ALLIED HEALTH UNIT 4 SAC 3
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nervous system, the senses and the endocrine system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
function of the nervous system
responds to changes inside and outside the body (maintain homeostasis)
label structure of a neuron
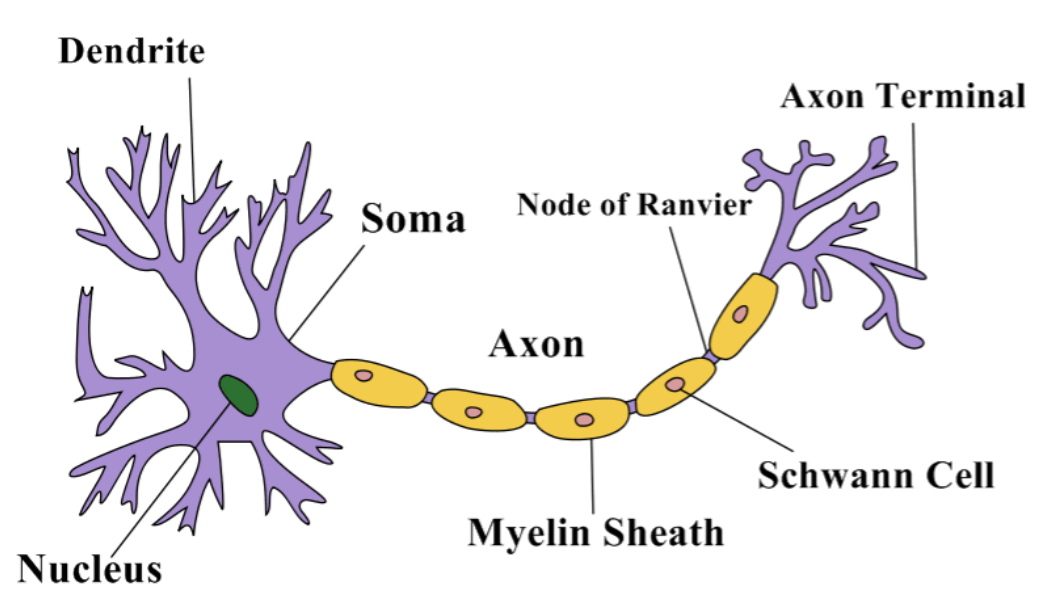
describe soma
is the central part that holds the nucleus
describe dendrites
acts as the primary recieving site for signals
describe axon
conducts electrical impulses
describe myelin sheath
insulating layer that wraps around the axon of a nucleus
describe nodes of ranvier
specialised gaps in the myelin sheath
describe axon terminals
specialised ending of an axon where it transmits signals
describe schwann cells
specialised glial cells of PNS
how are nerve impulses transmitted across the synaptic gap
role of neurotransmitters
are endogenous chemicals that allow neurons to communicate with each other
enables the brain to provide a variety of functions
role of receptors
converting stimuli from the environment into electrical signals that can be transmitted along nerve cells
label synapse between two neurons
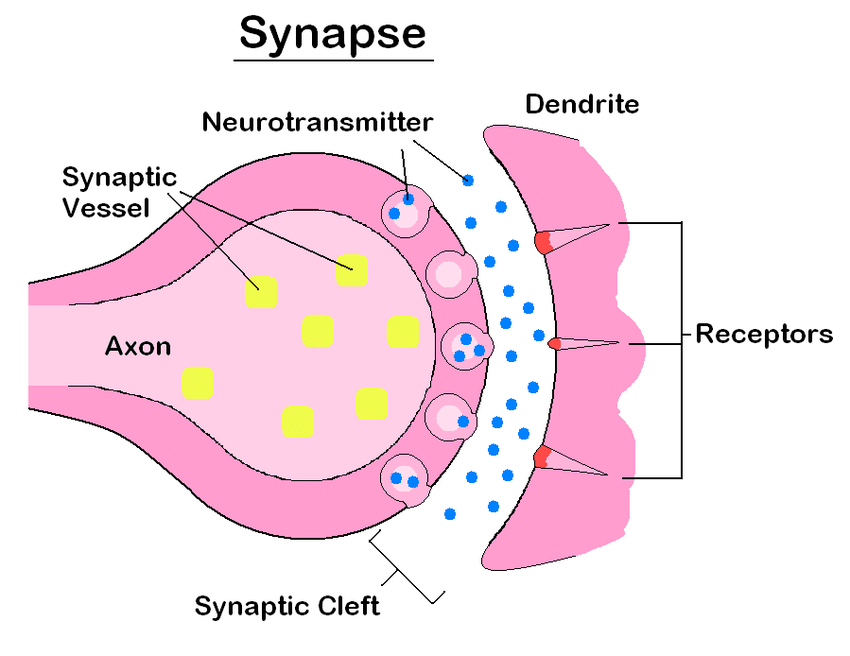
describe the features of the synapse between two neurons
involves a presynaptic neuron, a postsynaptic neuron, and a synaptic cleft
label the brain
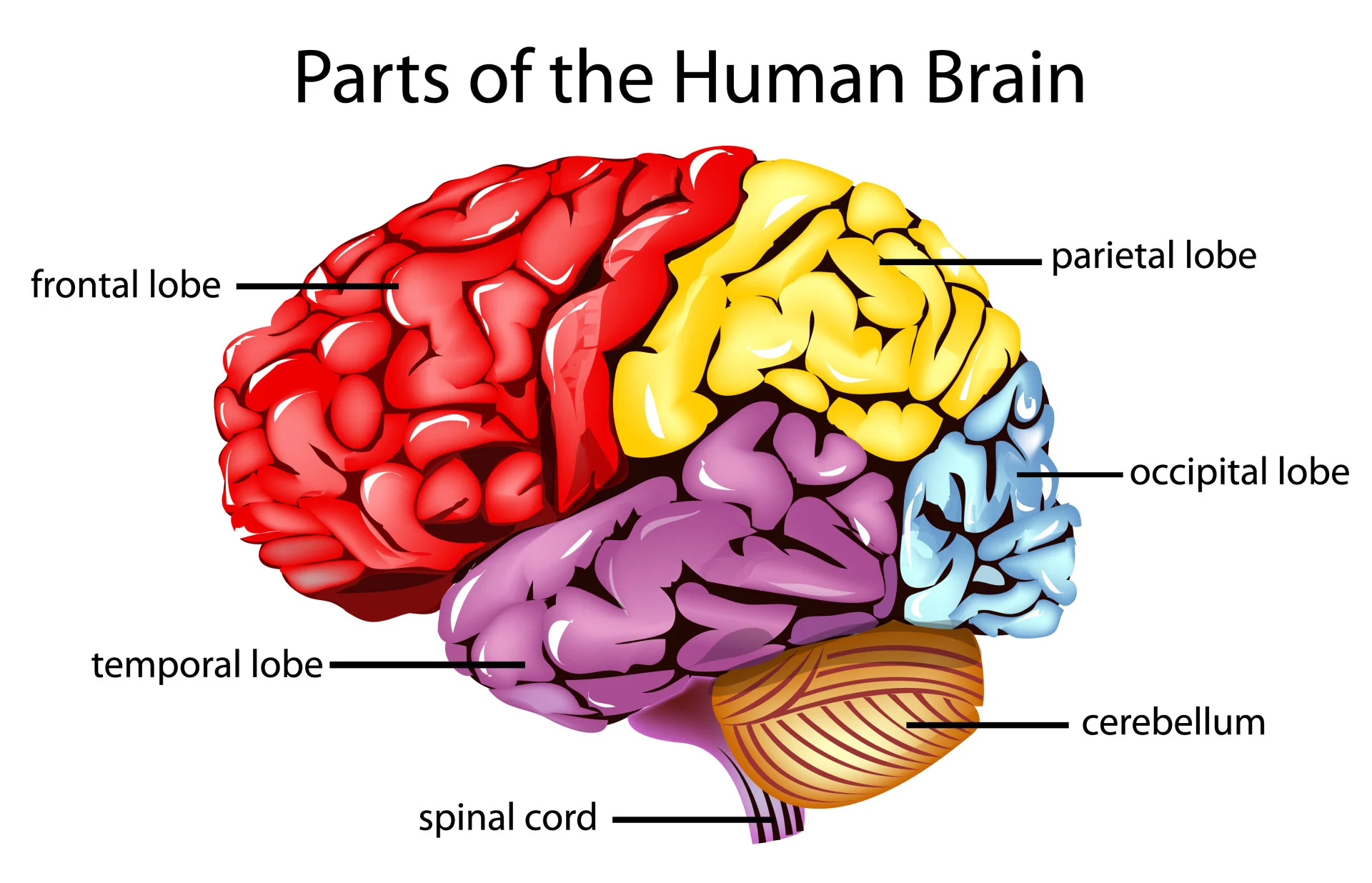
function of frontal lobe
involved in personality, characteristics, decision-making, and movement. also speech ability
function of parietal lobe
involved in identify objects, understanding spatial relationships, interpreting pain and understanding spoken language
function of temporal lobe
involved in short term memory, speech, musical rhythm
function of occipital lobe
involved with vision
function of the cerebellum
coordinate voluntary muslce movement
maintain posture, balance and equilibrum
function of the cerebellum in coordinating voluntary movement, posture, balance
identify parts of the brain stem
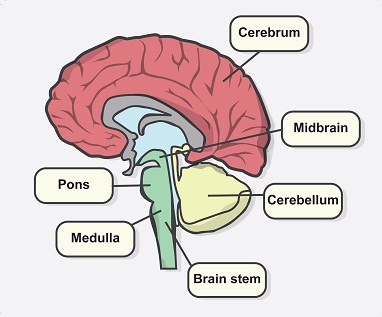
function of pons
