Business Management Unit 3 Outcome 1 Business Foundation
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1.2 Types of Businesses
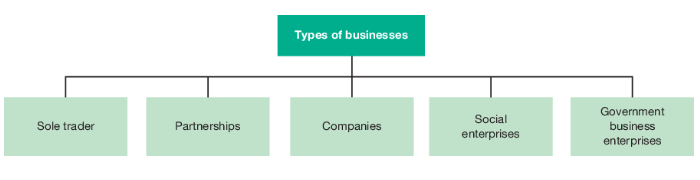
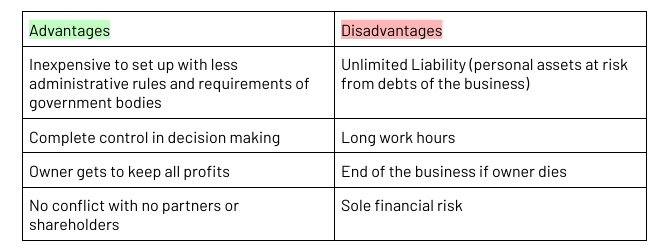
Sole Trader
a business owned and operated by one person
unincorporated business
Unlimited liability (personal assets at risk from debts of the business)
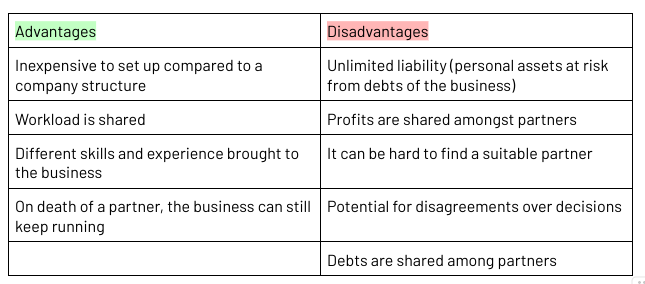
Partnership
A business owned by two or more people, generally up to a maximum of 20
Unincorporated business
A partnership is not separate legal entity and therefore has unlimited liability (personal assets at risk from debts of the business)
Some partnerships can have a silent partner who has a financial stake in the business but plays no role in the day to day operations of the business
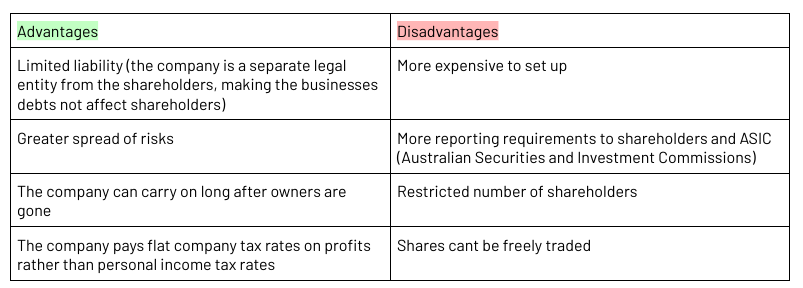
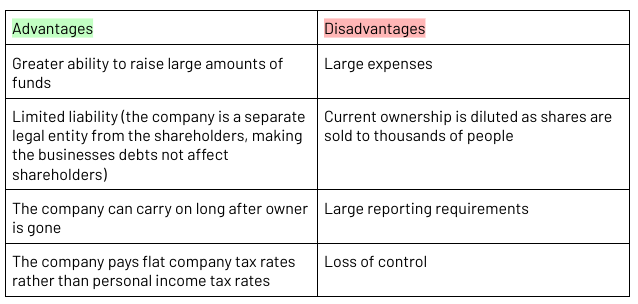
Companies
An independent legal entity made up of shareholders
Incorporated business (the company is a separate legal entity from the shareholders, making the businesses debts not affect shareholders)
Limited liability (the company is a separate legal entity from the shareholders, making the businesses
Private Limited Company (Pty Ltd)
A company with 1-50 non-employee shareholders
Incorporated business (the company is a separate legal entity from the shareholders, making the businesses debts not affect shareholders)
A private limited company will have the letters Pty Ltd after their name (Proprietary Limited)
Publicly Listed Company
A company with a minimum of 1 shareholder and no maximum, whose shares are openly traded on ASX (Australian Securities Exchange)
Incorporated business (the company is a separate legal entity from the shareholders, making the businesses debts not affect shareholders)
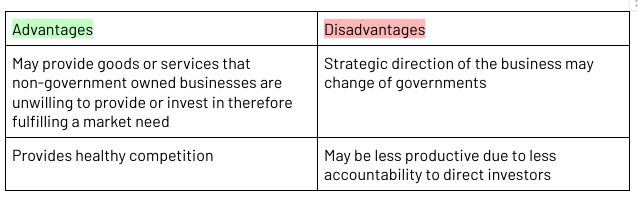
Government Business Enterprises (GBE)
A business owned by the government (federal or state level)
Aim to make a profit
E.g VicRoads
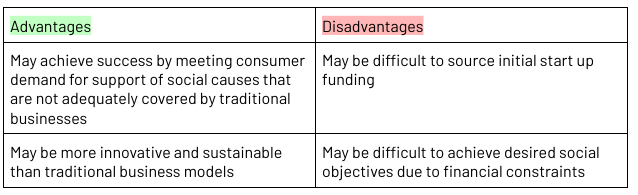
Social Enterprises
A business that exists primarily to fulfil a vision that benefits the community rather than shareholders (still want to make a profit)
Prioritise a social goal, and then aim to make a profit
Do not rely on donations as charities do
1.4 Business Objectives
are the stated goals a business aims to achieve within a certain time period
Types of Business Objectives
SPEMEMS
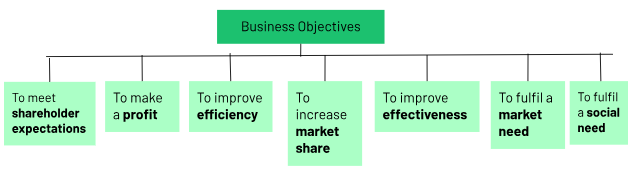
To meet shareholder expectations
Shareholders (not managers of the business): are the people who own the business, which means they expect to have a good return on their investment
They also expect the business to act in an ethical and socially responsible manner
To make a profit
Profit: the excess amount of money left once expenses have been paid (revenue less expenses = profit)
