Ophth: Review of summer concepts
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
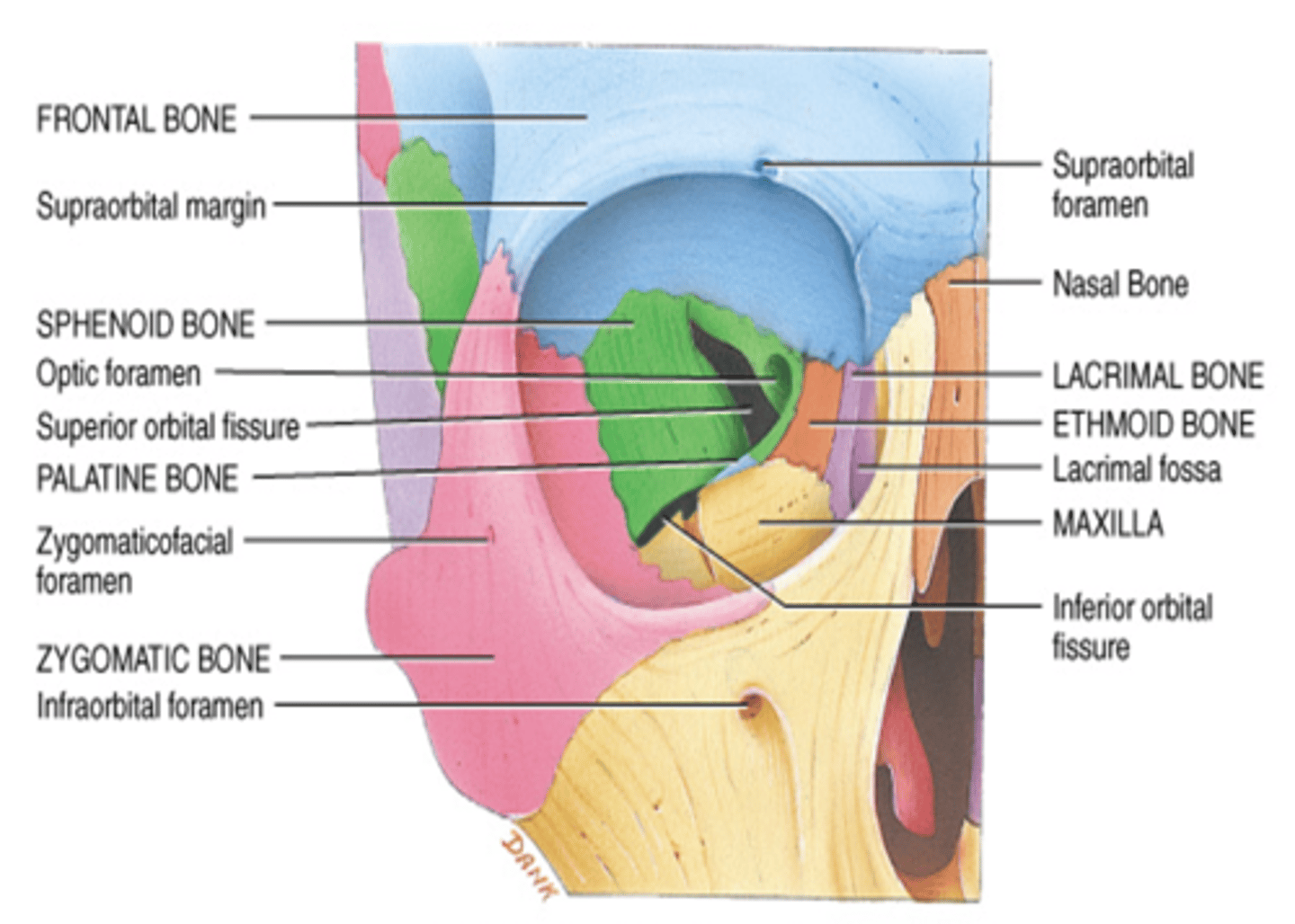
What bones make up the medial wall of the orbit?
Maxilla, Lacrimal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Frontal Bones
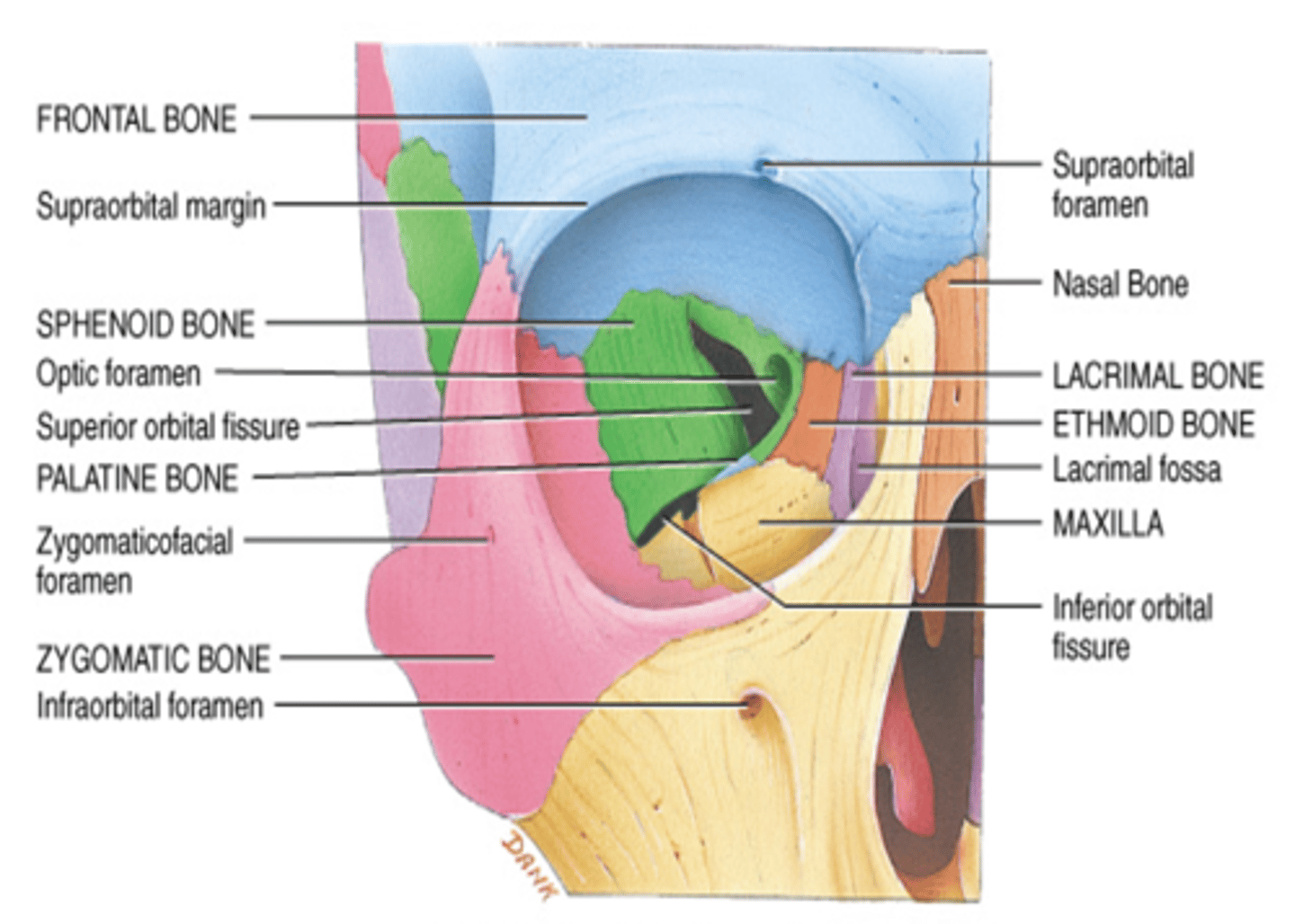
What bones make up the lateral wall of the orbit?