involved in tear production, chewing, blinking, focusing, vision, balance and facial expression
function of medulla
regulates bodily activities incluyding HR, blood flow, O2 levels
function of oblongata
regulating essential autonomic functions and relaying nerve signals
describe CNS
central brain system (brain and spinal cord)
the bodys processing center
Describe PNS
peripheral nervous system
the network of nerves that extends outside of brain and spinal cord
describe somatic nervous system
responsible for voluntary movement and sensory information processing
describe ANS
autonomic nervous system
regulates involuntary bodily functions without conscious thought including breathing, heart rate
describe sypathetic division
the "fight-or-flight" branch
prepares the body for intense physical activity and stress by increasing heart rate, rerouting blood to muscles, and suppressing non-essential functions
describe parasympathetic
responsible for the rest and digest response
describe general role of the sense in detecting changes in internal and external environmentDescribe
to act as biological monitoring systems, converting stimuli from the internal and external environment into electrical signals (nerve impulses) that the brain interprets to create perceptions, guide responses, and maintain homeostasis
identify the tongues taste buds
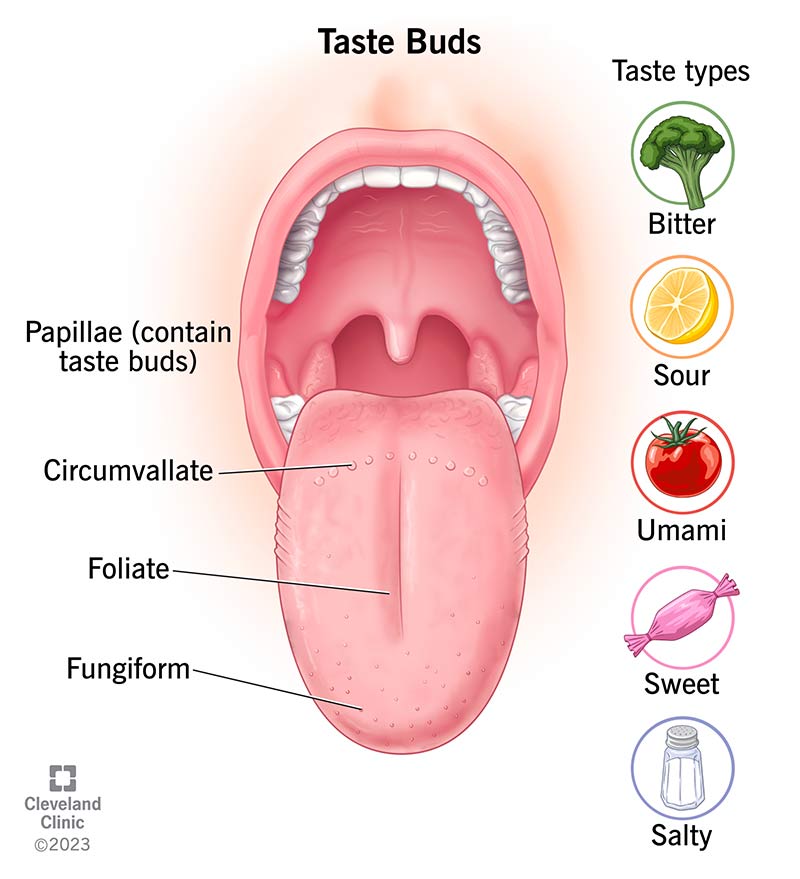
describe the basic taste sensations
(salty, sweet, sour, bitter, unami)
outline the role of chemoreceptors in detecting dissolved chemicals
describe the function of olfactory receptors in nasal cavity
certain chemical substances become dissolved in the thin layer of fluid covering the surface of mucous membrane and comes into contact with hairs
activates olfactory bulb which creates nerve signal to olfactory neuron
how is smell information transmitted to the brain
from odorant molecules in the air to the olfactory sensory neurons which convert into electrical signals. These signals then travel along the olfactory nerves through the cribriform plate to the olfactory bulb, the first relay station in the brain
label the main structures of the eye
