DNTL 10: Nomenclature (Week 1 Oral Biology)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Maxillary Arch contain what teeth?
Upper teeth
Mandibular Arch contain what teeth?
Lower teeth
Palatal Surfaces
Roof of the mouth.
Lingual Surfaces
Tooth surfaces closest to the tongue. Lower arch, mandibular arch.
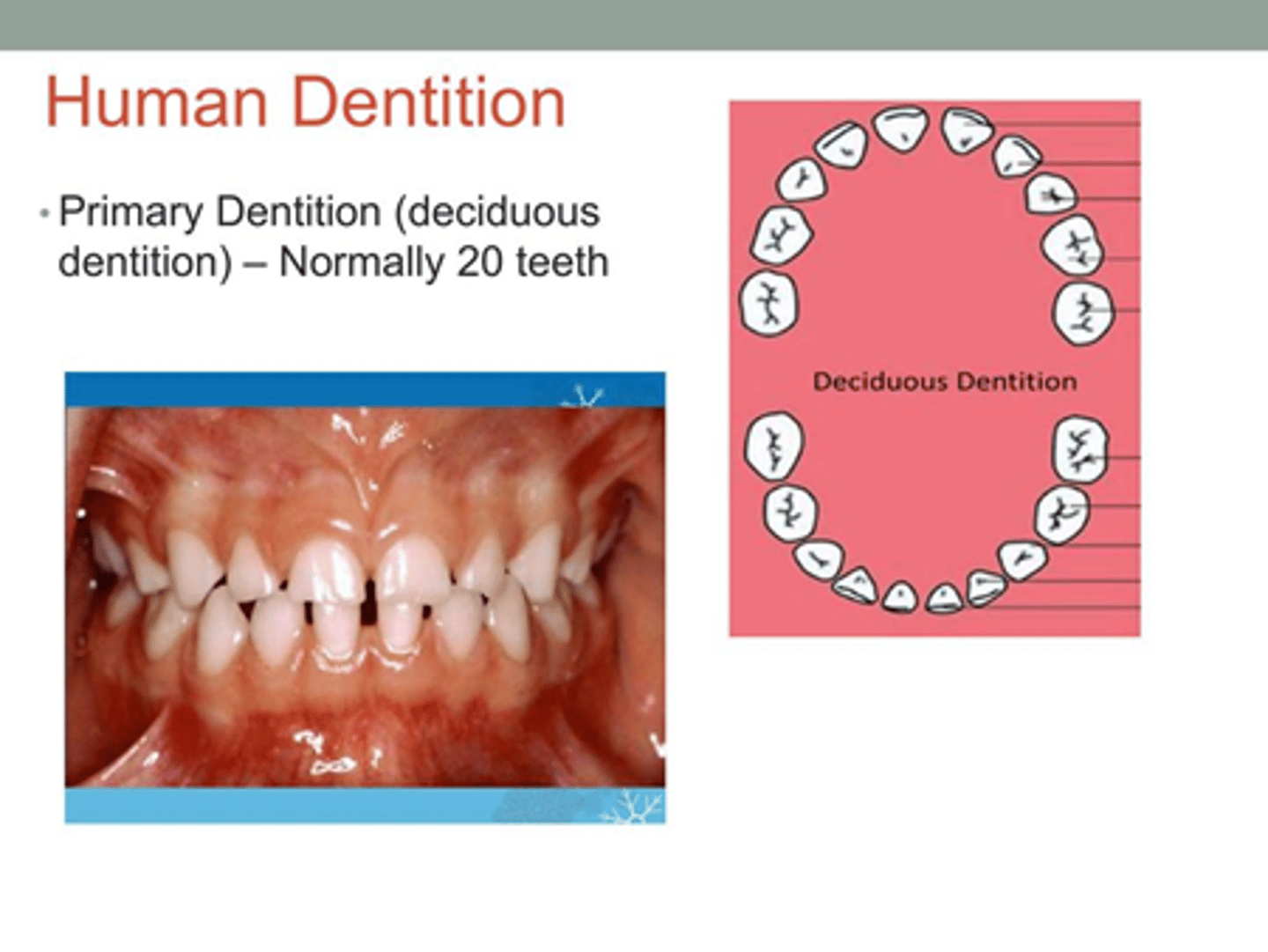
Primary (deciduous)
-Primary / deciduous Dentition, we are talking about the entire set of teeth, baby teeth.
