Chapter 5: Congenital and Genetic Disorders
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Where is genetic info stored in humans?
In chromosomes!
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome (22 pairs)
Homologous chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes that are the same size/shape have the same genes
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual
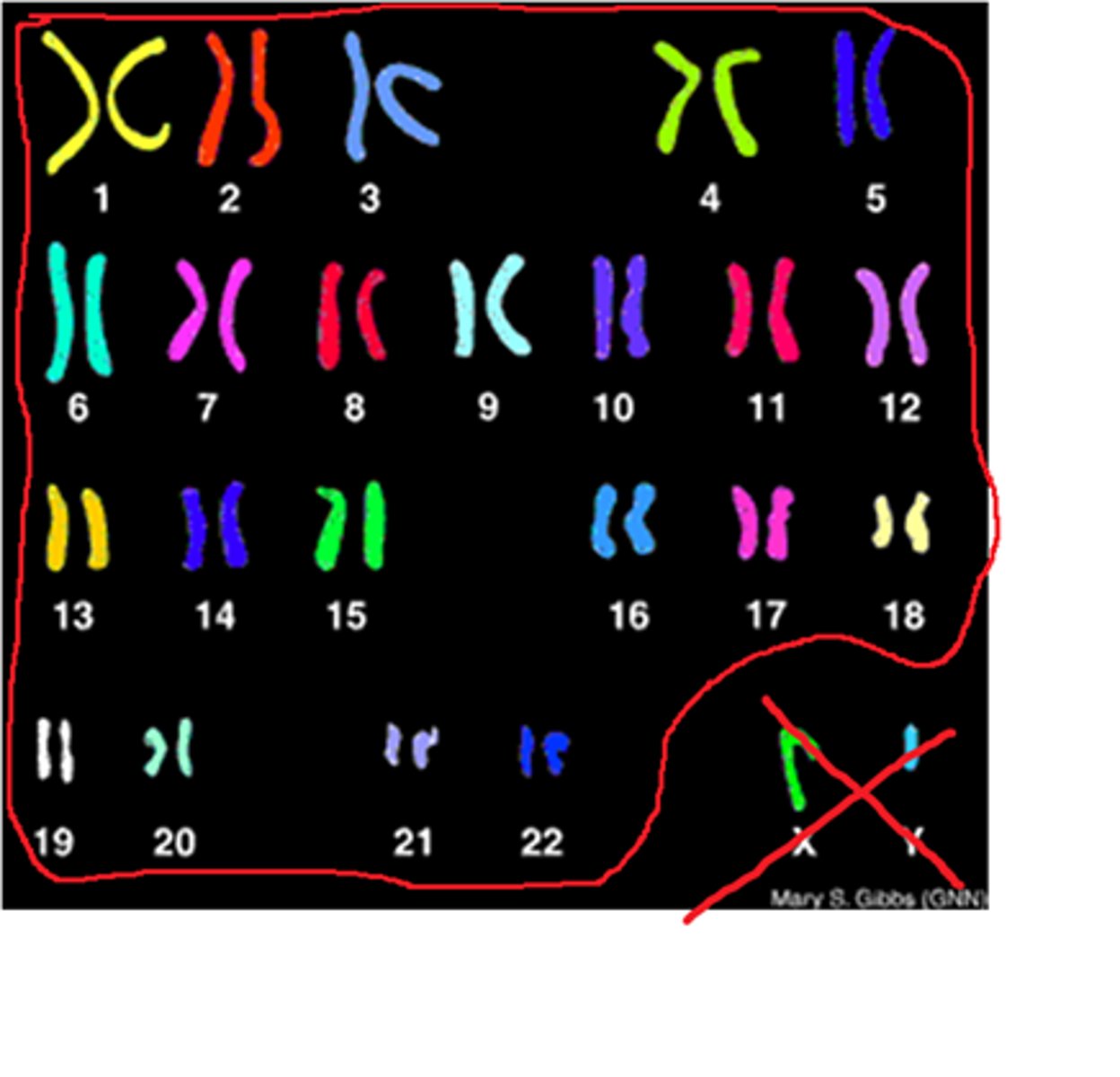
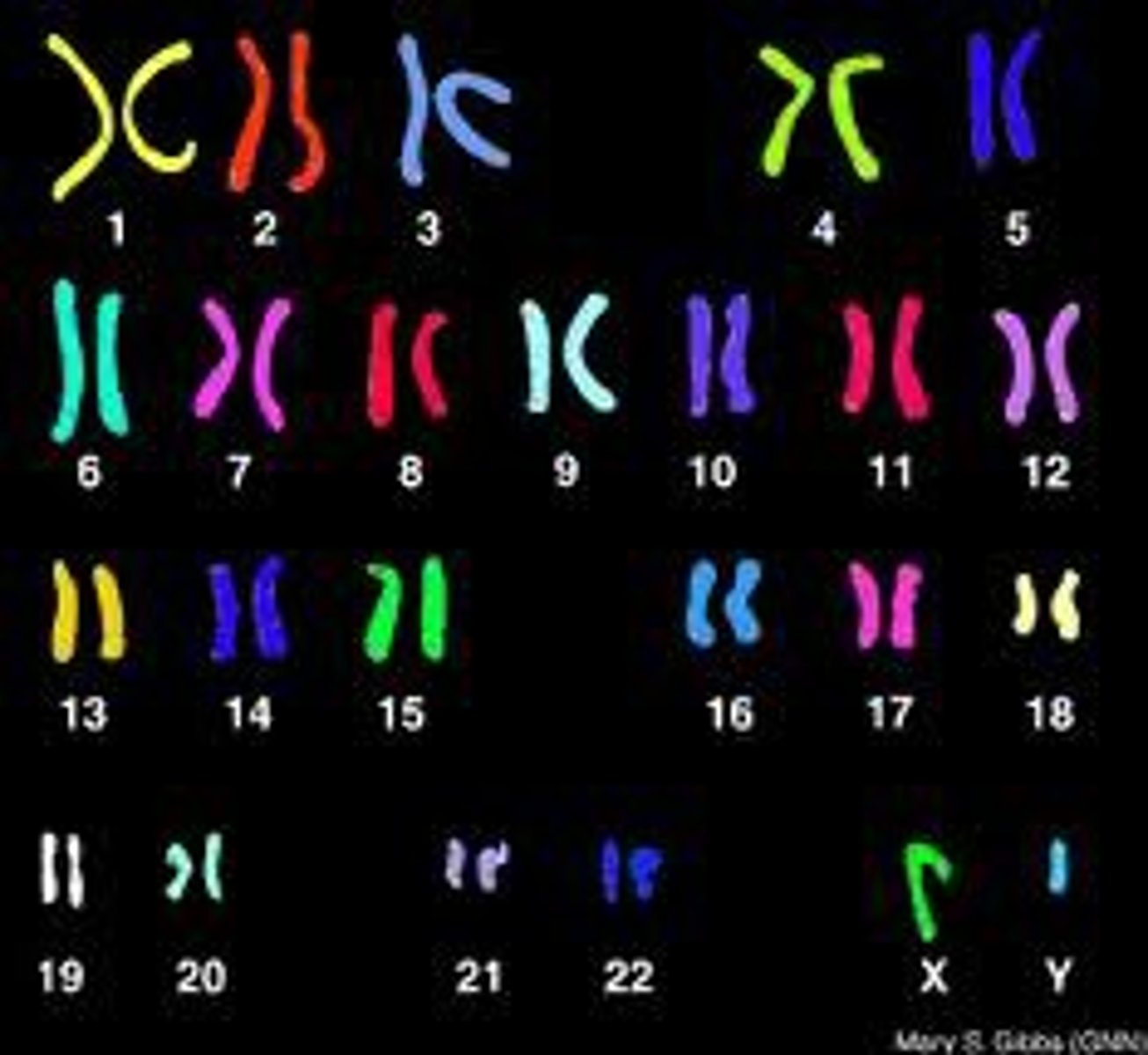
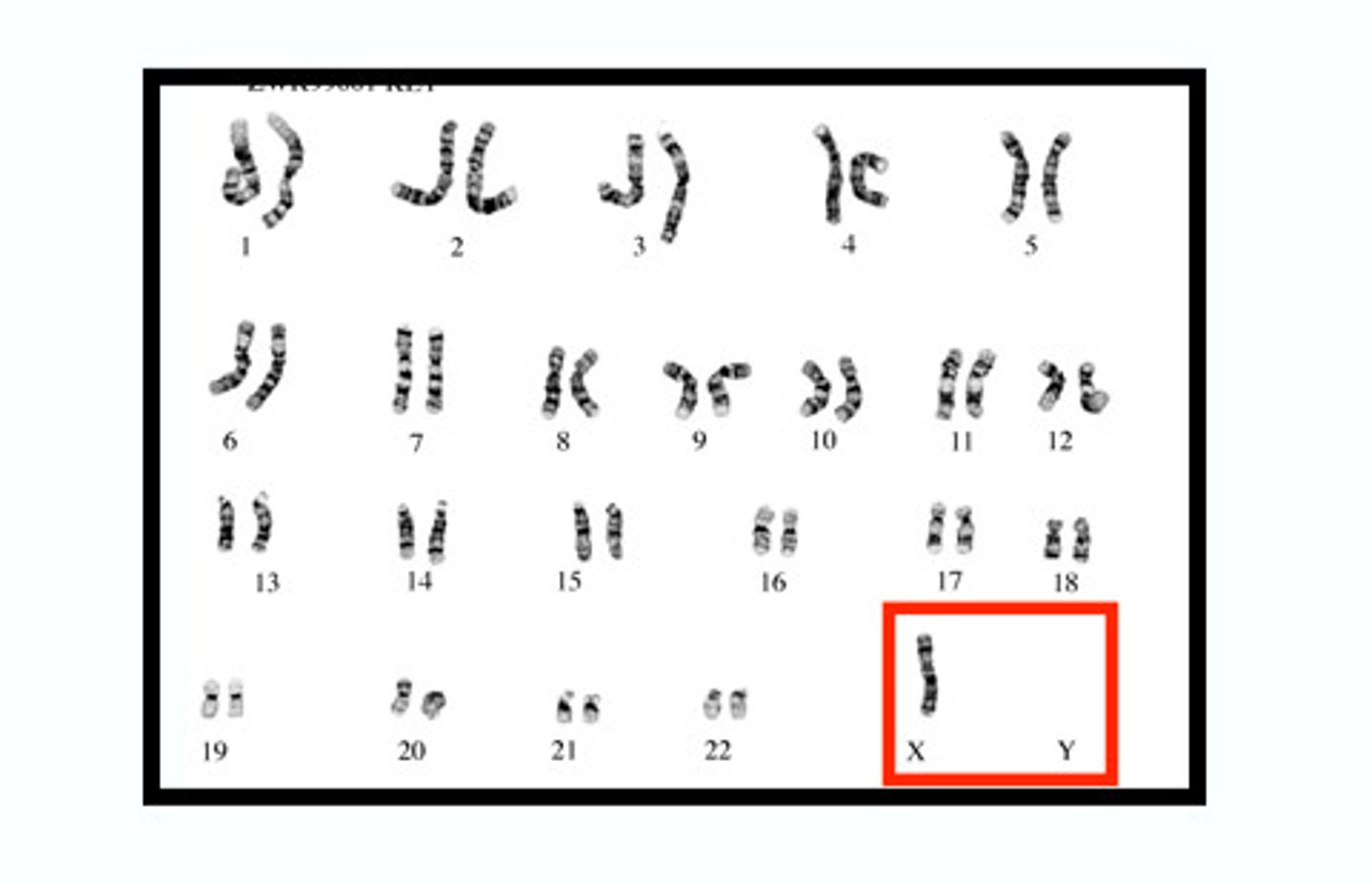
Karyotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs; used to diagnose congenital disorders
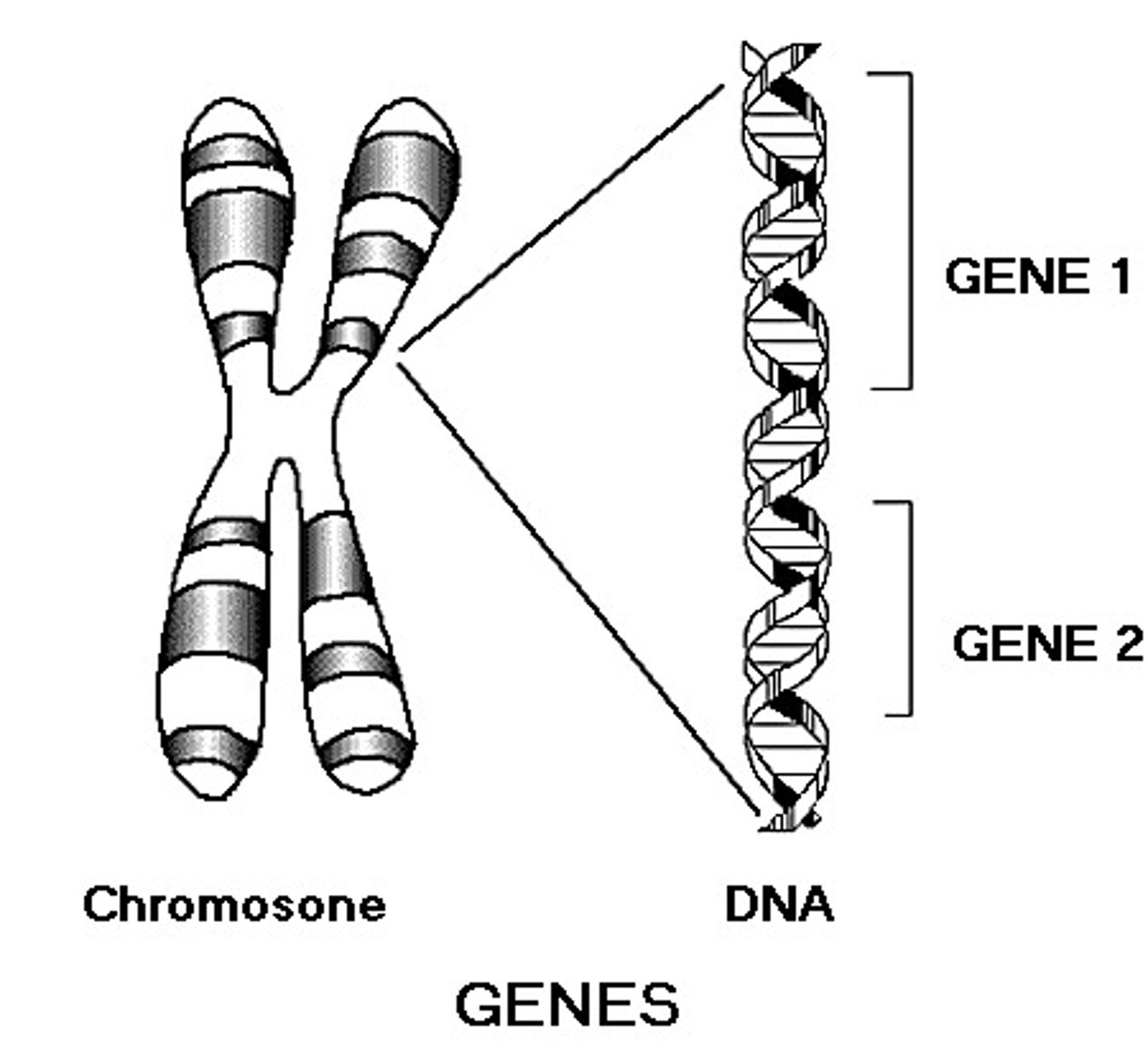
Genes
DNA segments that carry genetic information and determine traits
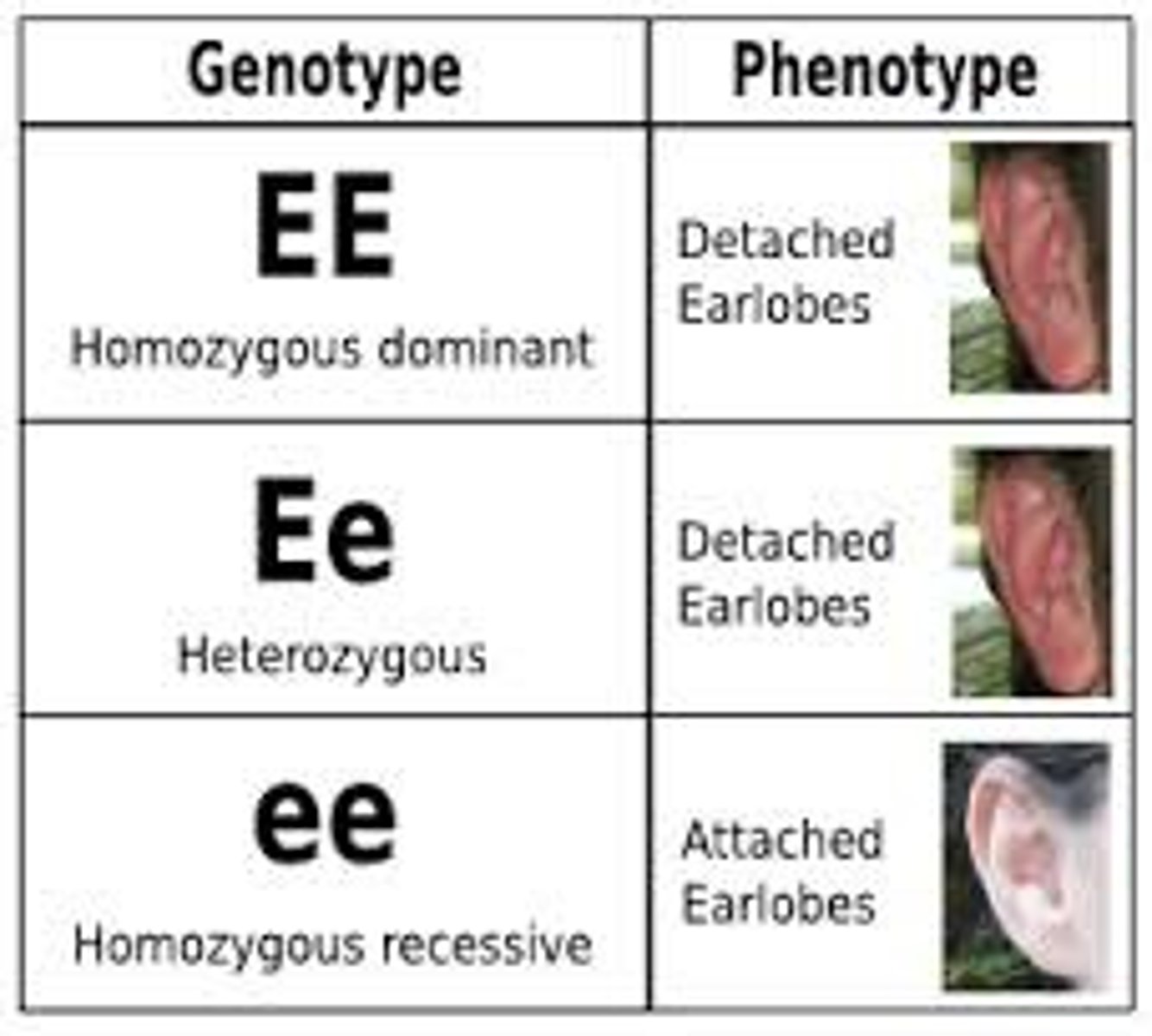
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism (not all genes are expressed all the time)
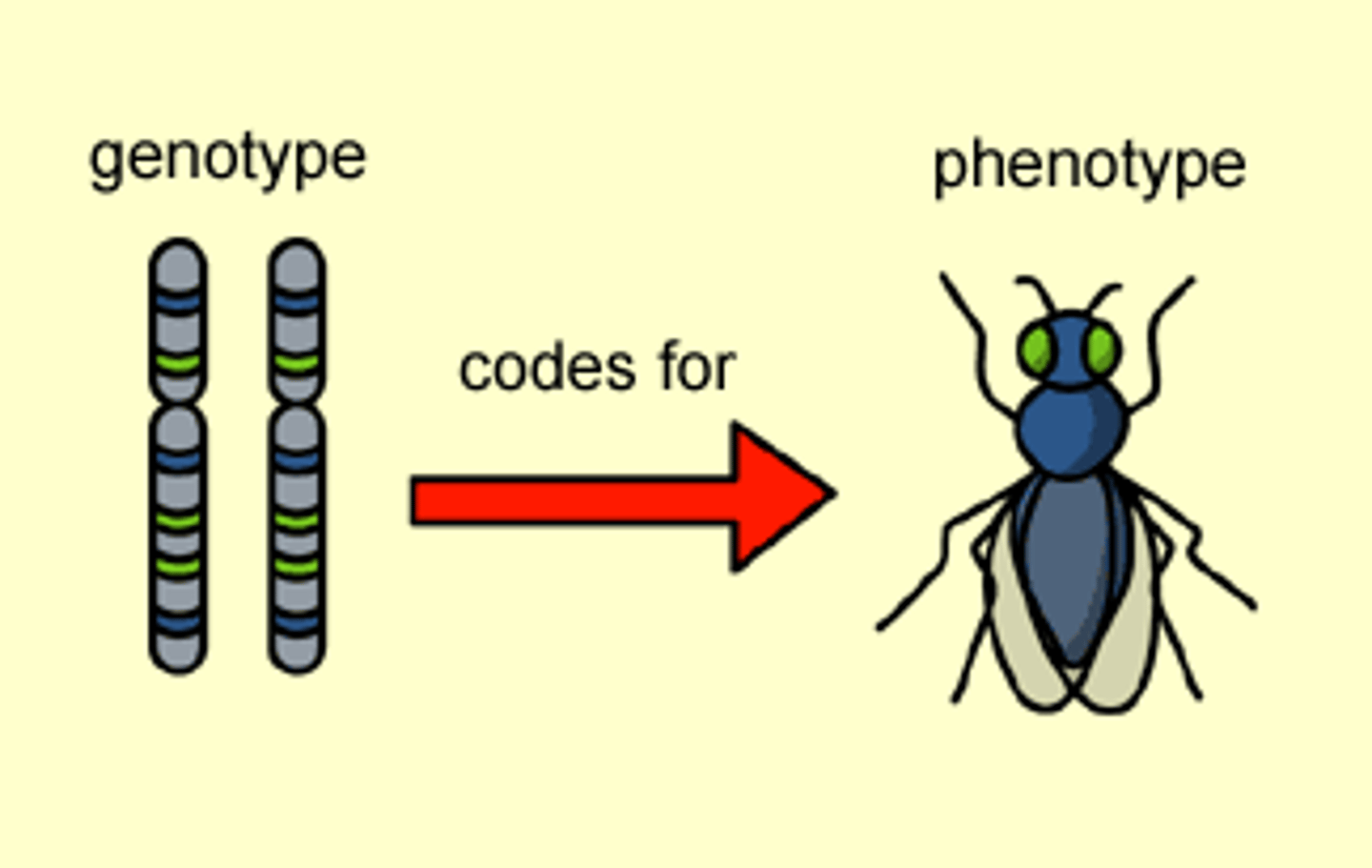
Phenotype
