International Economics Final Exam
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
256 Terms
For a given level of real income, the demand for real money balances is inversely related to:
the nominal rate of interest.
3 multiple choice options
The Fisher effect creates a link between _____ and ______.
inflation rates; interest rates
3 multiple choice options
Using the relationship between expected exchange rates and inflation differentials in combination with uncovered interest parity, we find that:
changes in inflation rates are directly related to changes in nominal interest rates.
3 multiple choice options
The cost of holding money is primarily the:
interest given up by not channeling it into savings.
3 multiple choice options
The real interest rate is equal to:
the nominal interest rate minus inflation.
3 multiple choice options
Incorporating the liquidity preference function into the simple model changes its outcome somewhat. What is the impact?
Changes in the growth of the money supply cause inflation and nominal interest rates to change, which affects the demand for real balances and causes further discontinuous influences on prices.
3 multiple choice options
The primary difference between the simple quantity theory of money and one in which interest rates matter is that with the more general model:
there are jumps in exchange rates.
3 multiple choice options
Of the following targets or nominal anchors, which is not useful for controlling domestic inflation?
real money demand measures
3 multiple choice options
If conditions hold for the long-run monetary exchange rate model, it can provide opportunities for nations to achieve less price-level volatility by:
constraining policy choices to respect a nominal anchor, such as a target for a nominal exchange rate.
3 multiple choice options
Other nominal anchors or targets, such as rules for monetary growth, sometimes fail to optimize economic conditions in the short run because:
low monetary growth may curb inflation but may also constrain growth of real income.
3 multiple choice options
If a nation uses one or a combination of nominal anchors, a trade-off is that it loses:
the ability to control its own monetary policy.
3 multiple choice options
When real interest parity holds:
real interest rates are equal across nations with different currencies
3 multiple choice options
If the Fisher effect holds, keeping the ____ fixed would force nations to keep inflation stable.
nominal interest rate
3 multiple choice options
The asset approach to exchange rates was developed because
PPP does not hold in the short run.
3 multiple choice options
When PPP does not hold in the short run, economists have developed an alternative short-run explanatory theory based on the idea that
currency values are influenced in the short run because they serve as short term assets.
3 multiple choice options
Assume that the U.S. interest rate is 2%, the European interest rate is 7%, and the future expected exchange rate in one year is $1.224. If the spot rate is $1.18, then the expected dollar return on euro deposits is
10.7%.
Assume that the U.S. interest rate is 2%, the European interest rate is 7%, and the future expected exchange rate in one year is $1.224. If the spot rate is $1.26, then the expected dollar return on euro deposits is
4.1%
3 multiple choice options
If uncovered interest rate parity holds, the interest rate at home is 5%, and Home's currency is expected to depreciate by 2%, then the foreign interest rate is
3%.
3 multiple choice options
If uncovered interest rate parity holds, the foreign interest rate is 8%, and the home currency is expected to depreciate by 5%, then the home interest rate is
13%.
3 multiple choice options
Using the UIP (uncovered interest rate parity) equation to determine the spot exchange rate, assume that the expected spot rate (after one year) for euros (in terms of dollars) equals $1.40, the current interest rate on euro deposits is 5.5%, and the current interest rate on dollar deposits is 4.5%. Which of the following current spot rates would satisfy the equation?
$1.414
1 multiple choice option
When expected dollar-euro exchange rates fall, the foreign expected dollar return curve shifts
in.
3 multiple choice options
When the European interest rate rises, the foreign expected dollar return curve shifts
out.
3 multiple choice options
Based on the graph, if i€ falls, the result is that
the foreign return line shifts down and to the left and the spot rate falls.
