Geology Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
Earn XP
Last updated 8:48 PM on 12/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following is the earliest (oldest) chapter of geologic time?
Precambrian
2
New cards
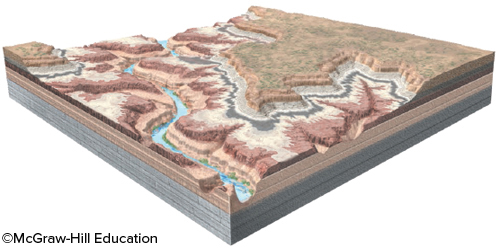
Which principle of relative age dating can be used to determine when the river formed on the landscape?
cross-cutting relations
3
New cards
Early Earth would have been inhospitable to many life forms of today because
the atmosphere lacked oxygen.
4
New cards
Which factor would help ensure survival of one species over another?
adaptable to environmental change
5
New cards
What is the main geologic feature for which Siccar Point in Scotland is famous?
a boundary between steep gray layers below and gently dipping red layer above
an unconformity
an ancient erosion surface
an unconformity
an ancient erosion surface
6
New cards
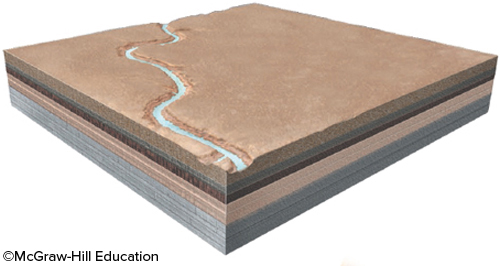
What is the youngest event represented in this block diagram?
erosion of a canyon by a river
7
New cards
In geology, determining time equivalency in rocks is called
correlation
8
New cards
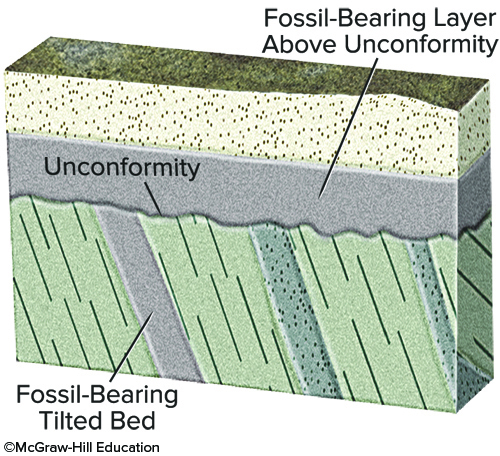
What would fossil ages from the geologic timescale tell us about the age of this unconformity?
The unconformity is younger than the fossil ages on the titled bed.
The unconformity is older than the fossil ages in layers above the unconformity.
The amount of time represented by the unconformity can be approximately bracketed by the ages of the fossils above and below.
The unconformity is older than the fossil ages in layers above the unconformity.
The amount of time represented by the unconformity can be approximately bracketed by the ages of the fossils above and below.
9
New cards
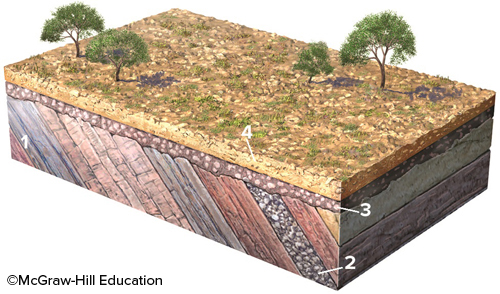
What type of feature is represented by the boundary between geologic units 2 and 3?
unconformity
10
New cards
The oldest rocks and minerals on Earth's surface have been found in Canada and Australia and are from the
Precambrian era
11
New cards
During what time period did dinosaurs exist on Earth?
