Comprehensive First Aid, Hygiene, and Sanitation for Military Personnel
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Why is personal hygiene important for soldiers?
It is crucial for clean and healthful living, which supports the unit's mission accomplishment.
What are the basic health guidelines for maintaining hygiene?
1. Keep your body clean; bathe daily. 2. Change underclothing daily. 3. Change wet clothing immediately. 4. Brush teeth twice a day. 5. Wash hands after certain activities. 6. Use personal utensils. 7. Use mosquito nets. 8. Drink only treated water. 9. Use designated areas for relieving oneself. 10. Exercise regularly. 11. Avoid venereal diseases. 12. Set an example of cleanliness.
What should you do if your clothing gets wet?
Change your clothing, shoes, or socks immediately to avoid illness.
What is the recommended frequency for brushing teeth?
At least twice a day, preferably after waking up and before bed.
What is the purpose of using mosquito nets?
To protect against mosquito bites and potential diseases they may carry.
What are the measures for maintaining sanitary conditions in military camps?
1. Build camps around a sanitary plan. 2. Control water supply and purify drinking water. 3. Locate heads and urinals away from food and water sources. 4. Maintain cleanliness in the galley. 5. Combat pests through proper waste disposal.
What is first aid?
Immediate and temporary care given to a victim of an accident or sudden illness before professional medical help is available.
What are the main objectives of first aid?
1. To save life. 2. To prevent further injury. 3. To preserve vitality and resistance to infection.
What should you do first when providing first aid?
Check for danger and then check for the victim's responsiveness.
What is the critical time to restore breathing to prevent brain damage?
Four minutes.
What are the types of hemorrhage?
1. Arterial Bleeding: bright red, spurting blood. 2. Venous Bleeding: dark red, steady flow. 3. Capillary Hemorrhage: oozing blood, common type.
How do you control external bleeding?
Use direct pressure, digital pressure at pressure points, compress and bandage, ligation, and elevation of the injured part.
What should you not do with an unconscious victim?
Do not try to give any solid or liquid substance by mouth.
What is the antidote for swallowed poison?
Dilute with water or milk to lessen the concentration of the poison.
What is the importance of personal cleanliness in a military setting?
It reflects the leadership, discipline, and supervision of the unit.
What should be done to prevent the spread of diseases in military camps?
Carry out continuous campaigns against insects and rodents, and maintain proper sanitation.
What is the recommended action if a casualty needs to be moved?
Seek assistance if possible and handle the victim gently.
What is the significance of washing hands with soap and water?
It helps prevent the spread of infections, especially after specific activities.

What should be done if a soldier is exposed to venereal diseases?
Avoid contact with infected persons and seek treatment at early stages.
What are the guidelines for constructing heads and urinals in military camps?
They should be located away from the galley and water supply, ideally downwind from these areas.
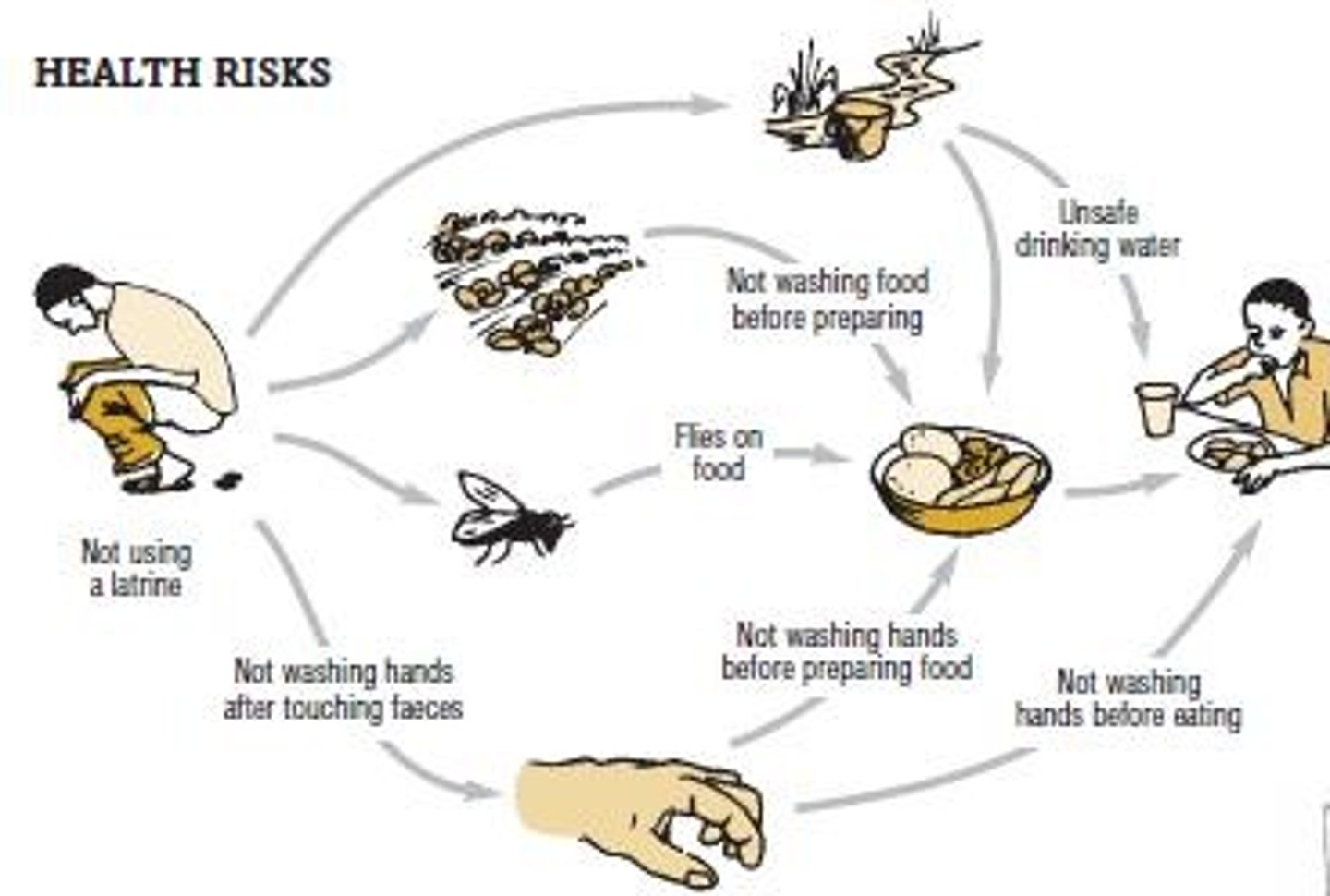
What is the role of a medical officer in water purification?
To approve the methods used for purifying drinking water.

What is the purpose of exercising regularly in a military context?
