Labeling cells
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
no pole
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
1. Label the features that are unique to plant cells
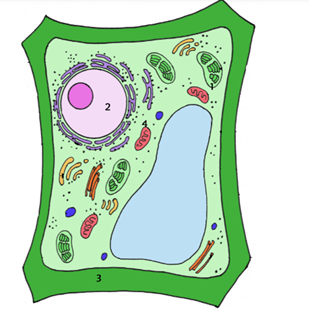
Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose that provides structure and protection.
Chloroplasts: These organelles contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert sunlight into energy.
Large Central Vacuole: This large, membrane-bound space stores water, nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure to keep the plant cell rigid.
Plasmodesmata: Channels that connect plant cells to one another, allowing communication and transport of materials between cells.
Plastids: Apart from chloroplasts, other plastids like leucoplasts and chromoplasts are found in plant cells. They store starch and pigments.
1. Label the features that are unique to animal cells
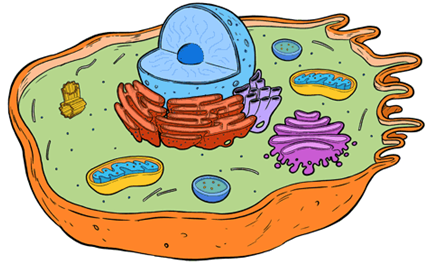
Centrioles 🌀
Appearance: Small, cylindrical, and often in pairs
Usually near the nucleus
Function: Helps in cell division (mitosis and meiosis)
Not found in plant cells
2. Lysosomes 🟡
Appearance: Small, round vesicles (often shown as yellow or light-colored)
Function: Contains digestive enzymes to break down waste and damaged cell parts
Mostly found in animal cells (rare in plant cells)
3. Small Vacuoles (Vesicles) 🫙
Appearance: Small, bubble-like sacs
Function: Temporary storage for nutrients, waste, or water
Plant cells have a large central vacuole, while animal cells have smaller, multiple vacuoles
4. Irregular Shape 🧩
Animal cells have a more rounded or irregular shape
Plant cells are more rectangular due to their rigid cell wall
1. Label the features that are unique to bacteria (prokaryotic) cells
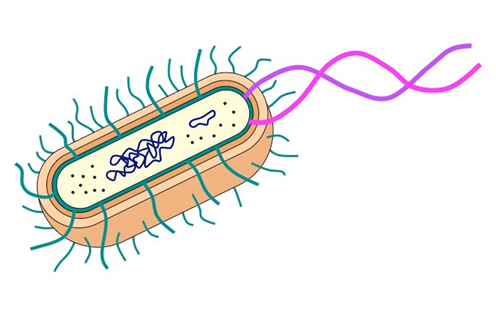
Nucleoid (DNA region) – Instead of a nucleus, bacteria have a single circular DNA strand floating in the cytoplasm.
Cell Wall (made of Peptidoglycan) – Provides structure and protection (unique to bacteria, though some other organisms have different types of cell walls).
Flagellum – A long, whip-like tail that enables movement.
Pili (Fimbriae) – Small hair-like projections that help bacteria attach to surfaces or exchange genetic material (via conjugation).
Plasmids – Small, circular DNA molecules separate from chromosomal DNA, often carrying antibiotic resistance genes.
idk
dlkfklsdjf