A businesses primary objective
Allows the business to grow and expand
To improve efficiency
Efficiency: refers to how well a business uses its resources (time, raw materials, labour, machinery, technology etc) in producing a good or service
To increase market share
Market share: the percentage of sales a business has compared with its competitors in the same industry
Result to increase in profit
To improve effectiveness
Effectiveness: refers to the degree to which a business achieves its stated objective
Businesses must ensure that it has measured tools in place, such as key performance indicators
To fulfil a market need
In terms of fulfilling a market need, businesses are often developed with the objective of filling a gap in the market where there is demand for product or services, but limited or no supply
To fulfil a social need
Social enterprises are often developed to fulfil a social need
They aim to improve the conditions of the world, and make a profit
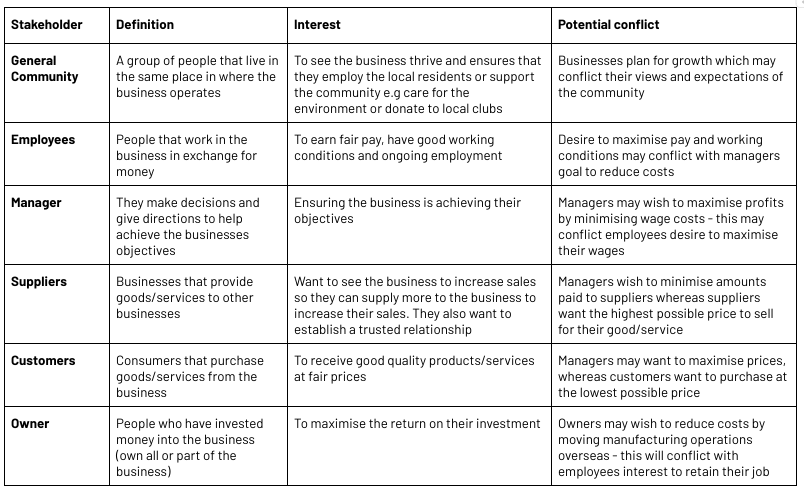
1.5 Business Stakeholders
GEMSCO
1.8 Management Styles
Management style: the way in which a manager makes decisions and how they lead and communicate with their employees
The style of the manager may come down to factors such as personality, skills and time available
Types of Management Styles
A Playful Cat Pounced Lazily
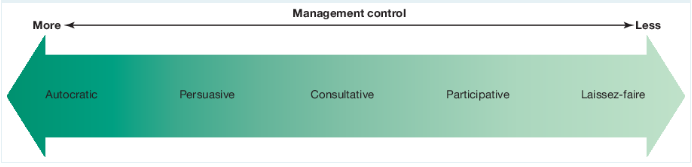
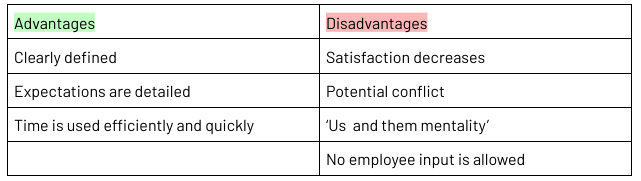
Autocratic Management Style
Where the manager makes the decisions and tells the employees what tasks to perform
This management style is very task-oriented and uses one-way communication
Best for when there is less time and when employees lack of skill or knowledge
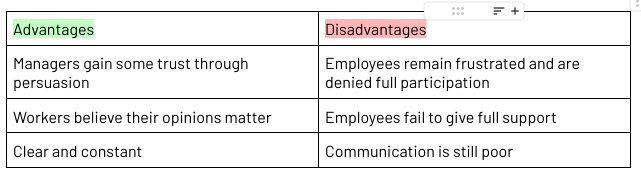
Persuasive Management Style
Where the manager makes the decisions and then explains to employees the reasoning to convince them why is it the most appropriate
Decisions are made by the manager, however the manager still tries to convince employees as why it is the best decision
Two-way communication
Best for when there is less time and when employees lack of skill or knowledge
Consultative Management Style
Where the manager seeks ideas and opinions of their employees before making a final decision themselves
Two-way communication
Best used when employees have a degree of skills and experience
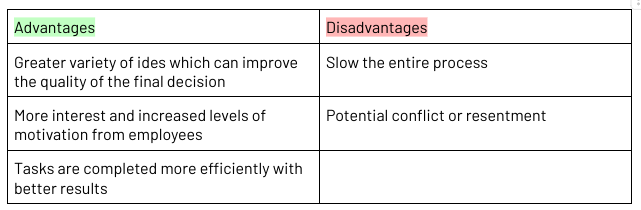
Participative Management Style
Where the manager and employees join together to make decisions as a team
Employees motivation can be increased
Two-way communication
Can be more time consuming
Good style when employees are highly skilled and experienced
Best used when there is an issue directly impacting the employees
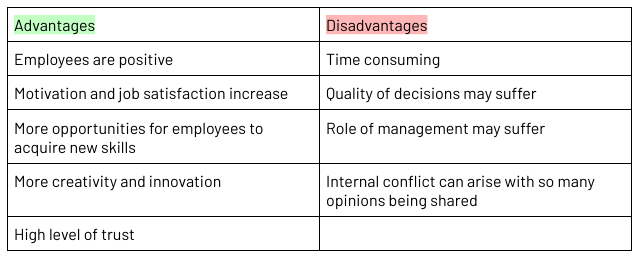
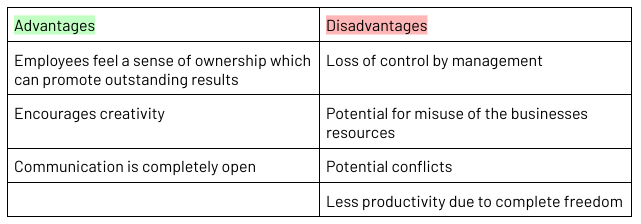
