Exam #4 (Practice Exam)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Last updated 10:18 AM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
In the human male, sperm is produced in the
Testes
2
New cards
Which of the following houses the growing and developing fetus?
Uterus
3
New cards
Where does the fertilization of the egg occur?
Uterine Tubes
4
New cards
In the human female, the typical uterine cycle is an average of:
28 days
5
New cards
Secondary sexual characteristics in the male are directly maintained by the hormone:
Testosterone
6
New cards
Secondary sexual characteristic in the female are directly maintained by which hormones?
Estrogen
7
New cards
The lining of the uterus that is discharged during the menstrual phase is the:
Endometrium
8
New cards
After an egg is released from the ovary it travels where next?
Uterine Tube
9
New cards
What provides oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients to the developing fetus?
Placenta
10
New cards
After childbirth a mother may nurse (breast feed) the baby. What is the first substance the baby received that is described as thin, yellow, milky fluid rich in protein and antibodies?
Colostrum
11
New cards
An individual’s physical characteristics or appearance is known as their:
Phenotype
12
New cards
The letters used to describe the genes passed on to offspring (children), such as FF, Ff and ff are called the:
Genotype
13
New cards
The ability to roll the edges of the tongue upward in a U-shape is inherited as a dominant trait. Which of the following genotypes would produce an individual that can roll their tongue?
TT and Tt
14
New cards
In humans, widow's peak (W) is dominant over straight hairline (w). If a heterozygous male (Ww) marries a female with a straight hairline (ww), what percent of their children can be expected to have widow's peak?
50%
15
New cards
In the following pedigree, what does the colored circle indicate?
An affected daughter
16
New cards
The hereditary material found in all cells is:
DNA
17
New cards
The enzyme that is used to join DNA nucleotides (A,T,C,G) together is:
DNA Polymerase
18
New cards
The function of transfer RNA (tRNA) is to:
Carry amino acids to mRNA (and Ribosomes)
19
New cards
A sequence of mRNA that is removed (because it is not needed) during transcription is a(n):
Intron
20
New cards
What is the name of process that makes proteins?
Translation
21
New cards
How many bases on mRNA equal one codon?
3
22
New cards
In DNA which nucleotide bases bond with each other?
Both C-G and A-T
23
New cards
In RNA which nucleotide bases bond with each other?
U-A
24
New cards
Trisomy 21 is called:
Downs Syndrome
25
New cards
When the ovary releases and egg it is called:
Ovulation
26
New cards
Which of the following can be caused by problems with chromosomes such as receiving an extra copy of a chromosome?
All of the above
27
New cards
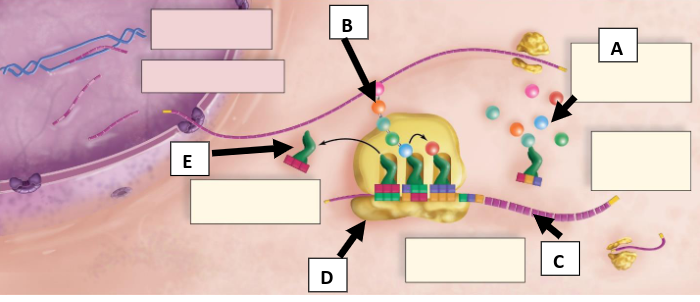
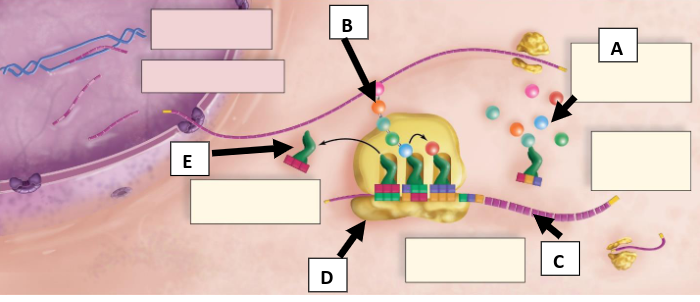
What is A pointing to (round objects)?
Amino acids
28
New cards
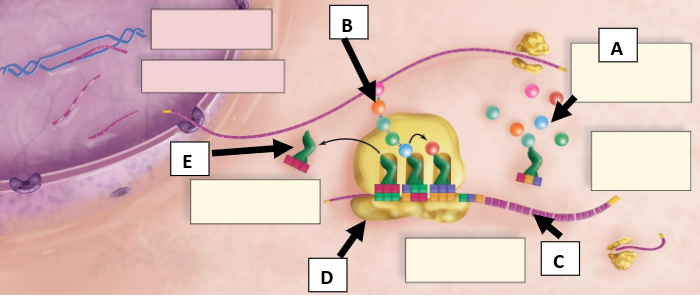
What is B pointing to (chain of round objects)?