Zygomatic & Frontal Bones
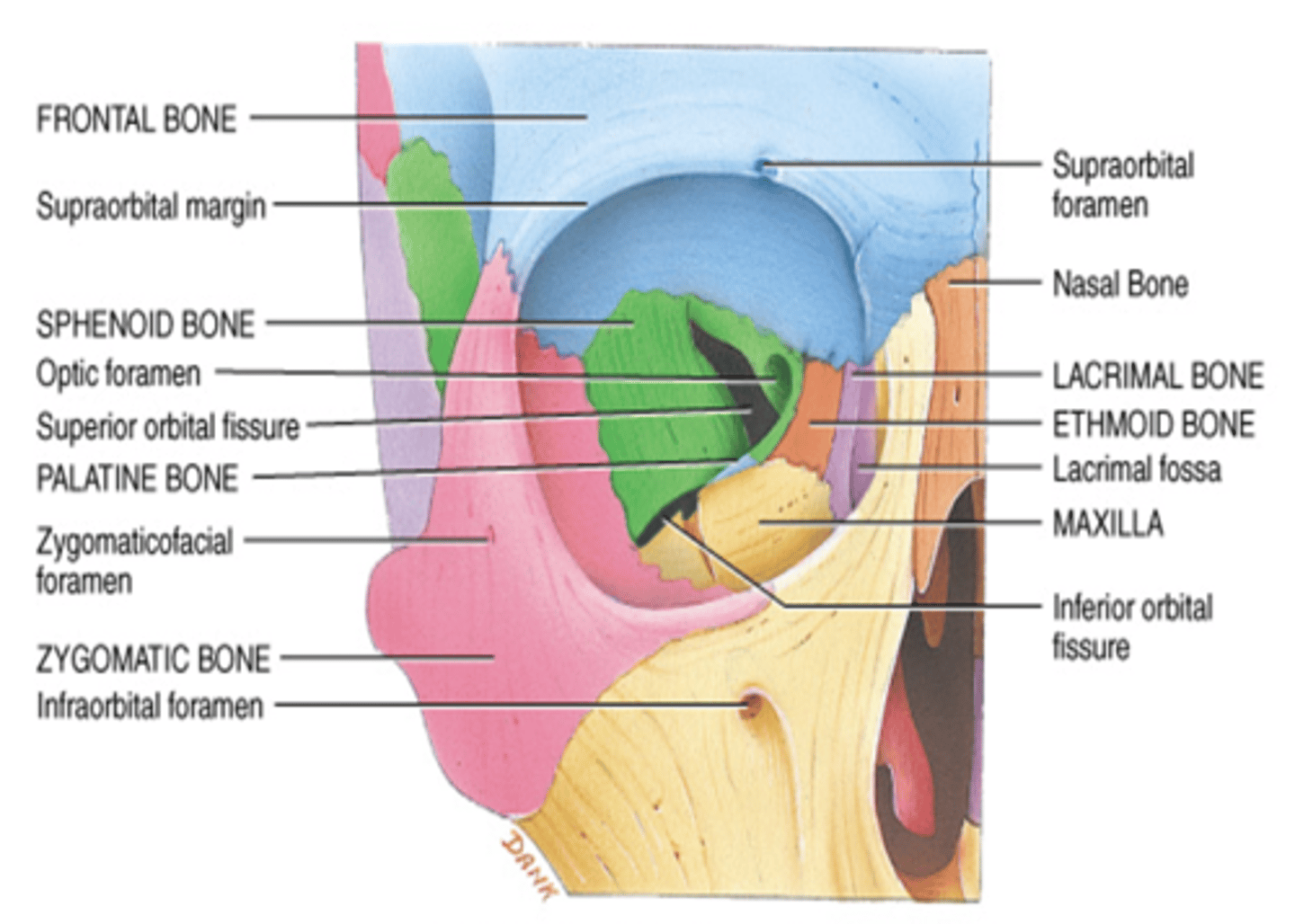
What bones make up the inferior wall of the orbit?
Maxilla & Zygomatic Bones
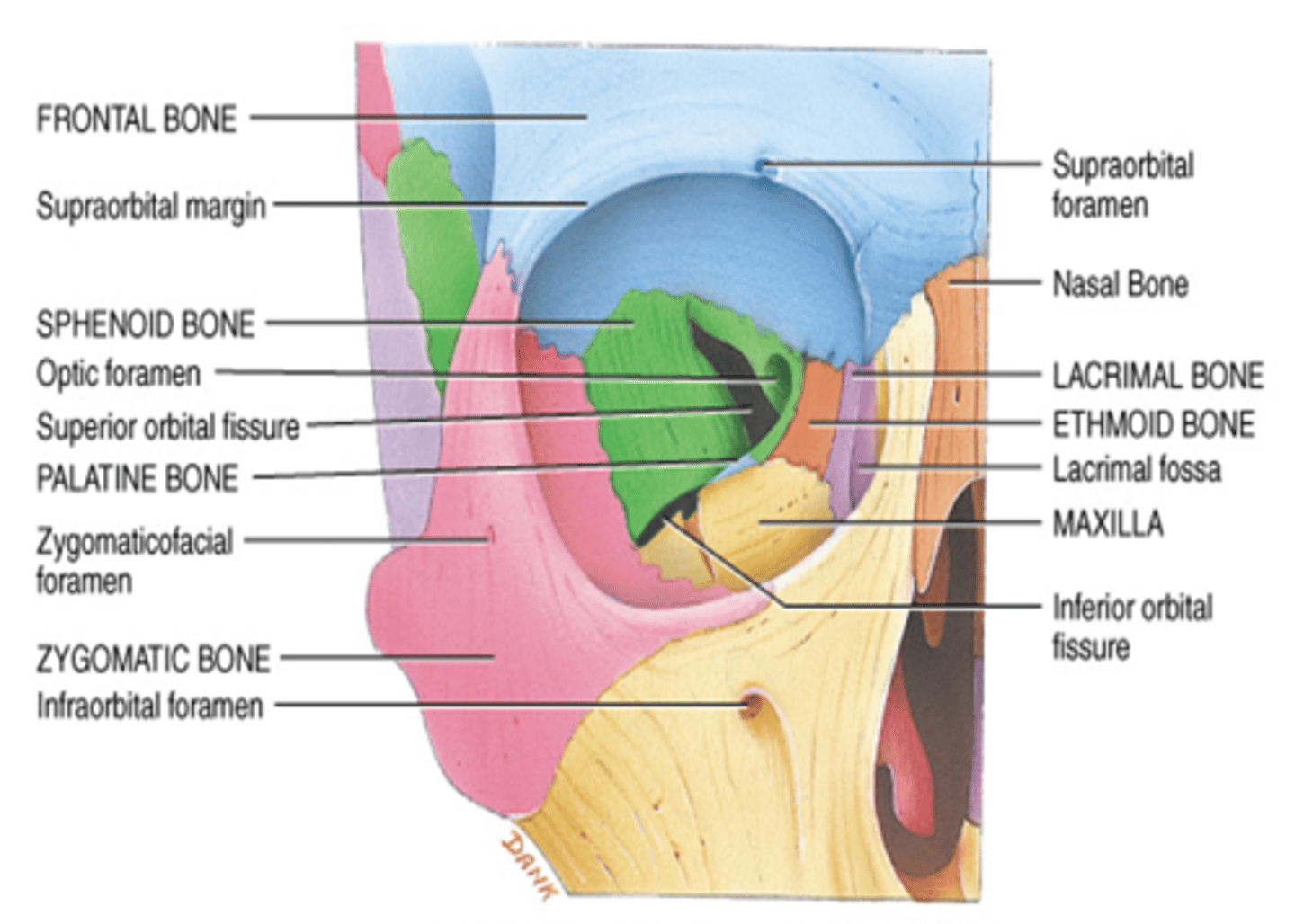
What bones make up the superior wall of the orbit?
Frontal bone
What divides the eye into posterior and anterior cavities?
The ciliary body and the lens
The anterior cavity is filled with what fluid?
Aqueous humor
What fluid fills the posterior cavity?
Vitreous humor
Eyelids AKA
Palpebrae
- Connected at the medial and lateral canthus.
What do the Meibomian (tarsal) glands secrete? And what does the secretion do?
Lipid rich product which keeps the eyelid from sticking together
Where are eyelids connected at?
The medial and lateral canthus
The Meibomian (tarsal) glands are modified ______________ glands that secrete ....
Sebaceous glands that secretes outer lipid layer to the tear film
Innervation of lateral rectus m
CN VI (Abducens)
Innervation of superior oblique m
CN IV (Trochlear)
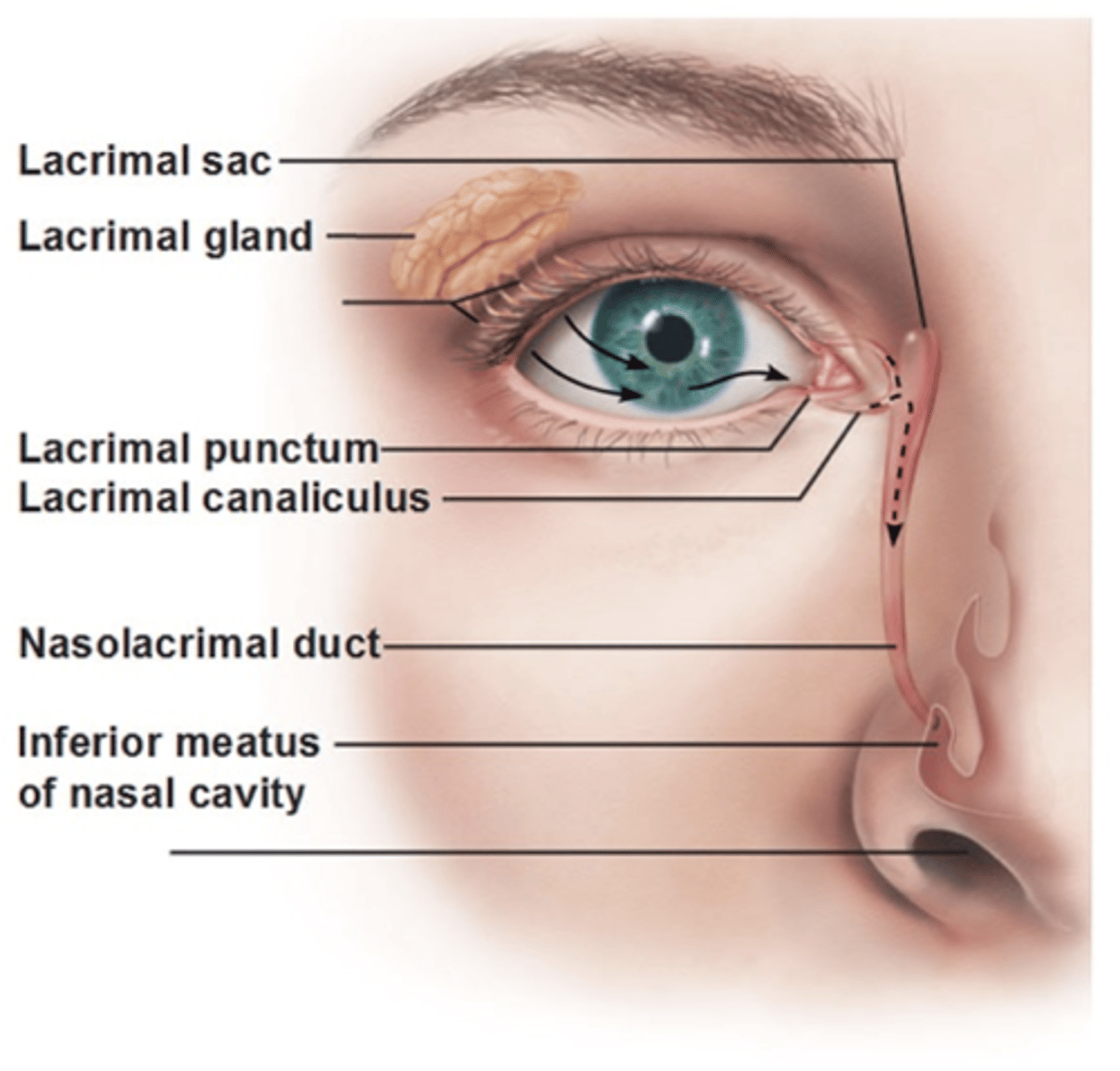
Lacrimal gland
Produces the aqueous portion of the tear film.
