Volcanoes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
explosive eruption
felsic magma under pressure; cooler temp
effusive eruption
mafic magma, lower pressure, higher temperature
A'a lava flow
rubbly, slow
Pahoe hoe lava
smooth, ropey, taffy
how lava cools
from the outside in
silicas affect on lava
makes lava not flow good; the more of it the less likely the lava is gonna flow
Pyroclastic's
rock material and lava violently ejected from the volcano
pyroclastic flow
hot gases and particles of rock flying through the air; stays close to the ground
pyroclastic fall
pyroclastic material is ejected into the air and falls back to the ground; can go over large distances
pyroclastic deposits
Accumulations of fragmental volcanic debris; ash, cinders, bombs
cinders
cunks of rocky lava
visocity
resistance to flow
felsic magma is generated at
subduction zones
Magma Properties
gas content, visocsity
gas content causes
explosively
influences of gas content
amount of gas on magma type, sub zones
water vapor is more soluble in
felsic magma
low viscosity
freely flowing
high viscosity
slow
influences on viscosity
molecular bonds
size and shape of a volcano are determined by
lava type
steep sided volcanoes are likely made of
felsic lava
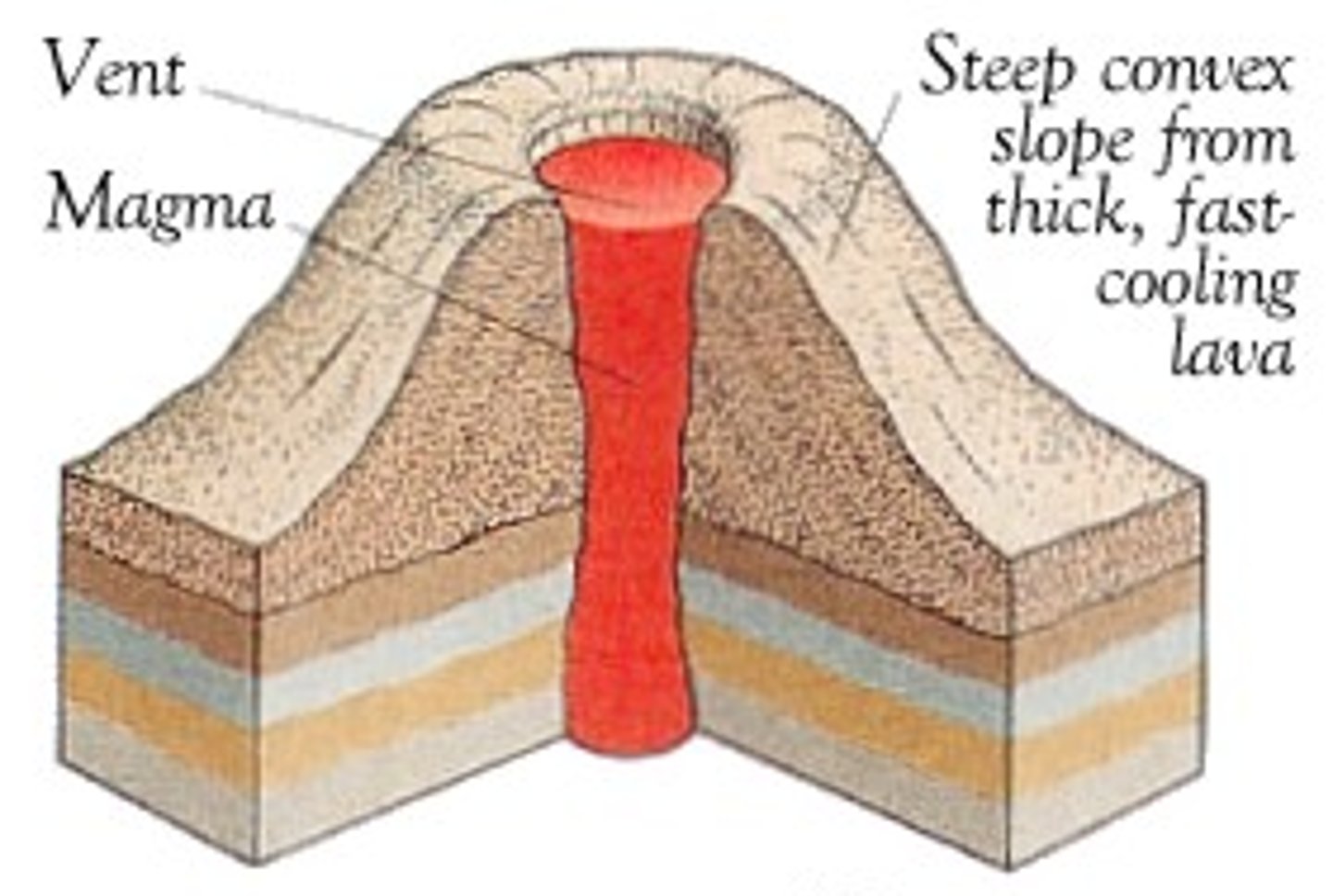
cinder cone volcanoe
- small magma chamber
- can have a field of them
- made of pyroclastic material not lava
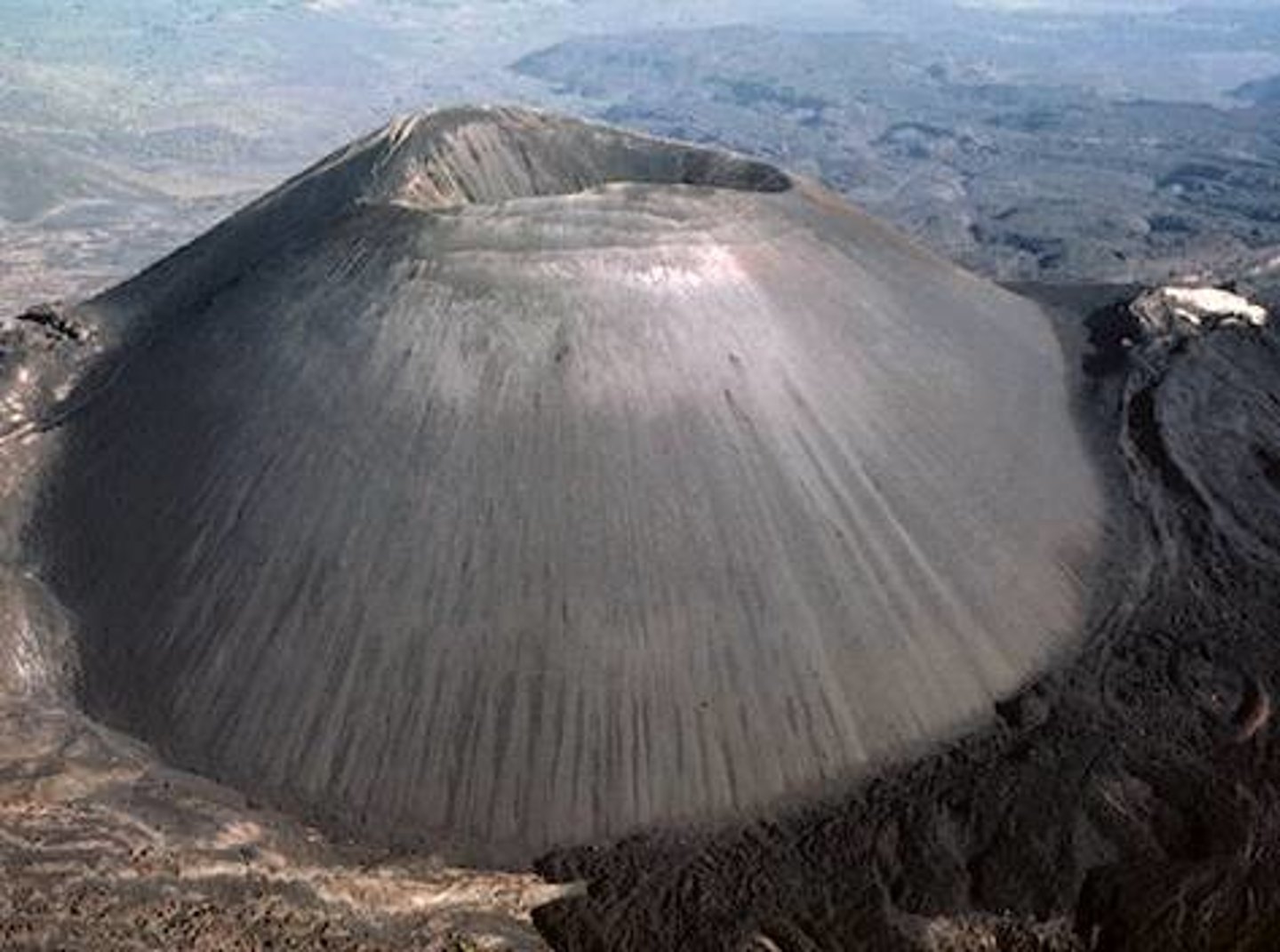

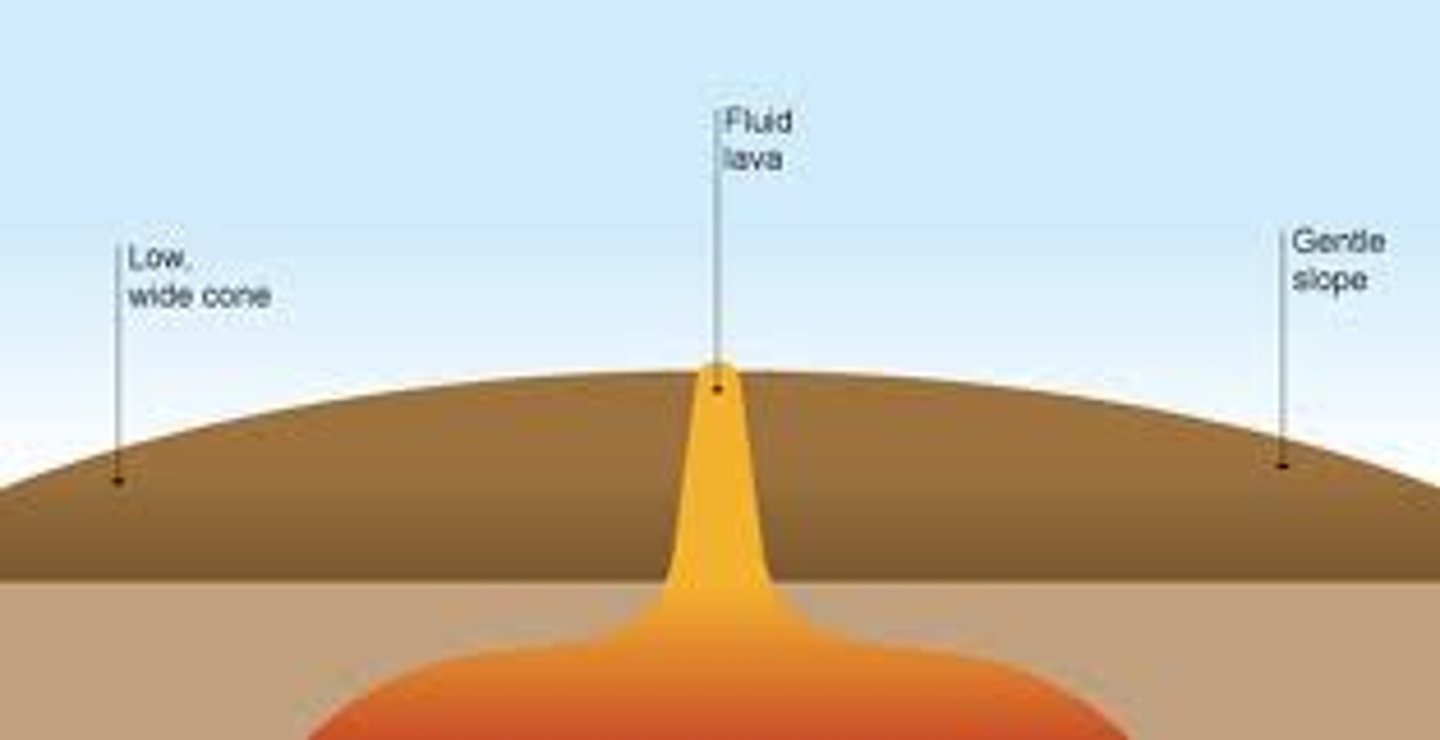
shield volcanoes
made of mafic lava, Hawaii, can erupt in many different directions in the chamber
caldera
the sunken collapsed part of volcano where lava comes out from ; the crater
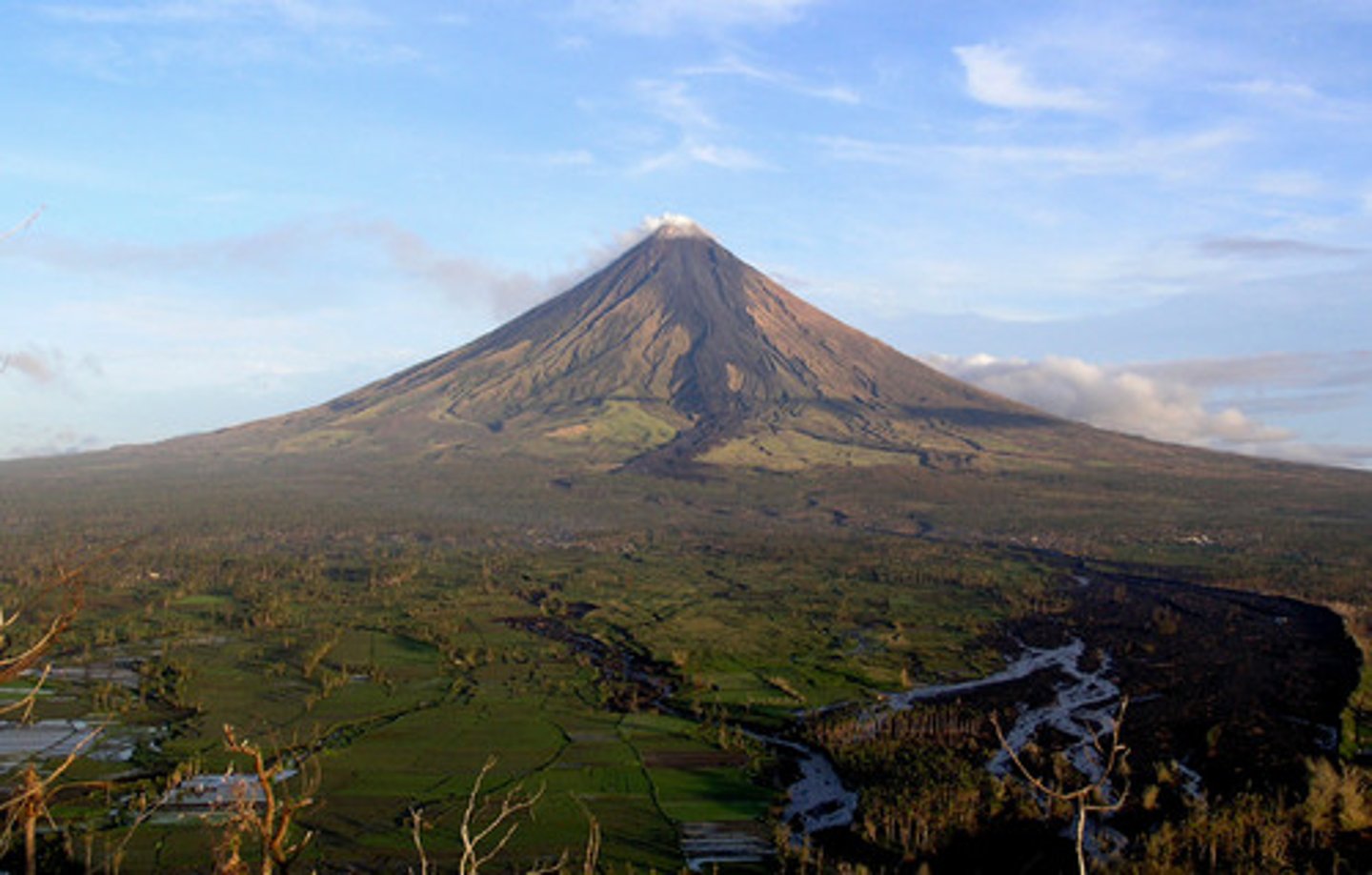
Stratovolcano
- what we think of a volcano
- explosive eruptions
-landslides are very common
- steep sided
- have different stratification from layers that make it up

stratification layers
felsic lava flow and pyroclastic material
dome complex
very felsic, don't erupt explosively, not very common
caldera formation
- after a volcano erupts the magma chamber is depleted
- took energy to erupt now have void where there is no magma so the broken rocks collapse down b/c no underlying support