3 multiple choice options
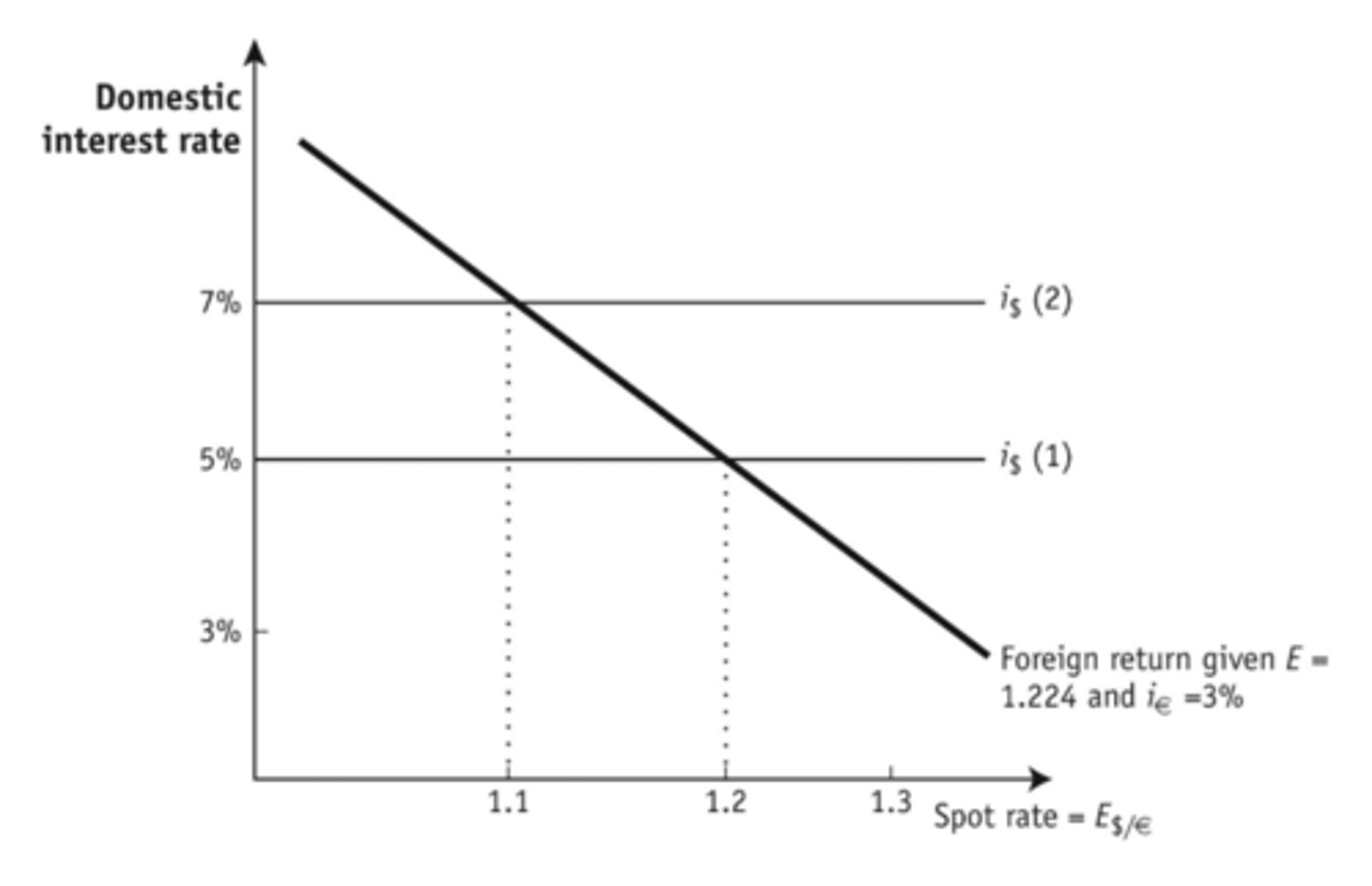
If domestic returns are greater than foreign returns, then
the spot rate is too high.
3 multiple choice options
The asset approach to short-run exchange rate determination relies on which three variables?
nominal domestic rates, foreign interest rates, and expectations of exchange rates.
3 multiple choice options
Using the UIP equation, what will happen to the spot rate for euros if the interest rate on euro deposits rises, ceteris paribus?
The spot rate to purchase euros will rise (dollar depreciation).
3 multiple choice options
Equilibrium, in the short run, is achieved when
differences in rates of return cause investors to purchase and sell currency and thereby change the spot rate of exchange.
3 multiple choice options
When the US interest rate falls, the foreign expected dollar return curve shifts
not at all.