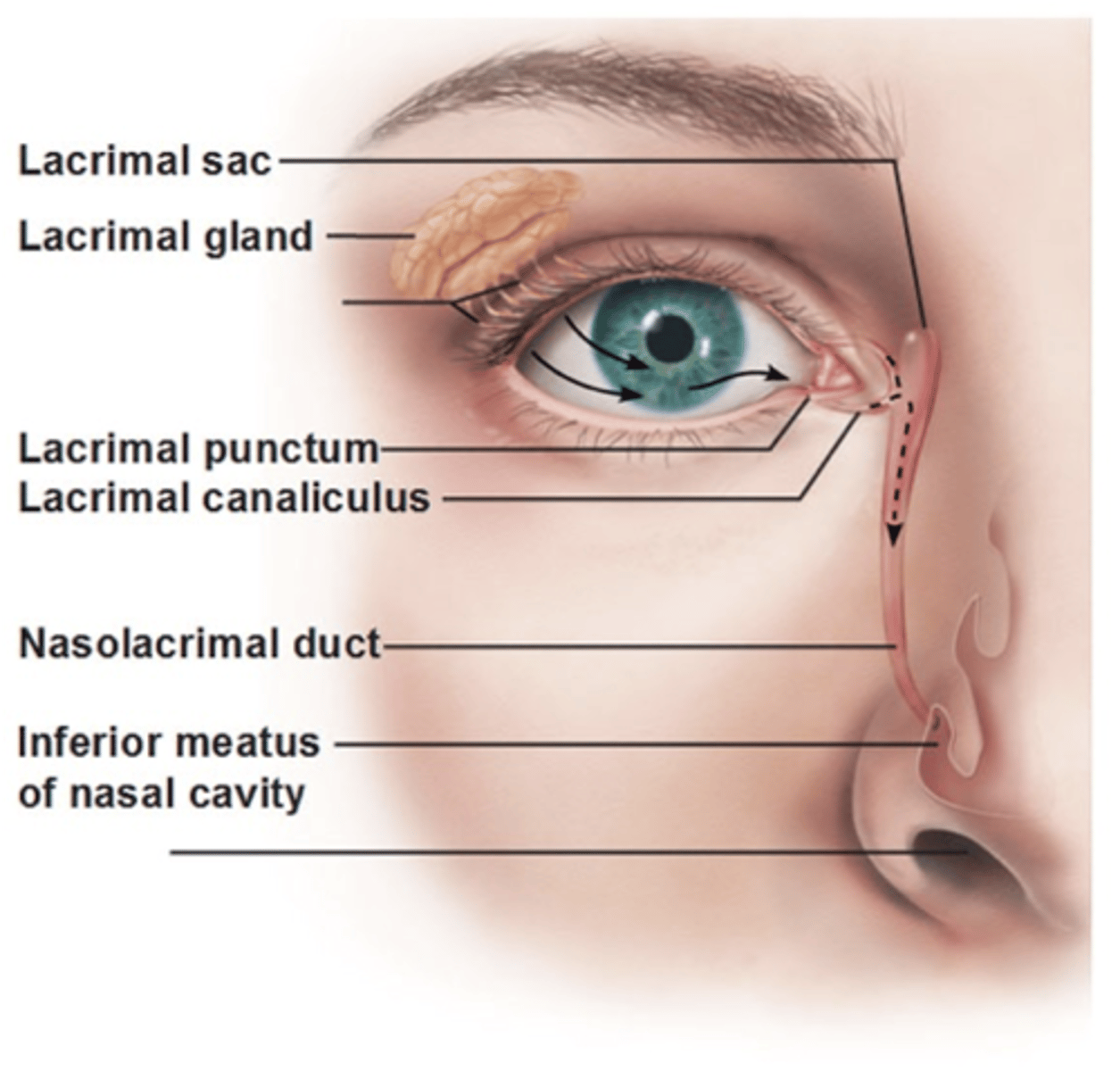
Lacrimal punctum
Small hole medial edge of eyelid. Valves that drain used tears away from your eye.
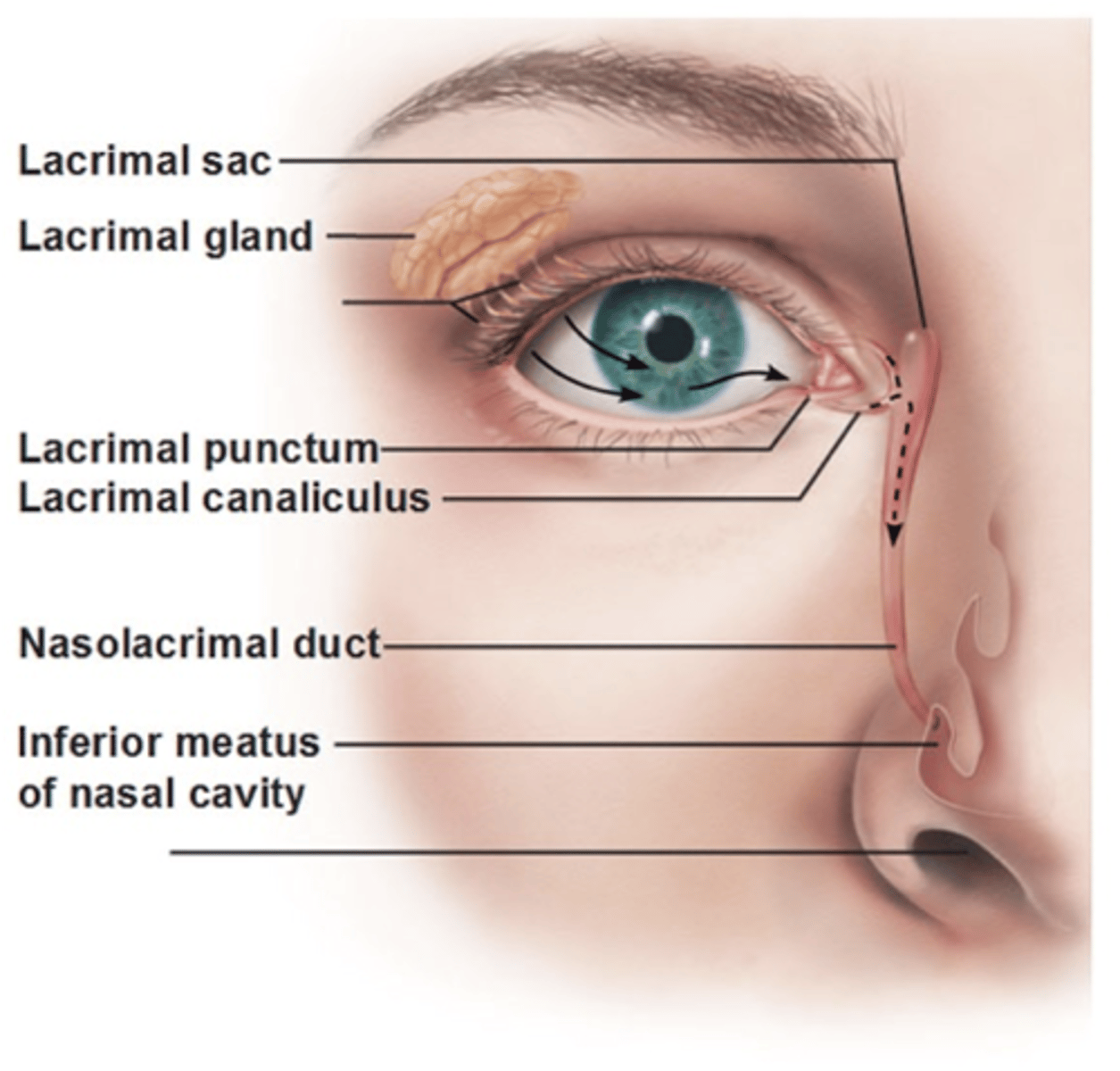
Lacrimal canaliculus
small channels that drain tears from eye surface into nasal cavity.
