Postpartum Period (week 6)
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
postpartum period
birth to return of reproductive organs to non-preganant state
6-12 weeks
uterus changes
involution immediately after placenta delivered
at umbilicus = 12hrs
descends 1-2cm every 24hrs
contactions
oxytocin via pituitary gland promotes homeostasis
lochia PP uterine discharge
initial = bright red + small clots
2hr PP = heavy period then decreases
rubra = 3-4 days = blood/trophoblast
serosa = 4 days - 2-4 weeks = brown/pink = blood, leukocytes, tissue
alba = >10-14 days = white
cervix changes
VAGINAL BIRTH
Os closes gradually
1 week = 1cm dilated
never pre-pregnancy state
vagina and perineum changes
size decreases
tone increases
introitus = edematous (swell) with episiotomy/laceration
never pre-pregnancy state
abdomen changes
6 weeks return to pre-pregnancy
placental hormone changes
decrease in human placental lactogen, estrogen, cortisol, insulinase
b/c of delivery of placenta
REVERSE diabetic effects
estrogen/progesterone decrease = diuresis (increase urine)
hCG - 3-4 weeks
pituitary hormones
prolactin rises in pregnancy, PP = drop in estrogen/progesterone = INCREASES
higher in 1st month of BF and until BF continues
ovulation and menses
non-lactating = return as soon as 27 days, mean = 7-9 weeks, 70% by 12 weeks
BF = 6 months til ovulation
urine component changes
glycosuria
lactosuria
BUN
proteinuria
ketonuria
b/c of prolonged labour/dehydration
fluid loss changes (urine)
PP diuresis (increased production of urine)
b/c decreased in estrogen/progesterone
urethra and bladder changes
trauma (forceps, etc)
anesthesia (decreased sensation)
increased bladder capacity
DECREASED urge to void
PPH RISK (uterus CANNOT contract)
intervention = encourage void/foley catheter
appetite changes
increased after birth, diet as tolerated
bowel movement changes
delay 2-3 days = normal
decreased muscle tone, dehydration, lack of food, pre-labour diarrhea
vaginal delivery
forceps/vacuum = anal sphincter laceration
C/S
abdo pain = gas build-up
can appear as referred shoulder pain
encourage fluids, fibre, early ambulation
breastfeeding changes
24hrs = little change + colostrum (nutrient rich, 1st type)
feel soft, become fuller/heavier as milk comes in
72-96hrs
non-breastfeeding changes
milk still comes in
breast feel full/engorged
resolve spontaneously
AVOID stimulation
well fitted/right bra
cardiovascular changes
hypervolemia of pregnancy = tolerates blood loss
vaginal = 300-500 mL
C/S = 500-1,000mL
respiratory system changes
immediate decrease of intra abdominal pressure
decreased progesterone = PaCO2 INCREASES
neurological system changes
reversal of adaptions to pregnancy
ex. carpel tunnel
*headache = hypertension
MSK system changes
stabilizes by 6-8 weeks
foot size may not decrease