The physical manifestations and expression of a person's genes
Birth defect
A structural abnormality that is present at birth
Congenital disorder
A functional or metabolic abnormality that is present at birth
What are some genetic factors that can cause congenital disorders?
Single-gene or polygenetic mutations, multifactorial inheritance, or chromosomal aberrations
What are environmental factors that can cause congenital disorders?
Disease, infections, or drugs taken during pregnancy
What are intrauterine factors that can cause congenital disorders?
Incorrect positioning during pregnancy or birth can cause congenital disorders
Causes of inherited disorders
1) Single gene expression
2) Chromosomal defect
3) Polygenic expression
Single-gene disorders
Genetic disorders caused by a single gene or mutation
Example: Sickle cell anemia

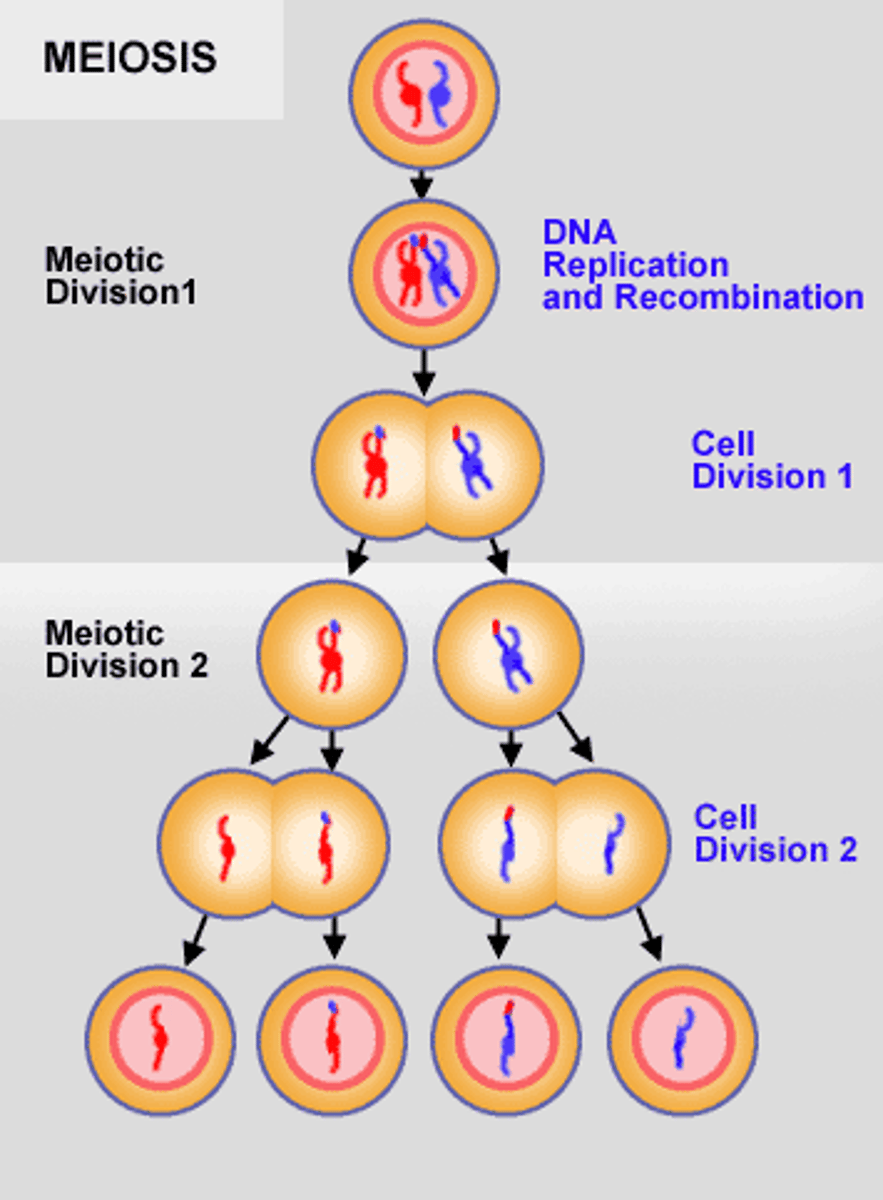
What are chromosomal aberrations?
