Monopsony
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:48 PM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
What is a monopsonist firm?
A firm that is the only buyer of a certain type of labour
\
→ Market power as there is a lack of demand side competition as there is only one buyer
e.g. NHS, schools, investment banks
\
→ Market power as there is a lack of demand side competition as there is only one buyer
e.g. NHS, schools, investment banks
2
New cards
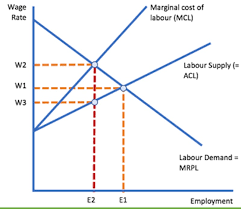
Monopsony diagram:
MCL = MRPL
→ If MCL > MRPL:
→ Change in TC > Change in TR from employing last worker
→ Firm should sack the last worker
→ If MCL > MRPL:
→ Change in TC > Change in TR from employing last worker
→ Firm should sack the last worker
3
New cards
What does the degree of market power of a monopsony depend upon?
The (%) of workers they employed
4
New cards
How does the market equilibrium compare to the perfectly competitive Labour market?
→ Workers are employed at a lower wage rate
→ Less workers employed under a monopsony
→ They have labour market and the power to restrict WR
→ They don’t want to (↑) WR as they know they have to do the same for all previous workers
→ Restrict employment as C (↑) → (↑)
→ Monopsony pays less than workers MRPL
→ The 2 dots show what they should be be paid and what they’re paid
→ If MRPL and Wm have a large distance
→ Indicated monopsony has a high degree of market power
→ Less workers employed under a monopsony
→ They have labour market and the power to restrict WR
→ They don’t want to (↑) WR as they know they have to do the same for all previous workers
→ Restrict employment as C (↑) → (↑)
→ Monopsony pays less than workers MRPL
→ The 2 dots show what they should be be paid and what they’re paid
→ If MRPL and Wm have a large distance
→ Indicated monopsony has a high degree of market power
5
New cards
What does the impact of a monopsonist depend upon?
→ Depends on the nature of the employer
→ Degree of the government exploitation
→ Low wage vs high wage industry
→ Depends on EDL
→ Depends on ESL
→ Degree of the government exploitation
→ Low wage vs high wage industry
→ Depends on EDL
→ Depends on ESL
6
New cards
Depends on the nature of the employer:
If wages set too low → workers go to another firm
→ Monopsonistic employers not interested in profit max
→ Operate at MC=MRPL
→ Care about welfare max → more likely to exploit workers
→ Don’t want to suppress wages/employment
→ Can’t afford to pay high wages
→ Monopsony may not have much market power
→ May be other buyers of labour
→ Private monopsony might have other objectives
→ However, private monopsony might not have wage at Wm as it damages their reputation
→ Monopsonistic employers not interested in profit max
→ Operate at MC=MRPL
→ Care about welfare max → more likely to exploit workers
→ Don’t want to suppress wages/employment
→ Can’t afford to pay high wages
→ Monopsony may not have much market power
→ May be other buyers of labour
→ Private monopsony might have other objectives
→ However, private monopsony might not have wage at Wm as it damages their reputation
7
New cards
Degree of government intervention:
CMA ensures market isn’t too concentrated
→ If one firm has too much market share
→ They regulate that firm or lower barriers to entry
→ Number of firms (↑) → may subsidise firms to enter market
→ Means more buyers of labour → less monopoly power
→ Workers aren’t exploited as much
→ Firms (↑) → output (↑) → DDL (↑) → buyers of labour (↑)
→ If one firm has too much market share
→ They regulate that firm or lower barriers to entry
→ Number of firms (↑) → may subsidise firms to enter market
→ Means more buyers of labour → less monopoly power
→ Workers aren’t exploited as much
→ Firms (↑) → output (↑) → DDL (↑) → buyers of labour (↑)
8
New cards
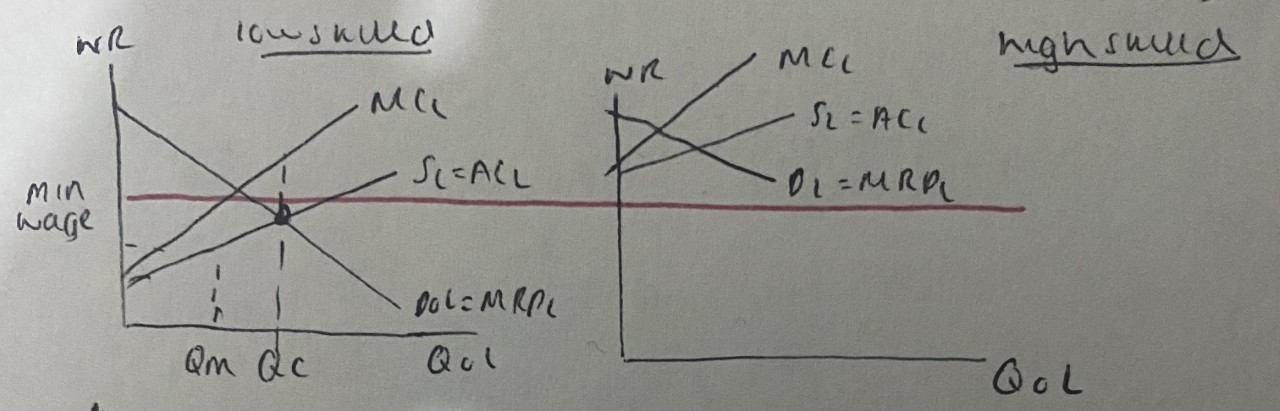
Low wage vs high wage industry:
Workers below WC are willing to work below minimum wage so they will be paid WC or the firm will be breaking the law
→ Workers above WC not willing to work at minimum wage
→ Demand higher wages → when WR (↑) → wages (↑)
→ For all previous workers → employment (↑) {Qm→Qc}
→ Monopsony has no incentive to restrict employment below Qc
→ When there is minimum wage → you don’t need to (↑) salary for all previous workers as you can pay them minimum wage
e.g. doctors regulate lots of training and skills so already paid minimum wage
→ Minimum wage has no effect
→ Workers above WC not willing to work at minimum wage
→ Demand higher wages → when WR (↑) → wages (↑)
→ For all previous workers → employment (↑) {Qm→Qc}
→ Monopsony has no incentive to restrict employment below Qc
→ When there is minimum wage → you don’t need to (↑) salary for all previous workers as you can pay them minimum wage
e.g. doctors regulate lots of training and skills so already paid minimum wage
→ Minimum wage has no effect
9
New cards
Depends on EDL:
Doctors have inelastic demand → can’t be replaced by capital
→ They have some power to force down wages and employment so they can’t exploit workers so much
→ Checkout assistants have wage elastic demand as they can be replaced by capital
→ Monopsony has more power to force down wages
→ Can exploit much more
→ They have some power to force down wages and employment so they can’t exploit workers so much
→ Checkout assistants have wage elastic demand as they can be replaced by capital
→ Monopsony has more power to force down wages
→ Can exploit much more
10
New cards
Depends on ESL:
The more wage elastic the ESL is:
→ The less the monopsony force down wages
→ More wage elastic could be through education and training
→ More skills → occupational mobility (↑)
→ So they can work in industries that pay more
→ If people lack occupational mobility and are employed by a monopsony → exploitation (↑) as you can’t leave the industry
→ As you lack transferrable skills
→ The less the monopsony force down wages
→ More wage elastic could be through education and training
→ More skills → occupational mobility (↑)
→ So they can work in industries that pay more
→ If people lack occupational mobility and are employed by a monopsony → exploitation (↑) as you can’t leave the industry
→ As you lack transferrable skills