integumentary system changes
gradual resolve of changes from pregnancy
immune system changes
immunosuppression returns to pre-pregancy state
immunosuppressed during pregnancy b/c did not want to recognize embryo as foreign
autoimmune conditions
can trigger a FLARE-UP
follow-up with specialist
vital sign changes
few alterations under normal circumstances
HR and BP return to pre-pregnancy levels in a few days
respiratory functions return rapidly to pre-pregnant function
PP assessment - 24hr
afternal initial recovery (1-2hrs) pt transferred to PP unit
9 components of TOA PP
type of labour/birth, unusual observations of placenta
GTPAL, age
anesthesia and analgesia used
condition of perineum
events since birth
condition and sex of newborn, other info
relevant info from prenatal record
miscellaneous info, IV drip
social factors
maternal/newborn - type of labour/birth, unusual observations of placenta
spontaneous or assisted (forceps, vacuum) vaginal birth
C/S birth
vertex presentation
time of ROM (artificial or spontaneous)
maternal/newborn - GTPAL, age
GTPAL
maternal age
gestational age
maternal/newborn - anaesthesia/analgesia used
none
epidural
spinal
local
maternal - condition of perineum
episiotomy = cut for birth
laceration
repair
intact
maternal - events since birth
vital signs
BP
fundas
lochia
intake/output
medications (dosage, time of admin, results)
length of time NB was skin-skin, with whom
response to NB
observation of family interactions, including siblings
newborn - events since birth
vital signs
blood glucose
nursed for __ (BF or formula or combo)
void
eye prophylaxis
vitamin K
skin-skin for __ min
family interactions
ex. held by siblings who are happy
maternal - condition and sex of NB, other info
time of birth
weight
BF or bottle
sex of baby
newborn - condition and sex of NB, other info
time of birth
apgar score at 1 and 5 min
sex
weight
name of healthcare provider
BF or bottle
maternal - relevant info from prenatal record
need for rubella vaccine
presence of infection
Hep B status
HIV status
bloody type
Rh status
GBS status and treatment
newborn - relevant info from prenatal record
mother’s GBS status and treatment
maternal - miscellaneous info, IV drop
IV drip
rate of infusion
meds added
ex. oxytocin
whether to open/close/continue/discontinue
newborn - miscellaneous info, IV drop
whether mother received MgSO4
time of last systemic analgesia
IV solution and rate
maternal - social factors
pt keeping or releasing NB for adoption
if pt wants to see NB
BF or bottle
allowing visitors or not
other preferences
newborn - social factors
NB up for adoption
PP assessment first 24hrs
Vital signs
BUBBLLEE
breasts
uterus
bladder
bowel
lochia
legs
episiotomy or C/S incision
emotional status
PP assessment
BP
temp
pulse
respirations
breath sounds
nipples
uterus
bladder
bowels/abdomen