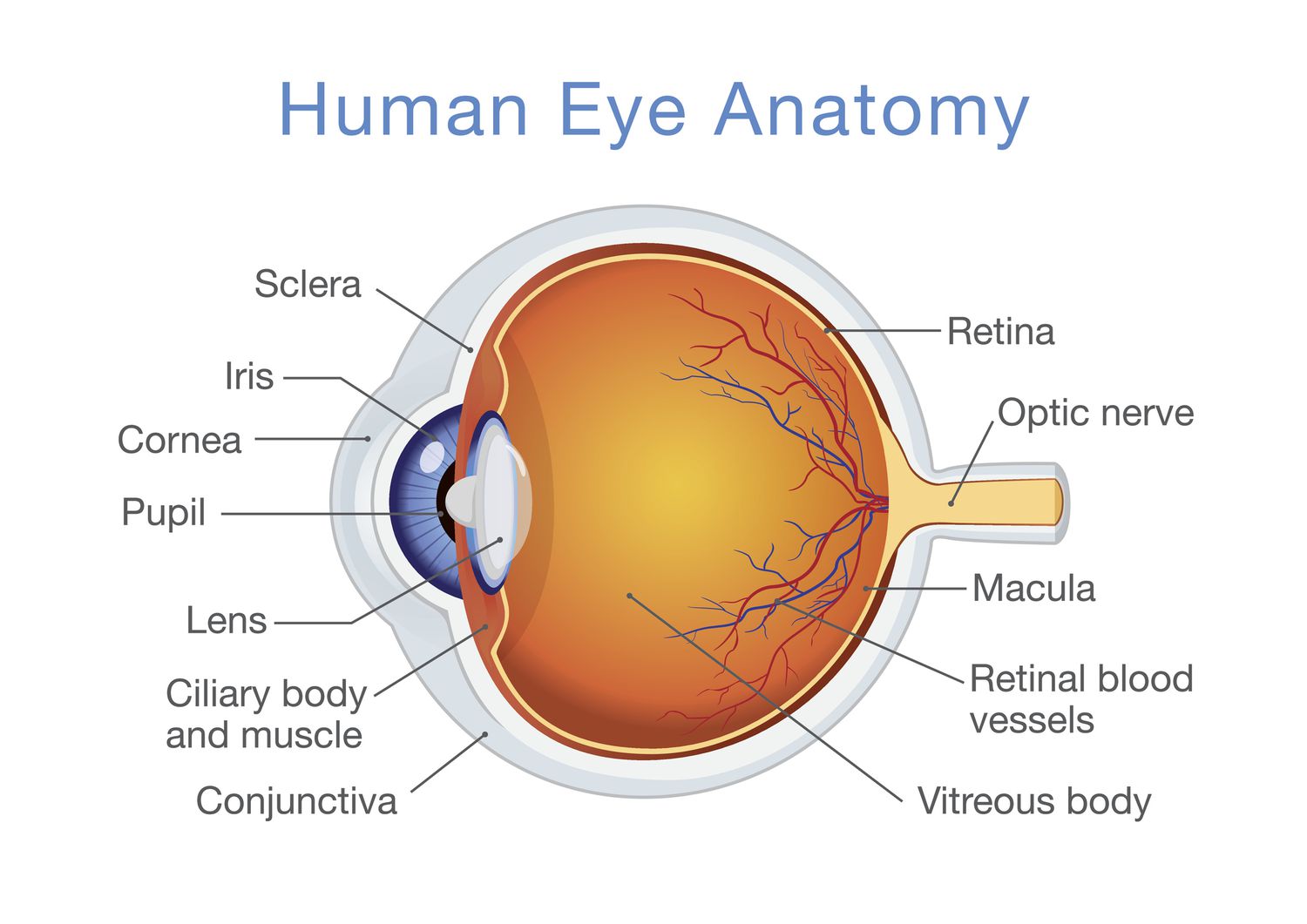
function of the cornea
to protect the eye and to focus light entering the eye
function of the sclera
acts as a protective outer layer and provides structural support for the eyeball
function of the iris
controls the amount of light entering the eye
function of the pupil
regulates the amount of light entering
function of the lens
focuses light on retina, enables clear vision
function of the retina
converts light into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as visual images
function of the macula
provides sharp, central vision, enabling us to see fine details, reconise faces and read
function of the optic nerve
transmit visual information from the retina to the brain
function of the aqueous humour
keeps your eye inflated and provides nourishment
function of the vitreous humour
maintains eye shape and contributes to image clarity
function of the choroid
nourish the outer retina by supplying it with oxygen and essential nutrients
stimulates sensory receptors
function of the ciliary body
producing aqueous humour, helping to focus, and maintaining the lens's position
contracts and relaxes ligaments
explain the process of vision
role of rods and cones
photoreceptor cells in the retina that convert light into neural signals for vision
explain how the eye adjusts for near and far vision
label main structures of the ear
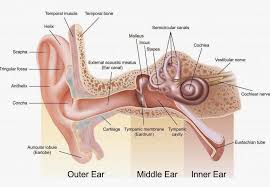
function of the pinna
collect and funnel sound waves into the ear canal
function of the external auditory canal
channel sound waves from the outer ear to the eardrum
function of the tympanic membrane
a sound receiver and transmitter
function of the ossicles
transmit and amplify sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear
function of the malleus
transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the incus
function of the incus
to receive sound vibrations from the malleus and transmit them to the stapes
function of the stapes
transmitting sound vibrations from the incus to the inner ear
function of the tympanic cavity