A mutation during meiosis that changes the number or structure of chromosomes
Multifactorial disorders
Congenital conditions caused by multiple genetic mutations and environmental exposures
Example: Type 2 diabetes
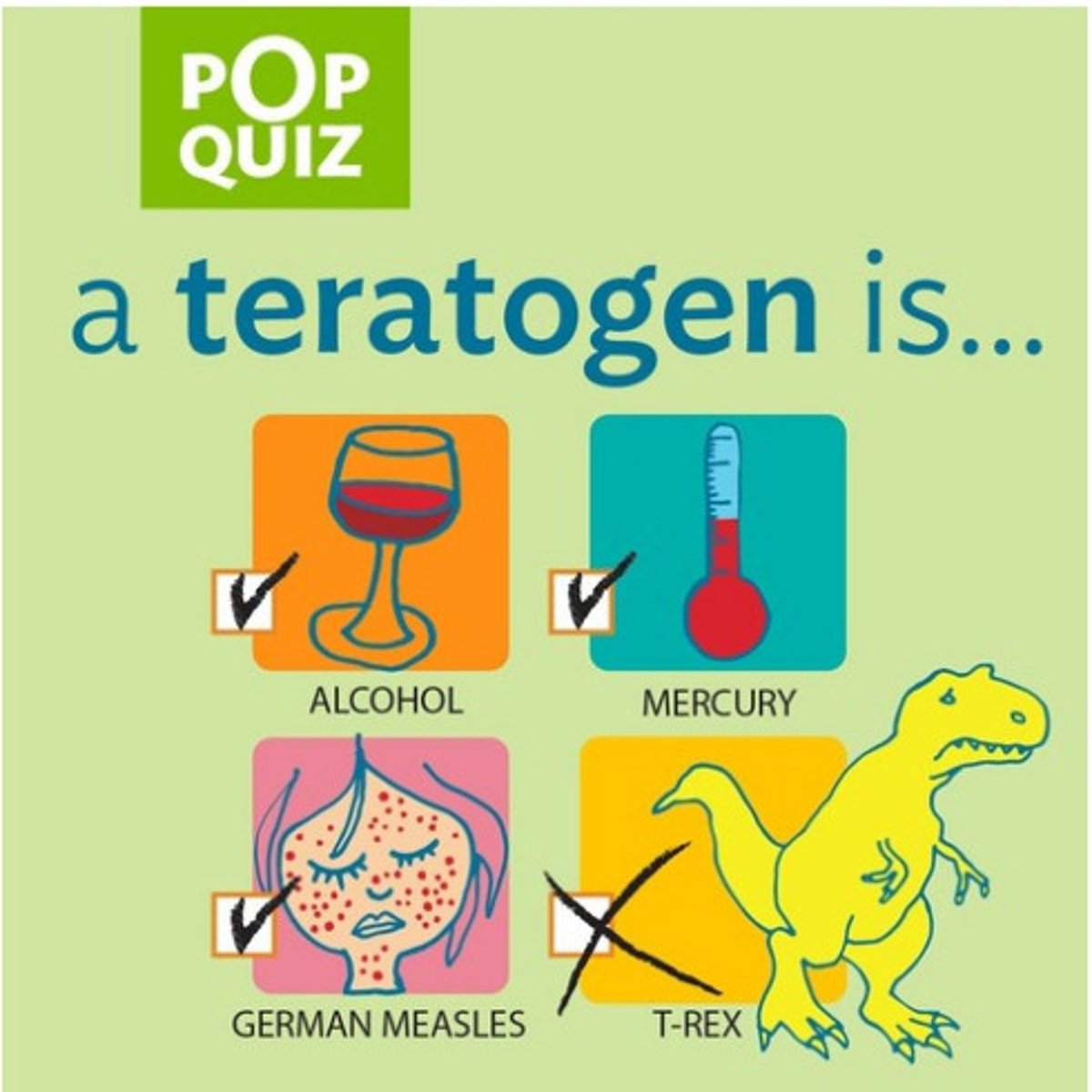
Teratogenic agents
Any drug, virus, infection, or substance that can cause damage during fetal development
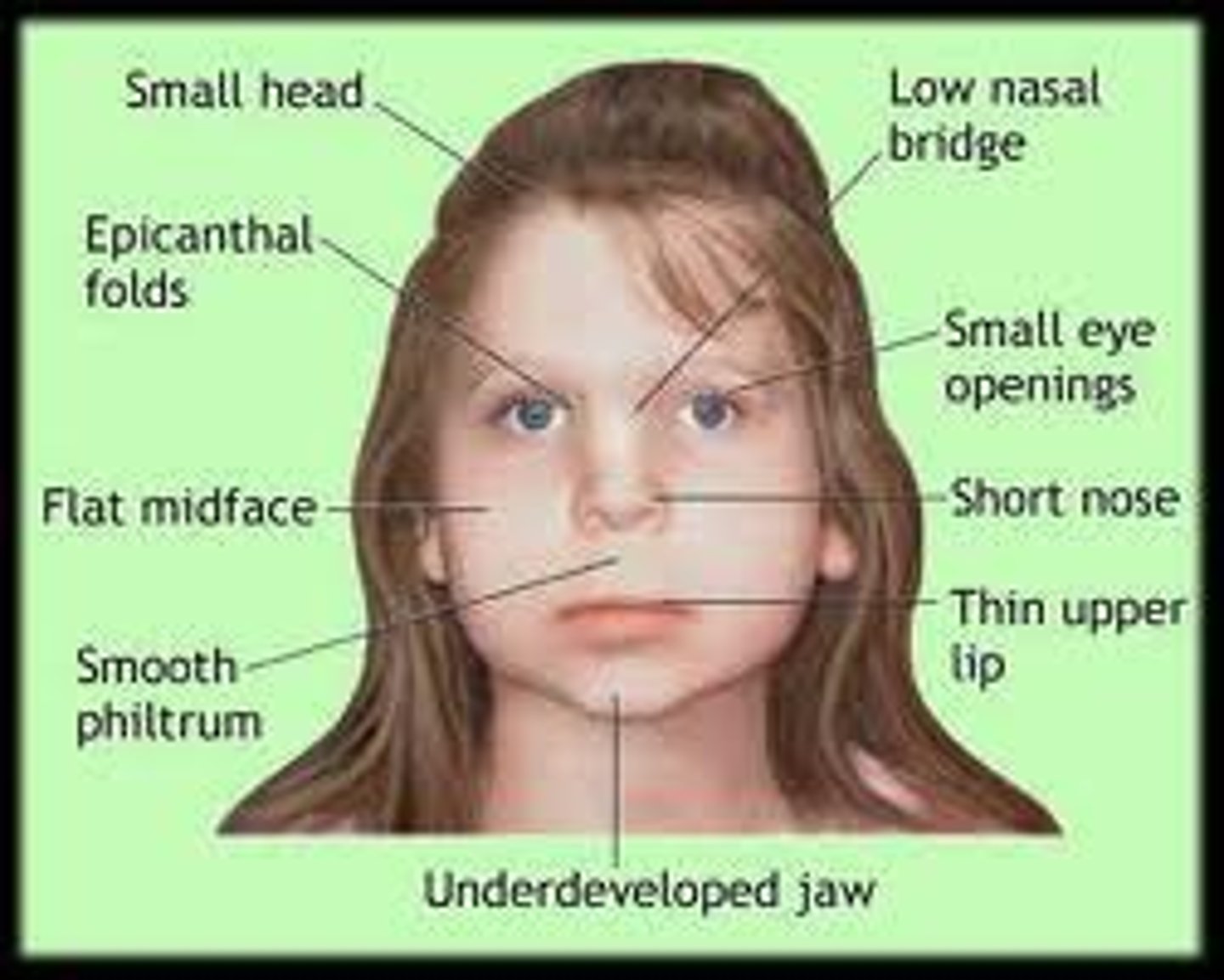
Fetal alcohol syndrome
What: physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking
S&S: Low birth weight, intellectual impairment, behavioral problems, CNS abnormalities, skull/brain deformities
How many single-gene disorders are known?
Over 6,000
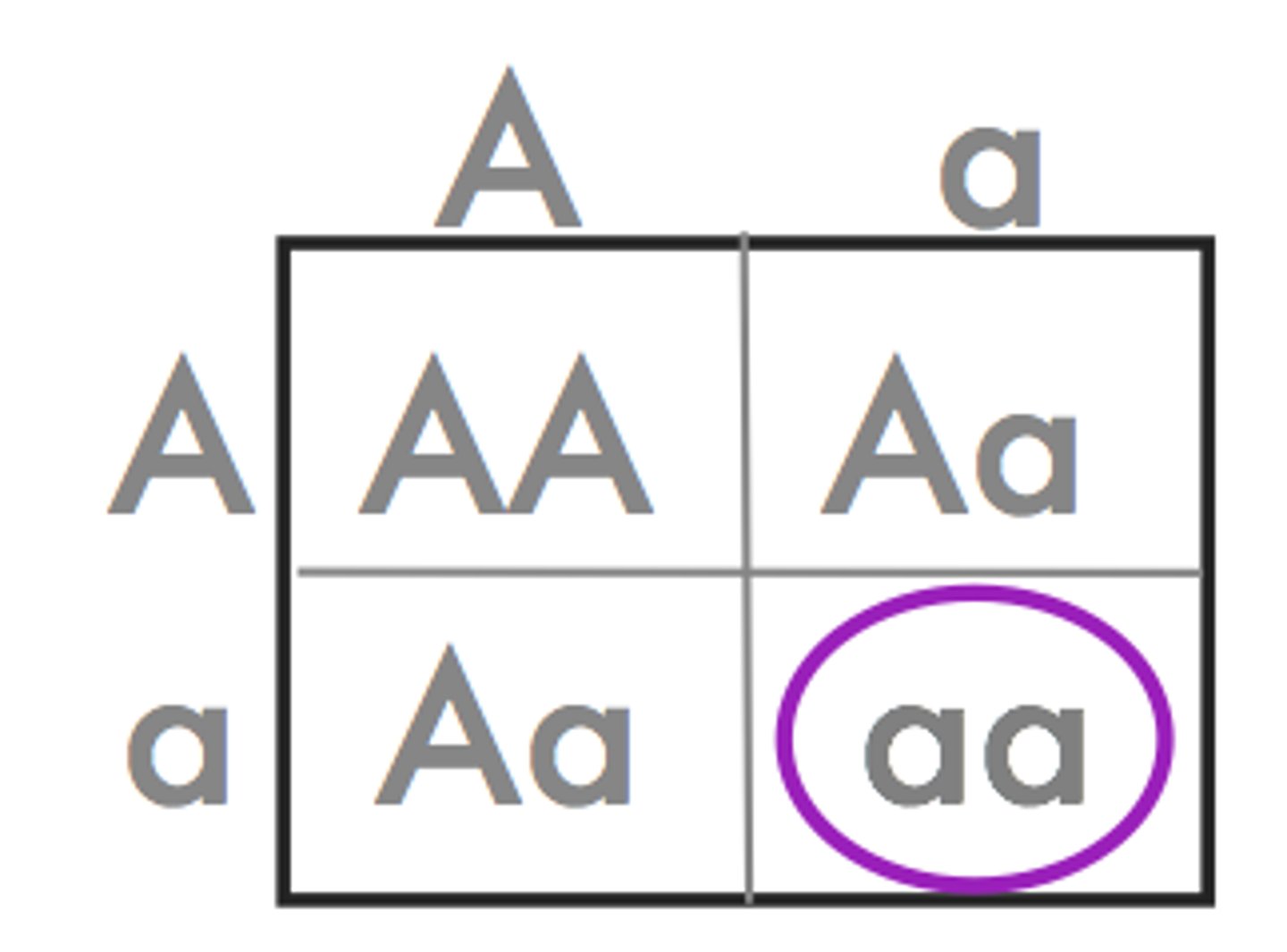
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
Caused by the presence of 2 recessive alleles on autosomes (homozygous recessive)
Examples: Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia, Tay-Sachs disease
Autosomal Dominant Disorders
Caused by the presence of 1 dominant allele on autosomes (heterozygous dominant)