lochia
legs
perineum/incision
rectal area
emotional status/energy
blood pressure - normal findings
consistent with baseline during pregnancy
orthostatic hypotension x 48 hrs
blood pressure - complications
HYPERtension
anxiety, pre-eclampsia, hypertension
HYPOtension = PPH RISK
temp - normal findings
36.2 - 38ºC
temp - complications
>38ºC
infection
pulse - normal findings
60-100 bpm
pulse - complications
TACHYcardia
pain, fever, dehydration, PPH
respirations - normal findings
12-24 breaths/min
respirations - complications
TACHYpnea = anxiety
BRADYpnea = effects of narcotics
breath sounds - normal findings
clear
breath sounds - complications
crackles = fluid overload
breasts - normal findings
day 1 = soft
day 2-3 = filing
day 3-5 = full, soften with BF
breasts - complications
firmness
heat
pain
engorgement
redness of breast tissue
fever
body aches
CAUSE = mastitis = infection
nipples - normal findings
skin intact
nipples - complications
redness
brusing
cracks
fissures
abrasions
blisters
CAUSE = latching difficulties
uterus - normal findings
firm
midline
24hrs @ umbilicus
descends 1-2 cm per day
uterus - complications
soft
boggy
higher than umbilicus
CAUSES
uterine atony = fail to contracts = PPH risk
deviated = lateral = bladder distension (full)
bladder - normal findings
able to void 8hrs after catheter removal
diuresis (increased urine)
bladder - complications
overdistended = uterine atony + excessive lochia
UTI = dysuria (painful urination), frequency, urgency
bowel/abdo - normal findings
BM 2-3 days
soft abdo
active bowel sounds in all quadrants
C/S passing of flatus
bowel/abdo - complications
no BM 3-4 days
diarrhea
lochia - normal findings
birth - 3-4 days = rubra
day 4 - 2-4 weeks = serosa (pink/brown)
>10-14 days = alba
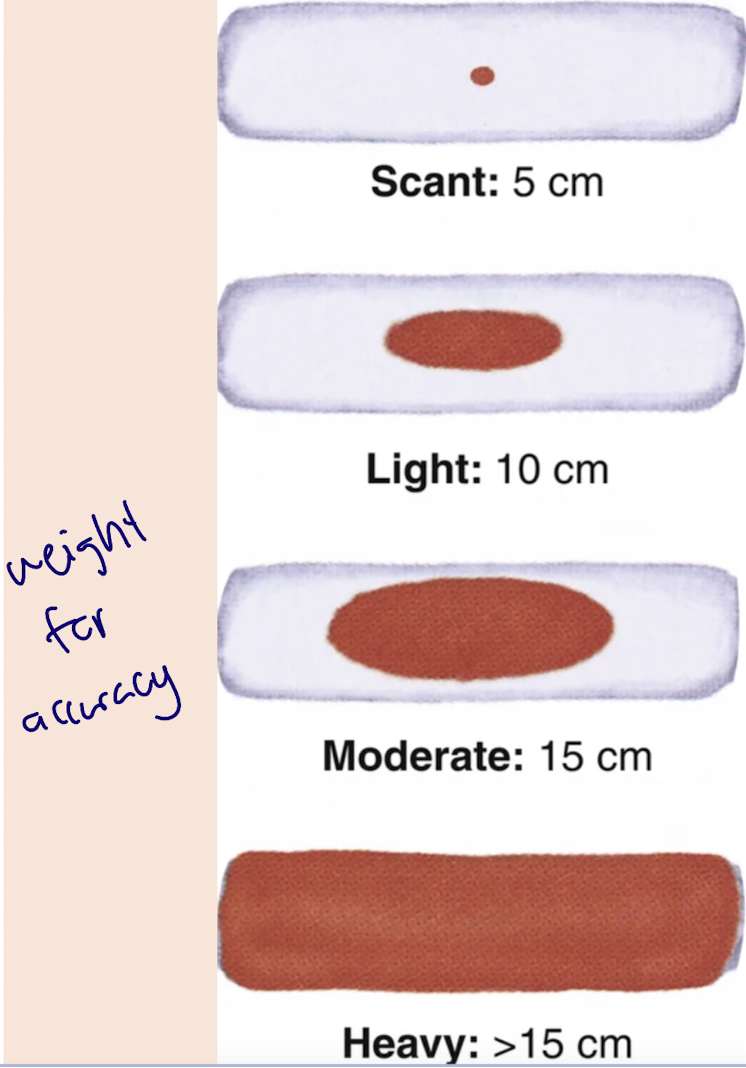
amount = scant-moderate
few clots, fleshy odour
lochia - complications
large amount = uterine atony, vaginal cervical laceration
odour = infection
legs - normal findings
peripheral edema possibly present
legs - complications
redness, tenderness, pain = VTE
perineum/incision - normal findings
minimal edema
laceration/epis = edges well approximated
C/S = incision dry/clean, well approximated
perineum/incision - complications
pronounced edema
hematoma
bruising
redness
warmth
drainage
infection
rectal area - normal findings
no hemorrhoids
if present, soft, pink
rectal area - complications
discoloured hemorrhoid tissue
severe pain
thrombosed hemorrhoid (dark blue, clots)
emotional status/energy - normal findings
able to care for self, infant
able to sleep
happy, excited
interested/involved in care
sad/tearful 3-14 days = PPB
emotional status/energy - complications
lethargy, extreme fatigue, difficulty sleeping = PPD
sad, tearful, disinterested in NB care = PP mood disorder
perinatal moods (5)
