Test 6 - Complex Animals - Annelids
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025-07-29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What does annelus mean?
little ring
The three classes of annelids
oligochaeta, hirudinea, polycheata
examples of oligochaeta
earthworms
examples of hirudinea
leeches
examples of polychaeta
marine worms
Do annelids have a coelom? What does this entail.
Yes, body cavity w/ true organ systems and muscular layers
What organ systems do annelids have?
digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory
What organ systems do annelids not have and what does it do instead?
respiratory, diffusion
What is diffusion? Why is it enough for small animals?
passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration, without using of energy.
Small size, large SA relative to volume
Thin body walls,
Moist surfaces, O₂ and CO₂ dissolve easily in water
Low oxygen demand, lower metabolic rates
What is metabolism and what does it tell you about an animal (high/low)?
sum of all chemical reactions in an organism that keep it alive, how it uses energy.
e.g. Break down food to release energy (catabolism), build up tissues using energy (anabolism).
High = uses energy quickly (small, active, endothermic), needs more O2 & food, fast digestion.
Low = opposite
Describe the thin, flexible, non-cellular outer layer covers the Annelid epidermis?
made of collagen-like proteins secreted by epidermal cells
prevents water loss
How are annelids segmented
sequence of departments by septa (walls between rooms)
How are annelid segments marked?
by annuli rings (in earthworms, each segment has one annulus)