Example: Huntington Disease, Marfan Syndrome
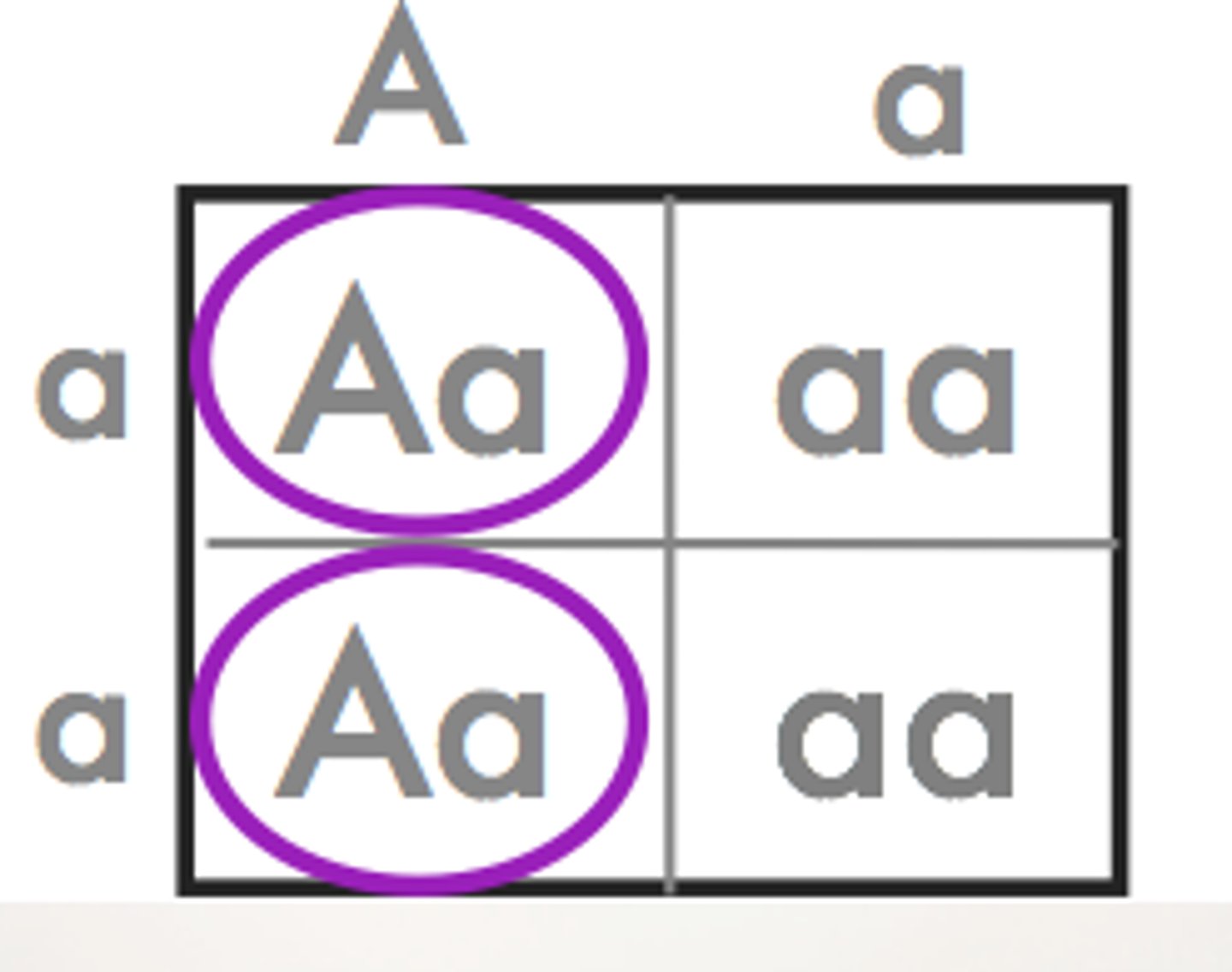
Delayed lethal genotype
When some conditions become evident later in life, the allele for the disorder may have already been passed on to the children
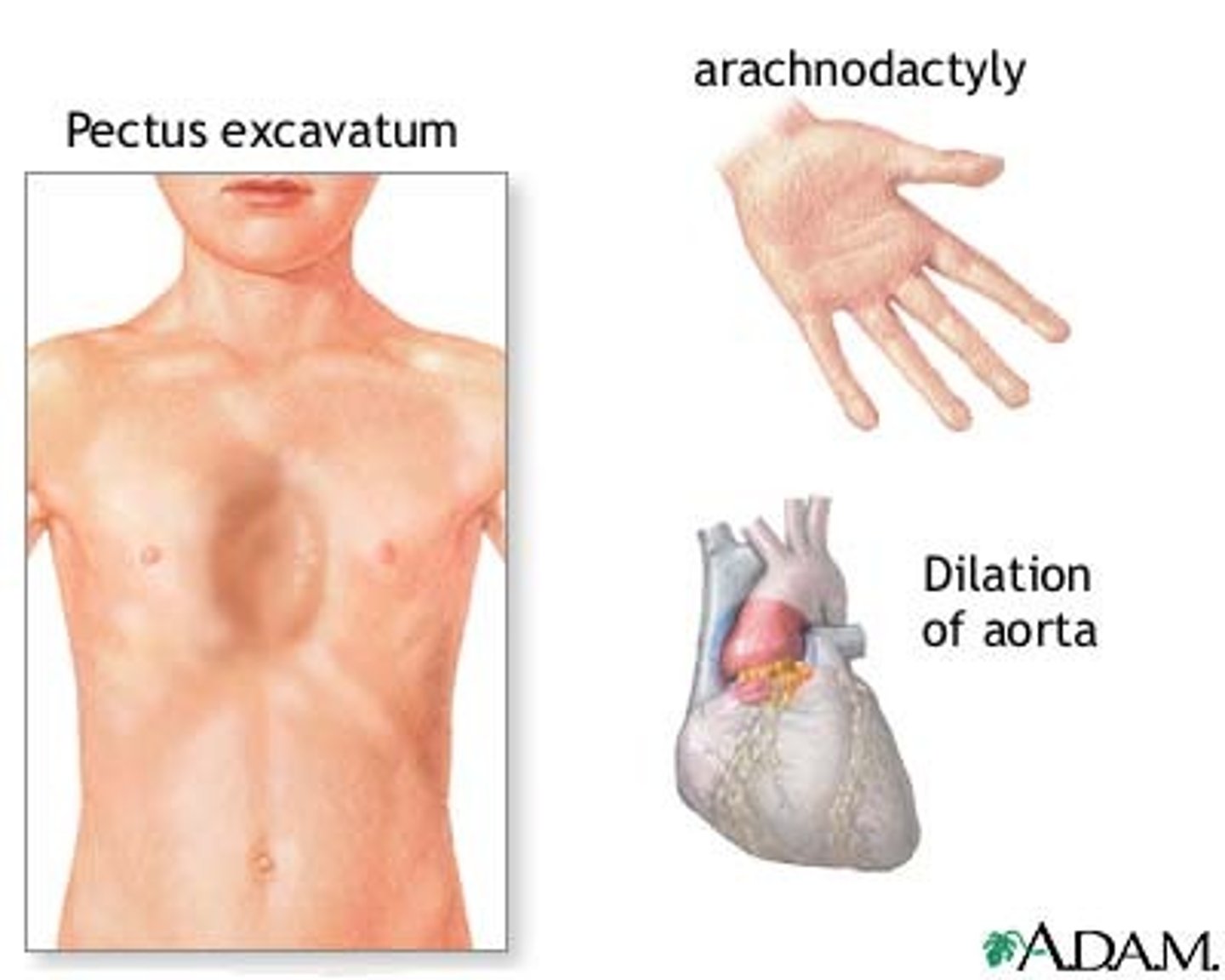
Marfan Syndrome
What: An autosomal dominant disorder in which a gene mutation causes abnormal fibrillin 1 protein --> causes connective tissue malfunctions
S&S: Long and thin fingers and limbs, spinal deformities
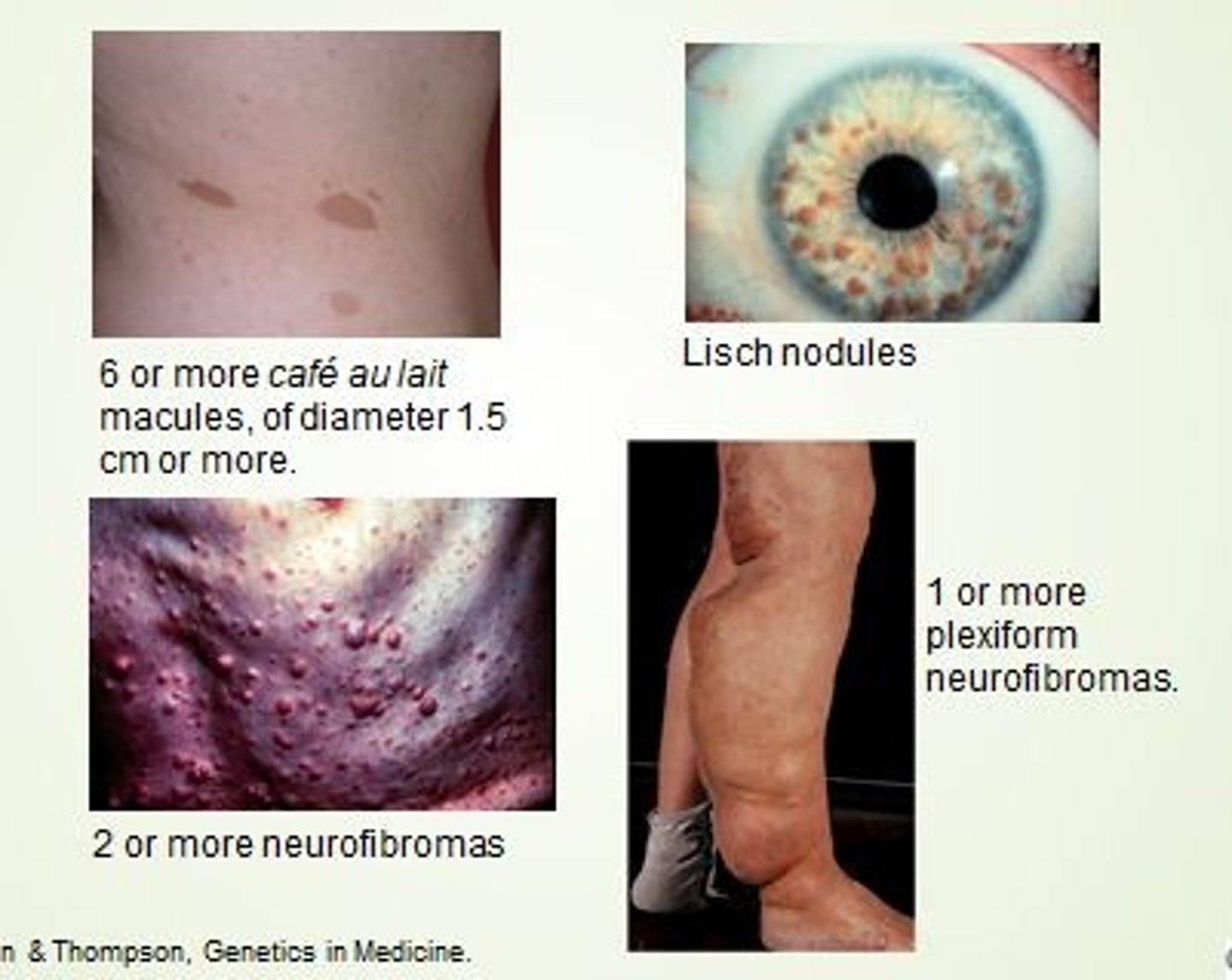
Neurofibromatosis
What: An autosomal dominant disorder --> causes by tumor of Schwann cells
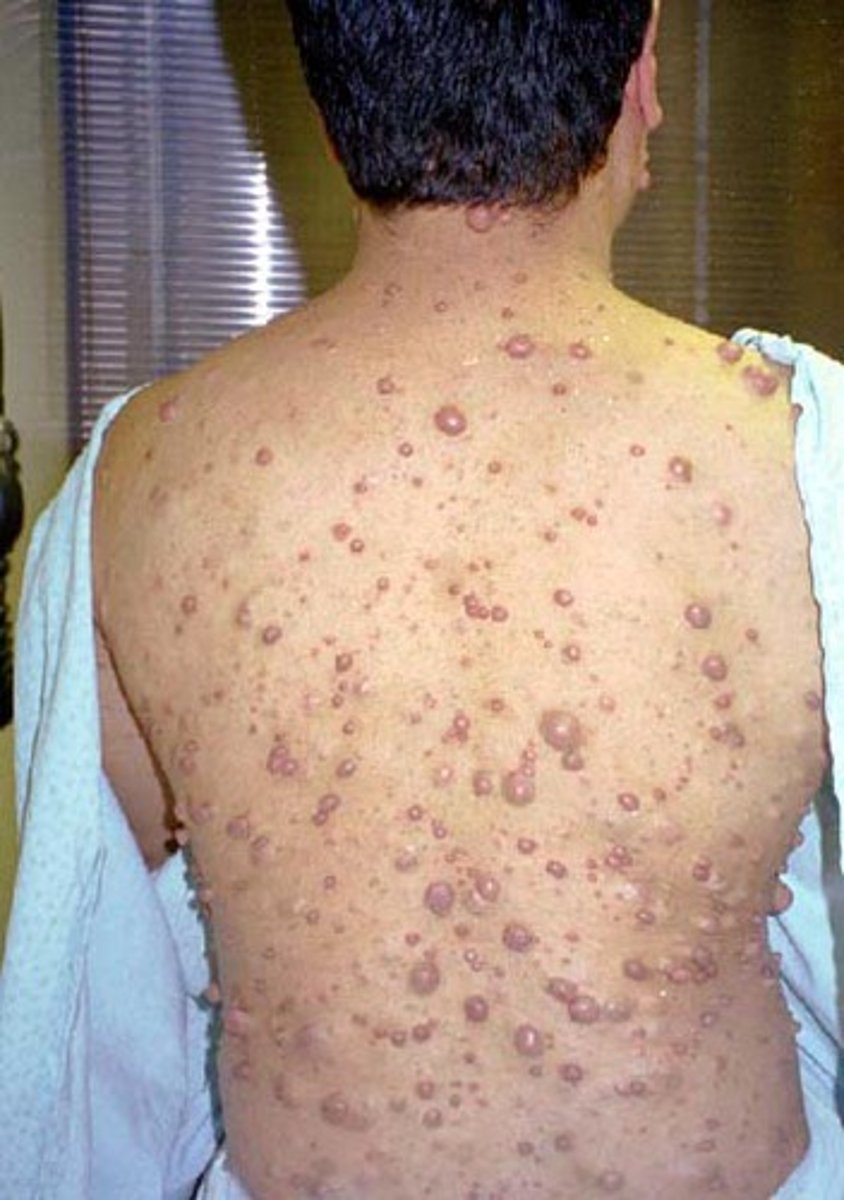
NF1
Develops in children --> causes tumors under the skin and skeletal deformities
NF2
Develops after age 15 --> Causes tumor of the cochlear nerve
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that actually display the phenotype
X-linked Dominant Disorders
Caused by the presence of 1 dominant allele located on the X chromosome (heterozygous dominant)