Mesozoic
12
New cards
The geologic timescale details and divides geologic time based upon
fossil data
13
New cards
Some fossil species are of little value to geologist for correlation because
they existed for a long period of geologic time
14
New cards
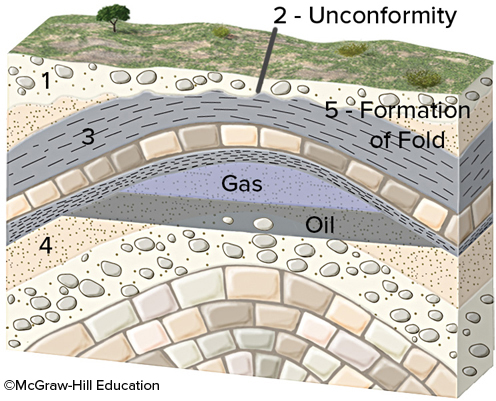
Which of the numbered features is the youngest?
conglomerate (1)
15
New cards
Which of the following is NOT accurately dated at between 4 and 4.6 billion years old?
isotopic ages on Earth's oldest known fossil shell
16
New cards
Upon what basis were the upper and lower boundaries of the Mesozoic Era defined?
abrupt changes in the types of fossils, representing mass extinctions
17
New cards
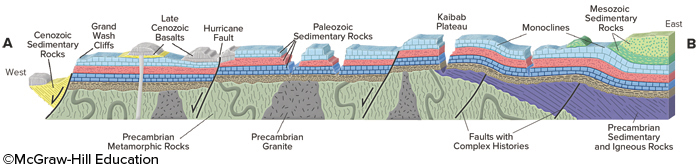
From this cross section of the Grand Canyon, what is the boundary between the various Precambrian rocks and the Paleozoic sedimentary units?
It is an angular unconformity in most places and a nonconformity where it overlies granite.
18
New cards
In which of the following time periods were mammals the dominant type of life?
Cenozoic
19
New cards
The oldest known rock found on Earth is dated at
over 4 billion years old
20
New cards

James Hutton inferred that the rocks below the contact at Siccar Point were vertical gray sandstone and shale and the rocks above were gently dipping red sandstone and conglomerate. Therefore, the histories of these rocks
are different
21
New cards
Which type of unconformity is produced when layers of sandstone and conglomerate bury an eroded surface of an igneous or metamorphic rock?
nonconformity
22
New cards
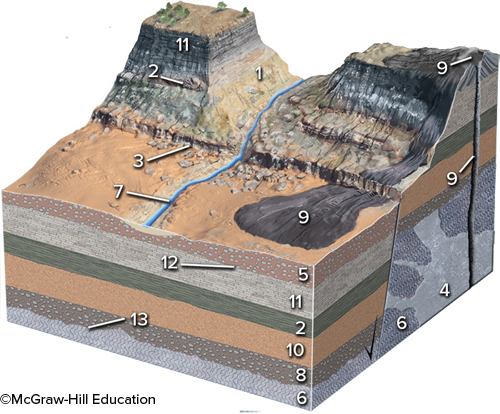
Of the following numbered units, which is the youngest?
unit 9
23
New cards
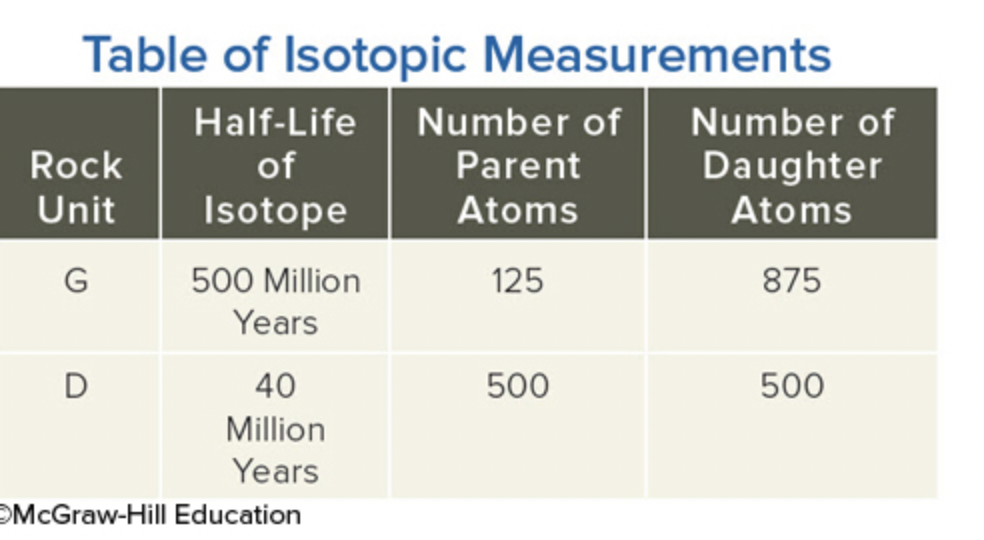
Using the data in this table, determine the age of the dike (unit D on this table).
