Web Development and Security chapter1
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of question-and-answer flashcards covering the key concepts from the lecture notes on web technologies, HTTP, XML, JSON, AJAX, and web architectures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What does web technology refer to?
The means by which computers communicate using markup languages and multimedia software packages; it involves HTML and CSS and enables interaction with hosted information like websites.
What are the three basic languages that make up the World Wide Web?
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
What does WWW stand for and what is it?
World Wide Web; a way of exchanging information between computers on the Internet; a network of pages and multimedia viewed with a browser.
What is a Website?
A collection of related Web pages and associated items.
How do Websites differ from Web applications in terms of content?
Web pages often feature static content; web applications rely on dynamic content that changes based on user actions or system updates.
What are the Structural Components of web applications?
Clients/browsers, Servers, Caches, Internet.
What are the Semantic Components used in Web technologies?
HTTP, HTML, XML, URIs or URLs.
What is Hypertext?
Text which contains links to other texts.
What is Hypermedia?
Hypertext that can include graphics, video, and sound, not limited to text.
What is a Web browser?
Displays web documents and enables users to access them.
What is a Web Server?
A program that waits for browser requests, retrieves information, and sends it to the browser or an error if not found.
What is a URL?
Uniform Resource Locator; the web address used to locate resources.
What are the two basic steps to make a web page?
Create an HTML file and upload it to a server.
What is HTML?
The markup language used to structure web pages; interpreted by web browsers.
What is HTTP?
A protocol used to access and transfer data on the World Wide Web; simpler than FTP and typically uses a single connection.
What are the key characteristics of HTTP?
Connectionless, Media Independent, Stateless.
What are the components depicted in HTTP architecture?
Web Server, Web Client, Server Side Script, HTTP Protocol, Database.
What are the two main types of HTTP messages?
Request messages and Response messages.
What does an HTTP Request message consist of?
A request line, headers, and optional body.
What does an HTTP Response message consist of?
A status line, headers, and optional body.
What is codec design in web applications?
Developing a UI for creating, testing, and deploying custom codecs; HTML5 video codecs include H.264; audio codecs include AAC, MP3, Opus; containers.
Name a few HTML5 video and audio codecs mentioned.
Video: H.264; Audio: AAC, MP3, Opus.
What is a container in the context of codecs?
HTML5 file formats that assemble encoded video and audio into a single file.
What is web application architecture?
A framework that clarifies how the connection is established between the client and the server and how components communicate; applies to various applications.
What happens when a user makes a request in web applications, in technical terms?
Various components (user interfaces, middleware, databases, servers, and the browser) interact; architecture ties these relationships together and maintains interaction.
What does AJAX stand for and what is it?
Asynchronous JavaScript And XML; not a programming language; uses XMLHttpRequest, JavaScript, and HTML.
What are the benefits of AJAX?
Web pages can be updated asynchronously without reloading the whole page; can request, receive, and send data in the background.
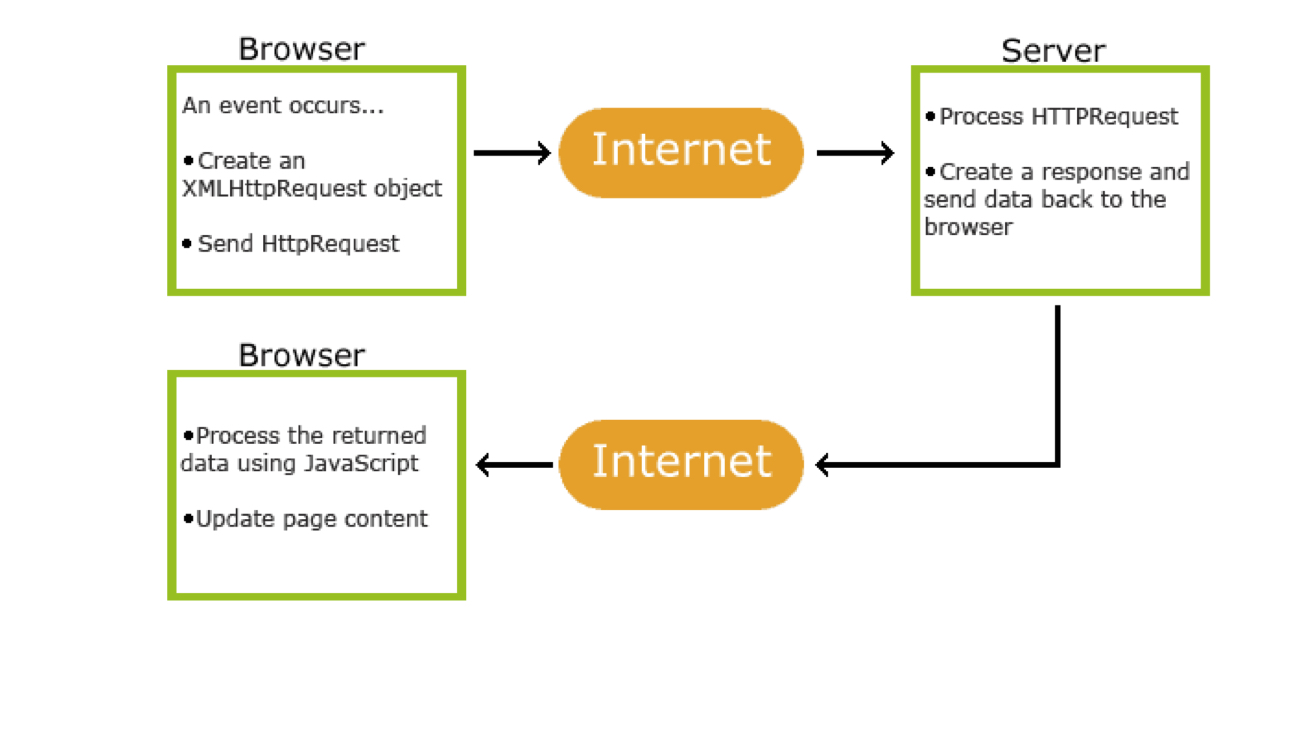
How does AJAX work? List the basic steps.
A browser event occurs; create an XMLHttpRequest object; send HTTP request; server processes; server sends a response; browser processes data with JavaScript; update page content.
What is XML?
Extensible Markup Language; a markup language designed to store and transport data; self-descriptive; W3C Recommendation.
Provide a simple XML example.
What is the difference between XML and HTML?
XML is designed to carry data with focus on data; HTML is designed to display data with focus on presentation; XML tags are not predefined.
What is JSON?
JavaScript Object Notation; a lightweight data-interchange format; language-independent and easy to read/write; based on a subset of JavaScript.
What are the two core structures in JSON?
An object (name/value pairs) and an array (ordered values).