How do annelids reproduce (sexual or asexual), and give examples.
sexual, cross fertilization, copulates to mix gametes
Sperm exchanged between two hermaphroditic worms, and fertilization happens in a mucus cocoon secreted by the clitellum
asexual, regeneration & fission
Are annelids hermaphroditic or dioecious?
hermaphroditic
What environments are annelids found in
terrestrial, freshwater, marine
Range of size for annelids
1mm - 3m
Parts of the earthworm digestive systems (7)
one way tube
mouth
anus
esophagus
crop (storage between digestion)
gizzard (grinds food)
intestines
Does the earthworm have a closed or open circulatory system
closed circulatory system.
How many blood vessels do earthworms have, what are their names, and what do they do?
2, dorsal & ventral blood vessels circulate
How many hearts do earthworms have, and what do they do
5, pumps blood into 2 blood vessels
What do earthworms use to carry their oxygen in their circulatory
hemoglobin
Describe excretory system of earthworms
nephridia (primitive kidneys) that get rid of waste from blood
Describe the nervous system of earthworms
cephalization with primitive brain & ventral nerve cord
compare the closed circulatory system to open. (3 each)
Closed:
Blood stays inside vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
More efficient at transporting
Higher pressure, faster circulation (tube)
Open:
Blood (hemolymph) flows freely into body cavities, bathing organs directly
Lower pressure, slower nutrient delivery
Less efficient, but uses less energy
What does the circular muscle do in earthworms
contracts to make worm thinner/longer
What does the longitudinal muscle do in earthworms