Polypeptide chain
29
New cards
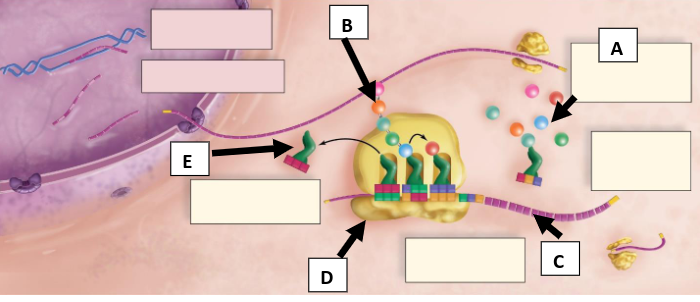
What is C pointing to?
mRNA with codons
30
New cards
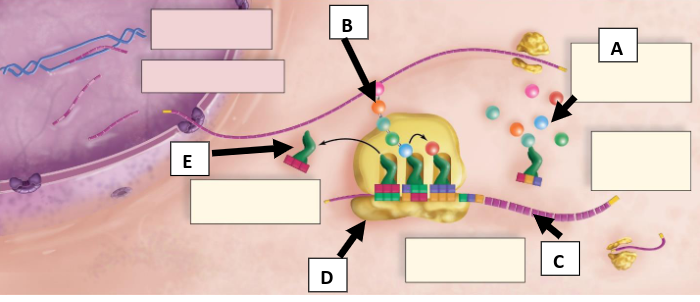
What is D pointing to?
Ribosome
31
New cards
What is E pointing to?
tRNA with anticodons
32
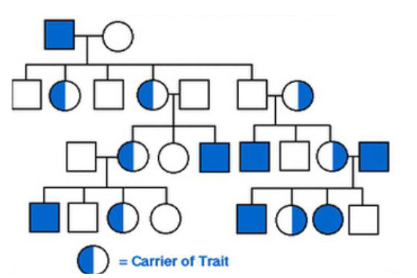
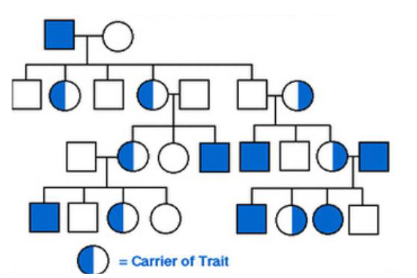
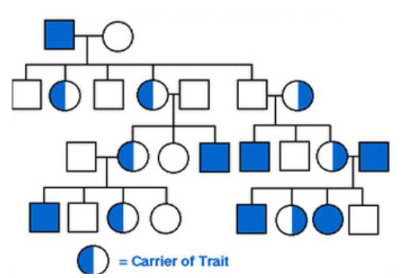
New cards
Who is more impacted (has the disease) by the disease shown?
Males
33
New cards
The pedigree shows the distribution of an X-linked disease.
True
34
New cards
Females are much more likely to be carrier than actually have the disease.
True
35
New cards
Widow's peak (W) is dominant over straight hairline (w). If a homozygous (for widows peak) male (WW) marries a female with a straight hairline (ww), what percent of their \n children can be expected to have widow's peak?
100% (Ww)
36
New cards
What if both parents were heterozygous for widow’s peak (Ww), what percent of children would likely have widows peak?
75%
37
New cards
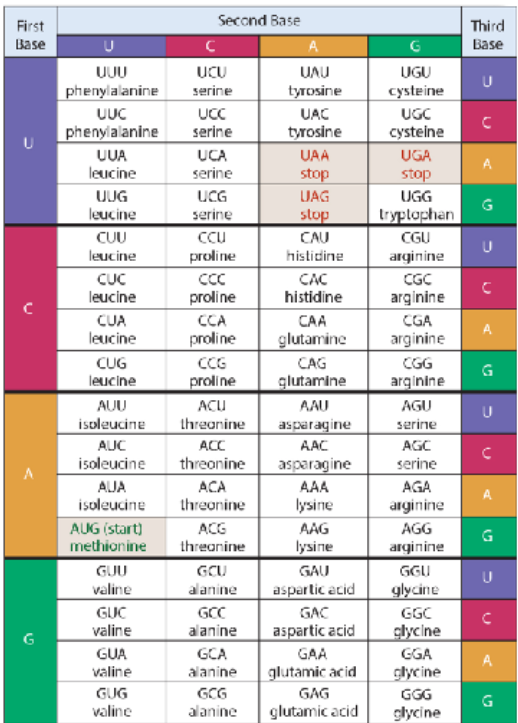
What amino acids do the following codons code for?