40,000,000
24
New cards
Isotopes that decay slowly are used to date
ancient rock
25
New cards
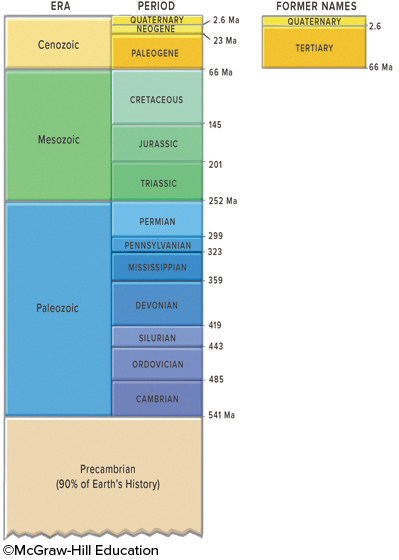
This figure shows the geologic timescale. Which period listed below would be part of the Paleozoic?
permian
pennsylvanian
Mississippian
Cambrian
pennsylvanian
Mississippian
Cambrian
26
New cards
Geologists look at rocks that were once at great depth, create high temperature and pressure conditions for rocks in the laboratory, and develop computer models in order to
investigate deep conditions and processes within the Earth
27
New cards
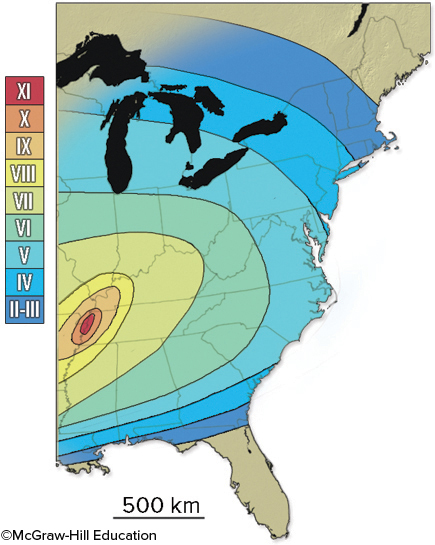
The Modified Mercalli Intensity rating map below shows intensity values that range from more than X to less than III. What does this map show?
The earthquake was not felt in southern Florida
28
New cards
Which of the following resulted from the large 2011 Tohuku earthquake in Japan?
severe ground shaking that damaged buildings near the earthquake
a deadly tsunami
destruction of a nuclear power plant
a deadly tsunami
destruction of a nuclear power plant
29
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a way that volcanoes and magma can cause earthquakes?
Volcanic explosions cause seismic waves
Volcanoes can load the crust, causing faulting and earthquakes
Many volcanoes have steep, unstable slopes that can cause landslides that shake the ground
Moving magma within or below the volcano can cause earthquakes.
Volcanoes can load the crust, causing faulting and earthquakes
Many volcanoes have steep, unstable slopes that can cause landslides that shake the ground
Moving magma within or below the volcano can cause earthquakes.
30
New cards

Which feature might indicate that this area has relatively recent earthquakes?
a change in topography across the structure
the presence of a fault scarp
the bends in streams
the steam channels on the right side that no longer continue onto the left side.
the presence of a fault scarp
the bends in streams
the steam channels on the right side that no longer continue onto the left side.
31
New cards
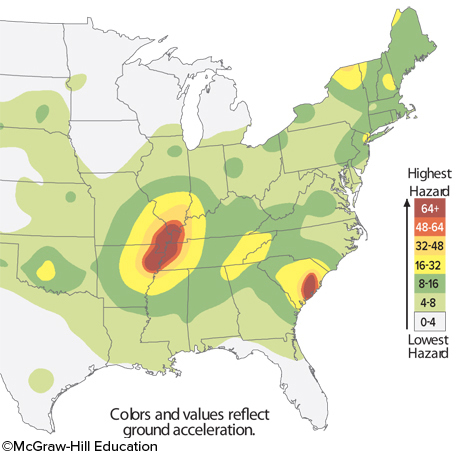
The image indicates that
two major zones exist for earthquake risk in the eastern United States.