Example: Fragile X syndrome
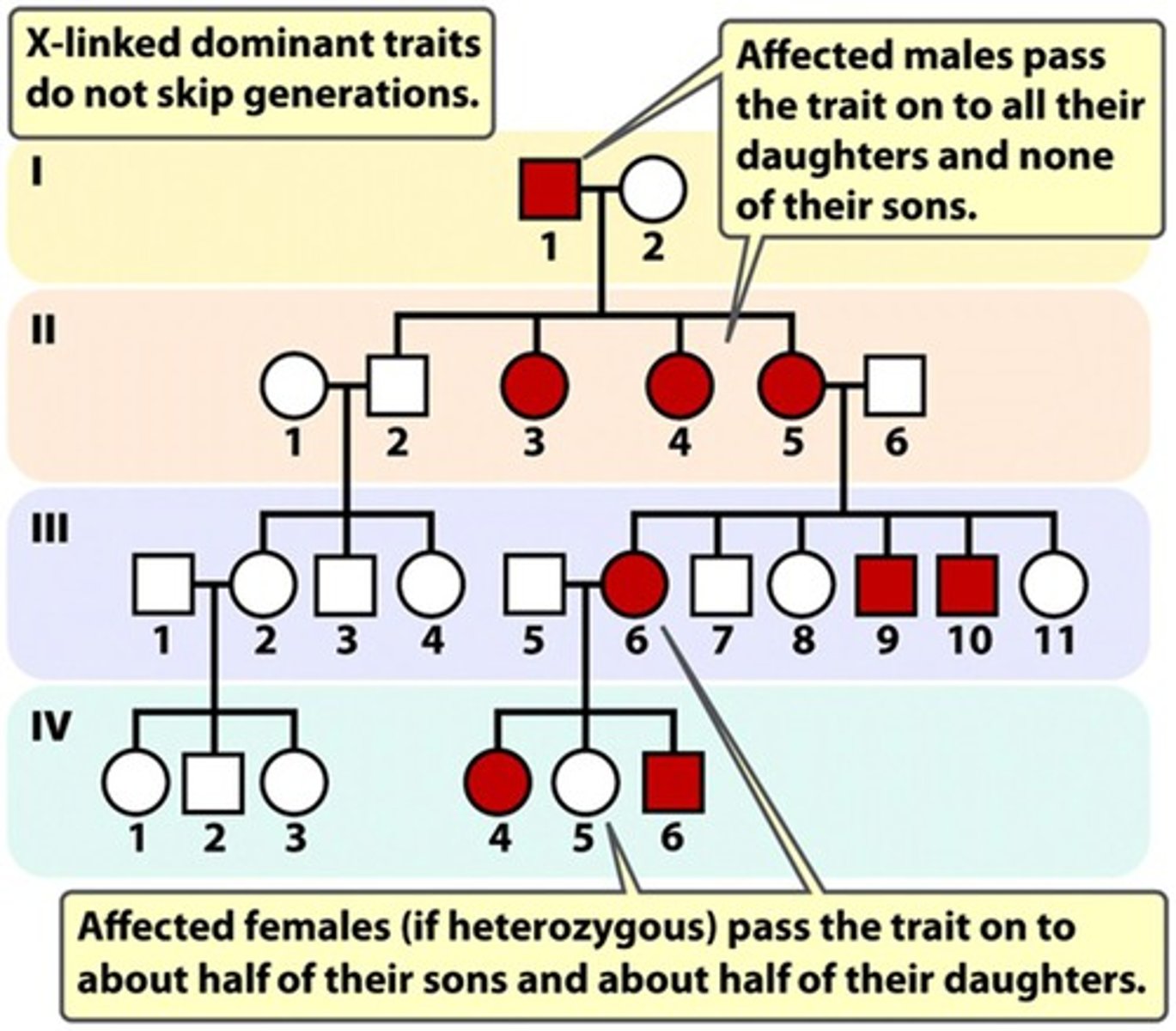
Fragile X Syndrome
An x-linked dominant disorder --> caused by mutation to a gene on the X chromosome --> causes moderate mental cognitive impairment

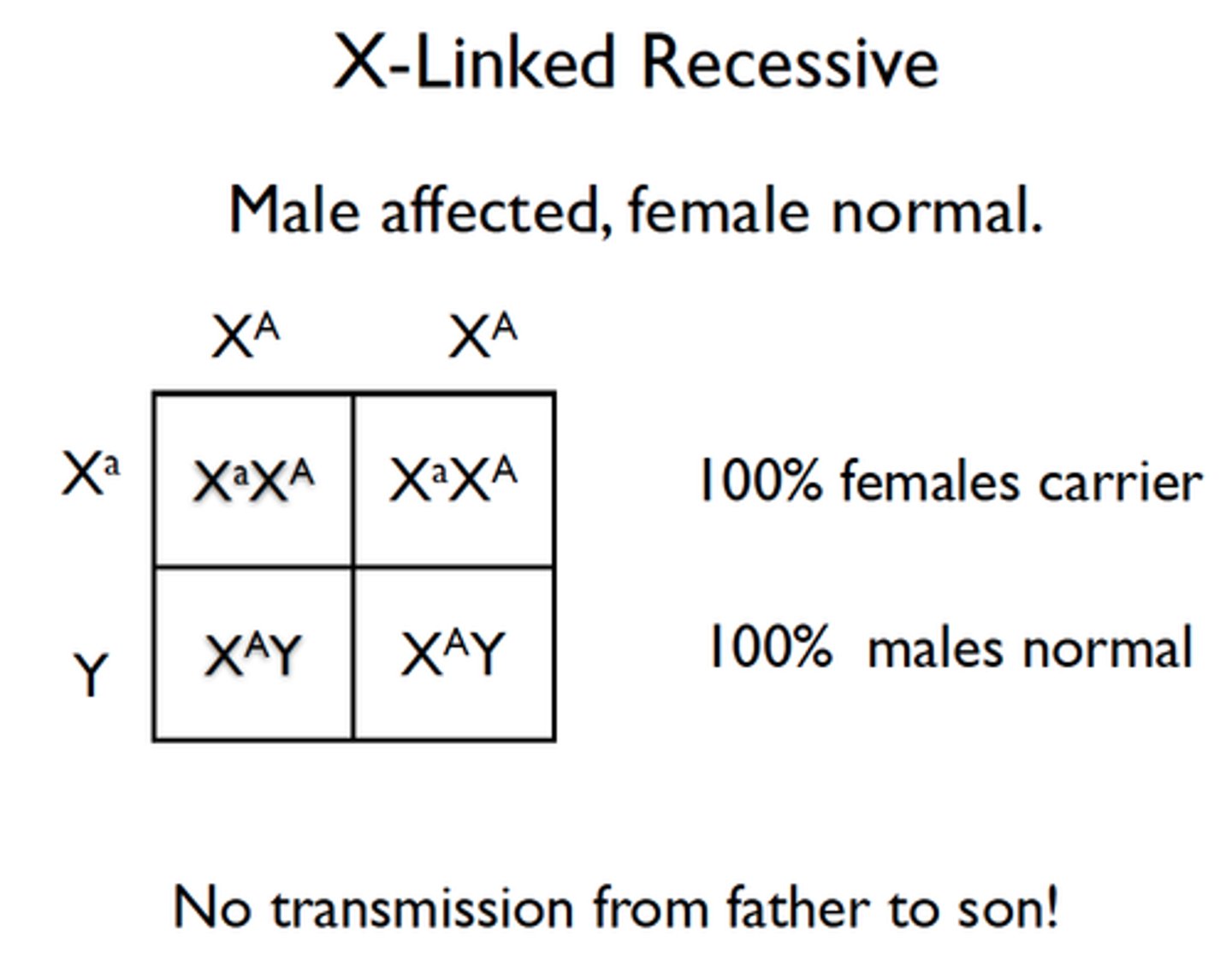
X-linked Recessive Disorders
Caused by the presence of 1 or 2 recessive allele located on the X chromosome --> heterozygous men and homozygous women are affected
Examples: Color blindness, muscular dystrophy, hemophilia
Aneuploidy
An abnormal number of chromosomes
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome (survivable)
Monosomy
Missing a chromosome (usually lethal)
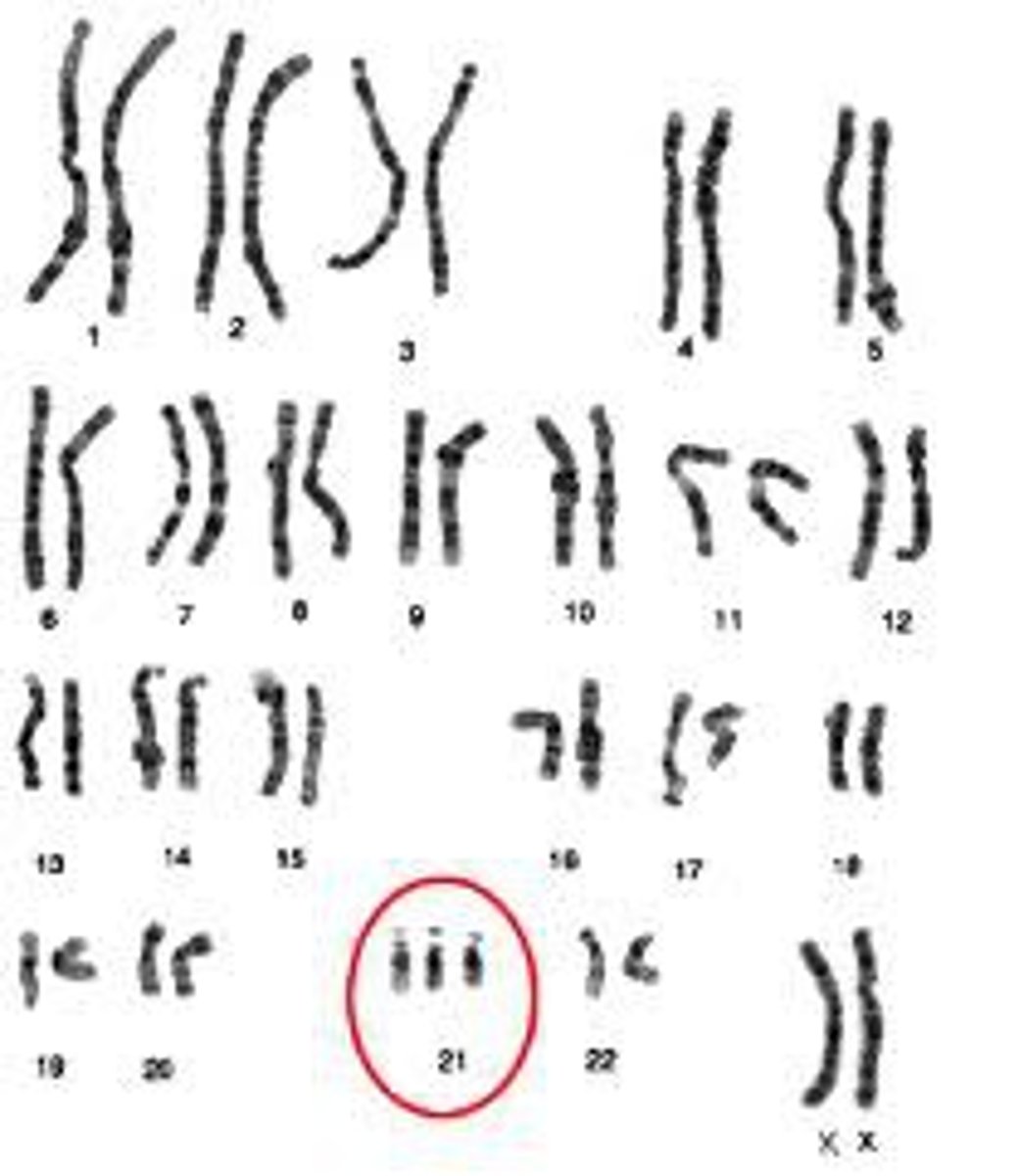
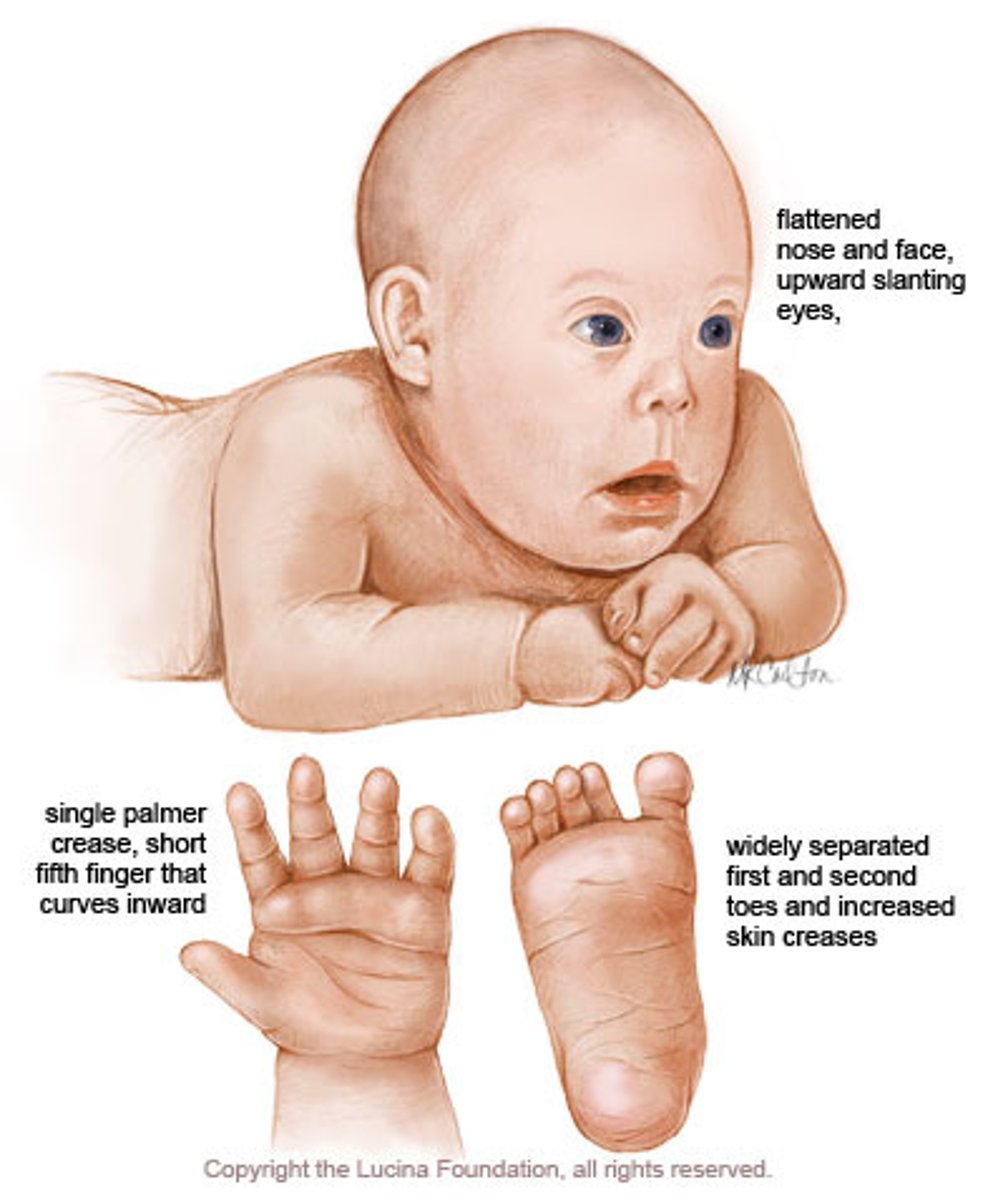
Trisomy 21
AKA Down Syndrome --> A condition of intellectual and physical disability caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
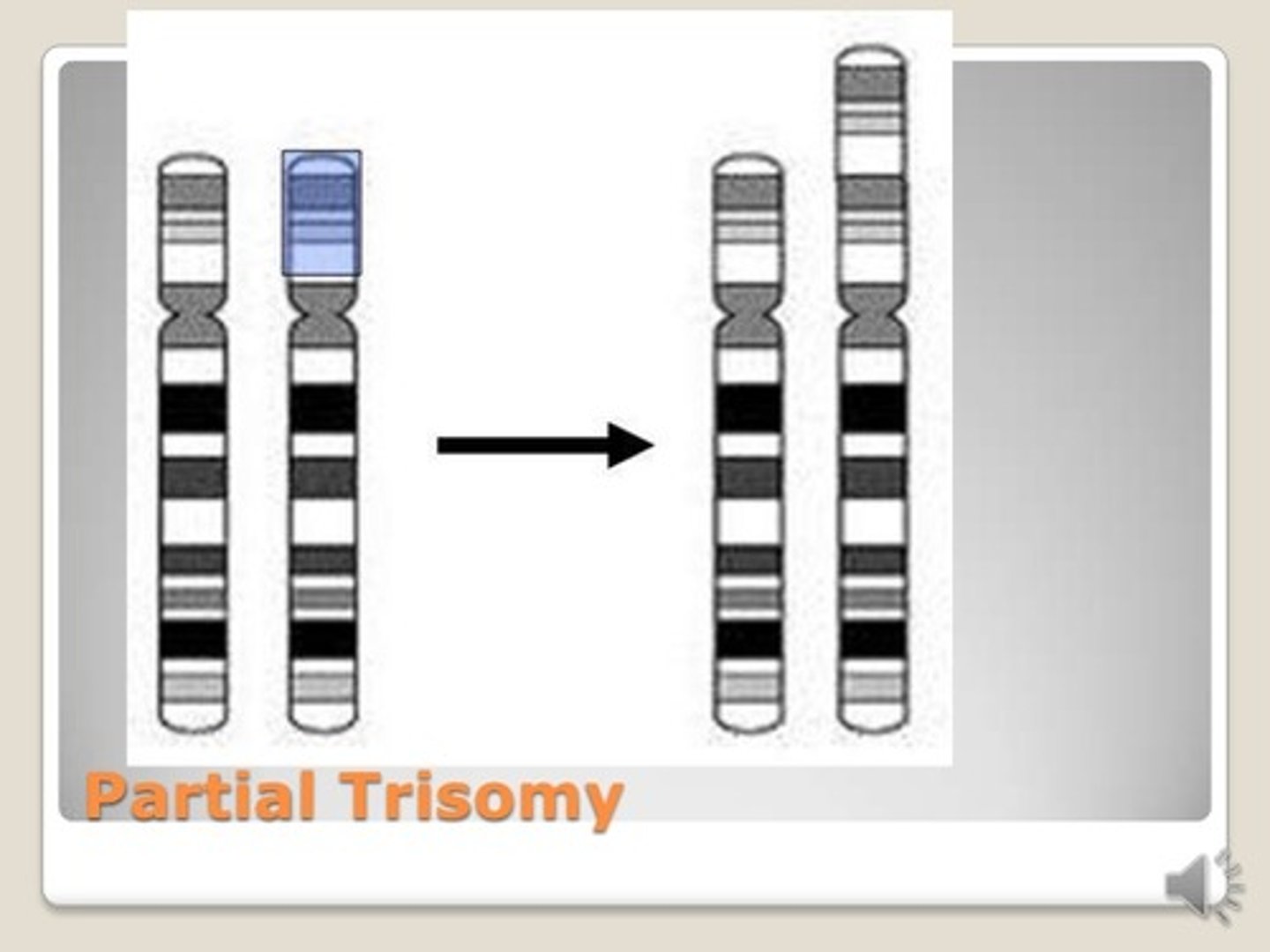
Partial Trisomy
Only an additional small section of a chromosome is present in each cell
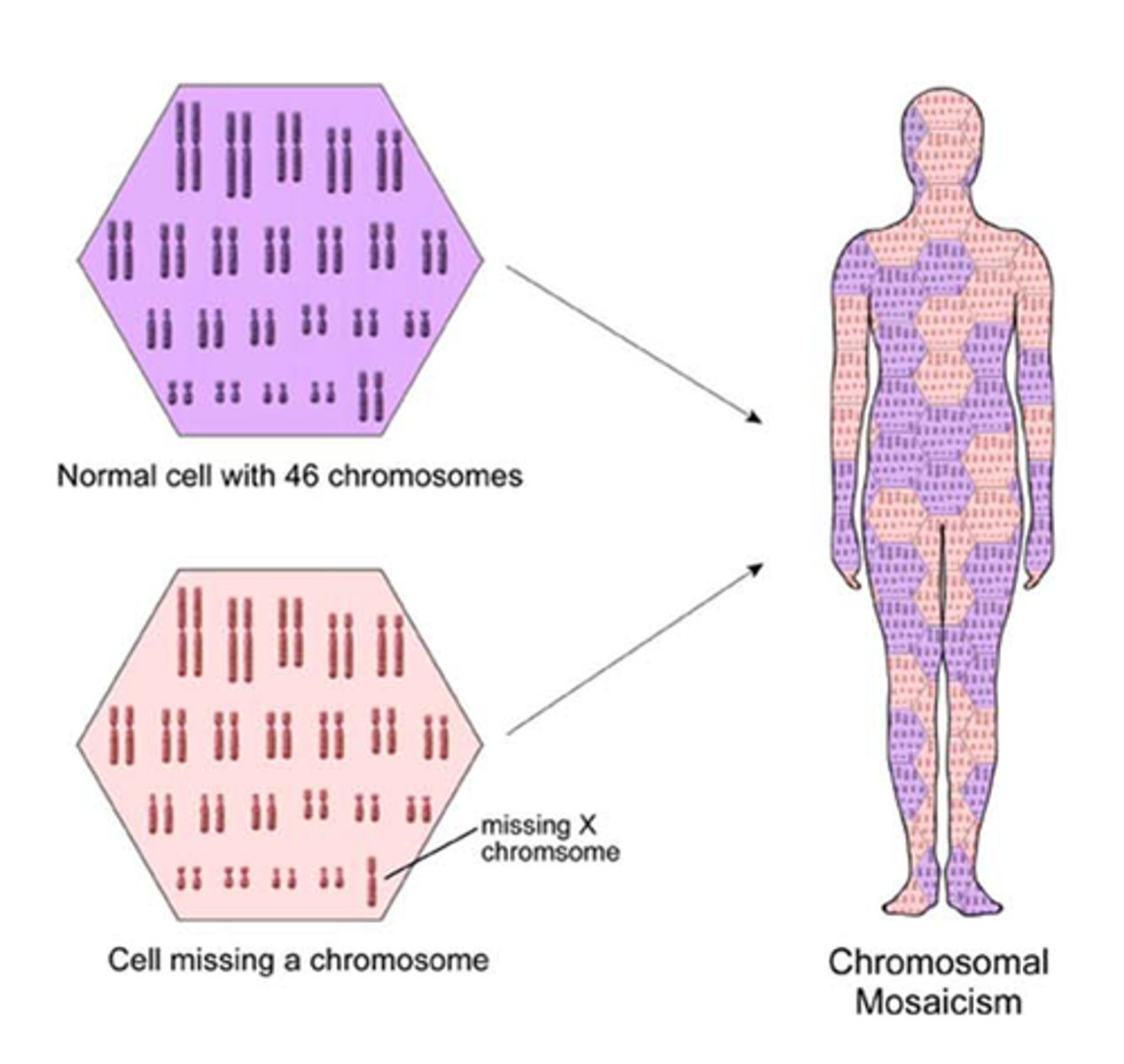
