excratory system (parts and purposes)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
functions of excratory system
regulation of volume and composition of bodiy fluids by removing wastes or addng substances
excretion meaning
seperating wastes from body fluids and eliminating them (out of the body)
what does the respiratory system excrete
CO2
whtat dies skin excrete
water, salts, and traces of urea in perspiration
what does the digestive system excrete
water, salts, lipids, pigments (like bile)
what does the term “wastes” refer to
any substance that is produced in excess of the body’s needs. build-up wastes can be toxic and disturb homeostasis in the body
nitrogenous wastes
from the breakdown of proteins in the liver - especially toxic.
what are the nitrogenous wastes
ammonia - highly toxic
urea - moderately toxic
uric acid - not as toxic
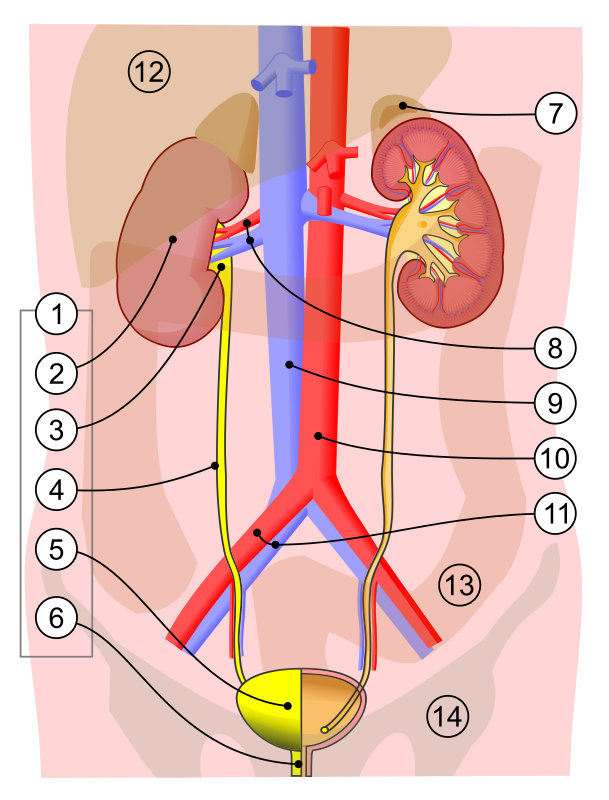
what is 2
kidney
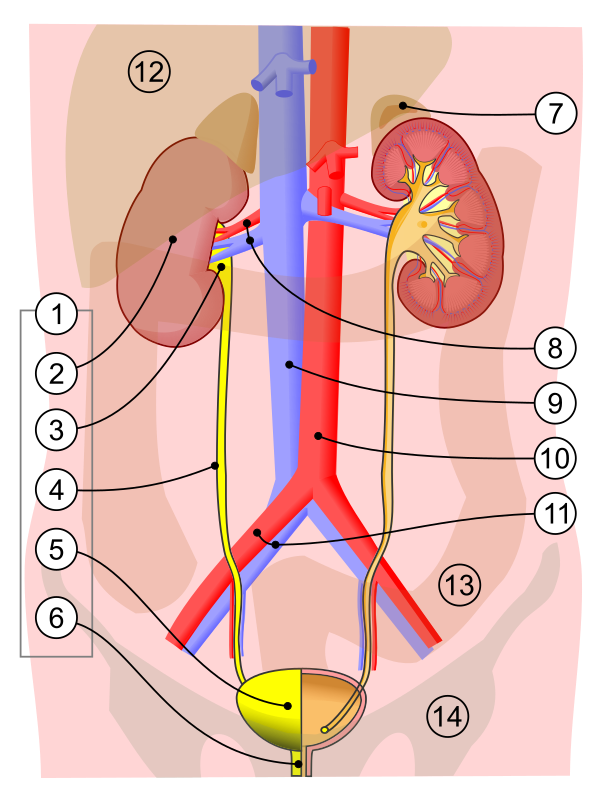
what is 3
renal pelvis
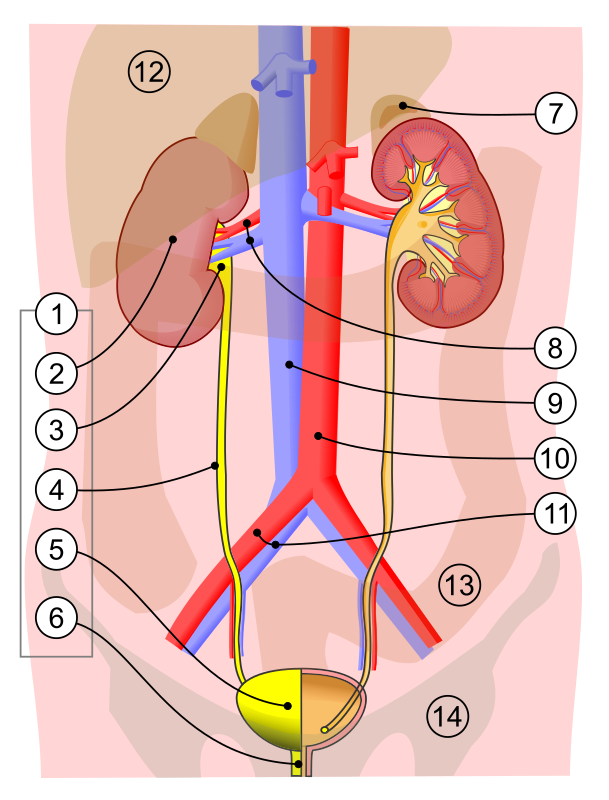
what is 4
ureter
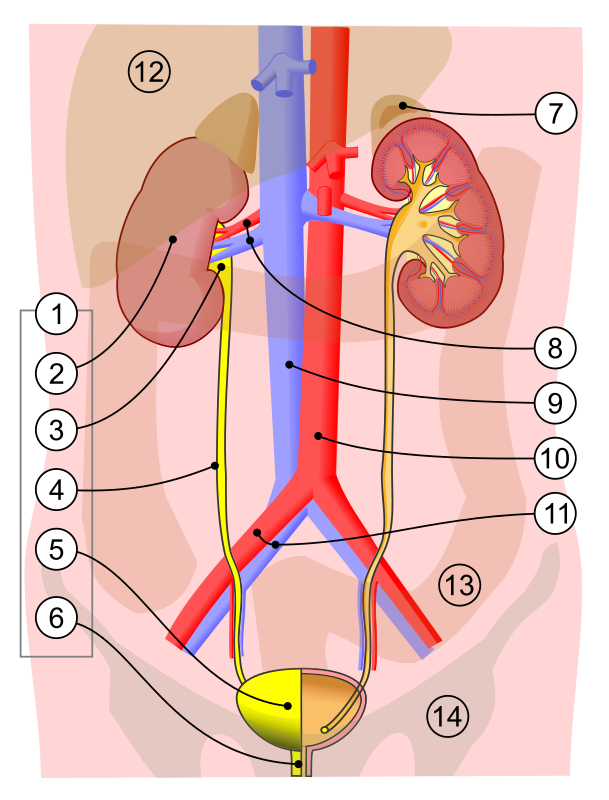
what is 5
bladder
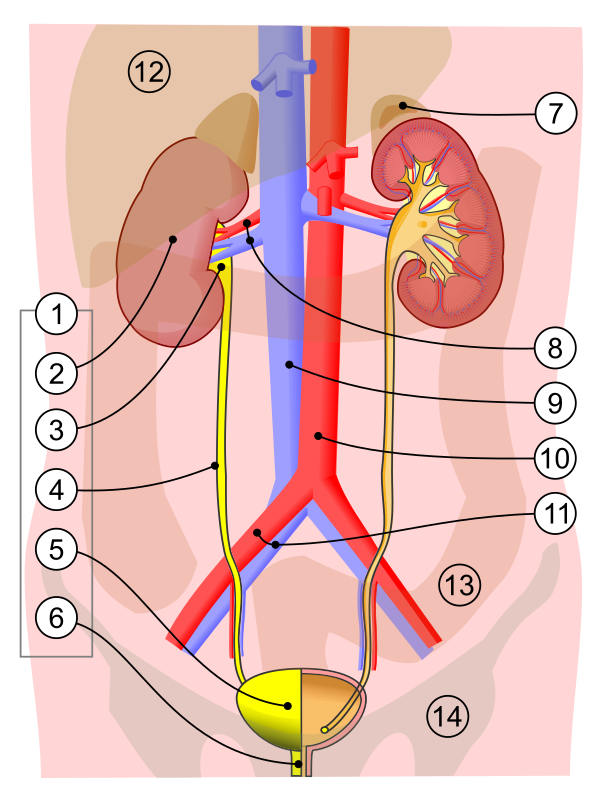
what is 7
adrenal gland
what is 8
renal artery and vein
what is 6
urethra
renal artery
connects kidney to the aorta and brings blood TO the kidney
renal vein
carries blood out of kidney and connects to the inferior vena cava
kidney purpose
remove waste in blood and produces urine
ureter
carries urine from kidney to bladder with peristalstic contractions.