Laissez-Faire Management Style
Where the manager leaves the majority of the decision making to their employees
Most employee-centred style
Employees need to be highly skilled and knowledgeable
Can increase motivation
Best used where a high level of creativity is important and can lead to outstanding outcomes
1.9 The appropriateness of management styles
MENT
Managers preference
Experience of employees
Nature of the task
Time
Managers Preference
A manager's personality, experience, values, beliefs and skills might mean they prefer to use particular management style
Experience of employees
A workplace with inexperienced staff might necessitate the use of an autocratic style
A team of experienced staff would indicate that a consultative or participative style would be appropriate
Nature of the task
When the business undergoes change, the manager may need to make decisions quickly and so may adopt an autocratic style
Time
An impending deadline might mean that an autocratic style is appropriate
An extended timeframe, with access to ample resources, might lend itself to a manager using a participative style
1.11 Management Skills
are the abilities that managers use to help them complete the tasks that are necessary for the achievement of business objectives
Types of Management Skills
CLIPDD
Communication
Leadership
Interpersonal-skills
Planning
Decision making
Delegation
Communication
Communication: is the ability to transfers of information from a sender to a receiver
Effective communication is clear and concise
Two-way communication is where the manager is able to send a message to the receiver as well as receive and listen to feedback
It can be non-verbal (body language) or verbal (words-written or verbally)
Leadership
Leadership: the ability of a manager to influence and motivate employees to achieve business objectives
effective leadership helps employees work towards a direction
It provides motivation for accepting the importance of the direction
Improves productivity
Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal Skills: the ability of a manager to communicate with a range of people while building strong relationships
Helps to create a positive work environment
Benefit from higher productivity, enhanced problem solving, fewer conflicts and higher quality outputs
If not used, employees can become defensive or display resentment
It is important for relationships to remain professional
Planning
Planning: the ability to define business objectives and determine methods or strategies that will be used to achieve those objectives
Provides a key to short term and long term success
Operational planning (short term): provides specific details of the way the business will operate to help achieve plans, usually daily, weekly or monthly e.g schedules