postpartum blues (PPB)
postpartum mood disorders (PMD)
perinatal anxiety disorders
perinatal depression
postpartum psychosis
postpartum blues (PPB)
baby blues
50-80%
tearful, agitation, mood swing, sleep/appetite disturbances, feeling overwhelmed
resolves in 2 weeks
DOES NOT interfere with care of self/NB
nursing education - PPB
validation, reassurance, education
normalize, encourage rest, relaxation techniques, time for self, plant day out of house, share feelings with partner, monitor self of S/S of anxiety/depression, seek out community recourses, be patient with self if BF
postpartum mood disorders (PMD)
23% report feelings of PPD or anxiety disorder
indigenous 87% higher chance
hx of colonization, intergenerational trauma, discrimination, racism, marginalization, poverty, lack of cultural safe care
biological, psychological, situation, multifactorial
higher risk with hx of anxiety, depression
strong risk factors - PMD
hx of psychiatric illness, depression, anxiety
prenatal symptoms of anxiety
onset of depression during pregnancy or PP
moderate risk factors - PDM
stressful life events
refugee/immigrant status
low social support
unfavourable obstetrical outcomes
low self-esteem
hx of physical or sexual abuse
intimate partner violence (IPV)
hx of reproductive trauma (ex. infertility)
grief re. miscarriage, stillbirth, infant loss
substance use, including tobacco
weak risk factors - PMD
low socioeconomic status
lack of significant other/partner
pregnancy unwanted
BF challenges
perinatal anxiety disorders
1 in 5 pt
GAD (gen anxiety), OCD, panic attacks, phobias, social anxiety, PTSD
increased risk with hx of anxiety
collaborative care - perinatal anxiety disorders
psychotherapy, CBT, ERP (exposure response prevention) (individual or group)
SSRIs and anti-anxiety meds = 2 weeks to be effective
nursing education
guidance, reassurance, recognizing triggers
family/social supports
perinatal depression
10-15%
mild-severe
intense and pervasive sadness with severe mood swings, guilt, inadequacy feed worries = incompetent parent
irritability = distinct characteristic
collaborative care - perinatal depression
psychotherapy
antidepressants
anti anxiety meds
postpartum psychosis
most severe PMD
50-80% more likely to develop psych disorder (biopoal)
50% = recurring PP psychosis
S/S 2 weeks PP
rapid onset of bizarre behaviour, hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, delirium/disorientation, extreme deficits in judgement, high impulsivity
risk factor = pre-existing bipolar disorder
collaborative care - postpartum psychosis
emergency = hospitalization
good prognosis if early identified/treated
antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, benzodiazepines, psychotherapy
PP nursing prevention interventions
excessive bleeding
infection
bladder distension