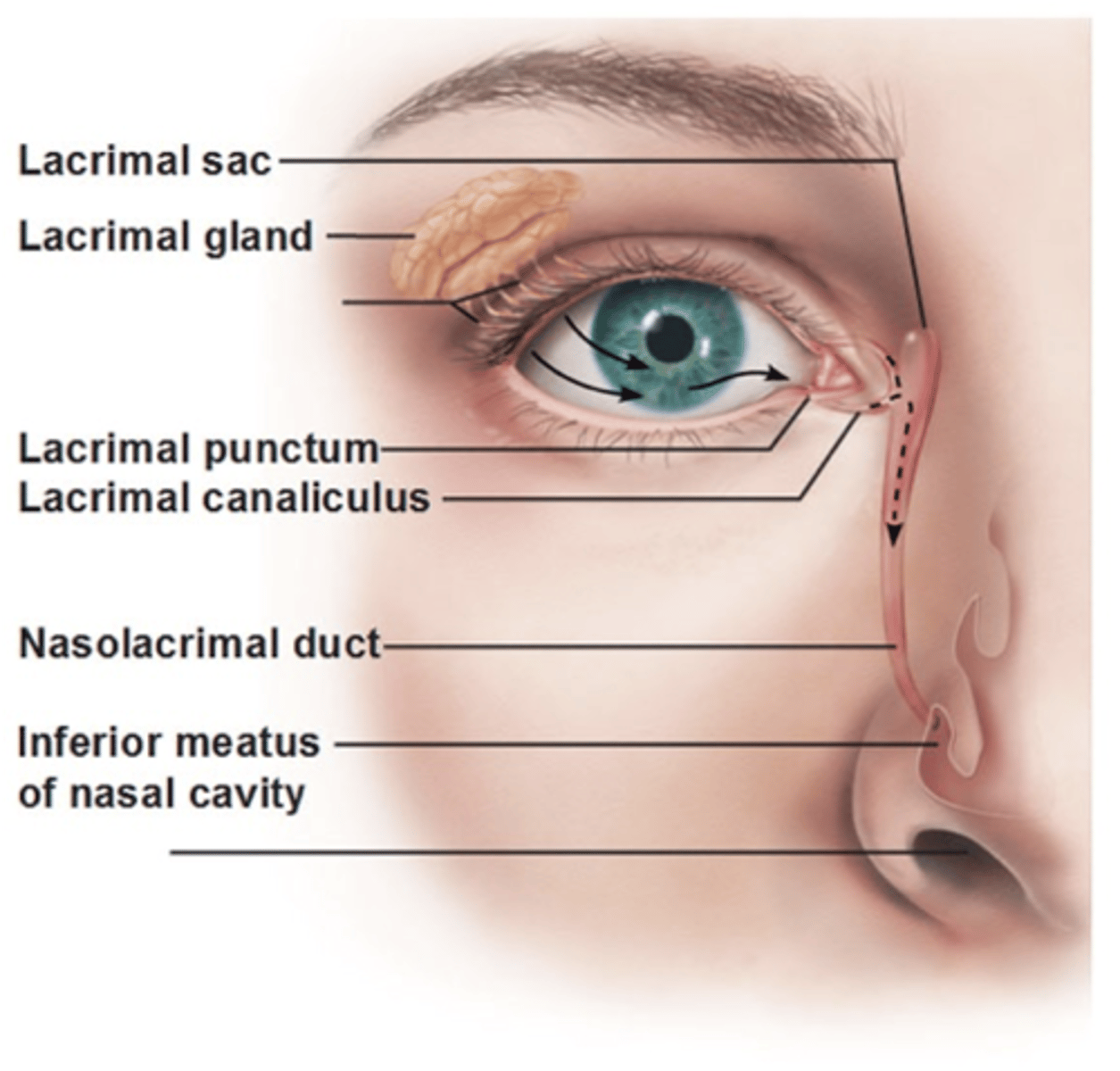
Lacrimal sac
Production and drainage of tears
- Reservoir for tear overflow
- Drains eye of debris and microbes
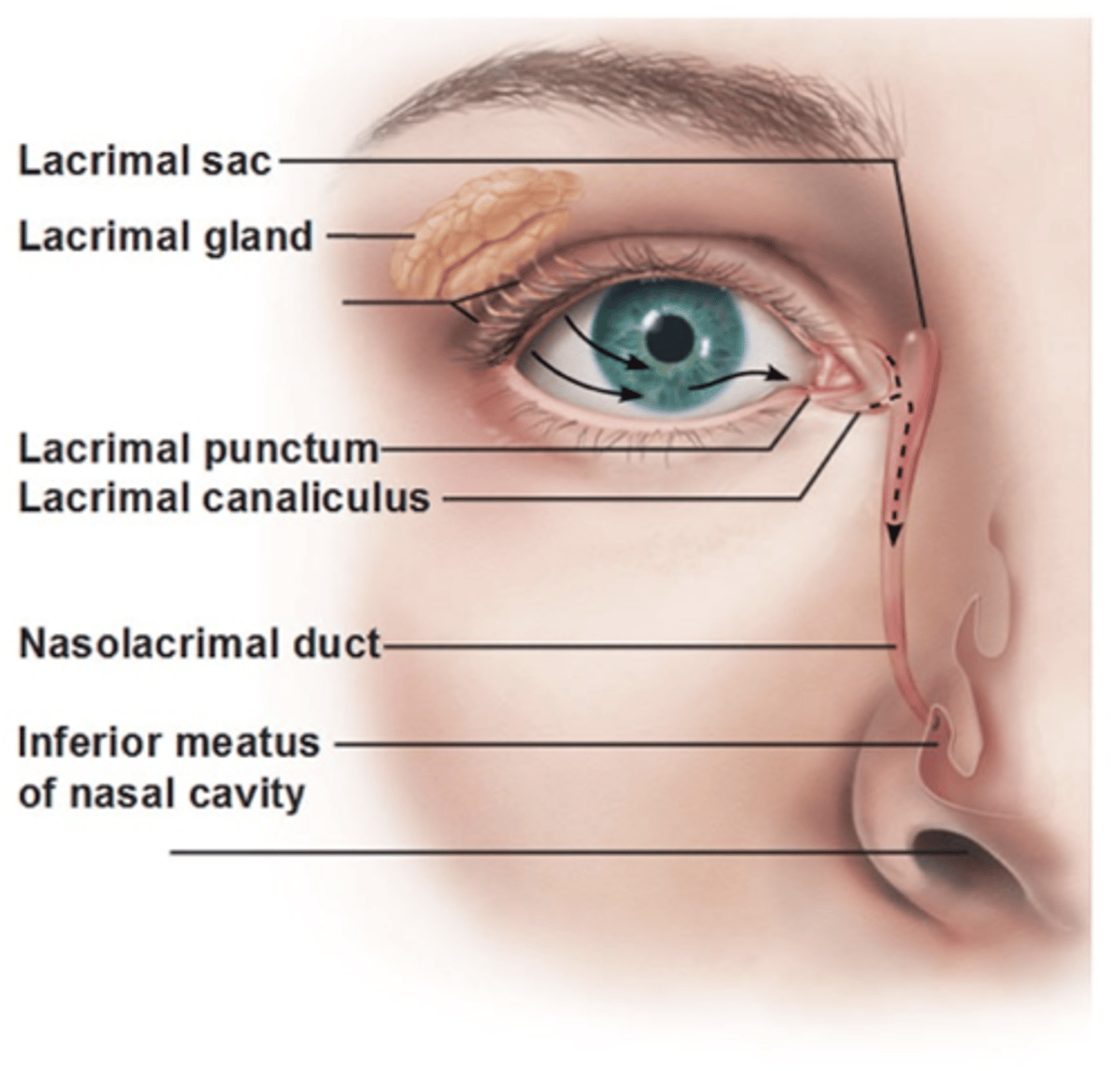
Nasolacrimal duct
Connects lacrimal canaliculus to lacrimal sac which drain tear fluid into nasal cavity.
Inferior concha
- Scroll shaped bone that is paired with superior and middle concha
- Along with the superior and middle nasal conchae, the inferior nasal concha works to filter, humidify, and warm the air that we breathe preventing cold air from reaching the lungs.
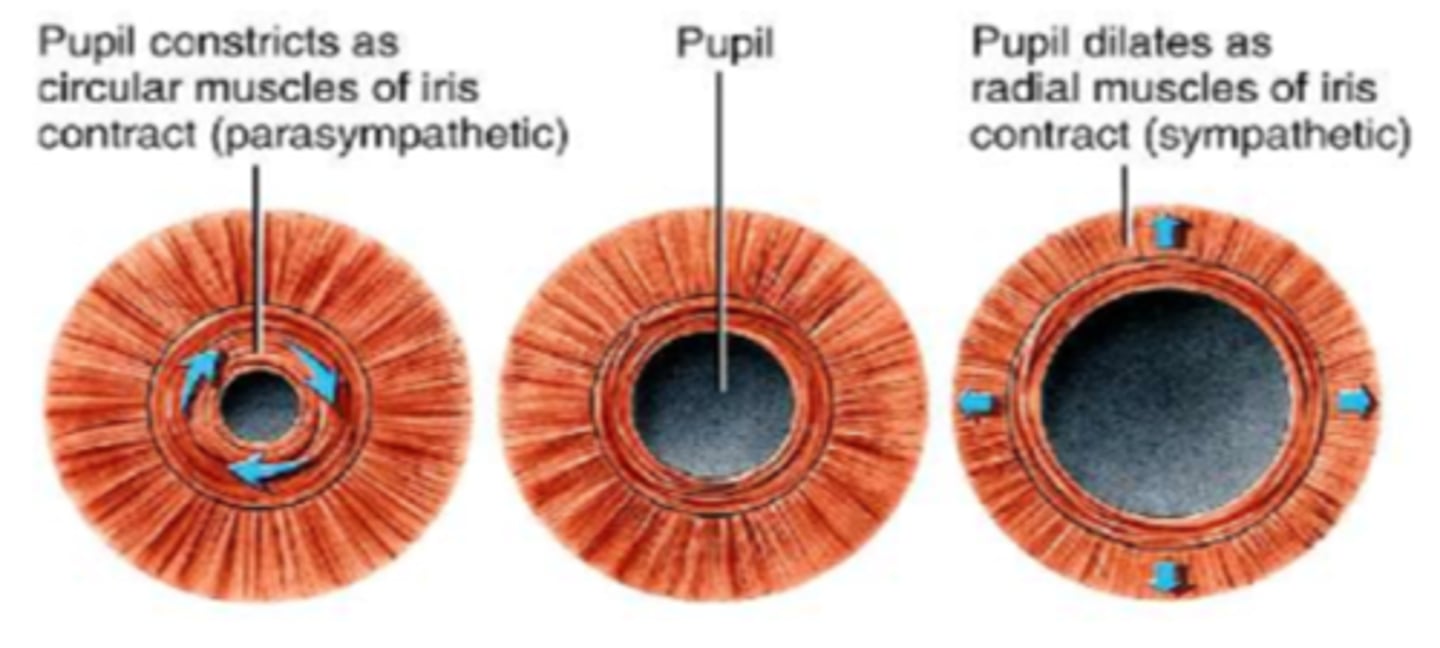
Sphincter pupillae m. (circular m., pupillary sphincter m.)