3 multiple choice options
A fall in real income will have which of the following effects on money demand?
The money demand curve will shift in.
3 multiple choice options
Whenever there is an excess supply of real balances, the short-run adjustment occurs because
savers and investors buy bonds and drive up their prices (drive down nominal rates of interest).
3 multiple choice options
When the public perceives that a monetary expansion will be temporary, what happens to nominal interest rates in the short run?
They will fall.
3 multiple choice options
A perceived permanent rise in the rate of money growth will cause what long-run effects in the economy?
a rise in the nominal rate of interest and a rise in inflation by the same percentage.
3 multiple choice options
An increase in real income _____ the demand for real money balances and thereby causes a ____ in the nominal rate of interest.
raise; rise.
3 multiple choice options
During the period 2001-04, the U.S. Federal Reserve lowered nominal interest rates on the dollar by more than the European Central Bank (ECB) did on the euro, a move that most market participants viewed as temporary. What was the effect on the dollar-euro exchange rate?
The dollar depreciated against the Euro.
3 multiple choice options
When a country's central bank temporarily switches from an expansionary to a more conservative monetary policy, one would expect the exchange rate to:
appreciate in the short run, then return to its initial value.
3 multiple choice options
If there is a temporary increase in the money supply in the Eurozone, ceteris paribus, what is the result for the United States?
The dollar appreciates against the Euro.
3 multiple choice options
When policy changes are temporary, then:
expectations do not change.
3 multiple choice options
A key assumption to ensure that domestic returns and foreign returns are in equilibrium is that:
there are no capital controls preventing the movement of capital.
3 multiple choice options
A nominal anchor is a commitment to keep nominal variables within limits, often tied to an external value or price. When nations do not incorporate such discipline into their monetary policy, exchange rates are often:
extremely volatile, because traders consider monetary shocks to be permanent.
3 multiple choice options
If there is a permanent increase of 8% in the domestic money supply, then which of the following will be true in the long run?
The home country currency will depreciate by 8%.
3 multiple choice options
When the exchange rate depreciates in the short run and then depreciates slightly in the long run, it implies that the domestic money supply has:
permanently risen.
3 multiple choice options
When the exchange rate appreciates in the short run and then depreciates to its original level in the long run, it implies that the foreign money supply has:
temporarily risen.
3 multiple choice options
In the short run, the nominal interest rate is affected by changes in the money supply perceived to be temporary, but once ____ adjust(s), the nominal interest rate ____ in the long run.
the price level; will revert to its former self.
3 multiple choice options
Monetary policy can be autonomous if:
the exchange rate floats and capital is mobile.
3 multiple choice options
Comparing the examples of Denmark and the United Kingdom in relationship to the European Monetary Union, the krone is pegged to the euro, whereas the British pound is not. What can be predicted then about their interest rates?
The United Kingdom can set its own interest rates and pursue an independent monetary policy, whereas Denmark's rates are virtually the same as those of the Euro.
3 multiple choice options
A country with fixed exchange rates:
monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run.
3 multiple choice options
If Japan seeks to control its exchange rates so that ¥100 = $1, which of the following policies should it NOT maintain?
a willingness to raise price levels.
3 multiple choice options
Why would making a permanent change in a monetary aggregate have an effect on exchange rates in a nation?
Traders form expectations of future exchange rates based on the anticipated long-run effects of monetary operations.
2 multiple choice options
If Bulgaria, for instance, wishes to keep its exchange rate with the dollar fixed, what monetary policy options are available to lower unemployment in the short run?
Bulgaria cannot use any monetary policy that would cause its short-run exchange rate to depreciate against the dollar.
3 multiple choice options
With fixed exchange rates and capital mobility:
interest rates in the home country and in foreign countries are equalized.
3 multiple choice options
Exchange rate interventions occur when a government:
buys and sells its own currency and other currencies on forex markets.
3 multiple choice options
During the U.S. Civil War (1861-1865), the Confederate states printed their own currency. Events occurred during the war that affected the exchange value of the Confederate dollars. What evidence was there that supports the theory of long- and short-run exchange rate determination?