32
New cards
Most earthquakes occur along
plate boundaries
33
New cards
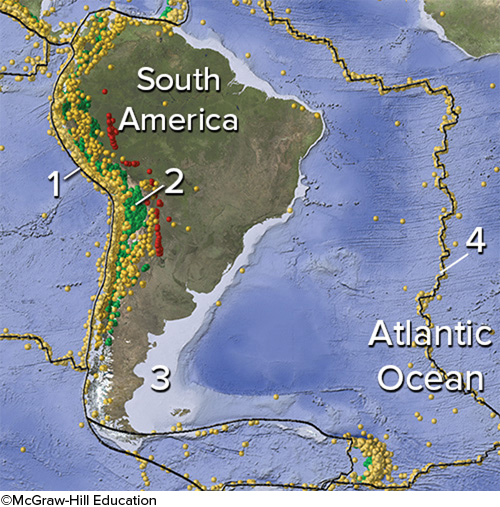
On this map of South America and adjacent areas, which site would have the deepest earthquakes?
2, Below the magmatic belt
34
New cards
Landslides and volcanic eruptions can cause a tsunami by
causing a large mass of rock to catastrophically displace the water
35
New cards
Earthquakes in subduction zones generally only occur at depths of
up to 700 km
36
New cards
Which of the following cannot cause a tsunami?
A strike-slip fault on land
37
New cards
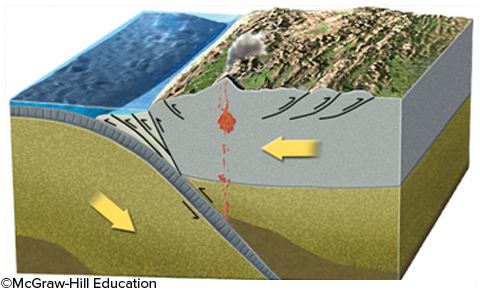
Most large earthquakes on subduction zones occur because of
faulting along the plate boundary
38
New cards
Which area did NOT have casualties caused by the Indonesian earthquake of 2004?
Indonesia
India and Sri Lanka
Islands in the Indian Ocean
The eastern coast of Africa
India and Sri Lanka
Islands in the Indian Ocean
The eastern coast of Africa
39
New cards
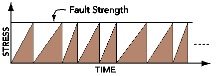
What is illustrated by this figure?
Stress increases until it matches the strength of the fault, and then stress decreases
40
New cards
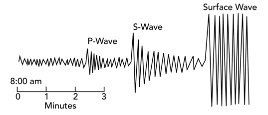
How would this diagram change if the seismic station was farther from the earthquake?
the p-waves would arrive later
the s-waves would arrive later
there would be a larger gap between the arrives of the p- and s-waves.
the s-waves would arrive later
there would be a larger gap between the arrives of the p- and s-waves.
41
New cards
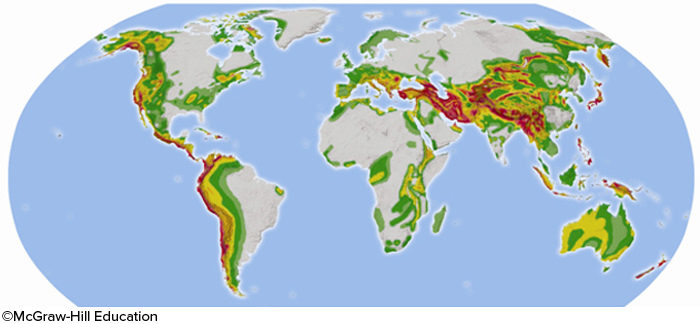
In the map below, areas of significant earthquake risk are shaded. Most high risk areas will be located
near a boundary between tectonic plates
42
New cards
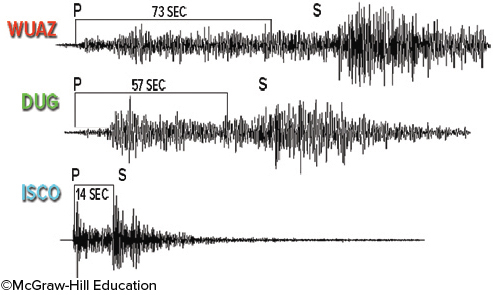
Based on the three seismograms, which seismic station was closest to the epicenter of the earthquake?
