OTC Exam 3- Insomnia, Eye/Ear, Home Diagnostics
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are the 5 stages of sleep?
Wake stage
Non-REM Sleep: N1, N2, N3
REM Sleep
What types of insomnia do we treat?
All of them except Chronic Insomnia
What impacts insomnia?
Antidepressants, AntiHTN med, Sympathomimetic amines (PSE and Phenylephrine)
Alcohol
Caffeine
Exercise
Environmental distractions
Nonpharmacologic for Insomnia?
Bed restriction
Regular sleep patterns
Comfortable sleeping space
Avoiding electronics 1-2 hrs before bed
Avoid napping (ONLY POWER NAPS)
Mindfulness meditation
DONT WATCH THE CLOCK
Pharmacologic for insomnia?
Benadryl 30 mins QHS/Doxylamine
Max sedation 1-3 hrs after dose
LIMIT TO 7-10 days
Adverse effects for insomnia meds?
ANTI SLUD
SEDATION DUH
What should we consider before prescribing insomnia meds?
BPH
Resp conditions
Angle closure Glaucoma
Dementia
Age
How does dry eye disease present?
Sandy, gritty sensation, lacrimation, and mild erythema
How do we treat Dry eye disease?
Warm washcloth to closed eye for 5 minutes
Ocular lubricant
Humidifier
When would we refer for dry eye disease?
When a patient is taking antibiotics, secretagogues, immunomodulators, cholinergics, corticosteroids, LFA-1 Antagonists
What ocular lubricants cause blurriness? When should they be taken?
Gel and ointment AT NIGHT!!
How do we administer eye drops/solution?
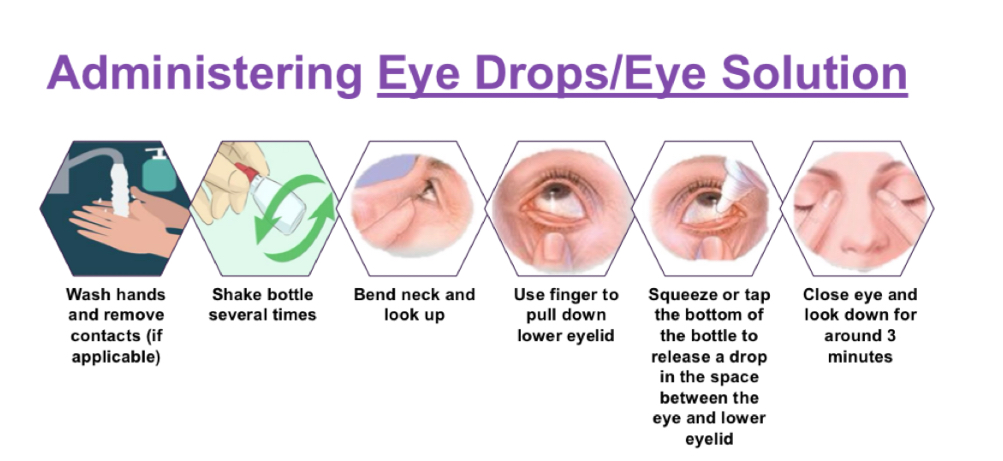
How do we administer eye gel/ointment?
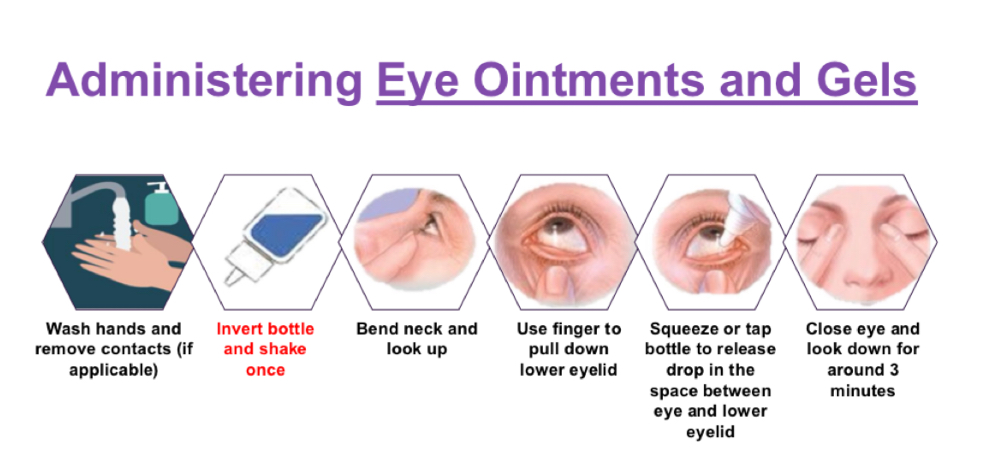
What if you need to administer more than one drop?
Wait 5 mins (drops)
Wait 10 mins (Gel/ointment)
What if you use both drops and gel/ointment?
