Scientific Method & The Research Process: Research Methods
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is research psychology
Applying scientific knowledge to real life and practical problems
What is the Scientific Method?
Involves formulating a specific question, and then finding the answer in a well-defined, systematic way
What is a Variable
a characteristic or condition that changes or has different values for different individuals
ex: eye colour is a variable because different people have eyes of different colours. the specified colour is the value of the variable “eye colour”
What is a hypothesis?
it is an educated guess about what will happen in a study that can be tested with data
a statement that provides a description or possible explanation about an association among variables
involves at least one variable
states a predicted outcome or relationship
based on prior theory or prior research, not a random guess
Hypothesis vs. Prediction
Hypothesis: a testable explanation for a phenomenon or a question you’re investigating
Prediction: a specific expected outcome that comes from the hypothesis. It tells you what to expect to see in a particular situation if your hypothesis is correct
What are the 5 steps of the scientific method
make informal observations about the world
form a specific research question or hypothesis
generate a testable prediction
make planned, systematic observations
support or refute the hypothesis
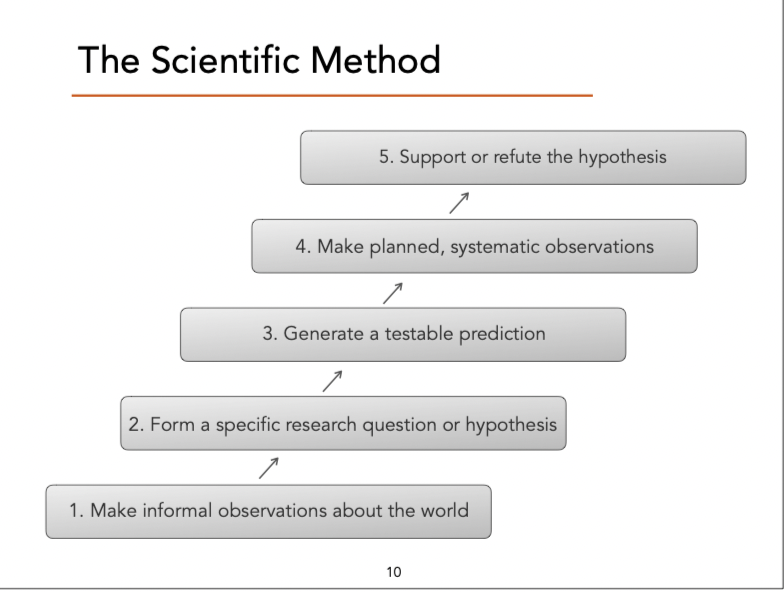
Step 1. make informal observations about the world
This begins with casual or informal observations of behaviour, events, or patterns in the world.
people often generalize beyond what they have directly observed
this is called induction or inductive reasoning: using a small # of observations as the basis for a general statement or conclusion about how things work
Step 2. Form a specific research question or hypothesis (form a tentative answer or explanation)
This step involves variables
what is changing? what is influencing what?
then you select the explanation
what is the most plausible, theoretically interesting, and most useful to study
the result is a hypothesis
it is tentative because it is not yet proven
Step 3. use your hypothesis ti generate a testable prediction
once you have your hypothesis you apply it to a specific, observable, real-world situation
a hypothesis can lead to many different predictions about a specific group, situation, and outcome
this step relies on deductive reasoning: moving from a general theory to specific predictions
Step 4. Make planned, systematic observations
after making predictions, the researcher shifts from logic to empiricism:
gaining knowledge through direct observation and measurement. data are collected in planned systematic ways
in this phase you design the study, select participants, choose measurement tools, collecting data under controlled conditions
Step 5. Using observations to support, refute, or refine the hypothesis
This step is about determining the answer to the research question
you compare the actual observations to what your hypothesis predicted
if the observations match the predictions it supports the hypothesis.
if the observations don’t maytch the predictions you refute (disprove) the hypothesis
usually then go back to step 2 and refine the hypothesis based on what you’ve learned
What are the 3 characteristics of the scientific method
Science is empirical: we obtain new knowledge through making observations
Science is public: we provide info to others about our methods and results so people can attempt to replicate them, evaluate them, and/or build on them
Science is objective: our own beliefs and biases should not influence the outcome of the research
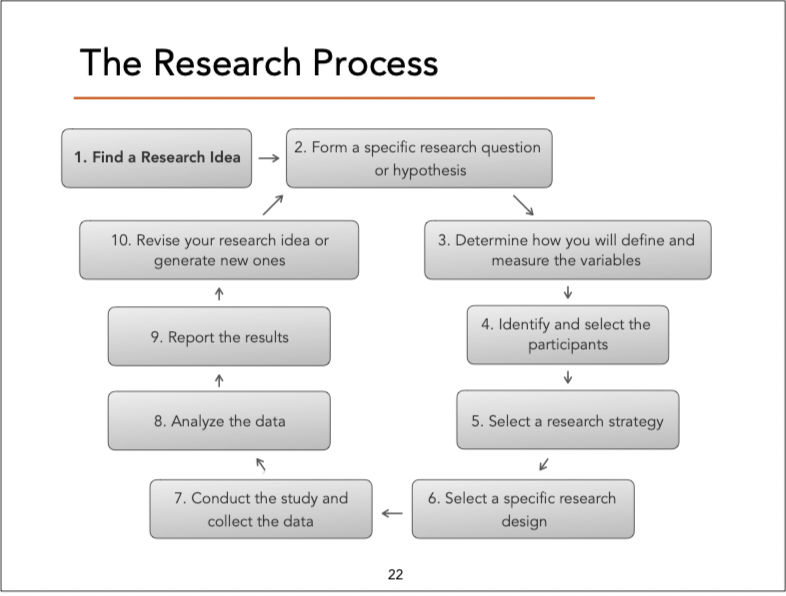
What are the 10 steps of the research process
find the research idea
form a hypothesis/tentative answer to your research idea
determine ho you wil define and measure your variables
identify the participants for the study, decide how they’ll be selected, and plan for ethical treatments
select a research strategy (descriptive correlational, non-experimental)
select a research design
conduct the study (collect the data)
evaluate the data
report the results
refine or reformulate your research idea
What are the characteristics of a good hypothesis?
Logical
testable
meaning all the variables, events, and individuals can be defined and observed
must involve real situations, events, and real individuals (cannot test a hypothetical situation)
refutable:
or falsifiable because this also equals it being testable
positive
must make positive statements about the existence of something or that a relationship occurs not just claim that nothing happens