houses and transmits sound vibrations via the ossicles
function of the eustachian tube
to equalize air pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere
function of the cochlea
to convert sound waves into neural impulses that the brain interprets as sound
function semicircular canals
detect and sense rotational or angular movements of the head
function of the round window
to decompress the fluid-filled cochlea, acting as a pressure release valve for the inner ear's fluid system
function of the vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
how are sound waves collected by the pinna and travel through the ear canal to vibrate the tympanic membrane
how vibrations are amplified by the ossicles and transmitted to the fluid-filled cochlea
role of hair cells in converting mechanical vibrations into electrical impulses
convert mechanical vibrations from sound waves into electrical signals from mechanotransduction
transmission of auditory information via the auditory nerve to the brain for interpretation
outline role of th esemicircular canals and vestibule in maintaining balance and equilibrium
function of the endocrine system
regulate physiological processes through release of hormones
metabolism-how body converts food into energy
growth and development-crucial
reproduction - controls processes
homestasis- helps maintain a stable internal environment
response to stress
mood and emotions
immune- helps defend the body from infections
explain how the endocrine system works in conjunction with the nervous system to coordinate and control body activities
describe the stimulus (hormone control)
changes in internal/external environment
drop in blood glucose levels
decribe the receptor (hormone control)
detects change
pancreas
describe the control centre (hormone control)
hypothalamus, putitary glands
describe the effector (hormone control)
target organ or tissue
describe response (hormone control)
change to restore homestasis
liver cells respond to insulin by taking up glucose
describe feedback (hormone control)
often negative feedback to regulate hormone levels
blood glucose levels return to normal