ISCO
43
New cards
Why does the United States have such varying risks of seismic activity?
some areas are near plate boundaries, while others are not
some regions in the continental interior have active fault systems.
volcanic activity can cause seismic risk in some areas.
some regions in the continental interior have active fault systems.
volcanic activity can cause seismic risk in some areas.
44
New cards
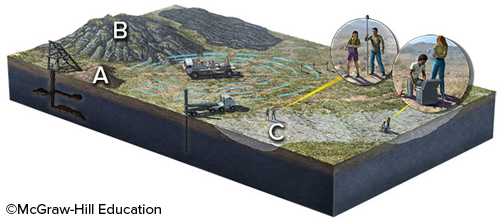
What location on the surface would provide easily gathered information about what is below the surface, without using expensive machines?
mine dump at A and rocky hill at B
45
New cards
What did geologists discover from studying the aftermath of the 1964 Alaskan earthquake?
Some parts of the coastline were uplifted and others subsided
46
New cards

What likely caused much of the damage shown in this photograph in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake?
fires that broke out after the earthquake
47
New cards
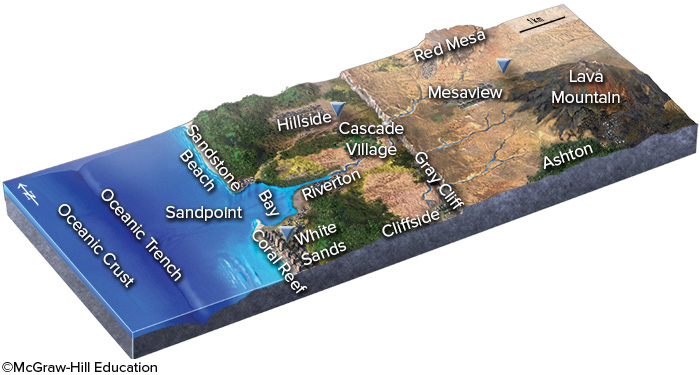
If an earthquake occurred near the oceanic trench in this figure, which one of the following hazards is likely to threaten the town of White Sands?
destruction by a tsunami
48
New cards
Which of the following may create earthquakes?
movement along faults
volcanic eruptions and magma movement
landslides
explosions and human activity
volcanic eruptions and magma movement
landslides
explosions and human activity
49
New cards
Which of the following are potential sources of destruction that may be caused either directly or secondarily by earthquakes?
landslides and rock falls
tsunami
aftershocks
fires
tsunami
aftershocks
fires
50
New cards
Which of the following is a characteristic of P-waves?
They compress and then expand the rock in the direction the wave travels.
51
New cards
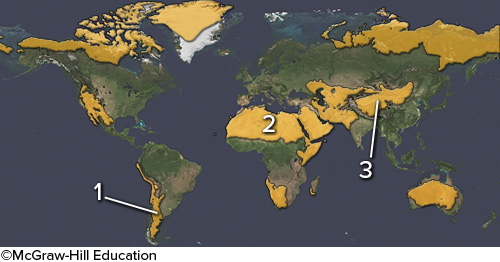
The area marked by number 2 on this figure is a desert primarily because
it experiences dry, descending air in the subtropics
52
New cards
All of the following are warm currents, EXCEPT
Canary Current
53
New cards
The thermohaline conveyor is driven by
cold saline water sinks in the North Atlantic
54
New cards
What is the main setting in which rain forests occur?
near the equator
55
New cards
Which of the following landscape features is NOT common in deserts?
alluvial fan
playa
rock varnish
dry wash
playa
rock varnish
dry wash
56
New cards
Based on data collected in Hawaii, since about 1960 the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has
consistently increased, except for yearly variations
57
New cards
Which of the following are NOT associated with a hurricane?