◦contraction causes constriction of pupil
◦Parasympathetic system
◦Innervated by CN III
◦Miosis or myosis
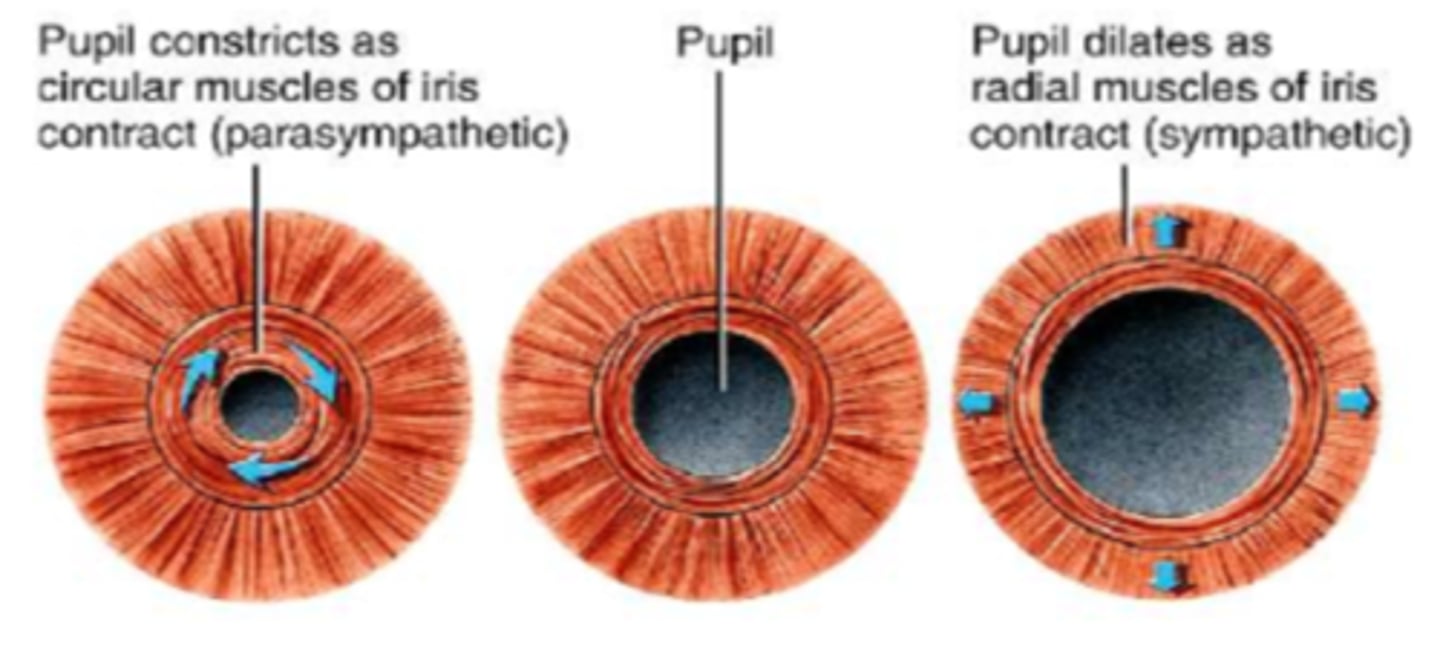
Dilator pupillae m. (radial m., pupil dilator m.)
◦Contraction cause pupil dilation
◦Sympathetic system
◦Innervated by CN III
-Mydriasis
Which muscles are responsible for constriction?
Circular Smooth Muscles
Which muscles are responsible for dilation?
Radial Smooth Muscles
Contraction of the sphincter pupillae muscle causes _______________ of the pupil
Constriction
Is constriction of the pupil a parasympathetic or sympathetic response? And what CN is this nn by?
Parasympathetic; CN III
Constriction of the pupil is also called...
Miosis or myosis (constriction)
What does contraction of the dilator pupillae m cause?
Dilation of the pupil
Is contraction of the pupil via radial muscles a parasympathetic or sympathetic response? And what CN is this nn by?
Sympathetic; CN III
Contraction of the pupil via radial muscles is also called...
Mydriasis (dilation)
Function and nn of the orbicularis oculi m
Closes eye tight
Innervated by CN VII (Facial)
Function and nn of levator palpebrae m
Elevates superior eyelid
Innervated by CN III (Oculomotor)
Bulbar conjunctiva covers the ____ aspect of the eye
Anterior
What is the role of sclera?
maintains shape of the globe
The cornea provides a clear, refractive layer that helps focus light onto the
Retina
What is the center aperture of the iris
The pupil
The retina contains _______, ___________, ___________ & ____________
Rods, cones, macula & fovea
What is presbyopia?
Natural loss of accommodation due to age
- Inability to focus on objects at a normal reading distance starts around age 40
What is astigmatism?
Refractive errors horizontally and vertically
What is myopia?
Nearsightedness (Can see near, but not far away)
*Images are formed in front of the retina causing blurry vision at a distance.
What is hyperopia?
Farsightedness (Can see far but not close up)
*Image focuses behind the retina.
What is amblyopia?
Reduction of vision in one eye due to eye-brain inability to work together
What is color blindness?
Defective or absent color perception
What is diplopia?
Double vision
What is emmetropia?
"Normal" refractive condition of the eye = clear vision
20/20
What is anisometropia?
Refractive power of one eye differs from the other
- One pupil is larger than the other.
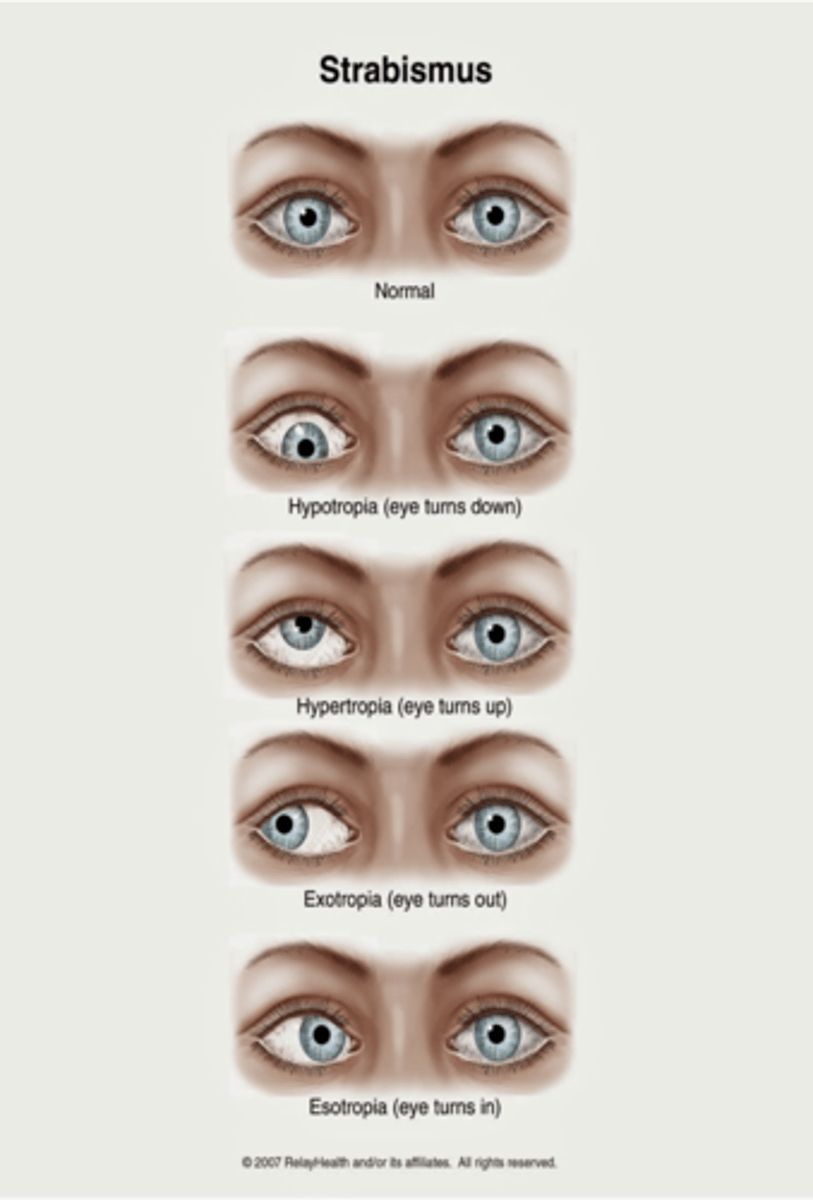
What is strabismus?
Misalignment of eye
Color blindness is usually ___________: X-linked
Hereditary
What colors is color vision based on the perception of what colors?
Red, green and blue
- If perception defect is one color, that color will be perceived as a combo of the other two
What color blindness deficiency is most common?