label the glands
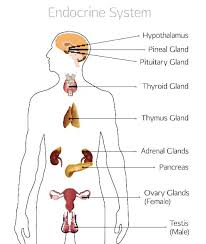
hypothalamus hormones
antidiuretic hormone - regulates water balance by increaseing water reabosorption in the kidneys helping maintain blood pressure by constriciting blood vessels
dopamine - acts on areas of the brain to give you feelings of pleasure and motivation
pituitary gland hormones
Growth hormone - stimulates growth bones and tissues, protein synthesis, cell regeneration
thyroid stimulating hormone - stimulate the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones, T3 and T4. regulating metablois, heart rate and body temperature
pineal gland hormone
melatonin - is essential for regulating sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythm
thyroid gland hormones
thyroxine - increase metablic rate and supports growth and development
calcitonin - lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclast and decreasing calcium reabsorption by the kidney
parathyroid gland hormones
adrenal glands hormones
epinephrine - initiates the "fight-or-flight" response to prepare the body for intense physical exertion
cortisol - acts as the bodys primary stress response system regulating metabolism, BP, and immune function
pancreas hormone
insulin - lowers blood glucose by promoting uptake of glucose into cells and stimulating glycogen stoarge in the liver
glucagon - raises blood glucose by stimulating break down of glycogen in glucose in the liver
ovaries gland hormones
osteogen - regulates the female reproduction system, stimulates secondary sex characteristics maintaning the menstrual cycle and pregnancy, promotes healthy cholestrole levels (overall female health)
progesterone - preparing the uterus for pregnancy by thickening it lining to support a fertilised egg
testes gland hormones
testosterone - to regulate sex drive, bone strength and muscle mass and to promote sperm production
inhibin b - to inhibit the secretion of follicles stimulating hormone from pituitary gland creating a negative feedback loop in the hypothalamic pituitary gonadal access to regulate reproductive functions