Drops first, wait 10 mins then gel/ointment
What if you wear contacts? (Gel/ointment)
BAK in it?
Take out contacts, administer, and replace after 15 mins
How does allergic conjunctivitis present?
Eye erythema, Burning, Dryness, Swollen eyes, Pruritus, Lacrimation w/ or w/o discharge
How to treat for Allergic Conjunctivitis?
Non Pharm:
Allergen avoidance
Cold compress every 3-4 hrs for itching and redness
Pharm:
1st: Artificial tears as needed for symptoms
2nd: Antihistamine/mast cell stabilizer combo, Decongestant, decongestant/antihistamine combo
When do we refer for contact dermatitis of the eye lid?
INFECTION or if OTC treatment doesn’t fix it after 3 days or IT GETS WORSE w/ treatment
How does diagnosed Corneal Edema present?
Corneal swelling, distorted/blurry vision, Halos/starbursts in visual field, Dryness, Discomfort
How to treat for Diagnosed Corneal Edema?
1st: Topical Hyperosmotic therapy (2%, 5% NaCl solution)
Higher strength more effective but more likely to cause irritation
How does minor eye irritation present?
Red and itchy
How to treat Minor eye irritation?
Sterile saline/irrigation solution (SHORT TERM & NO CONTACT CLEANING)
How does Contact Dermatitis of the eyelid present?
Swelling, scaling, redness, sunburn?
How to treat Contact dermatitis of the eyelid?
Avoid risk factors (Cosmetics, Detergent, UV radiation)
Oral antihistamine
Cold compress 3-4x daily for inflammation and Pruritus
How does Age related Macular degeneration present?
Wet (20%)
Sudden vision loss
Haziness/blurriness
Distorted vision
Dry (80%)
Asymptomatic sometimes distorted vision
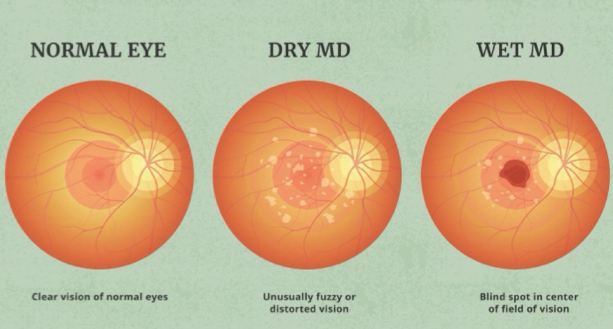
How do we treat AMD?
Non Pharm:
Exercise
Heart healthy diet
Manage chronic disease states
Pharm:
AREDS or AREDS 2 Supplementation
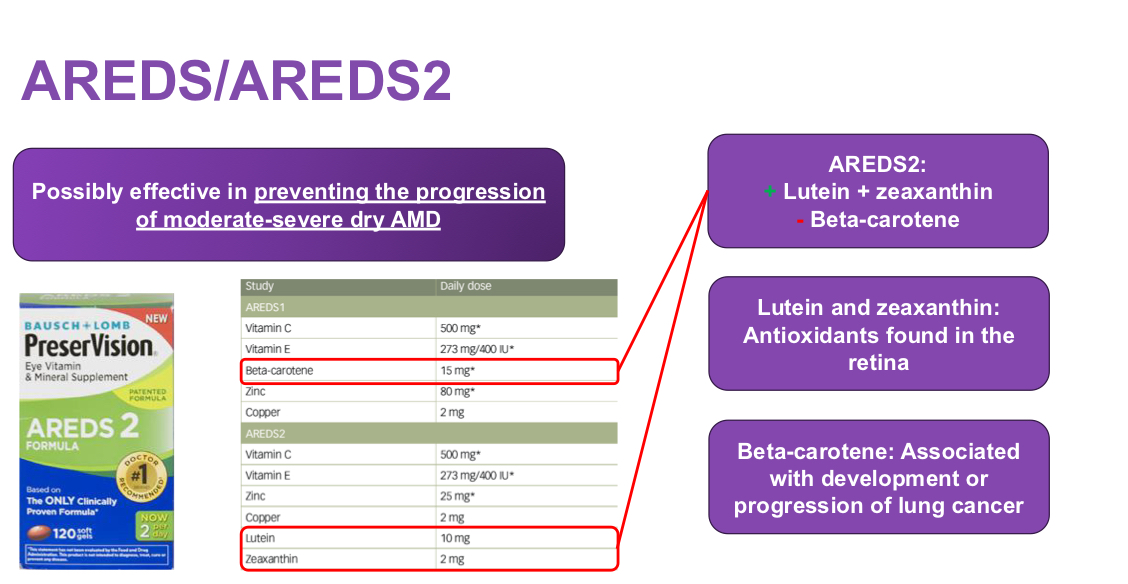
When do we refer for AMD?
