Lesson 21: Skeletal muscle
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Functions of muscular system
PRODUCTION OF BODY MOVEMENTS
STABILIZING BODY POSITIONS
ORGAN VOLUME REGULATION
DISPLACEMENT OF SUBSTANCES WITHIN THE ORGANISM
HEAT GENERATION
What are the types of proteins in each myofibril of muscle fiber
Contractile proteins: Actin, myosin
Regulatory proteins: Troponin, Tropomyosin
Giant Accessory proteins: Titin nebulin
Contractile proteins
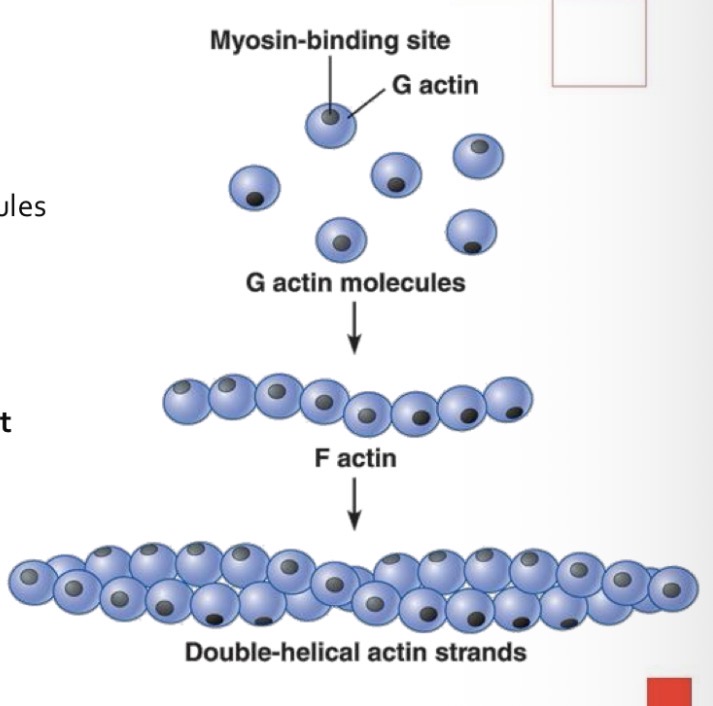
The fine filament is formed by the aggregation of actin molecules
Each actin molecule contains a myosin binding site.
The actin aggregates clump together in a helical arrangement
to form two strands of filamentous actin or F actin.
Regulatory proteins
Allow muscle fibers to start or stop contracting
Tropomyosin: fibrillar protein, which in a
resting state covers the binding sites of actin,
preventing their interaction with the myosin heads.
Troponin: consist of 3 subunits: ITC
3 subunits of troponin
- I: affine for actin
- T: affine for tropomyosin
- C: affine for calcium
How does tropomyosin deattach from actin binding site?
Through binding of calcium with tropnin c
Thick myosin filaments
Each thick filament is made up of hundreds of myosin molecules
Each myosin consists of 2 interlocking subunits
Each of subunits has a long tail and a head
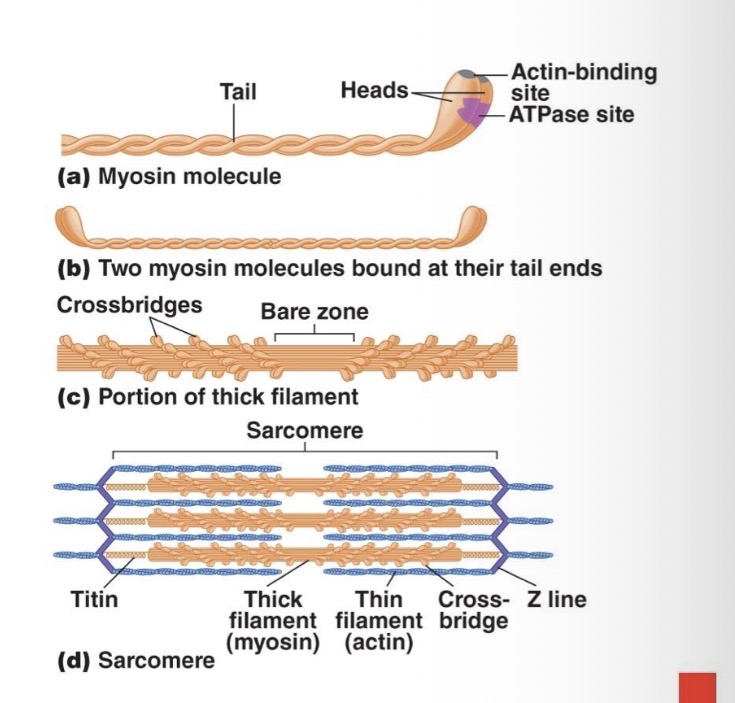
What does the head of myosin do
It generates the mechanical force
Has a actin binding site and ATPase site that hydolyzes atp
Titin and nebulin function
Titin:
• Stabilizes the position of the myosin filaments.