To maintain physical health and prevent the negative effects of inactivity.
What should be done with food in the galley?
Store it in clean receptacles and dispose of waste properly.
What is the first step in managing severe bleeding?
Apply direct pressure to the wound.
What should be done if a soldier has a critical injury?
Seek immediate medical attention and follow first aid protocols.
What is the antidote for a swallowed poison?
Dilute with water or milk to lessen the concentration of the poison.
What should be done immediately for inhaled poison?
Ensure proper ventilation by moving the casualty to open air.
How should a contacted poison be treated?
Wash the affected area immediately with soap and water.
What is the first step in treating a snake bite?
Expose the wound and remove clothing, shoes, and jewelry.
How can you determine if a snake bite is from a poisonous snake?
Look for two rows of teeth and fang marks on the victim.
What are the immediate signs and symptoms of a snake bite?
Headache, vomiting, faintness, confusion, and unconsciousness within one hour.
What should be done for a non-poisonous snake bite?
Cleanse and disinfect the wound with soap and water or antiseptic.
What is the treatment for a poisonous snake bite?
Rest the casualty, keep them still, apply a broad bandage, and immobilize the limb.
What should you avoid doing when treating a snake bite?
Do not cut the wound, apply a tourniquet, or wash the bitten area.
What is shock?
A condition where there is insufficient blood in circulation, leading to extreme body weakness or collapse.
What are the main causes of shock?
Hemorrhage, severe injuries, and asphyxiation.
What are the signs and symptoms of shock?
Pale skin, cold and clammy skin, rapid weak pulse, and rapid shallow respiration.
What is the first step in treating shock?
Control any bleeding.
What is a fracture?
A break in the continuity of the bone.
What are the two types of fractures?
Open (compound) fractures where the bone breaks through the skin, and closed (simple) fractures where the skin remains intact.
What are common signs and symptoms of a fracture?
Deformity, pain, crepitation, discoloration, swelling, and possible loss of pulse below the fracture.
What is the purpose of splinting?
To immobilize an injured part of the body and relieve pain by minimizing movement.
What are the classifications of burns based on depth?
First degree (reddened skin), second degree (blisters), and third degree (destroyed skin and underlying tissues).
What is the treatment for a first-degree burn?
Immerse in cold water until pain ceases, then apply dry dressing.
What should you never do with a second-degree burn?
Never break a blister.
What is the treatment for a third-degree burn?
Cover with sterile dressing and do not remove charred clothing.
What is fainting?
Loss of consciousness caused by a temporary reduction of blood supply to the brain.
What are common causes of fainting?
Emotional stress, hunger, and fatigue.
What is the treatment for fainting?
Seat the victim with knees apart and head down; if unconscious, lay them on their back with head turned to one side.
What is the mouth-to-mouth method of artificial respiration?
Clear the airway, position the casualty on their back, seal the airway, and blow forcefully into their mouth or nose.
What is the chest-pressure arm-lift method of artificial respiration?
Position the casualty on their back, apply pressure on the lower ribs, and lift their arms vertically.
What is closed-chest heart massage used for?
To revive a casualty with no heartbeat by applying pressure on the breastbone.