excessive bleeding - prevention
maintain uterine tone
uterine atony = matain tone and prevent bladder distension
1g = 1mL = weighing peri pads
infection - prevention
hygiene
clean environment
change peri pads frequently
bladder distension - prevention
empty bladder frequently
running tap
pour water over perineum
sitz bath
nursing interventions - promotion
pain relief ex/ ibuprofen at discharge
comfort and rest
ambulation and exercise (decrease chance of VTE)
nutrition (normal cal, increased 350-450 cal if BF)
bowel function (prevent constipation by ambulation, fluids, fibre)
breastfeeding (ASAP)
future pregnancy planning
rubella
not immune - subQ injection immediate PP period
MMR = live attenuated = safe fro BF
avoid pregnancy for 4 weeks
DO NOT give if immunocompromised (mother/household)
Rh isoimmunization
injection of Rh immune globulin within 72hrs of birth (second, 1st was during 3rd trimester)
postpartum complications (3)
Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH)
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
Infection
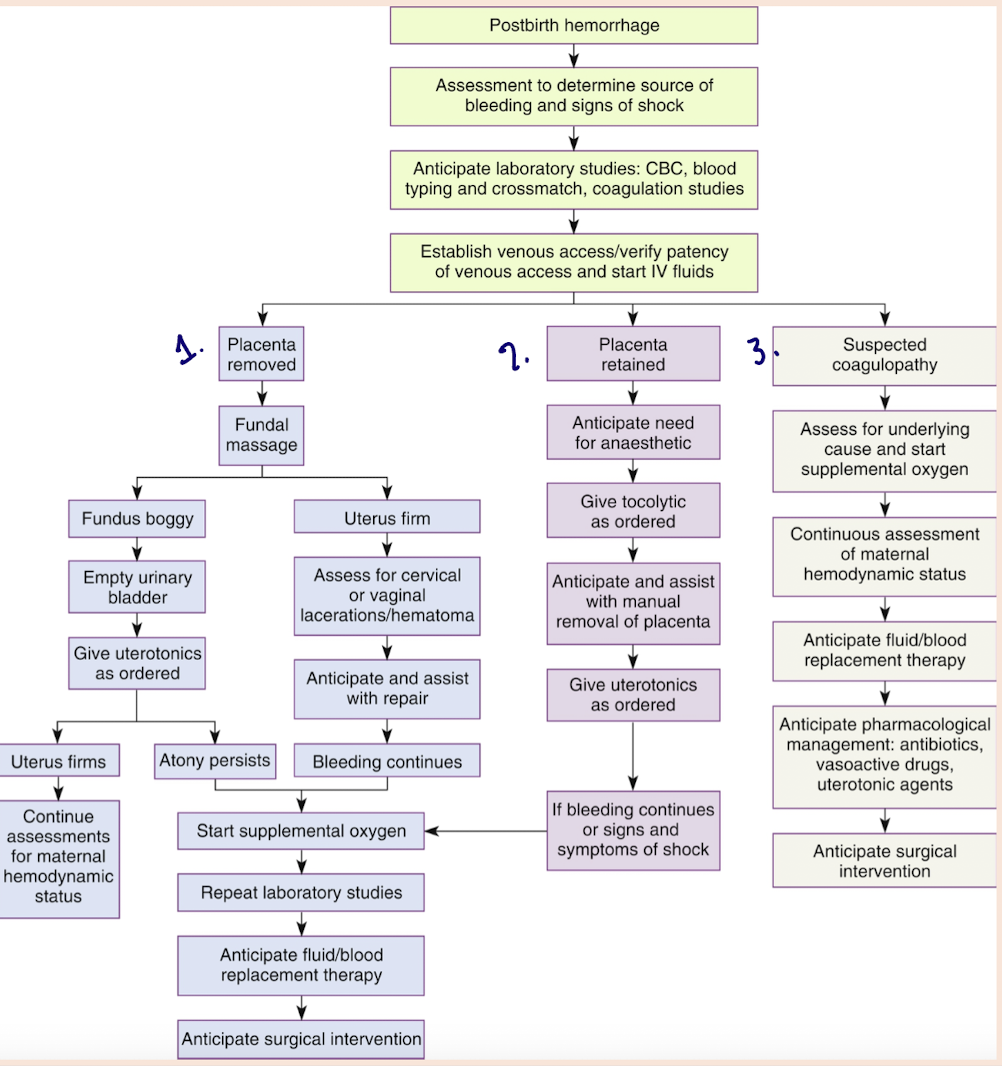
PPH
leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide
>500mL (vaginal)
>1,000 mL (C/S)
primary - 24hrs of birth
secondary = >24hrs - <12 weeks (generally)
risk factors of PPH
4 T’s
tone
tissue
trauma
thrombin
tone - PPH risk factor
uterine atony
overdistended uterus (LGA, multi fetuses, hydramnios, distension with clots)
anesthesia/analgesia
previous hx of uterine atony
high parity
prolonged labour
oxytocin induced labour
MgSO4 admin in labour or PP
chorioamnionitis
uterine subinvolution (fail to return to normal size)
obesity
trauma - PPH risk factor
laceration of birth canal
trauma during labour (forceps, vacuum, C/S)
rupture uterus
inversion of uterus
manual removal of retained placenta
tissue - PPH risk factor
retained placental fragments
placenta accreta, increta, percreta
placental abruption
placenta previa
thrombin - PPH risk factor
coagulation disorders (clotting disorders)
PPH nursing assessment
find uterus boggy
massage and keep hands on
pull call-bell = emergency
collaborative care = PPH kit
place IV - CBC
empty bladder
PPH meds admin
MRP = eternal exam (retained placenta, clots)
verbalize out loud what you have done
always someone documenting times/interventions
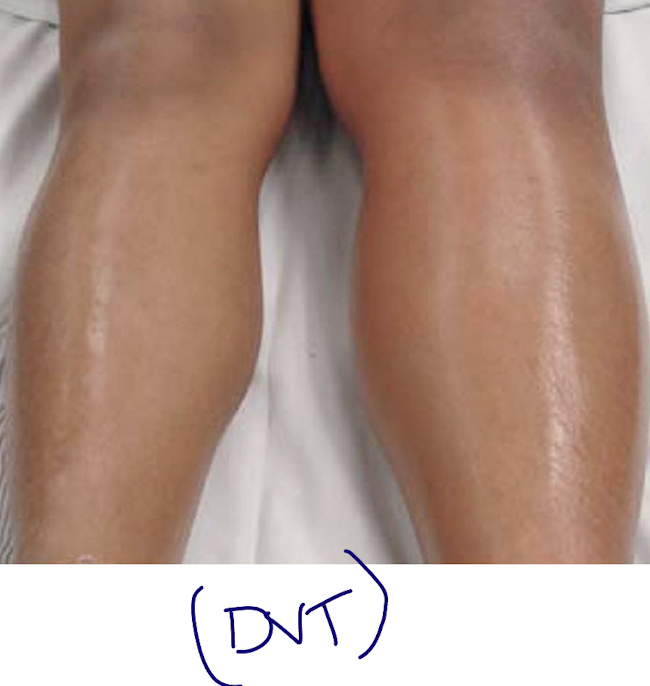
venous thromboembolism
superficial, deep (DVT) or pulmonary (PE)
15 x risk of thromboembolism in pregnancy/PP
restless/agitation
DVT S/S - Venous Thromboembolism
unilateral (no bilateral) leg pain
calf tenderness
swelling
redness
warmth
Pulmonary Embolism - Venous Thromboembolism
dyspnea
tachycardia
apprehension
COUGH
hemoptysis
fever
syncope (faint)
superficial venous thromboembolism - collaborative care
analgesia (pain reliever)
rest with elevation
compression stockings
heat