• Its elasticity returns the stretched muscles to their resting length
Nebulin:
Nebulin helps align the actin filaments in the
sarcomere.
What controls skeletal muscle movement
CNS
What is a motor unit
A neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates make up a motor unit.
What are the 3 basic steps of contraction
Muscle fiber excitation
Excitation contraction coupling
Contraction cycle
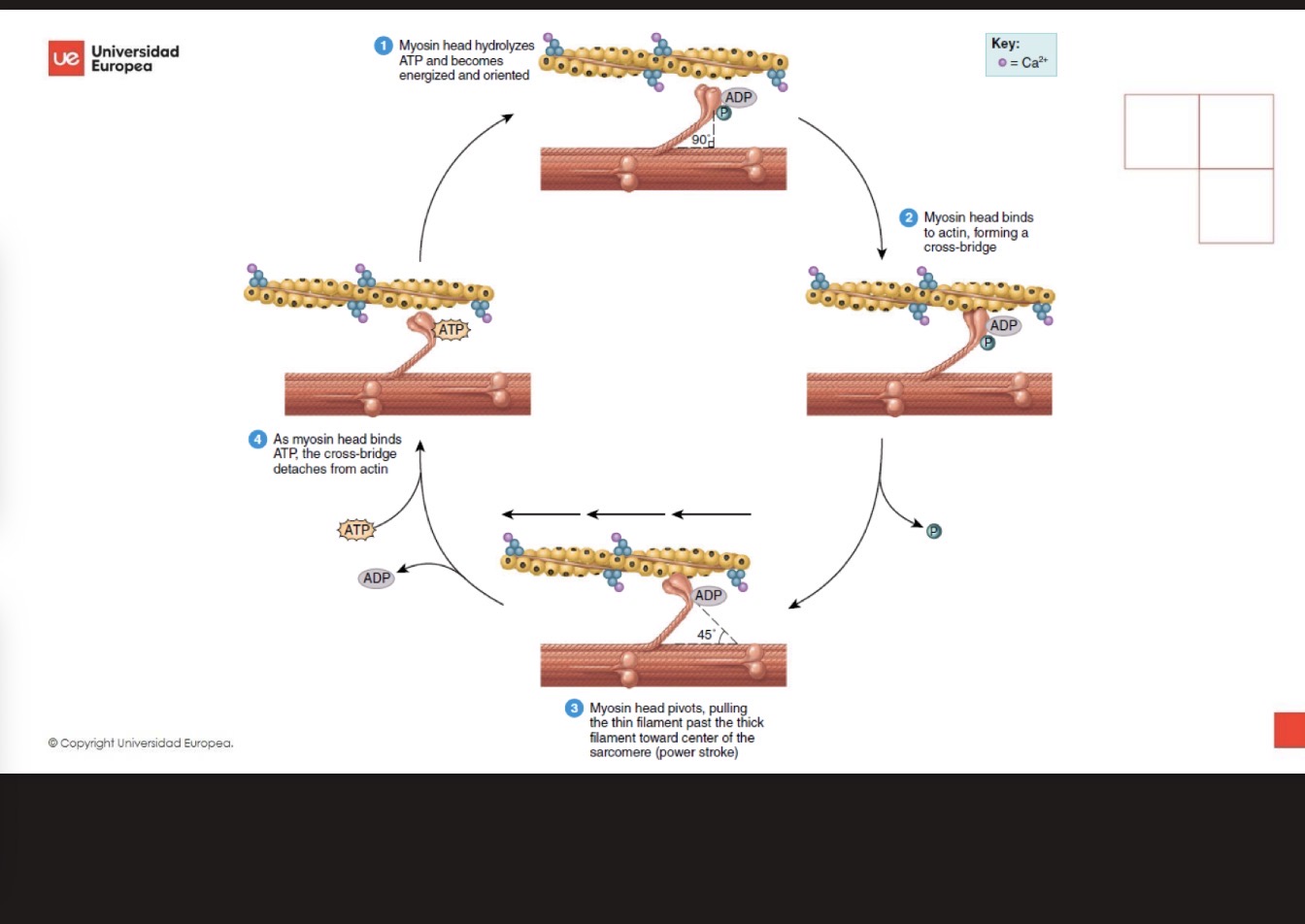
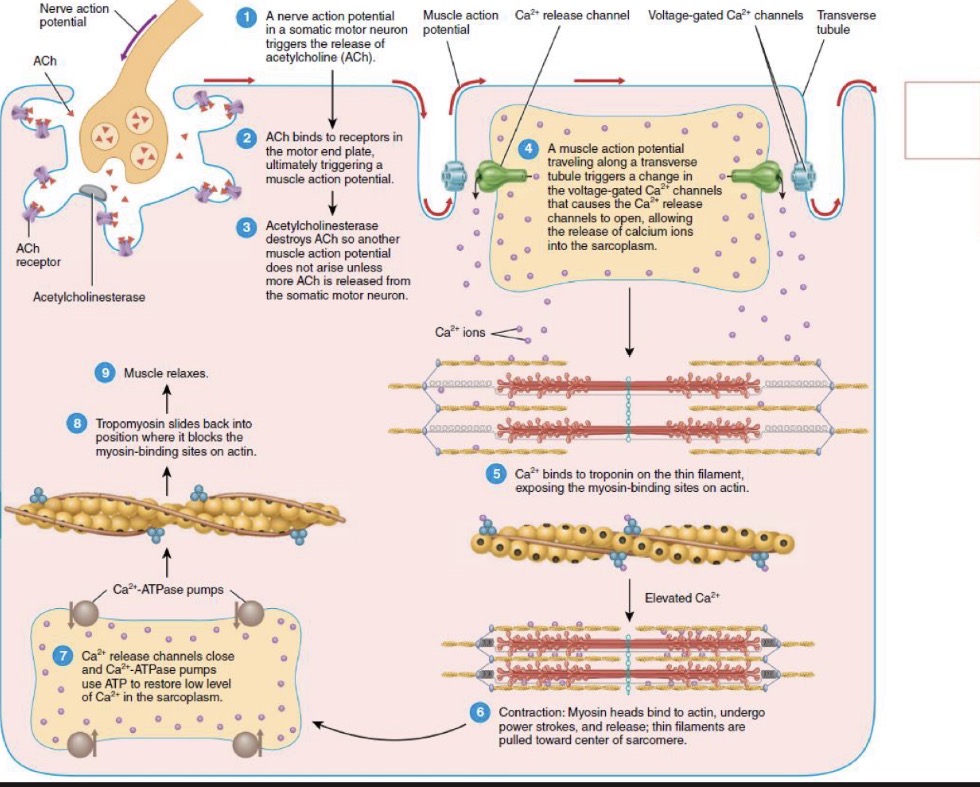