Signs and symptoms of infection
Blunt trauma
Chemical/thermal exposure
>72 hrs w/ w/o OTC treatment
Sensitive to light
Blurred vision
Significant eye pain
What kind fo contact lenses are used for visual correction?
Rigid Gas Permeable lenses
Who shouldn’t use contacts?
Acute dry eye disease/ocular infection
History of poor lens care
Occupational exposure to toxins/chemical irritants
Use of medications that discolor secretions??

When should you recommend Hydrogen peroxide and a rinsing product?
If they have a:
Preservative allergy or intolerance
History of ocular infections (MOST EFFECTIVE DISINFECTANT)
When should you recommend a multipurpose solution?
If they have a:
Preference for one product
Infrequently use it
Poor adherence/can’t follow directions for use
Price
How does excessive/impacted cerumen present?
Feeling of ear fullness, Transient hearing loss
How do we treat excessive/impacted cerumen?
Non Pharm:
Manual removal by PCP
Irrigation w/o carbamide peroxide
Pharm:
Carbamide peroxide 6.5% - 5-10 drops in affected ear w/ or w/o irrigation keep in place for several minutes up to twice daily
How do water clogged ears present?
Feeling of ear fullness, Transient hearing loss, discharge or drainage, pruritus or PAIN
How do we treat Water clogged ears?
Non pharm:
Ear plugs
Shower caps
Blow dryer on low heat
Risk avoidance
Pharm:
Isopropyl Alcohol 95% in anhydrous glycerin 5% - 4-5 drops in affected ear and keep in place for 1-2 mins
When to refer w/ ear disorders?
INFECTION SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Blunt trauma
Impaction w/ foreign object
Any disorder affects middle ear or Eustachian tubes
Patients < 12 yrs
> 4 days of self treatment w/o improvement/worsening
What are types of Home diagnostics?

What are the key counseling points for BP?
Keep a log of BP readings
If monitoring therapy, take reading every morning after rising
Be alert for BP changes w/ Meds
Don’t use products that affects readings (Tobacco, Caffeine, PSE)
DONT adjust meds based on home measurements unless instructed
Contact PCP if elevated
What does the guidelines define HTN as?
BP >/= to 130/80
What is elevated HTN?
120-129/less than 80
What is stage 1 HTN?
130-139/80-89
What is Stage 2 HTN?
140+/90+
What is considered a HTN Crisis?
Over 180/over 120
Large gauge = ________ Needle size
Small!
What is the max range for a glucometer?
400-600 mg/dL
What should we counsel patients using Blood glucose monitors?
DONT SHARE/REUSE LANCETS
What happens when a wrong sized cuff is used?
Too small → False High reading
Too big → False Low reading
What are the limitations of using alternative testing sites? When should you use your fingertip?
Variation of glucose concentration throughout the body
Rapid changes in glucose
Fingertip should be used:
Possible hypoglycemic episode
History of hypoglycemic unawareness
Site results don’t agree with feelings
How often should patients check A1c?
Every 2-3 months
What happens when an egg gets fertilized?
Trophoblactic cells produce Human Chorionic Gonadotropic Hormone (hCG)
How do pregnancy tests work?
HCG hormone levels as early as 1-2 weeks after fertilization are detected in the urine
THEY ARE THE MOST SENSITIVE WHEN USED 1 WEEK AFTER FIRST DAY OF MISSED PERIOD
What produces a false positive in Pregnancy tests?
Miscarriage or birth within previous 8 weeks
Medications: Profasi (hCG injection)
Ovarian cysts
What produces a false negative in pregnancy tests?
Performed on or before the 1st day of missed period
Waxed cups used for urine collection
Refrigerated urine
Diluted urine (USE MORNING PEE)
If received a negative result for a pregnancy test what should happen next?
Review test procedure and ensure proper technique
Test again if period hasn’t come in another week
What is infertility? Types of tests?
Medical inability to conceive after 1 year
Basal thermometer/urine test
How do urine ovulation tests work?
It detects LH surge which typically occurs 24-48 hrs prior to ovulation
Best time to conceive is 24 hrs after LH surge
What indicates an LH surge? No surge?
No surge: Circle, test again at same time
Surge: :)
What can lead to false positives for ovulation tests?
Fertility meds (Clomiphene)
PCOS
Menopause
Pregnancy, breastfeeding
Discontinuation of oral contraceptives
Impaired liver/kidney function
Tetracyclines (NOT oxytretacycline/minocycline)
How can you get a false positive with Illicit drug tests?
Decongestants, Dextromethorphan, Antidiarrheal, Cough medicines w/ Codeine, Sertaline-Benzos, Propanolol-Amphetamines
What can lead to false positives in UTI tests?
Phenazopyridine (discolors urine)
Menstruation
What can lead to false negatives?
Vegetarian diet
Tetracycline
Vitamin C