contract to make worm shorter/thicker
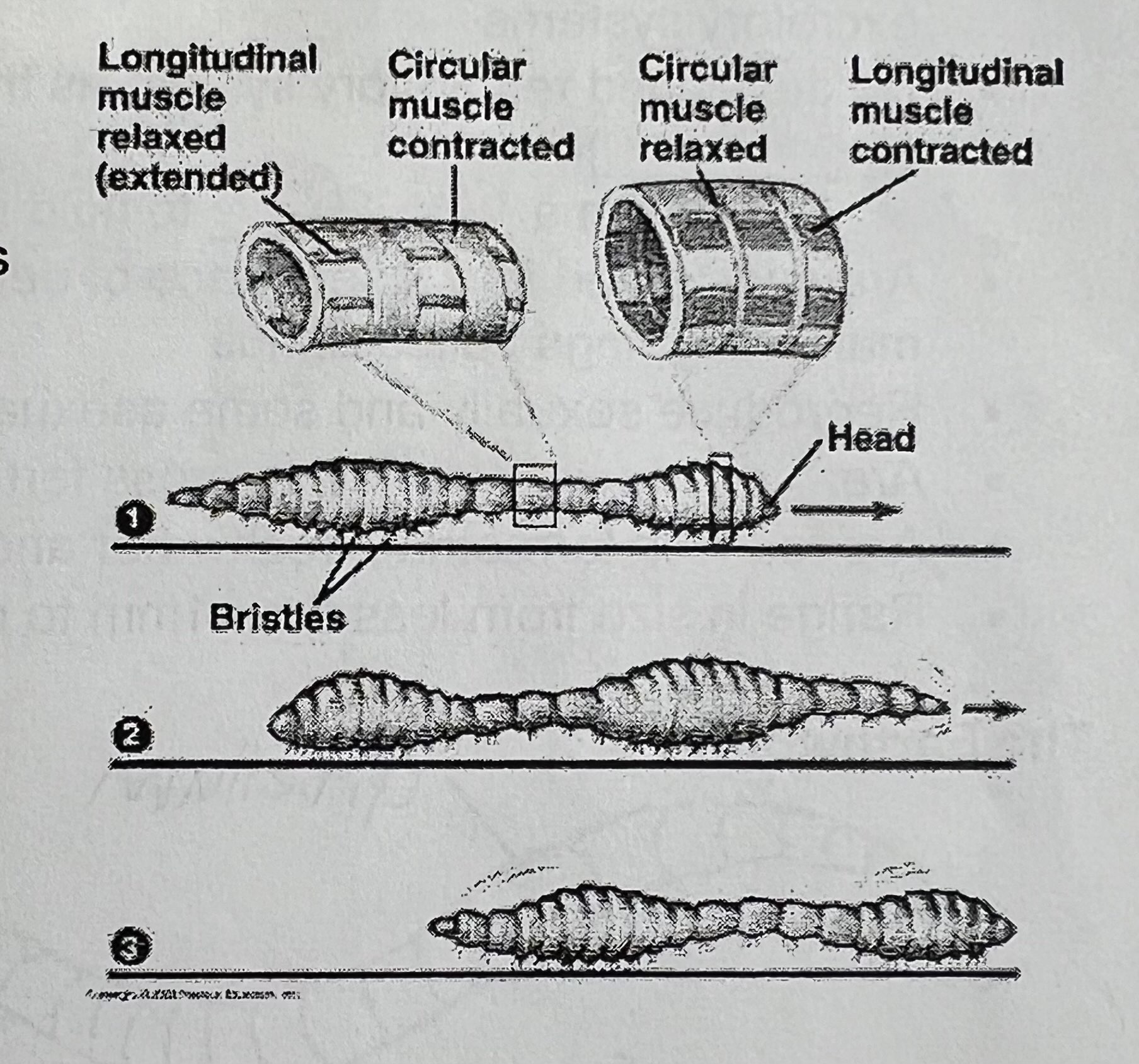
Look at this image and memorize
Good
How are annelines ecologically important (8)
base of many food chains
houses parasites like Protozoa, Platyhelmenthes, & Nematodes
aerate & mix soil (surface & mineral, through travel)
constructive to mineralization & nutrient uptake by vegetation
composts, turns dead organic matter into soil
cycle nutrients & minerals through their casts (worm poop)
increase nitrogen, phosphates & potach (potassium based) levels
burrowing and keeping the soil structure open (aerating soil and providing a path for drainage)
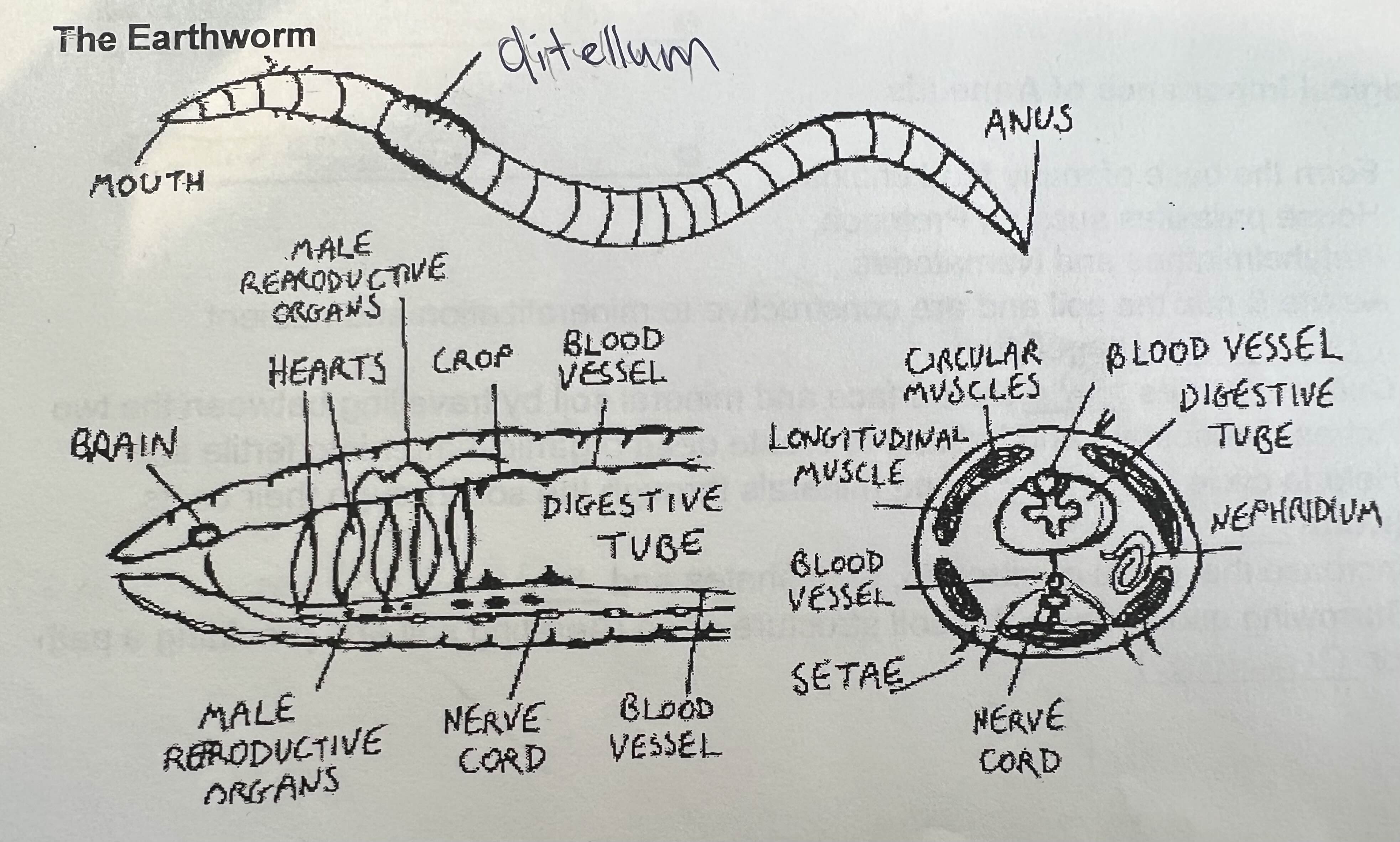
Name all the parts of this earthworm and their functions.
mouth: soil & organic matters, no teeth (uses muscular action to push soil and food into mouth)
anus: exit
clitellum: produces mucus for reproduction and cocoon for eggs
brain: ganglion, controls sensory input & corrdinates movement
heart: 5 aortic arches pumping blood thorugh closed circulatory system
male reproductive organs: produce and release sperm
nerve cord: trans nerve signals between ganglion & body segments
blood vessel: dorsal & ventral vessals circulate
digestive tube: absorbs nutrients, eliminates waste
circular muscles: around segments, contracts to lengthen
longitudinal muscles: contracts to shorten
Setae: tiny bristles on each segment that anchor worm to soil
nephridium: excretory organs in each segment that remove metabolic waste and maintain fluid/
How do many annelids and earthworms especially feed
detritus feeders
how many germ layers
3
what symmetry
bilateral
direct or indirect development in earthworms
direct