Chromosomal mosaics
Trisomies occurring only in some cells of the body
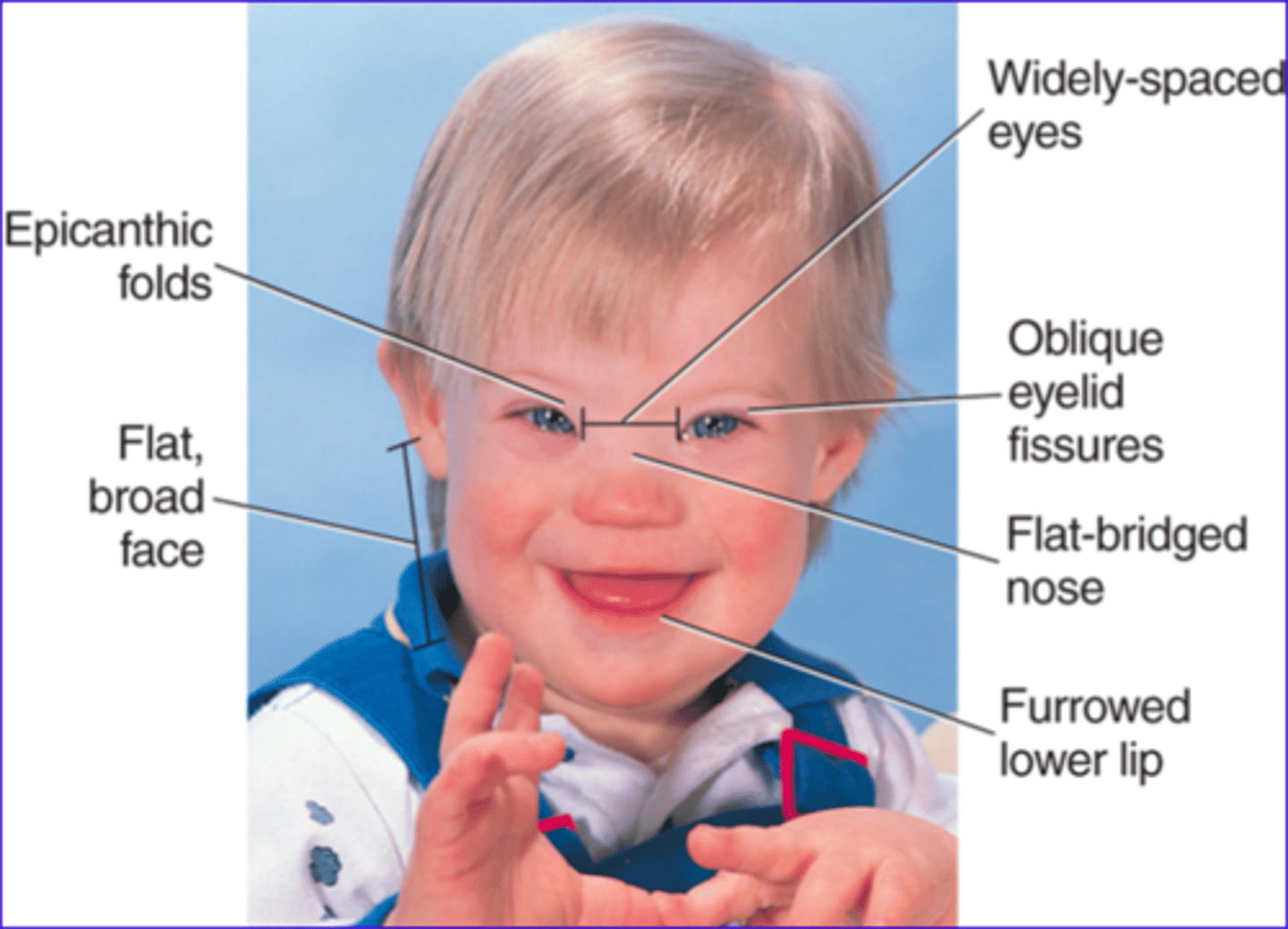
Characteristics of Down Syndrome
Closed set eyes, single line creases on hand, protruding tongue, curved small fingers, high risk for deformed heart, weak muscle tone
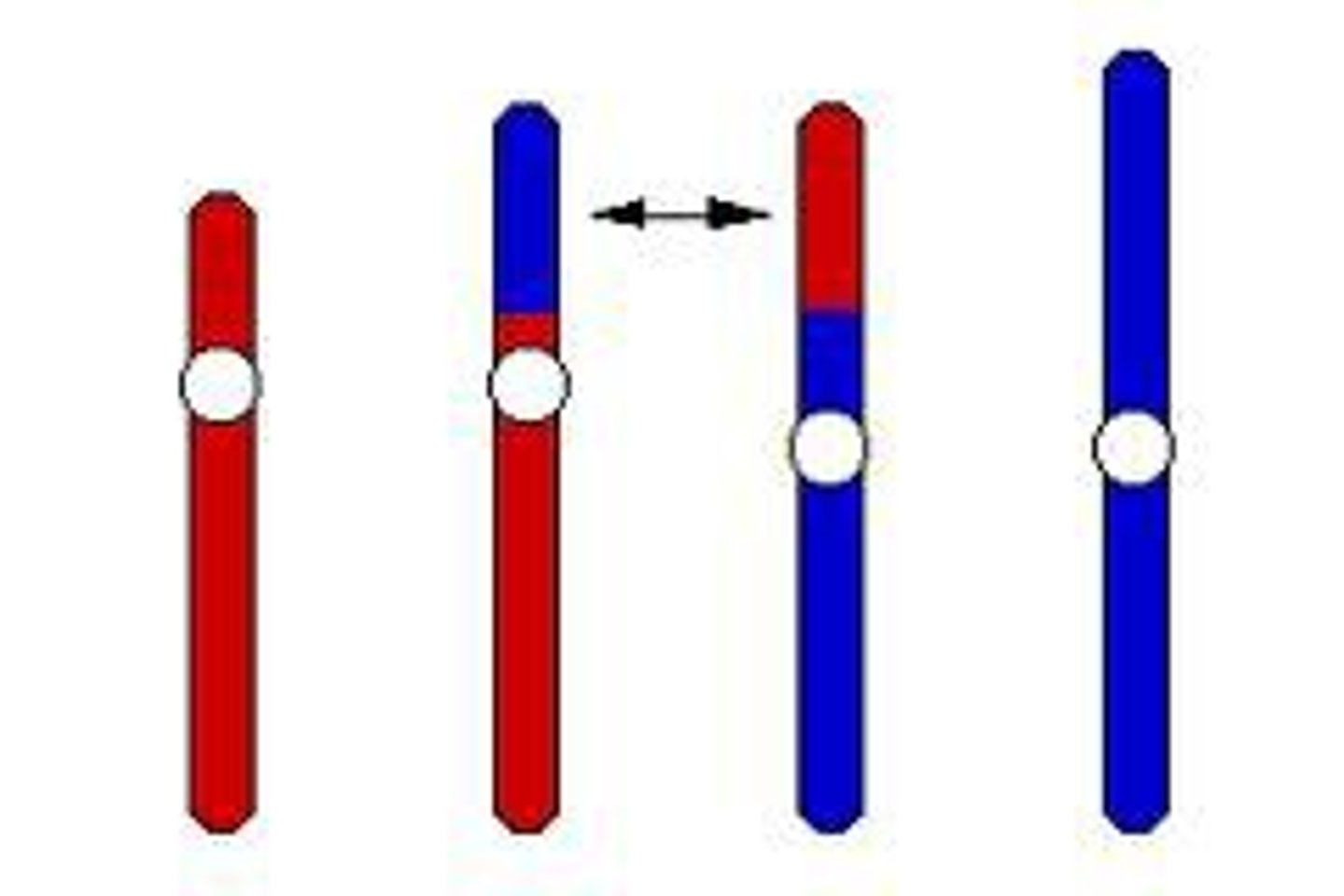
Translocation
An error in meiosis in which a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome
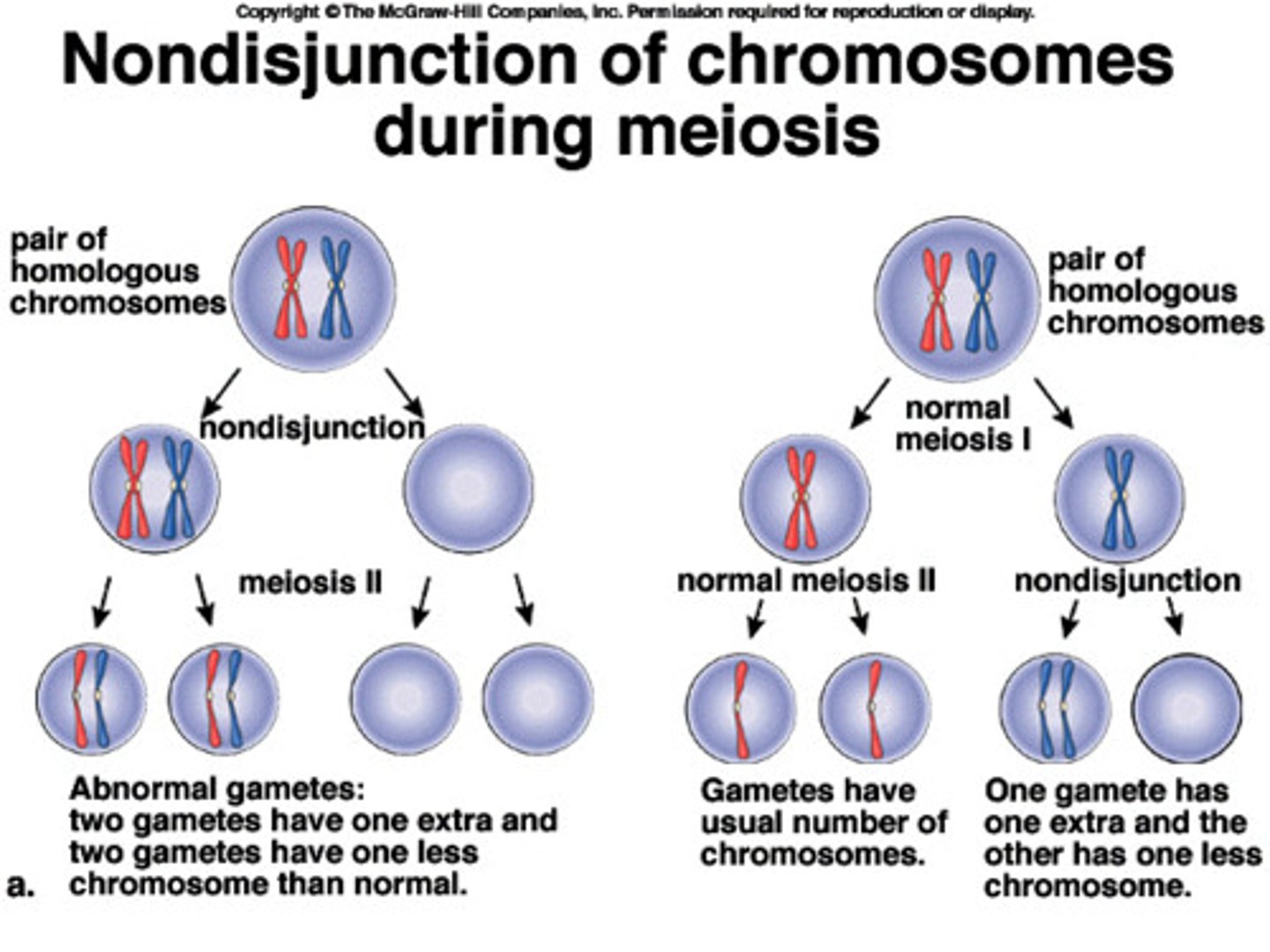
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate
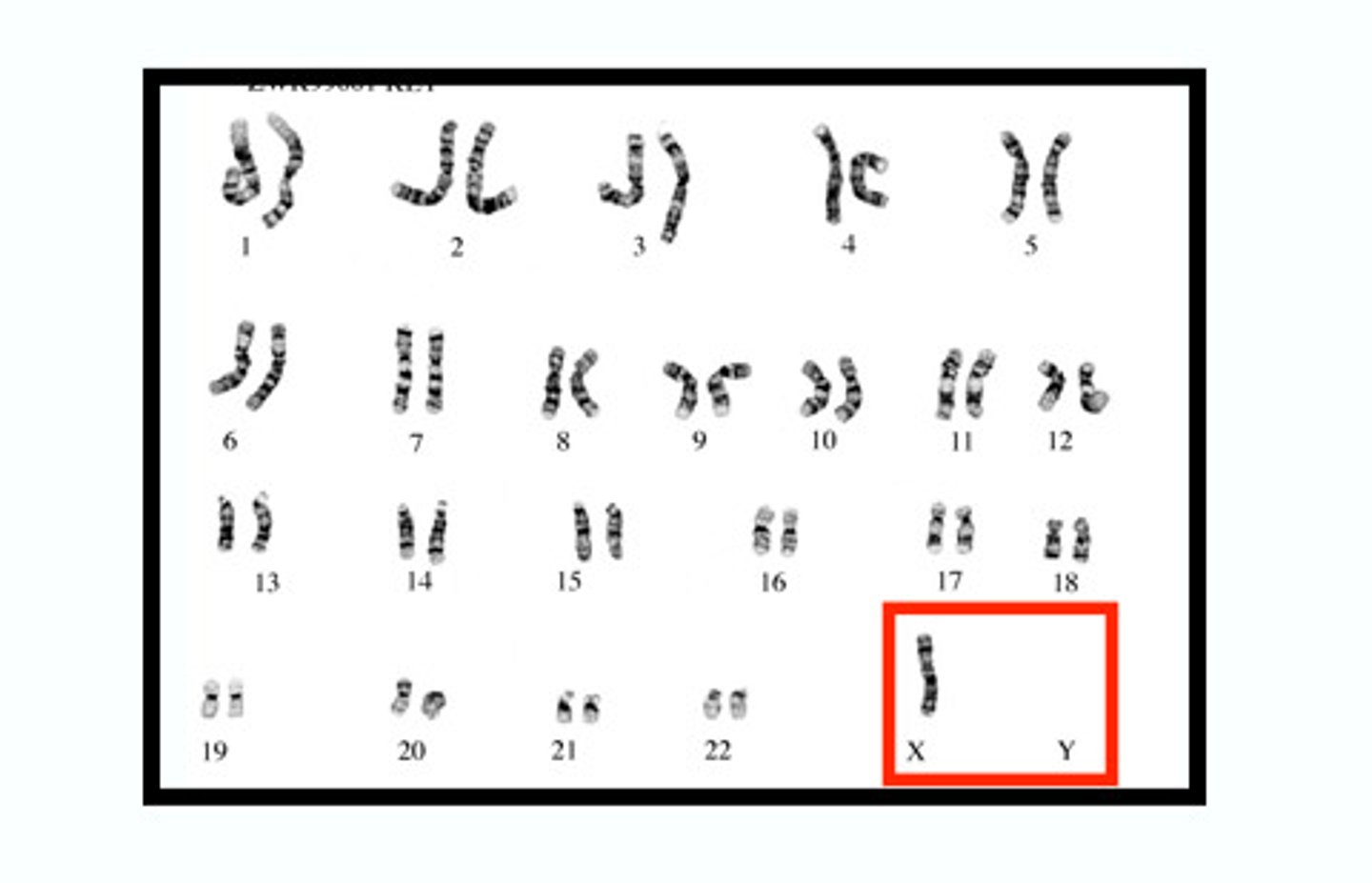
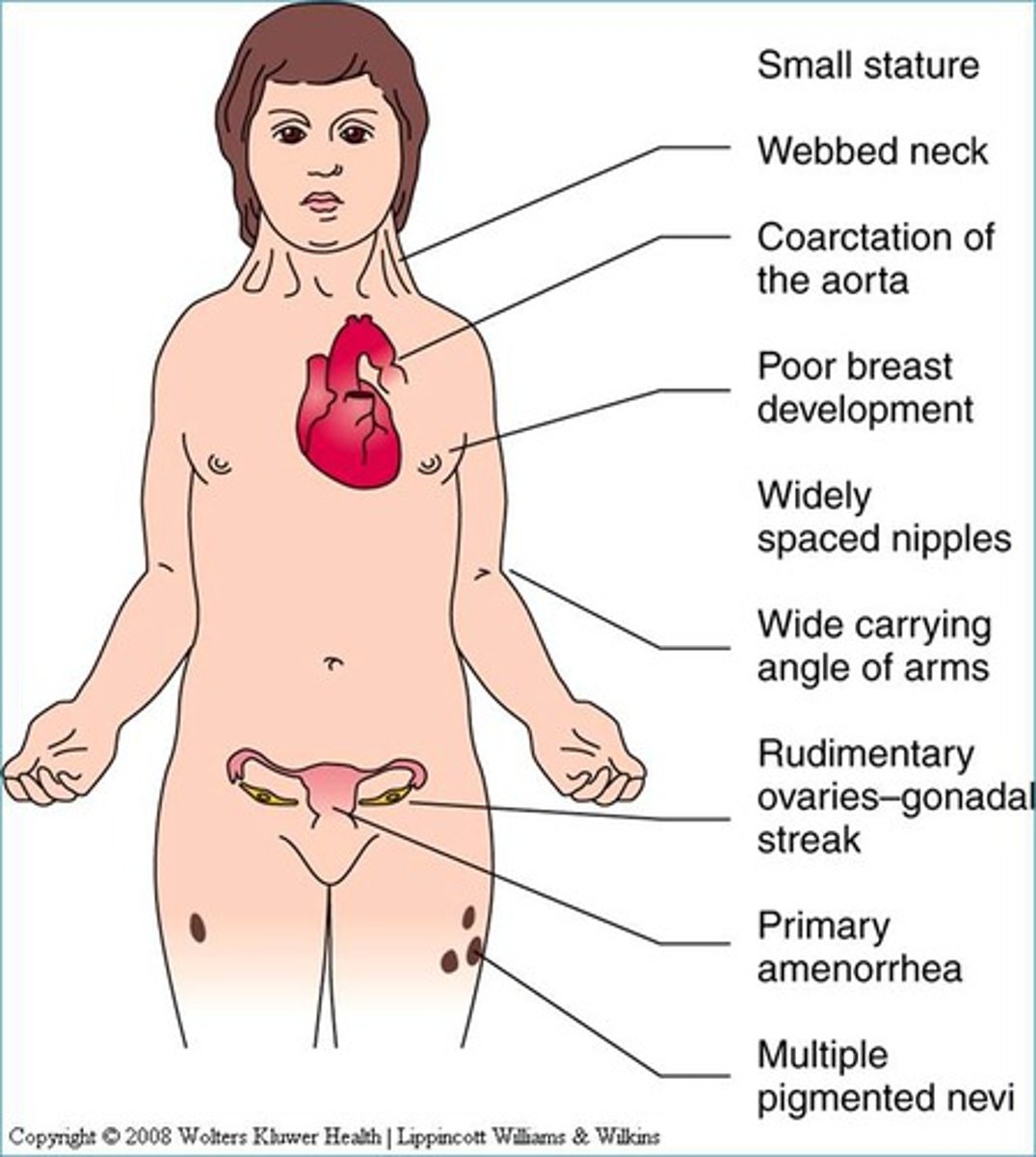
Turner syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in females in which parts or all of an X chromosome is missing
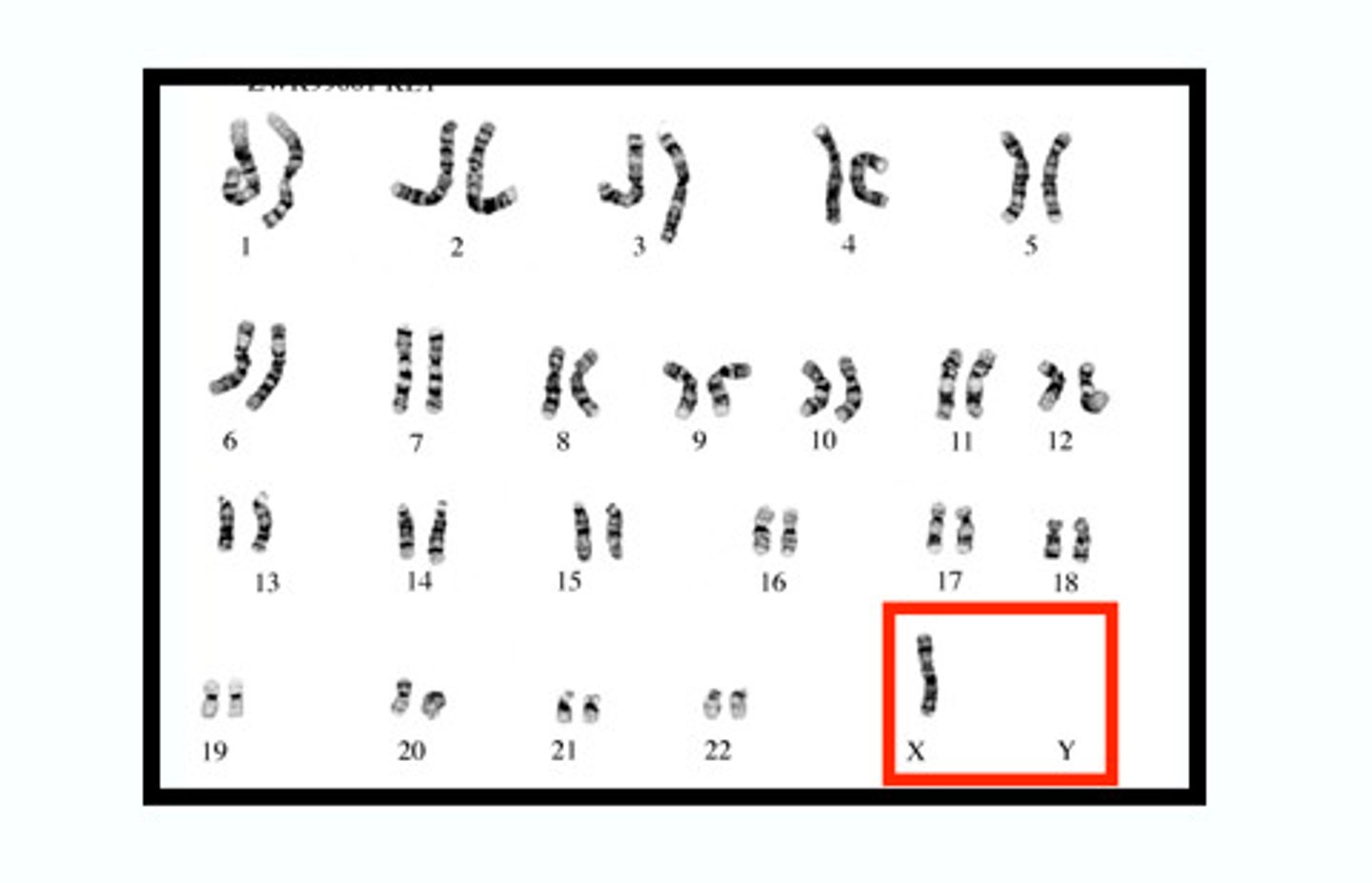
Characteristics of Turner Syndrome
Short stature, webbed neck, underdeveloped ovaries and breasts
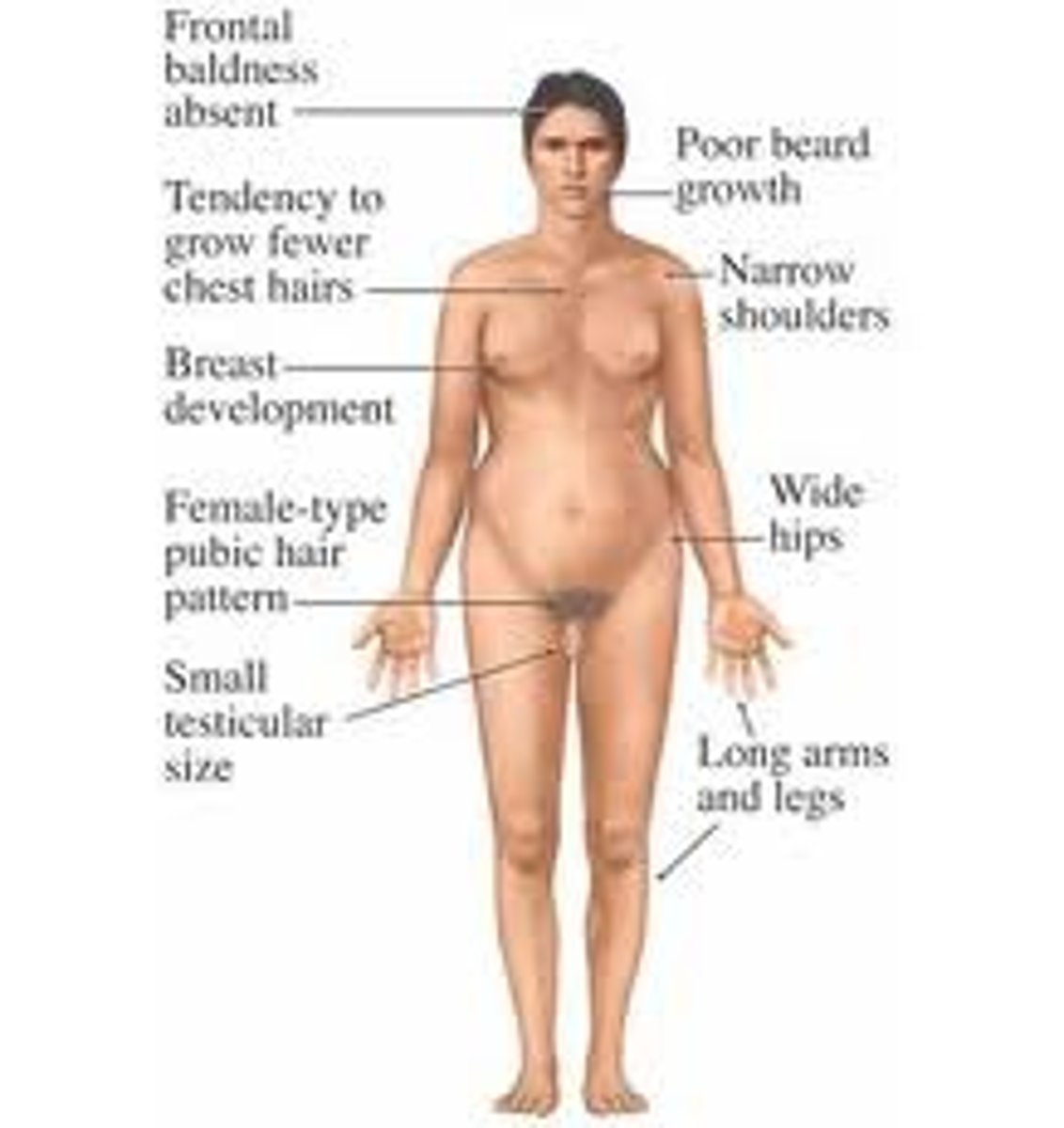
Klinefelter syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in which someone has at least two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome
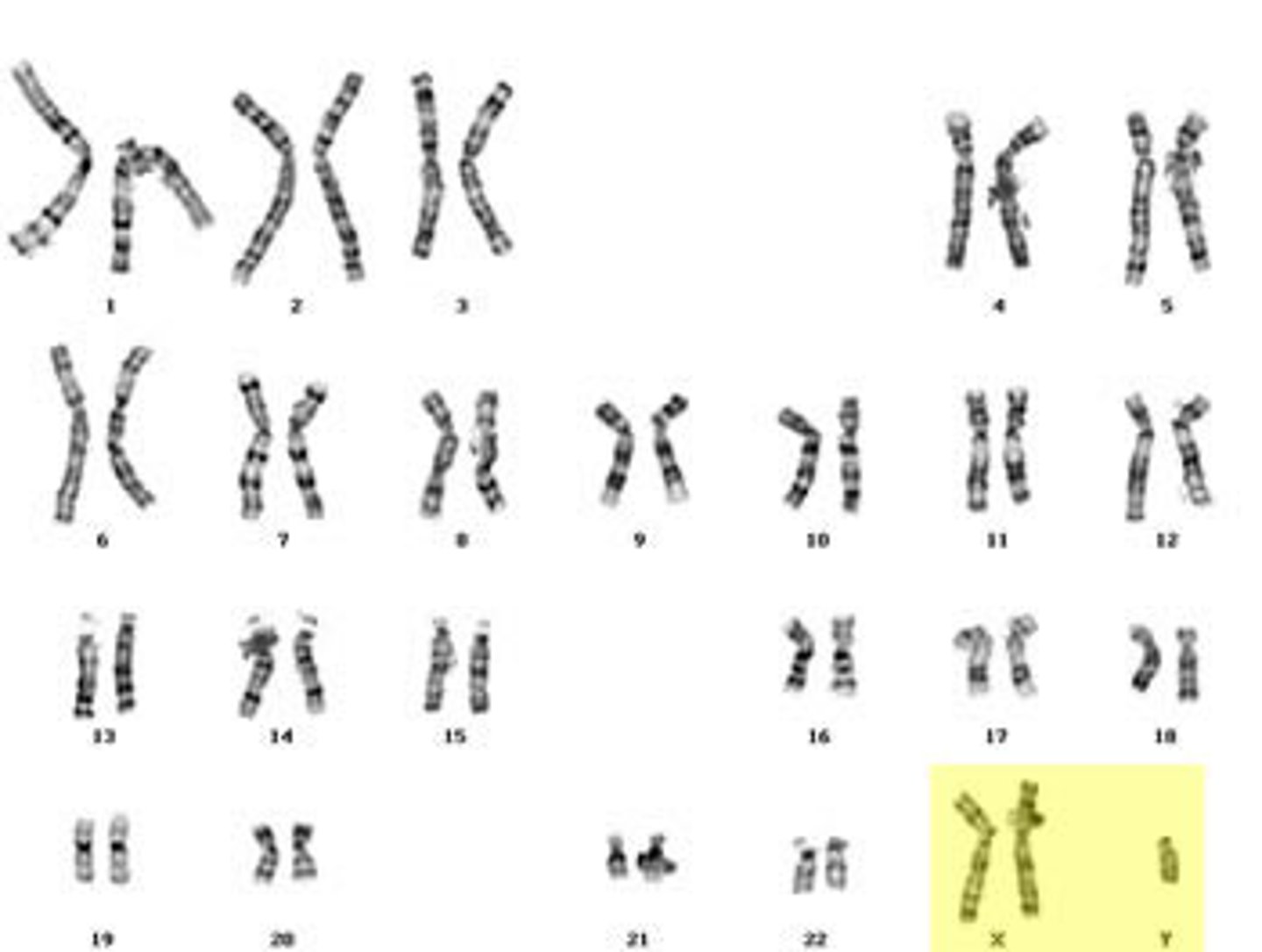
Characteristics of Klinefelter syndrome
Male appearance, female-like breasts, small testes, sparse body hair, long limbs
Mitochondrial DNA
A small amount of DNA that is located in the mitochondria; does not have any repair mechanisms
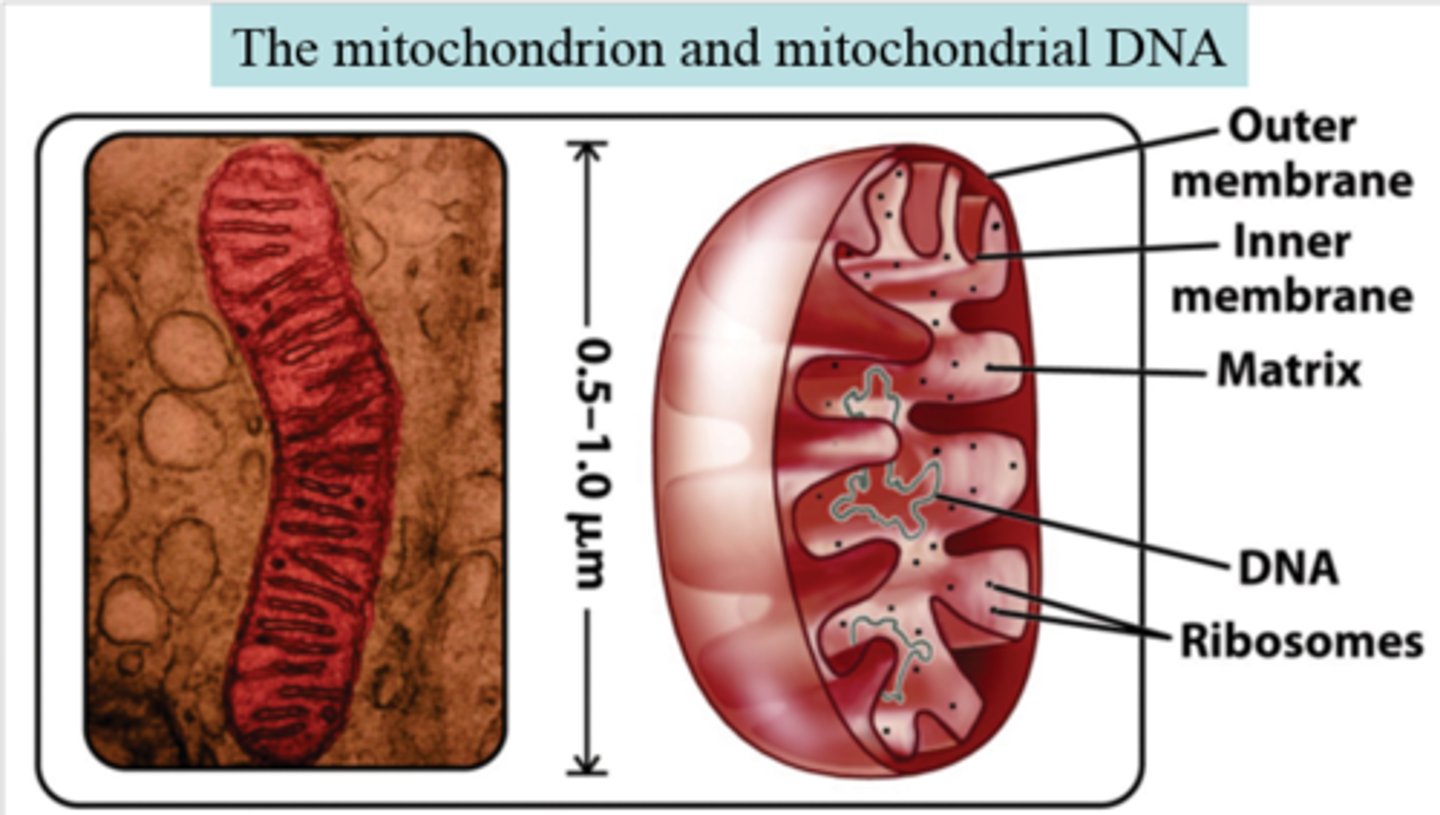
Mitochondrial DNA Disorders
Disorders that occur when the mitochondrial genes are mutated --> cause neuromuscular disorders
S&S: Weakness, poor muscle development, slow growth
Developmental Disorders
Exposure to drugs, chemicals, or radiation during childbearing years can cause developmental delays/issues
Exposure to teratogens during time frame will be the most harmful to the fetus?
Exposure during the first 2 months (organogenesis) will cause the most damage
TORCH
Maternal infections that can cause abnormalities:
Toxoplasmosis
Other
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes
When is diagnostic testing available to mothers?
Mothers/babies can get tested before conception, during the first trimester, and after birth