Red-green
How do we test for color blindness?
Using Ishihara plates
What does 20/50 mean
Pt sees at 20ft what a person with normal vision can see at 50ft
What is hypotropia?
Downward alignment (tropias are constant)
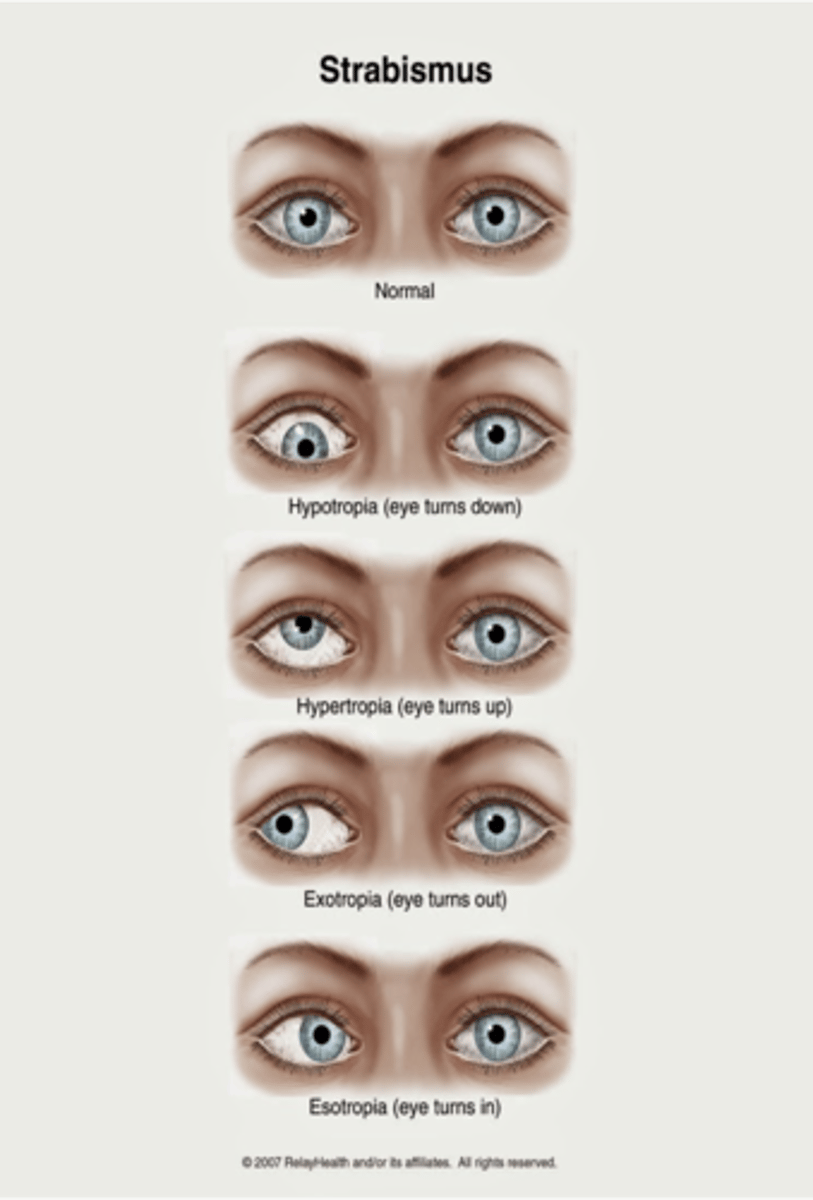
What is hypertropia?
Upward alignment (tropias are constant)
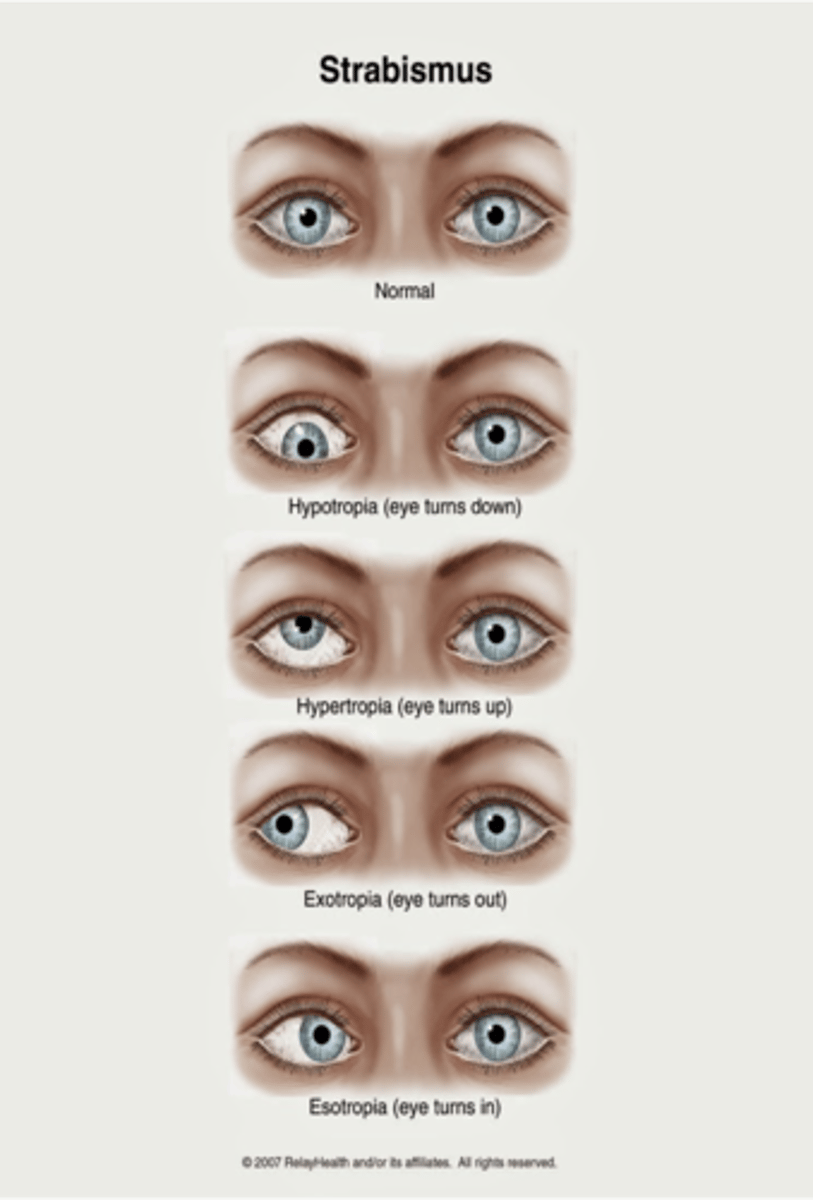
What is exotropia?
Outward alignment (tropias are constant)
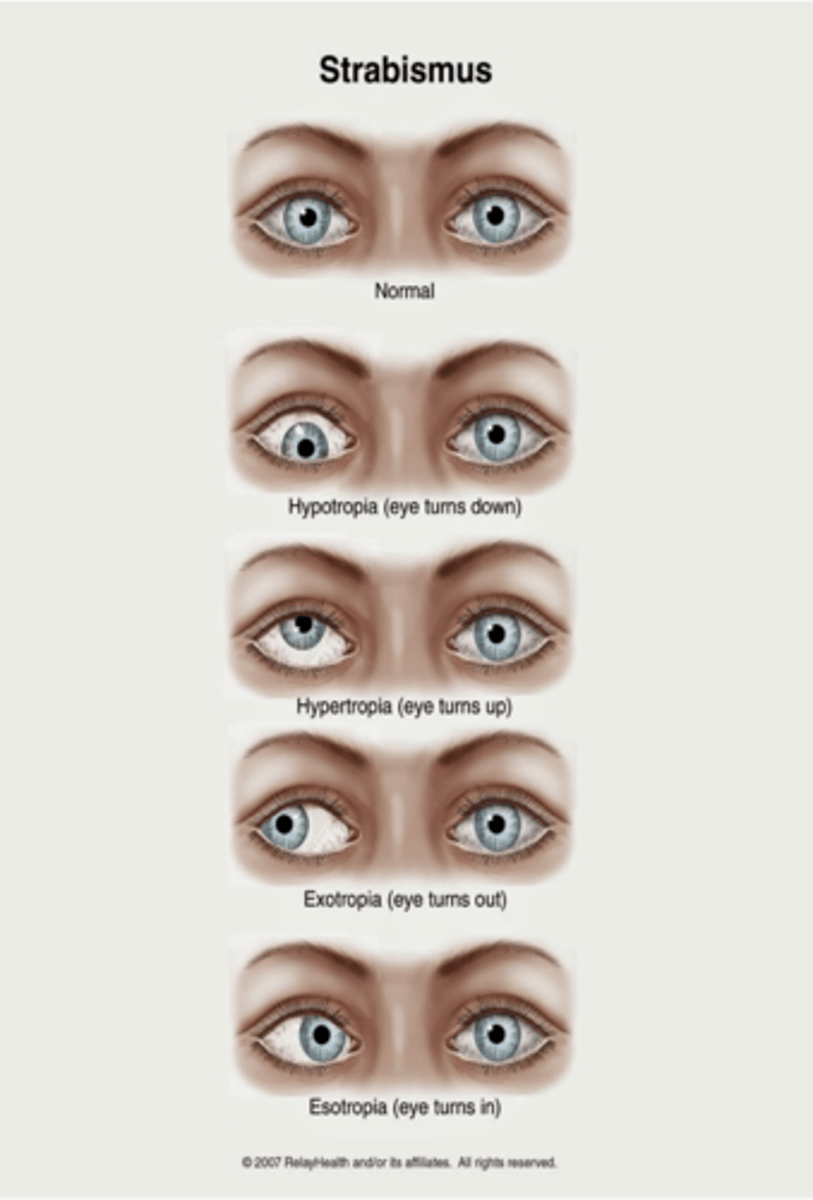
What is esotropia?