Speculators traded for profit and based their valuations on the long-run expectation of the exchange rate, which tracked closely the probability of a victory for the South.
3 multiple choice options
The trilemma refers to all of the following except
price controls
3 multiple choice options
During the period 2001-04, the U.S. Federal Reserve lowered nominal interest rates on the dollar by more than the European Central Bank (ECB) did on the euro, a move that most market participants viewed as temporary. What was the effect on the dollar-euro exchange rate?
The dollar depreciated against the Euro.
3 multiple choice options
Based on the graph, if the dollar rate of interest increases from 5% to 7%, what result will occur in the short run?
The spot rate for dollars will appreciate to $1.10.
3 multiple choice options
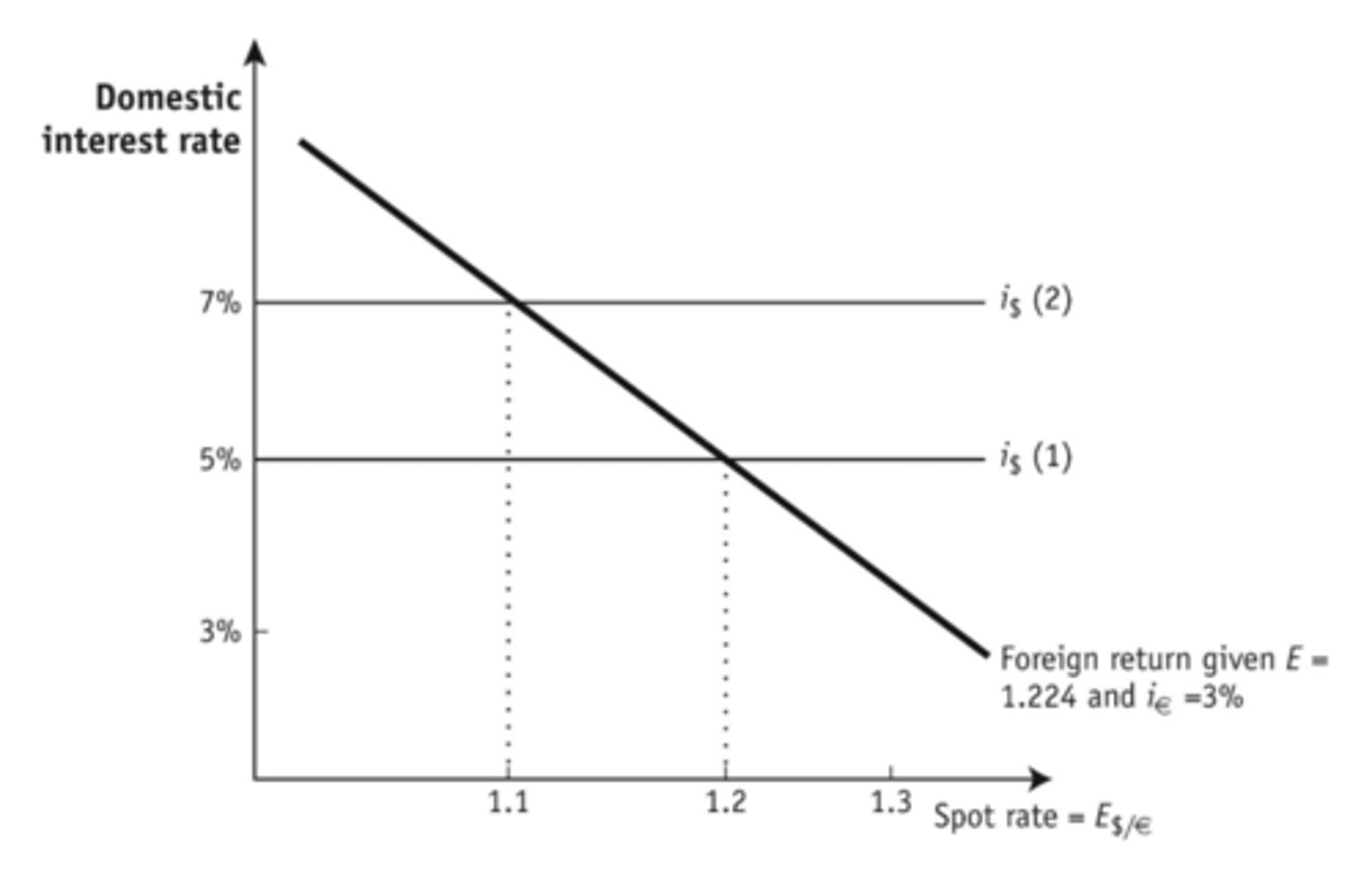
When policy changes are temporary, then
expectations do not change.