high atmospheric pressure
58
New cards
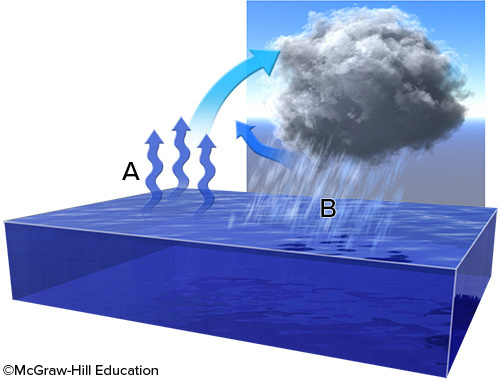
What is the relationship between water vapor at point A and water droplets at point B?
water evaporates at point A, rises, and then cools and condenses at point B
59
New cards
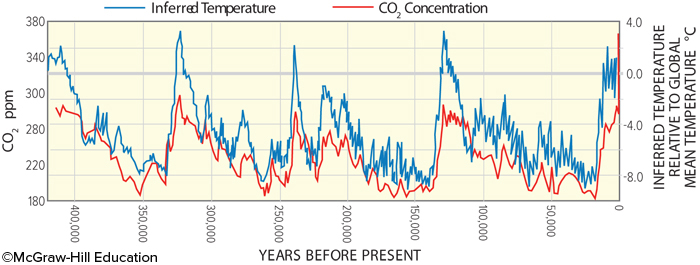
This plot of ice-core data shows measurements of CO2 content and interpretation of temperatures. These data show
that CO2 concentration and temperature generally increase and decrease over the same time periods
60
New cards
Global belts of prevailing winds are caused by
the higher spin velocity and higher atmospheric solar heating at the equator
61
New cards
To create a sea breeze
the warm air over the land rises, creating low pressure. Cool air over water sinks, creating high pressure. This creates an onshore breeze
62
New cards
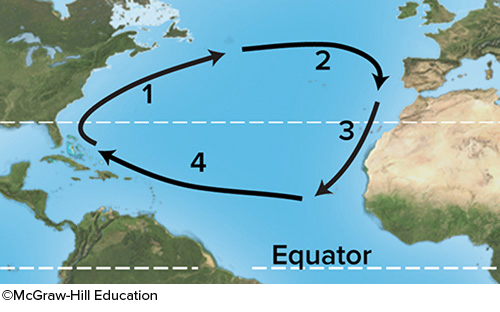
For these ocean currents in the Atlantic, which of these currents is mostly likely to be a warm current?
1
63
New cards
What topic was NOT discussed in the opening of the climate chapter?
the monsoon of India
the role of the Himalaya in climate
the Brahmaputra River of India and Bangladesh
the role of the Himalaya in climate
the Brahmaputra River of India and Bangladesh
64
New cards
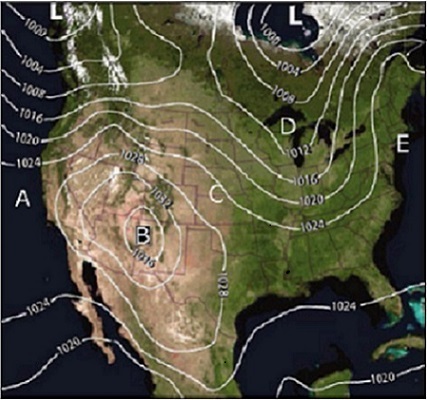
What location on this map is closest to an area of relatively high pressure?
b
65
New cards

What desert feature is shown in this photograph?
natural stain
66
New cards
El Niño is a condition that brings increased precipitation to the eastern Pacific Ocean basin when
strengthening of an ocean current results in warmer sea temperatures in the eastern pacific
67
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a setting that can form a desert?
near cold, upwelling ocean currents
in the subtropics due to atmosphere circulation patterns
in a rain shadow of a mountain range
in cold, dry polar regions
in the subtropics due to atmosphere circulation patterns
in a rain shadow of a mountain range
in cold, dry polar regions
68
New cards
In the Northern Hemisphere, most surface current flow
in clockwise, oval loops
69
New cards
Monsoons are caused by
seasonal heating of land masses in summer that changes wind directions
70
New cards

Which of the following landscape features is shown in this photograph?