Inward alignment (tropias are constant)
What is Esophoria?
Inward (phorias are latent or transient)
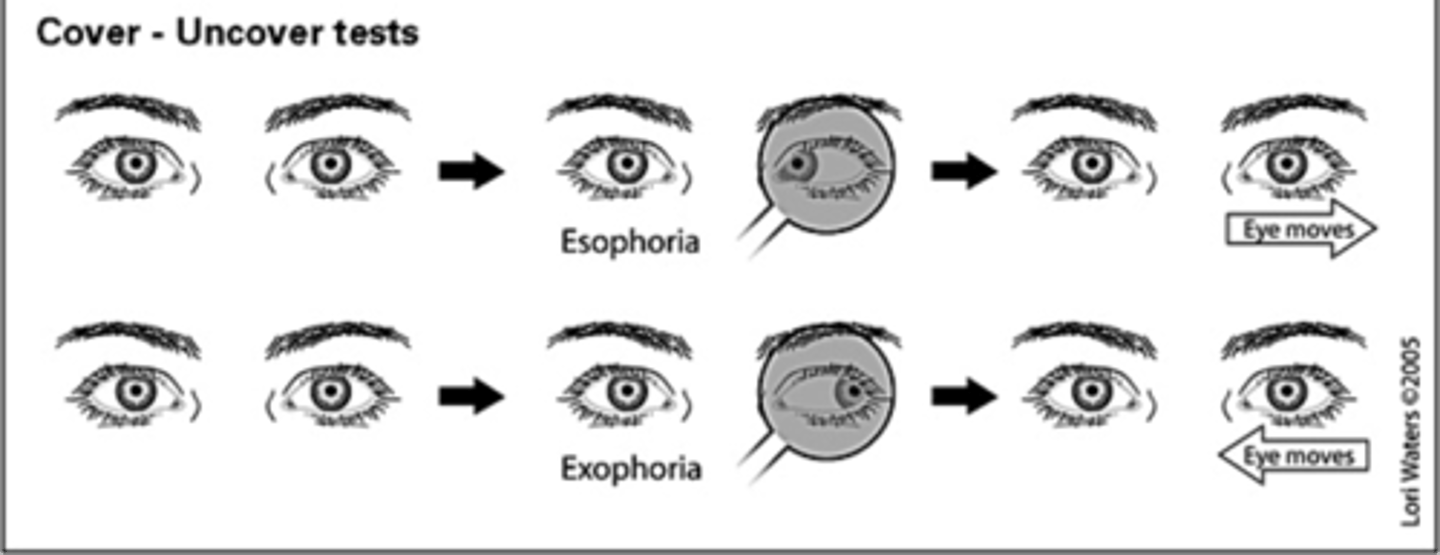
What is exophoria?
Outward (phorias are latent or transient)

What is anisocoria?
Pupillary inequality of less than 0.5mm
What is normal eye pressure?
10-21mmHg
A lesion of the temporal and nasal optic n would cause what
Inability to see through the left eye
(#1)
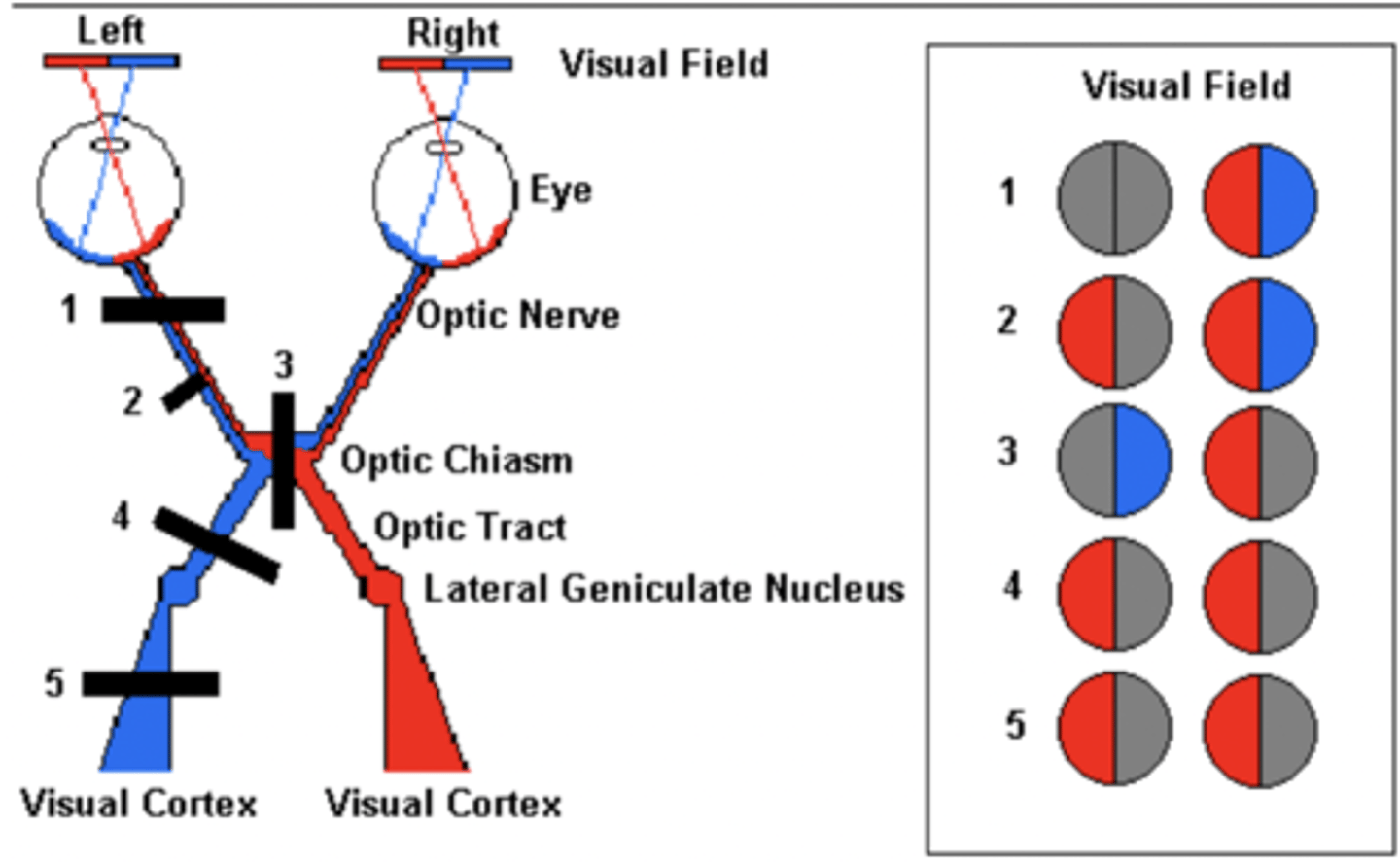
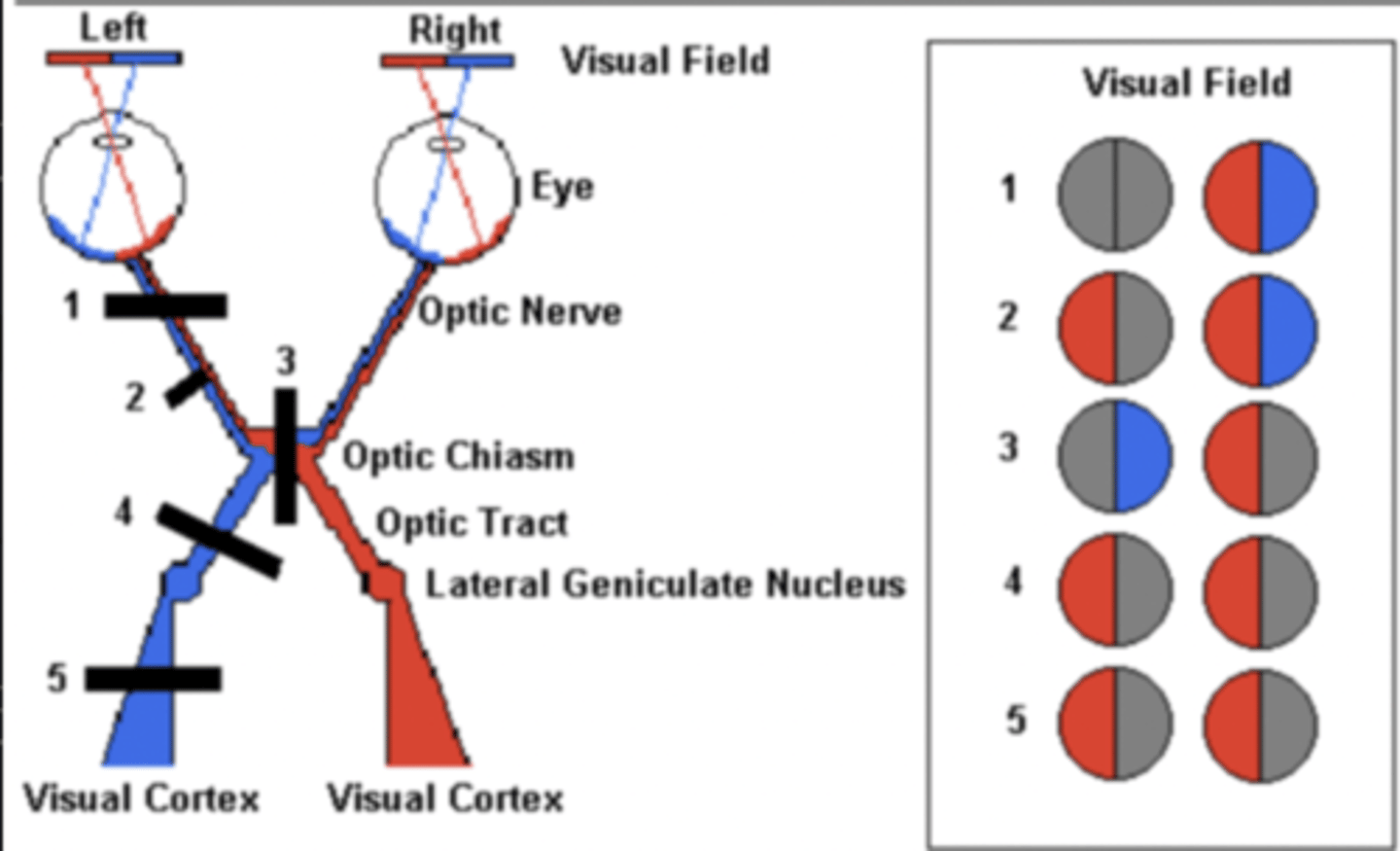
A lesion at the optic chiasm would cause what
Inability to see thru the lateral portions of the left and right eyes
(#3)
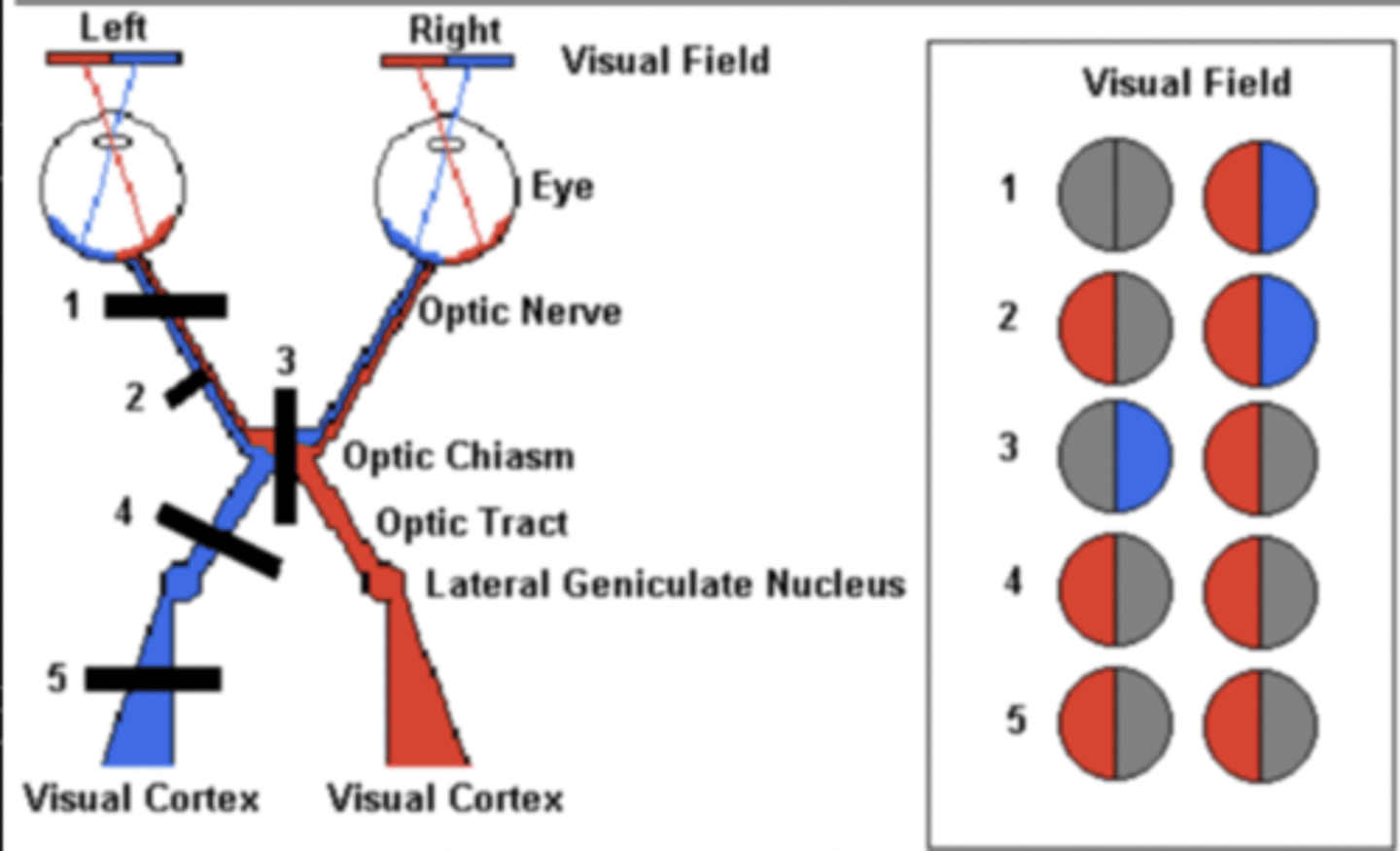
A lesion at the optic tract (closer to the optic chiasm) would cause what
Loss of vision in the medial aspect of the left eye and lateral aspect of the right eye