urinary bladder
temporarily stores urine and has ruggae (folds that allow for expansion - like stomach)
urethra
carries urine from bladder to outside of the body - part of the reproductive system for male (sperm release)
urinary sphincters
2 sphincters:
innermost sphincter - involuntary controls (release after max capacity)
outermost sphincter - voluntary controls (learned from childhood)
renal artery
connects to aorta and carries blood to kidneys
renal vein
vein connecting infeior vena cava and kidney
kidney
removes wastes from blood and creates urine
ureter
tube that carries urine from kidneys to bladder and is controlled with peristalsis
urinary bladder
temporarily stores urine in bladder and alerts the brain when half full. Can expand with ruggae in the bladder (folds in the stomach which allow for expansion)
urethra
carries urine from bladder to out of he body. 4 cm for females, 20 cm for males. In males, there is a sphincter that separates the pathway vas deferens and the bladder
urinary sphinter
2 sphincters - involuntary and voluntary, voluntary learned with age, and involuntary for when the bladder reaches maximum capacity
where does urine collect in the kidney
renal pelvis
renal tissue is made of
outer section - renal cortex
inner section - renal mendulla
what are nephrons
nephrons are the functional units of the kidney. This is where all the filteration occurs
nephron components
filter - bowman’s capsule
tube - proximal and distal tubule and loop of henle
duct