alluvial fan
71
New cards
The Coriolis effect in the atmosphere is due to
the atmosphere rotating faster at the equator than at the poles
72
New cards
Tropical rain forests are clustered near the Intertropical Convergence Zone, which is
a curved boundary where winds converge near the equator
73
New cards

This wind-blown dust deposit (loess)
began as clay and silt that were produced by grinding of rocks along ice-age glaciers
74
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a reason why rain forests are disappearing?
trees are cleared for small farms so that people can live off the land
cattle ranching
commercial logging for tropical hardwoods, such as mahogany
construction of dams for hydroelectric power
cattle ranching
commercial logging for tropical hardwoods, such as mahogany
construction of dams for hydroelectric power
75
New cards
What happens when a glacier encounters the sea or a lake?
large blocks of ice collapse off the front of the glacier and become icebergs
76
New cards

What features are shown in this photograph?
pinnacles and sea stacks
77
New cards
When will an area experience high tide?
when the moon is directly overhead or on the opposite side of Earth
78
New cards
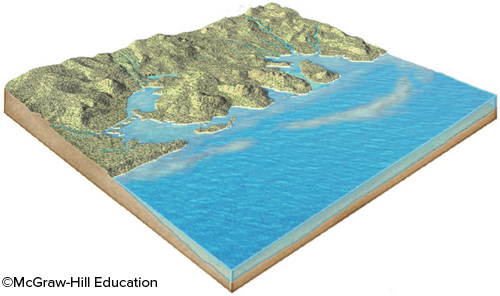
What geologic event is probably indicated by this irregular coast, with estuaries?
a rise in sea level
79
New cards

What are these sharp, glacially carved ridges?
arête
80
New cards
What is the main way that position of the continents can influence global sea level?
continents at high latitudes provide a setting in which large ice sheets can form
81
New cards
What is probably the least expensive approach for avoiding shoreline hazards?
forbid the building of houses or other structures in high-risk areas
82
New cards
What does a curved glacial ridge (esker) record?
meltwater channels below or within a glacier
83
New cards
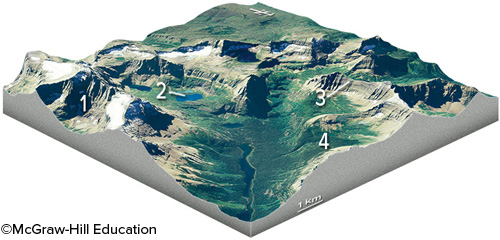
Which feature on this diagram is an arête?
3, a steep ridge
84
New cards
What is the typical setting of a sea cave or sea stack?
on a promontory
85
New cards
What is the relationship between plucking and abrasion on a glacially-scoured landscape?
Abrasion occurs on the upflow side of a mound or hill that is scoured, while plucking occurs on the downflow side.
86
New cards
What does a terminal moraine represent?
a pile of sediment deposited at the end of the glacier
87
New cards
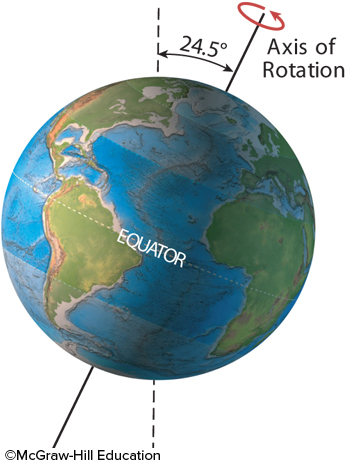
The present-day tilt of Earth's axis of rotation is 23.5º degrees. What would be the result of more tilt, as shown here?
high latitudes would receive more direct sunlight, causing warmer summer
a decrease in glacial activity
an increase in the effects of the seasons
a decrease in glacial activity
an increase in the effects of the seasons
88
New cards
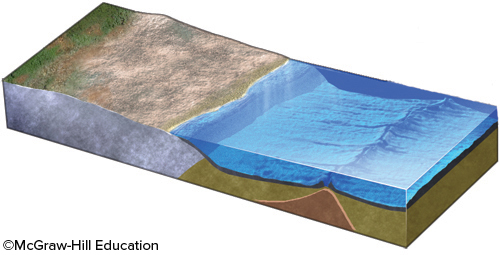
An increase in the rate of seafloor spreading along this ridge would cause
the ridge to become broader
seawater to be displaced out of the ocean basin
a rise in sea level
seawater to be displaced out of the ocean basin
a rise in sea level
89
New cards
If all the ice on West Antarctica was melted, how much would it cause global sea level to rise? If you do not remember the approximate size of this rise, the volume of ice is 3,000,000 km3 and the surface area of the world's ocean is 361,000,000 km2.