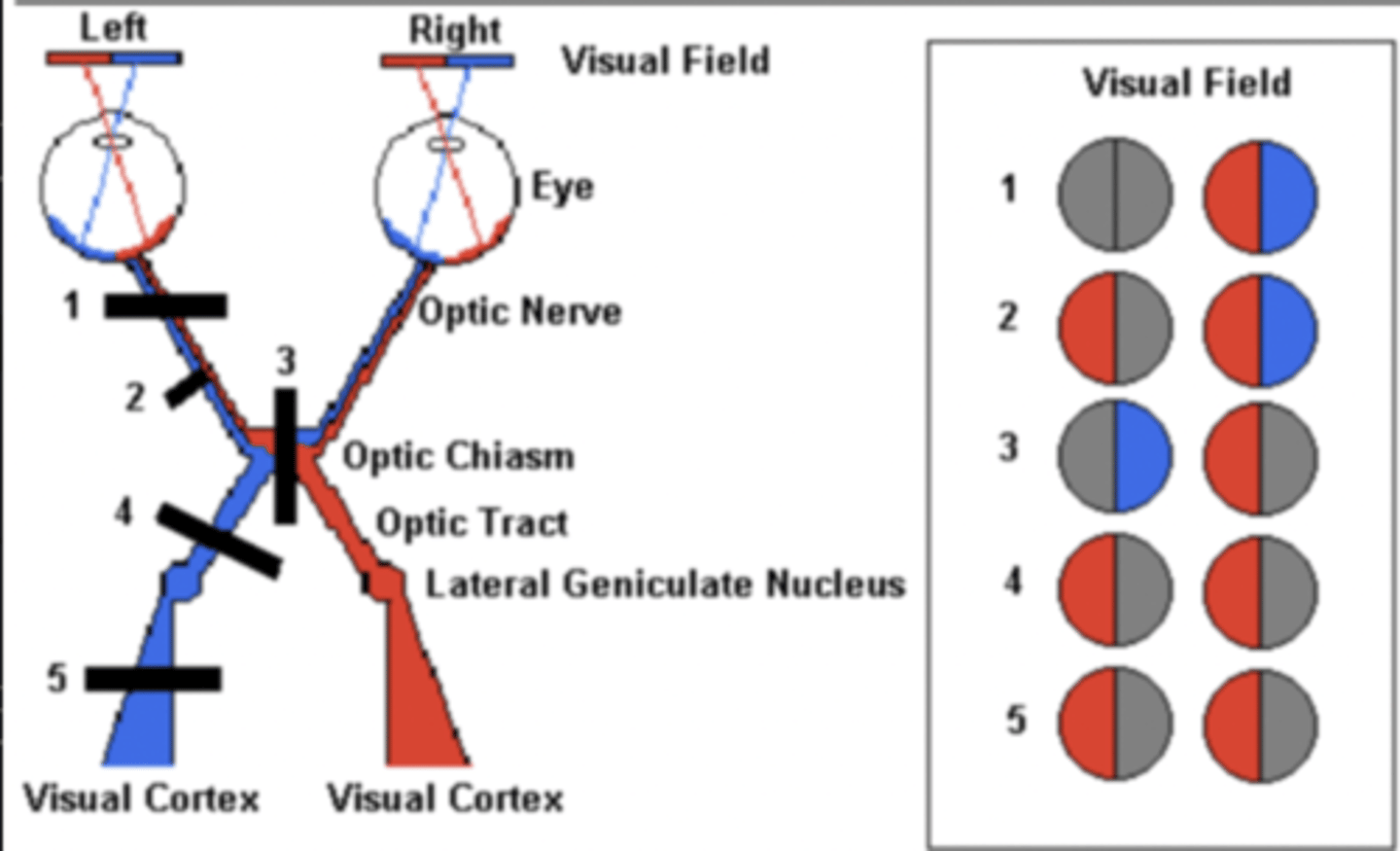
A lesion at the optic tract (further away from the optic chiasm) would cause what
Loss of vision in the medial aspect of the left eye and lateral aspect of the right eye
Slit Lamp
- Instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye.
- It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope.
- The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segment and posterior segment of the human eye,
- It gives a closer look at the different structures at the front of the eye and inside the eye.
- It’s a key tool in determining the health of your eyes and detecting eye disease.
- The slit lamp also gives a detailed view of the back of the eye as well. To do this, your ophthalmologist will dilate (widen) your pupils with dilating eye drops.