AUG: Start/Methionine \n CAA: Glutamine \n AAG: Lysine \n UAG: Stop \n GGC: Glycine
38
New cards
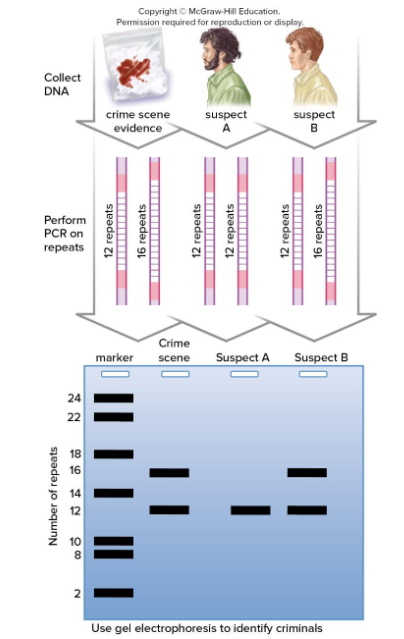
The police are investigating a crime. They found DNA at the crime scene and ran it through gel electrophoresis to determine to examine the DNA fragments. The police had two suspects in connection to the crime and also ran their DNA. Which of the suspects do you think the police will charge with the crime?
Suspect B
39
New cards
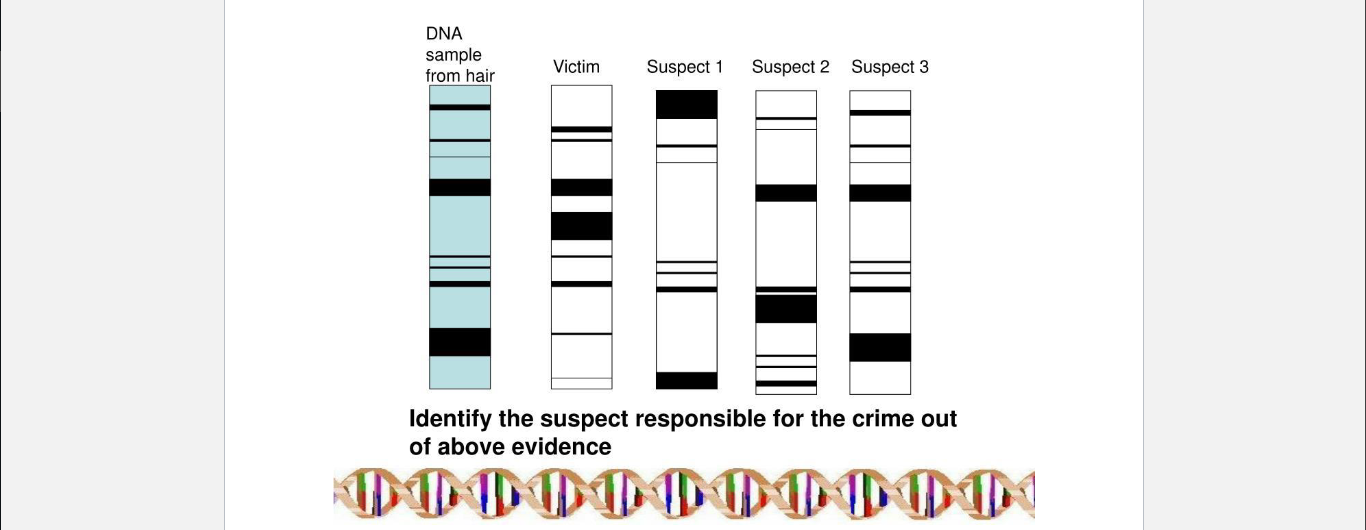
A sample of DNA was taken from hair and sequenced, as was the DNA of the victim and 3 suspects. Who’s DNA matches the sample?
Suspect 3
40
New cards
Of the following, which are 6 defects or diseases that can result when there are problems with chromosome 19. (7)
Colorectal cancer, Muscular dystrophy, Deafness, Atherosclerosis (hardening of arteries), Alzheimer’s, Hemolytic anemia, Acute myeloid leukemia, Insulin resistant diabetes mellitus