Who should get tested for congenital diseases?
Those with a family history, a previous child with disability, older pregnant women
Alpha-fetoprotein testing
Determines the level of this fetal protein in the pregnant woman's serum, high levels indicate neural tube defect
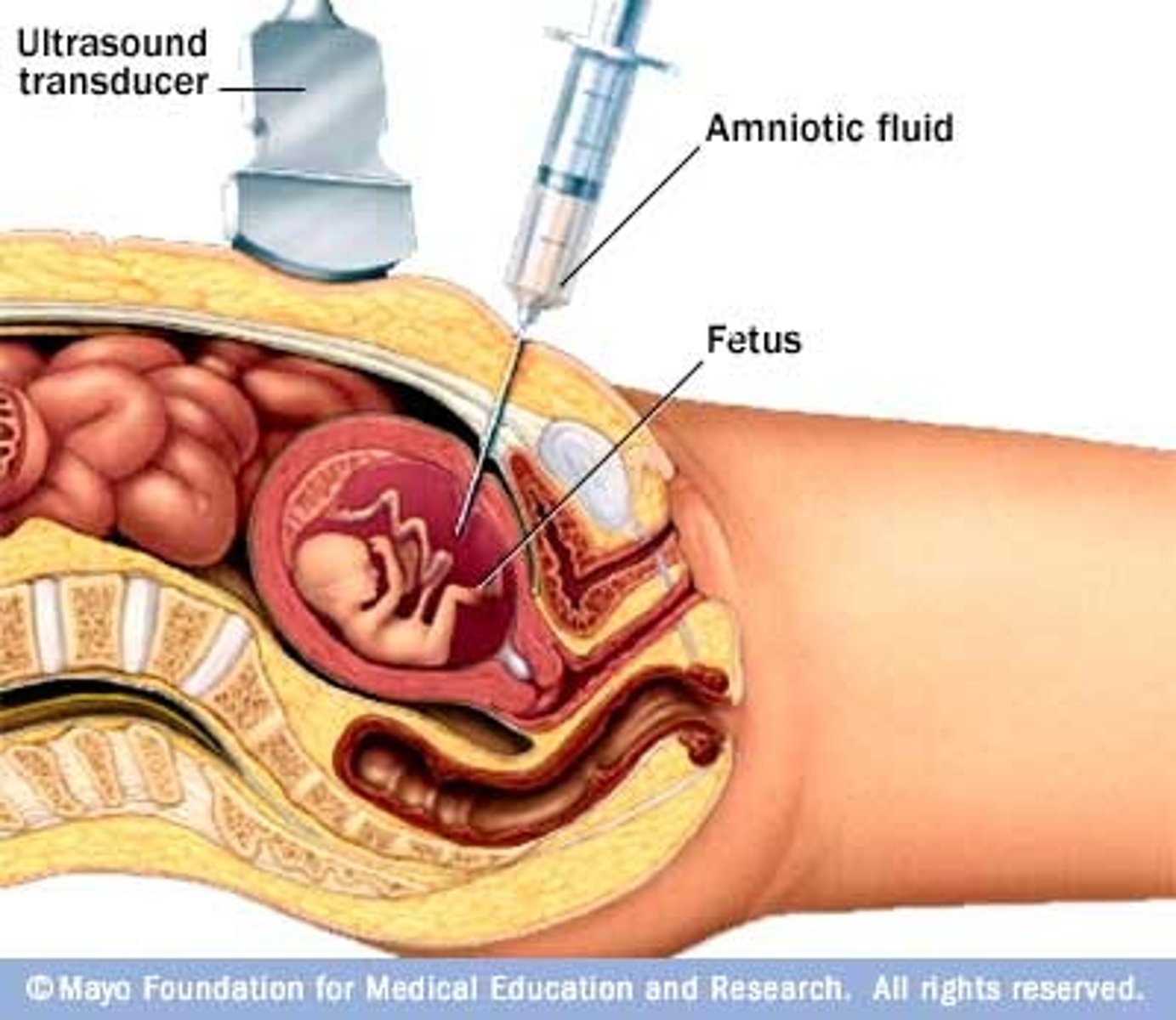
Amniocentesis
An invasive procedure used to diagnose congenital disorders --> a needle punctures the amniotic sac to collect fluid for analysis
Chorionic villi assay
An invasive procedure used to diagnose congenital disorders --> a needle punctures the placenta to collect a tissue sample for analysis
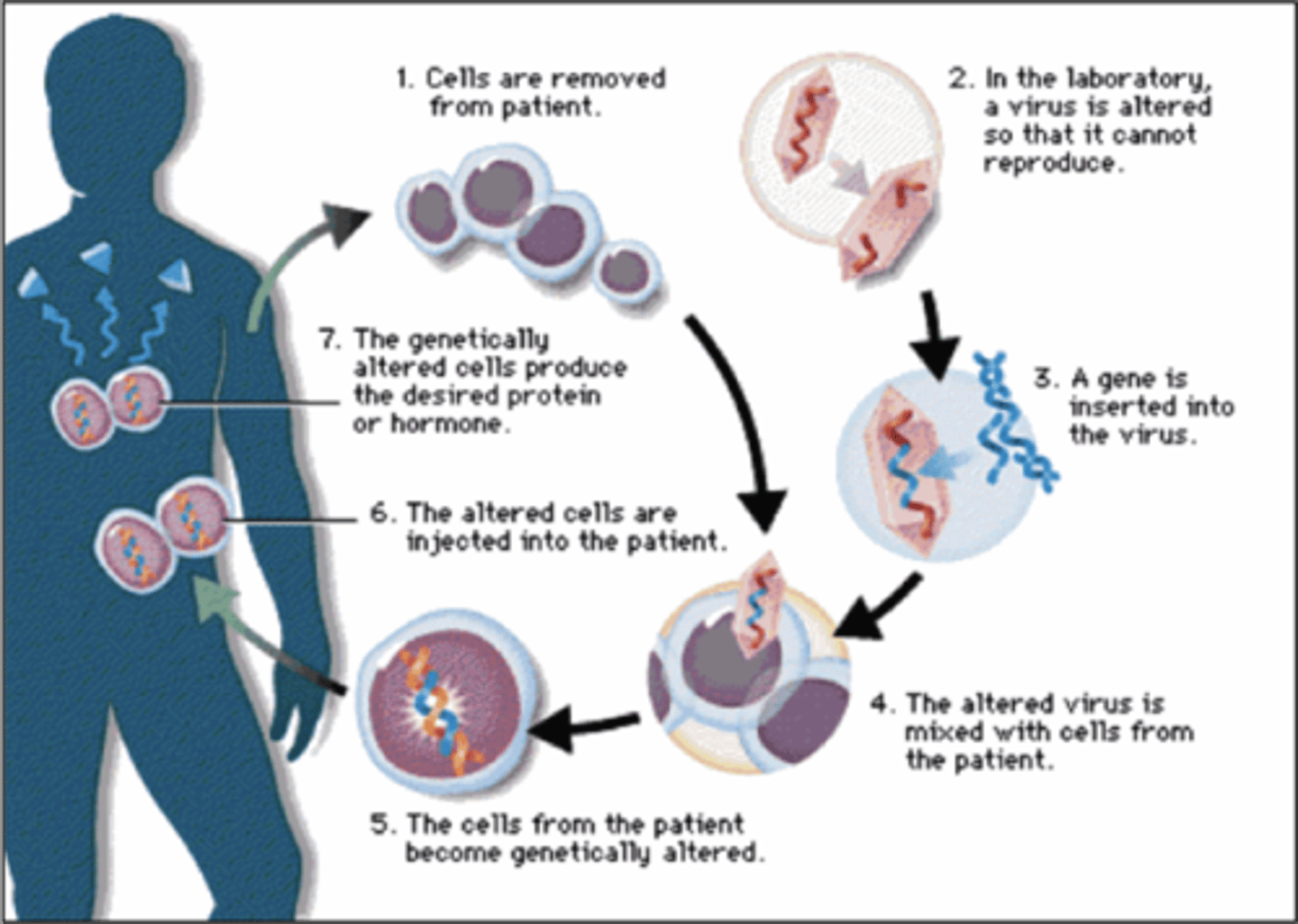
Genetic Engineering
The process of isolating, copying, and transplanting genes in humans and animals

What is the goal of genetic engineering?
To correct malfunctions or mutations in the genome that could produce unwanted diseases
Gene Therapy
The production of drugs that will inhibit the expression of certain disease-causing genes