-Primary dentitions are missing all 8 premolars and the 4 wisdom teeth!
- Incisors = 8
- Canines = 4
- Premolars = 0
- Molars = 8
TOTAL=20
Permanent (adult teeth)
- Incisors = 8
- Canines = 4
- Premolars = 8
- Molars = 12
TOTAL=32
Primary teeth development
at 6 week of embryological development. Generally speaking mandibular incisors come in first,
Primary Teeth Exfoliation
At 4-6 years old, When maxillary and mandibular central incisors will begin to fall out/exfoliate. When adult teeth get closer to the root of primary teeth, blast cells and clast-cells cause resorption of primary teeth and then primary teeth exfoliate.
Which are whiter primary or permanent teeth?
Primary teeth
Tooth Anatomy
crown, root, enamel, dentin, pulp, , cementum, root canal, periodontal membrane, Nerve and blood supply
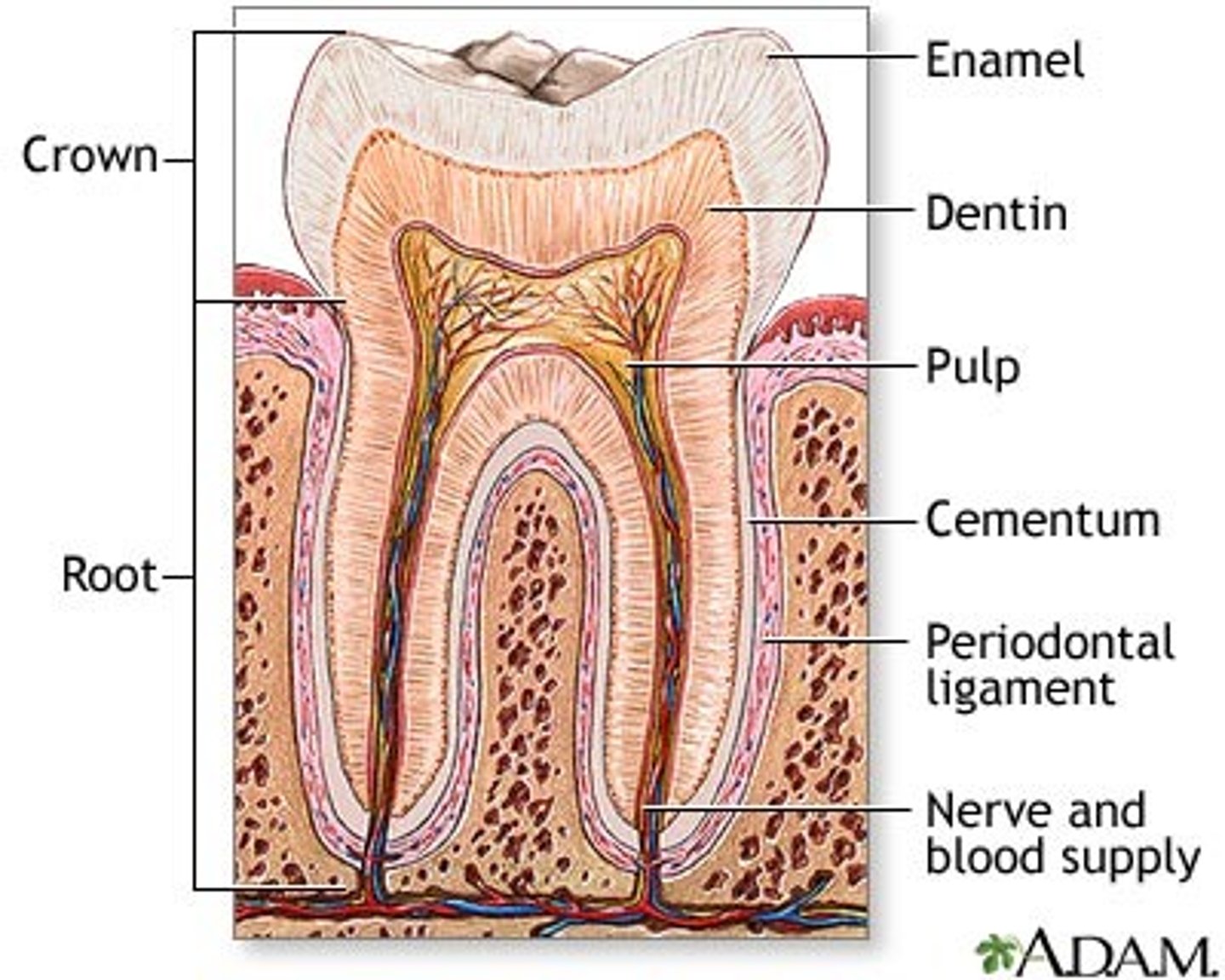
Enamel
apparent part to patient, outside structure of tooth. Hardest structure in the human body, much more dense than bone.
