Applied PK Lecture: Nguyen (July 3rd)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
AED oral absorption is ______.
Slow
In seizure emergencies AEDs are delivered ___________ for immediate effect
intravenously
What are the four important AED that come in IV form?
Phenytoin
Fosphenytoin
Levetiracetam
Lacosamide
How are AED loading and maintenance doses administered?
Loading doses as IV and maintenance dose as PO
What is phenytoin’s loading dose and maintenance dose?
Loading dose: IV 20mg/kg (max 1500mg)
Maintenance dose: PO PHT 300mg PO qhs
What is fosphenytoin’s loading dose and maintenance dose?
Loading dose: IV 20 PE/kg (max 1500mg)
Maintenance dose: None
What is levetiracetam’s loading dose?
IV 60mg/kg (max 4500mg)
What are the two ADEs that require therapeutic drug monitoring and what are the values?
Phenytoin: 10-20 mg/L
Fosphenytoin: Same as PHT
What can fast IV administration of admixtures with propylene glycol cause?
It can cause vein extravasation and cardiotoxicity.
What happens to Phenytoin IV in solution over time?
Phenytoin IV will precipitate out of solution in 1-2 hours and must be used within 1 hour.
How is Fosphenytoin dosed to make it interchangeable with Phenytoin?
Fosphenytoin is dosed as phenytoin equivalents (PE).
What serious but rare side effects can occur with fast IV administration of phenytoin and fosphenytoin?
Purple Glove Syndrome, severe hypotension, and life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
What is Purple Glove Syndrome, and what causes it?
Purple Glove Syndrome is caused by extravasation by propylene glycol and may occur very rarely with fosphenytoin.
What serious cardiovascular side effects can result from fast IV administration of phenytoin and fosphenytoin?
Severe hypotension and life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
What rate should the IV administration of phenytoin not exceed to prevent serious adverse drug events (ADEs)?
The rate of IV administration of phenytoin should not exceed 50 mg/min.
What rate should the IV administration of fosphenytoin not exceed to prevent serious adverse drug events (ADEs)?
The rate of IV administration of fosphenytoin should not exceed 150 mg/min.
How does administering phenytoin with tube feeds affect its absorption?
Administering phenytoin with tube feeds reduces its absorption in the gut.
What should be done to tube feeds to ensure proper absorption of phenytoin?
Tube feeds must be stopped 2 hours prior to and 2 hours after phenytoin administration.
What percentage of phenytoin is protein bound?
90%
What kind of phenytoin is pharmacologically active?
Only the free phenytoin (like 10% because 90% of it is protein bound)
What is low protein status and what does it do to protein binding?
Low protein states include:
Hypoalbuminemia
Renal dysfunction
Elderly
Critically Ill
There will be less than 90% protein binding
How to know which equation to use when correcting total phenytoin level in patients with low albumin?
Hemodialysis? Do 0.1 instead of 0.2
Hypoalbuminemia? Do 0.25 instead of 0.2
If patient is both Hemodialysis and Hypoalbuminemia go with Hypoalbuminemia equation
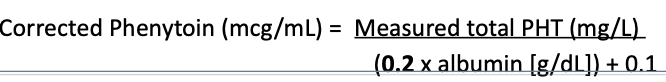
What are the two important AED inducers?
Carbamazepine and Phenytoin
What is the broad spectrum AED inhibitor?
Valproic acid
Which AED requires renal adjusting?
Levetiracetam
Elimination rate of phenytoin ________ at higher doses
decreases
A typical phenytoin dose is 300mg daily
If dose is <300mg increase doses with ___ mg
If dose is >300mg increase doses with __ mg
100 mg
30 mg