Tactical planning (medium long term): is flexible, adaptable planning, usually 1 to 2 years e.g trying to achieve business objectives
Strategic planning (long term): planning for the following 2 to 5 years e.g where the business wants to be in the market
Planning process (DADIM)
Define objective
Analyse the environment. With a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats)
Develop alternatives
Implement the plan
Monitor and evaluate
Decision Making
Decision Making: the ability to make a choice on a course of action from range of alternatives
6-step decision making process (IGDACE)
Identify the problem
Gather information
Develop alternatives
Analyse the alternatives
Choose an alternative and implement it
Evaluate
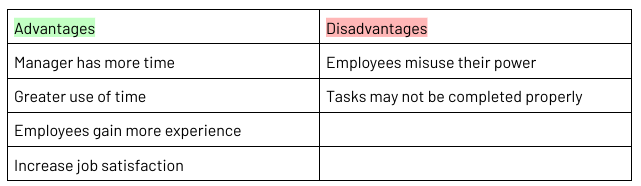
Delegation
Delegation: the passing of authority and responsibility from a manager to employee to achieve objectives
Can help free a manager's time and spread the workload
Delegation occurs in three main ways:
To an employee with strong skills and experience
To a group of employees with a variety of skills and abilities
To an employee without skills or experience who has a mentor (another employee) to develop their skills
1.13 Corporate Culture
Corporate culture: is the shared values and beliefs of the people within a business
Is an internal factor
Two types are official and real
Official corporate culture
What the business wants the shared values and beliefs of the people in the business to be
Just because the business makes official documents, doesn't mean people within the business follow them
Official documents e.g written policies, objectives for the business etc
Real corporate culture
Refers to the actual underlying value, beliefs and behaviours of the people within the business
Benefits of a positive business culture
Reduced staff turnover (amount of money being taken from the business)
Improved productivity
Allows the business to select its best employees (high demand to work there)
Elements of corporate culture
CCHRP
Core values
Communication
Heroes
Rituals and celebrations
Physical environment
Core Values
What the business values most and will not change even when the business changes
Core values can act as guideposts
Communication
Businesses have open two-way communication with managers and employees to demonstrate how they value relationships
Heroes
Are those that the business ‘looks up’ due to the way they demonstrate the business desired values e.g employee of the month
Heroes can be a person to look up to within the business
Rituals and Celebrations
Rituals are those things that occur regularly within a business e.g annual awards ceremony
Physical Environment
The space in which employees work in another element of the corporate culture e.g a more open space