Dentin
Largest by volume, underneath enamel
Pulp
is a soft tissue.
Contains: nerve, blood vessels and connective tissue that nourishes the tooth, form dentin and provides sensory feedback.
Cementum
coating on the root of the tooth. Do not remove cementum, remove calculus.
Periodontal membrane
soft tissue that holds teeth in their sockets
Referred as periodontal ligament (PDL)
Gingiva
Gums
Cervix (CEJ)
cementum enamel junction, where two structures come together.
Where the crown (covered in enamel) meets the root (covered in cementum)
Alveolar bone
bone
it is the specialized bony structure that forms the ridge of the maxilla (upper jaw) and mandible (lower jaw) where the teeth are housed and supported.
anatomic root
The portion covered by the cementum, the tissue that covers the root surface
Apical foreamen
The small opening located at the root apex (tip). Entry port for blood vessels.
Dentinoenamel Junction
boundary between dentin and enamel
Anatomic crown
fixed size. Entire part of the tooth covered by enamel.
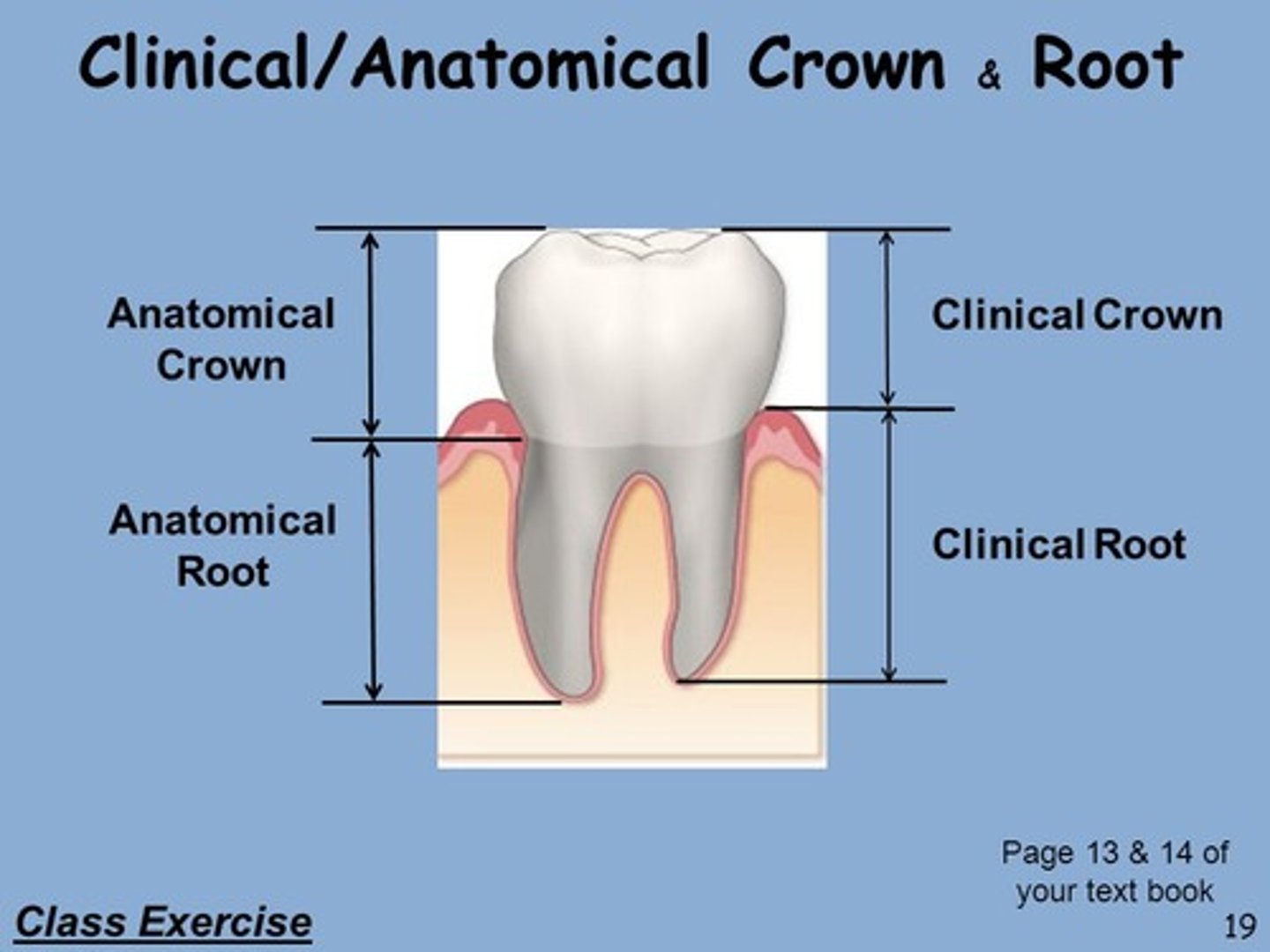
Clinical Crown
It is anything you can see, clinical crown includes any portion of the tooth that is visible above the gumline.
MIDLINE
divides body into left and right. Oral cavity divided at the midline, equal left and right halves.
MESIAL
CLOSEST SURFACE TO THE MIDLINE
DISTAL
FURTHEST SURFACE AWAY FROM THE MIDLINE
Facial (labial)
Canine to centrals or Canine to Canine. Teeth surfaces adjacent to the lips
Buccal
surfaces adjacent to buccal mucosa. Pre molars and molars
Palatal
surfaces on the inside surfaces of the teeth adjacent to the palate. Roof of mouth. Maxillary teeth.
Lingual
surfaces adjacent to the tongue. Teeth on the Mandibular arch.
Posterior teeth
Premolars and molars
- Occlusal surface ( on molars and pre-molars)
