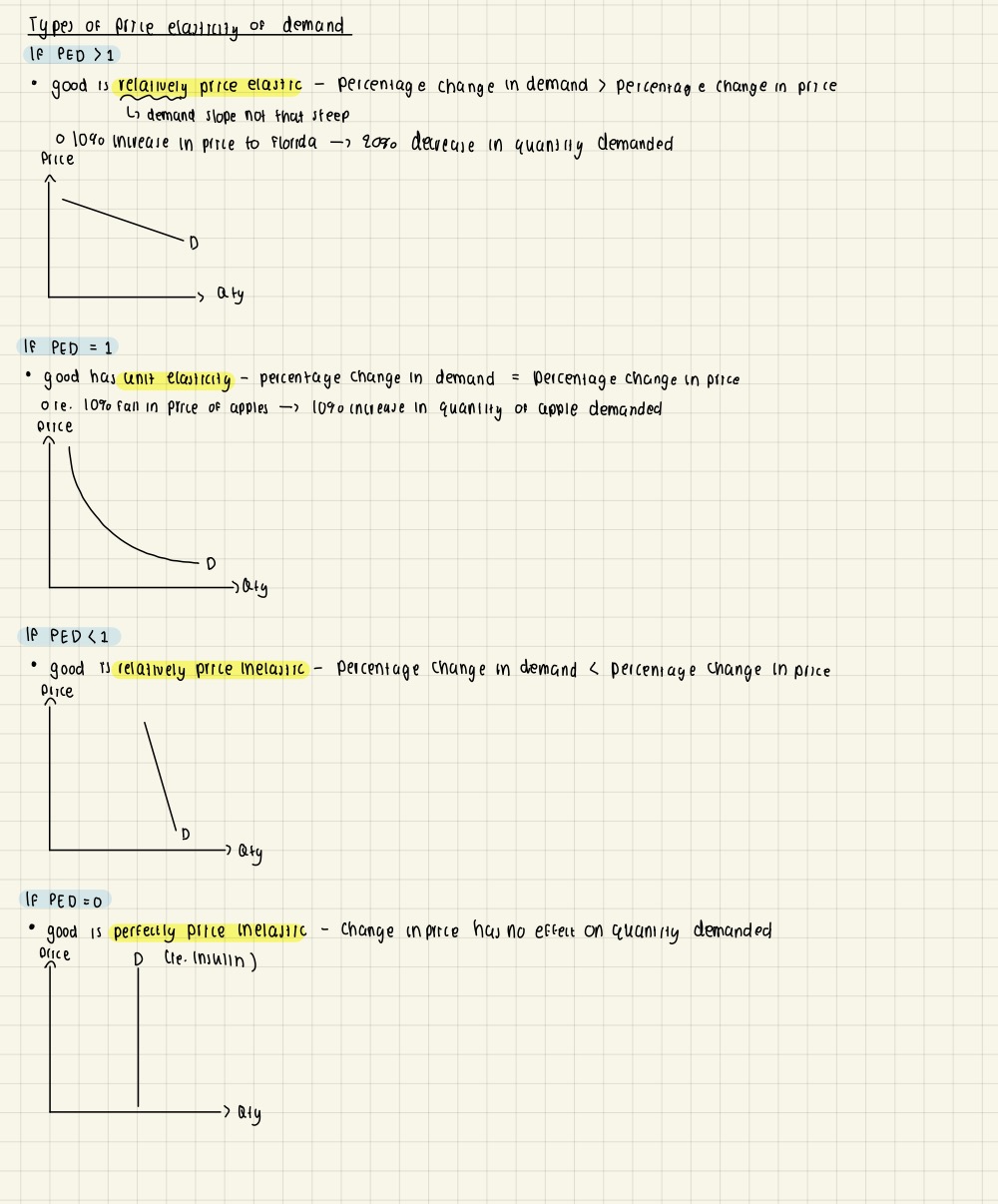
Interpret numerical values of price elasticity of demand 2
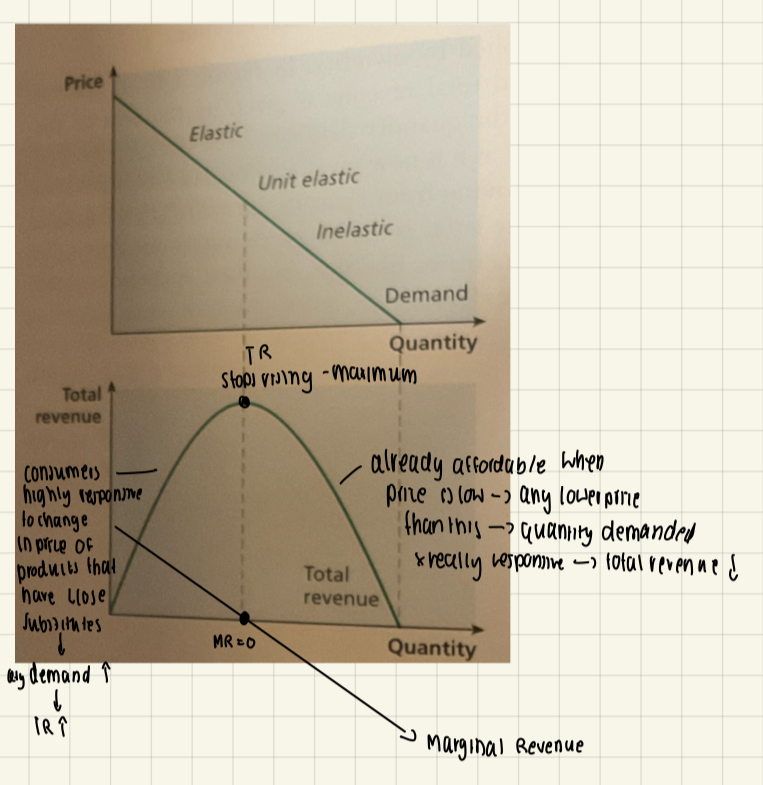
The relationship between price elasticity of demand & total revenue (including calculation)
Total revenue = total amount of money received by producers from selling a given quantity of a good / price per unit of goods x quantity sold
If demand is price elastic:
Price increases, quantity demanded decreases, total consumer spending decreases, total revenue decreases
If demand is price inelastic:
Price increases, quantity demanded not affected, quantity sold stays relatively the same, Revenue increases
Definition of income elasticity of demand
The responsiveness of demand for a good/service to a change in real income
Formula of income elasticity of demand

Interpret numerical values of income elasticity of demand
Normal goods (positive) - as income increases, quantity demanded increases
Luxury: YED more than 1
Necessity: YED in between 0 & 1
Inferior goods (negative) - as income increases, quantity demanded decreases, therefore, quantity sold decreases with the same price causing sales revenue to decrease
Definition of cross elasticities of demand
Responsiveness of demand for good A given a change in price of good B
Formula to calculate cross elasticities of demand

Interpret numerical values of cross elasticity of demand
Substitute goods: XED positive (if XED is more than 1 - indicates a close substitute)
In competitive demand
Complementary goods: XED negative
In joint demand
Unrelated goods: XED = 0
The factors influencing elasticities of demand
Availability of substitutes
narrow definition - price elastic ; broader - price inelastic
number of close substitutes (the higher the number, the higher the elasticity)
Luxury & necessity goods
Proportion of income spent on the good
Evaluation point:
PEDs are forecast, estimate
Time period