1 meter to 10 meters
90
New cards
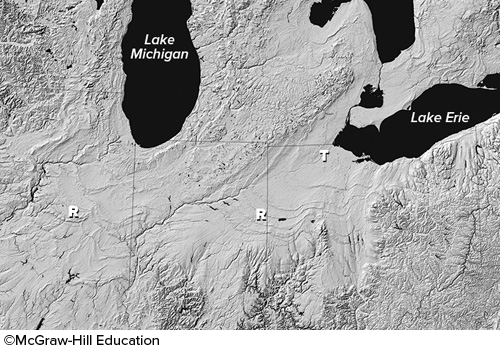
What is the origin of smooth troughs (T on this figure) cutting across the landscape in the Great Lakes area?
glaciers carved the smooth troughs
91
New cards
Sand and other sediment
can move laterally along the coast if waves approach the beach at an angle
92
New cards
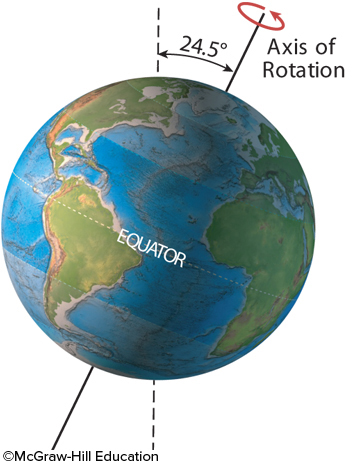
The present-day tilt of Earth's axis of rotation is 23.5º. What would be the result of more tilt, as shown here?
a decrease in glaciers
93
New cards
There are two high tides and two low tides in each 25-hour period because
Earth completes a full rotation every 24 hours but the Moon moves too
94
New cards
What is a primary reason an increase in glaciers on land would cause sea level to fall?
glaciers tie up large volumes of water that would otherwise be in the sea
95
New cards
Which of the following is NOT an approach communities have tried to address shoreline problems?
lowering the local sea level
96
New cards
High tides are higher than average and low tides are lower than average when
the moon and the sun are aligned relative to the Earth
it is a full moon
it is a new moon
it is a full moon
it is a new moon
97
New cards
What are some possible influences of ocean currents on glaciation?
cold currents can cool the land allowing glaciers to form if there is sufficient precipitation
cold currents can inhibit the growth of glaciers because they put less moisture into the atmosphere
warm currents can warm parts of continents, inhibiting glaciation.
warm currents bring warm moist air that can increase precipitation and snowfall if the temperature is cold enough
cold currents can inhibit the growth of glaciers because they put less moisture into the atmosphere
warm currents can warm parts of continents, inhibiting glaciation.
warm currents bring warm moist air that can increase precipitation and snowfall if the temperature is cold enough
98
New cards
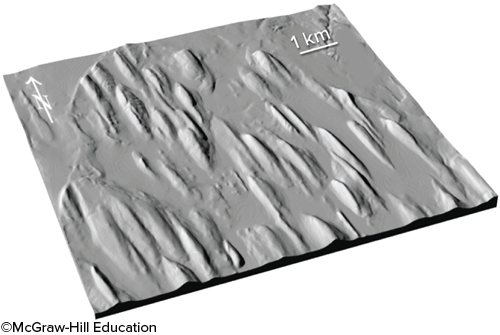
What do these teardrop-shaped hills (drumlins) record?
erosion and sculpting of soft materials by a moving glacier
99
New cards

What is this bowl-shaped, glacially carved feature?
cirque
100
New cards
Which of the following can we use to recognize prehistoric slope failures?
sedimentary deposits
orientation of beds and other geologic structures
masses of rock fragments that are unusual for an area
hummocky topography
orientation of beds and other geologic structures
masses of rock fragments that are unusual for an area
hummocky topography