- Grinding
Anterior teeth
Canine through centrals
-Incisal edge: ( instead of occlusal)
- Incising
Proximal
Tooth surfaces adjacent to tooth surfaces.
Interproximal
spaces between proximal surfaces
Contact area
where two teeth are touching.
Height of contour
no more and no less of stating the width of the tooth. Identifying the widest part of the specific tooth, can be different on Mesial or Distal.
Embrasures
Are the OPEN spaces between teeth. They consist of occlusal embrasures, incisal embrasures, buccal embrasures, lingual embrasures, gingival embrasures
Root apex or apices
root of the tooth.
Lines angles
where two surfaces meet.
Point Angles
The point at which three surfaces meet
EX: Mesiolabioincisal, Mesdiolinguoincisal, DIstolabioincisal, Distolinguoincisal
Universal Numbering System (Permanent Teeth)
1------>16 maxillary arch
32<------17 mandibular arch
Palmer Method
Tooth numbering system commonly used in orthodontics
Universal tooth numbering designation system
Used in United States
Universal tooth designation system (Primary teeth)
A----> J (Maxillary arch)
T<---- K (Mandibular arch)
**All Pre-molars are missing and wisdom teeth
International Standards organization designation system (primary teeth)
Quad 5 |. Quad 61, 62, 63, 64, 64, 65
Quad 8 | Quad 7
*Primary teeth go up to 5
*They continue the quad numbering after permanent teeth quads.
International Standards organization designation system (Permanent teeth)
Quad 1 | Quad 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28
Quad 4 | Quad 3
*Permanent teeth extend to 8
Bottle rot
primary teeth are extremely rotting, decay.
Gingivitis
inflammation of gums
Peridontitist
is an oral health condition that causes sore, bleeding, swollen gums. Left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss, bone loss, bad breath .