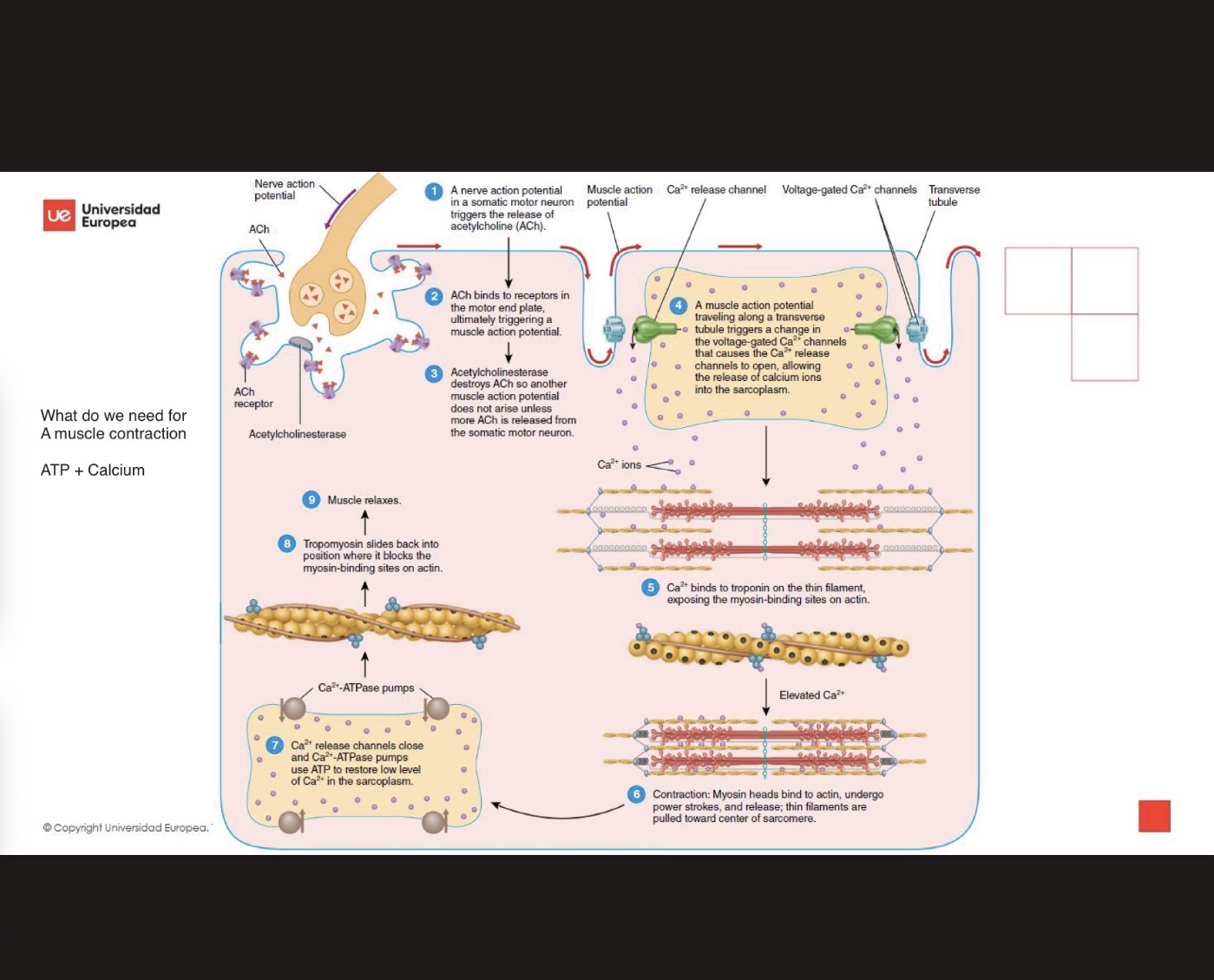
Excitation and relaxation cycle
Two conditions that causes mucle fibers to relax after contracting
The breakdown of ACh by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which determines the termination of muscle action potentials
The closure of the channels that release calcium to the sarcoplasm, so that the calcium is trapped in the SR membrane
What is most important components
ATP and Calcium
What is wave summation?
When multiple stimuli appear before complete relaxation of the muscle, the following contraction is more intense because it begins when the fiber has a higher tension level.
What is an incomplete tetanus contraction
When a fiber is stimulated faster (20-30 stimuli) per second)
Only partially relax between stimuli
What is a complete tetanus contraction
More tgab 80-100 stimuli per seconds with no relax
What is muscular fatique
inability of a muscle to contract strongly after prolonged activity, due to: Release of calcium, glycogen, oxygen