which type of lava would be runny(low viscosity)
mafic
which type of lava would have high viscosity
felsic
Which type of lava will let gasses escape easily
mafic
rhyolite igneous rock
felsic, more explosive, pyroclastic deposits, low temp
basalt rock
mafic, less explozive, lava flows, higher temp
more felsic means more
explosive and viscous
volcanic hazards
Lava flows, Lahars, Pyroclastic flows, Ash falls, Volcanic landslides, explosive blast
Lava flow
slow moving, cools from outside in
Pyroclastic flow
high density mixture of hot,driy rock fragments and gases, generate quickly, very destructive
Ash falls
jaged fragments produced from explosive volcanic eruptions, cause haze
lahars
eruption mixed with water, water sitting on top of a volcano, muddy river
how to predict if a volcano will erupt
- earthquake activity
- changes in heat flow
- changes in shape
- increase gas and steam
weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
erosion
entrainment, rocks being picked up and moved
production of sedimentary rocks
weathering, erosion, transport, deposition, lithification
physical weathering
taking a solid rock/mineral and making them into smaller pieces
freezethaw
water continuously seeps into rocks where it freezes and expands
salt wedging
salt seeps into rocks cracks and expands and contracts
root wedging
the roots of a plant (typically a tree) wedge into a crack in a rock and, as the plant growns, splits the rock.
sand blasting
How wind mechanically weathers rock
How physical weathering increases chemical weathering
more broken up rock increases SA which increases chances
chemical weathering
-takes place at the surface or near surface,
-need oxygen and water
Acidic water
helps speed dissolution process along
minerals with ionic bonds
makes them nonresistant to chemical weathering
Silcate Minerals
very resistant to chemical weathering
minerals with iron
weak resistants to chemical weathering
Felsic and weathering
more resistant to weathering
influences on chemical weathering
climate, type of rock, time of exposure
immature
non resistant minerals
mature
resistant minerals