1 multiple choice option
An increase in the money supply in the short run changes ____, whereas in the long run, ____ change.
interest rates; inflation rates
3 multiple choice options
If there is a temporary increase in the money supply in the eurozone, ceteris paribus, what is the result for the United States?
The dollar appreciates against the euro.
3 multiple choice options
Given expectations of future exchange rates, when foreign returns are greater than domestic returns, investors will ____ domestic assets, _____ domestic currency, ____ foreign currency, and _____ foreign assets.
sell; sell; buy; buy
3 multiple choice options
International variables are linked through trade and financial flows. Therefore, what trilemma is faced by a nation that wishes to keep its exchange rates with other nations fixed?
If it wants to control its own monetary policy under fixed exchange rates, then it must restrict foreign investment.
3 multiple choice options
What are the consequences for a nation that keeps its exchange rate fixed, holds its own domestic interest rates below market to encourage domestic spending, and allows free foreign investment?
Domestic and foreign investors will invest in other nations, causing a sell-off of the domestic currency, and, to maintain fixed rates, the central bank will have to buy its own currency, depleting its treasury reserves.
3 multiple choice options
Central banks control exchange rates by intervention. If a nation such as Japan wished to peg its market rate at a certain level, such as ¥125 = $1, what should it do if the actual market rate begins to appreciate to ¥100 = $1?
It should sell dollars to purchase more of its own currency.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following explains why a monetary policy in a nation with an exchange rate peg, such as Denmark, would not be possible?
The nation must keep its price level and nominal interest rate equal to the price level and nominal interest rate in the nation to which it pegs.
3 multiple choice options
A short-run appreciation of the British pound relative to the euro would be consistent with:
either a temporary fall in the British money supply or a temporary rise in the European money supply.
3 multiple choice options
When the exchange rate appreciates in the short run and then depreciates to its original level in the long run, it implies that the domestic money supply has:
temporarily fallen.
3 multiple choice options
If a country's government wants to maintain monetary policy autonomy, then:
it can impose strict capital controls and maintain a fixed exchange rate, or it can maintain capital mobility but not a fixed exchange rate.
3 multiple choice options
The circular flow concept of a closed economy helps to explain why
GDP, GNI, and GNE are equal.
3 multiple choice options
When a closed economy is compared with an open economy, what situation exists?
In a closed economy, because there are no exports or imports, no international transfers, and no service payments, GDP, GNE, GNI, and GNDI are all equal.
3 multiple choice options
Whenever there is a deficit in the current account, GNDI is
less than GNE.
3 multiple choice options
In a closed economy, income is
equal to domestic production.
3 multiple choice options
If a government spends $100 billion on national defense, $50 billion on public infrastructure, $25 billion on civil services, and $75 billion on unemployment benefits, then its total consumption expenditure is
$175 billion.
3 multiple choice options
Payments by a Japanese auto manufacturer to its workers in the United States are
an increase in U.S. GNDI.
3 multiple choice options
In an open economy, GNI is equal to
GDP minus factor service imports plus factor service exports.
3 multiple choice options
The disposable income of a nation is known as gross national disposable income, which can be defined as
income earned from production plus net factor income from abroad plus net unilateral transfers.
3 multiple choice options
The term "net unilateral transfers" refers to
gifts, charitable contributions, and aid to foreign residents minus the same types of transfers to residents of the home nation.
3 multiple choice options
The current account of the balance of payments is calculated as
the sum of the trade balance, net factor income from abroad, and net unilateral transfers.
3 multiple choice options
When calculating GDP in an open economy, we adjust GNE by
subtracting imports and adding exports.
3 multiple choice options
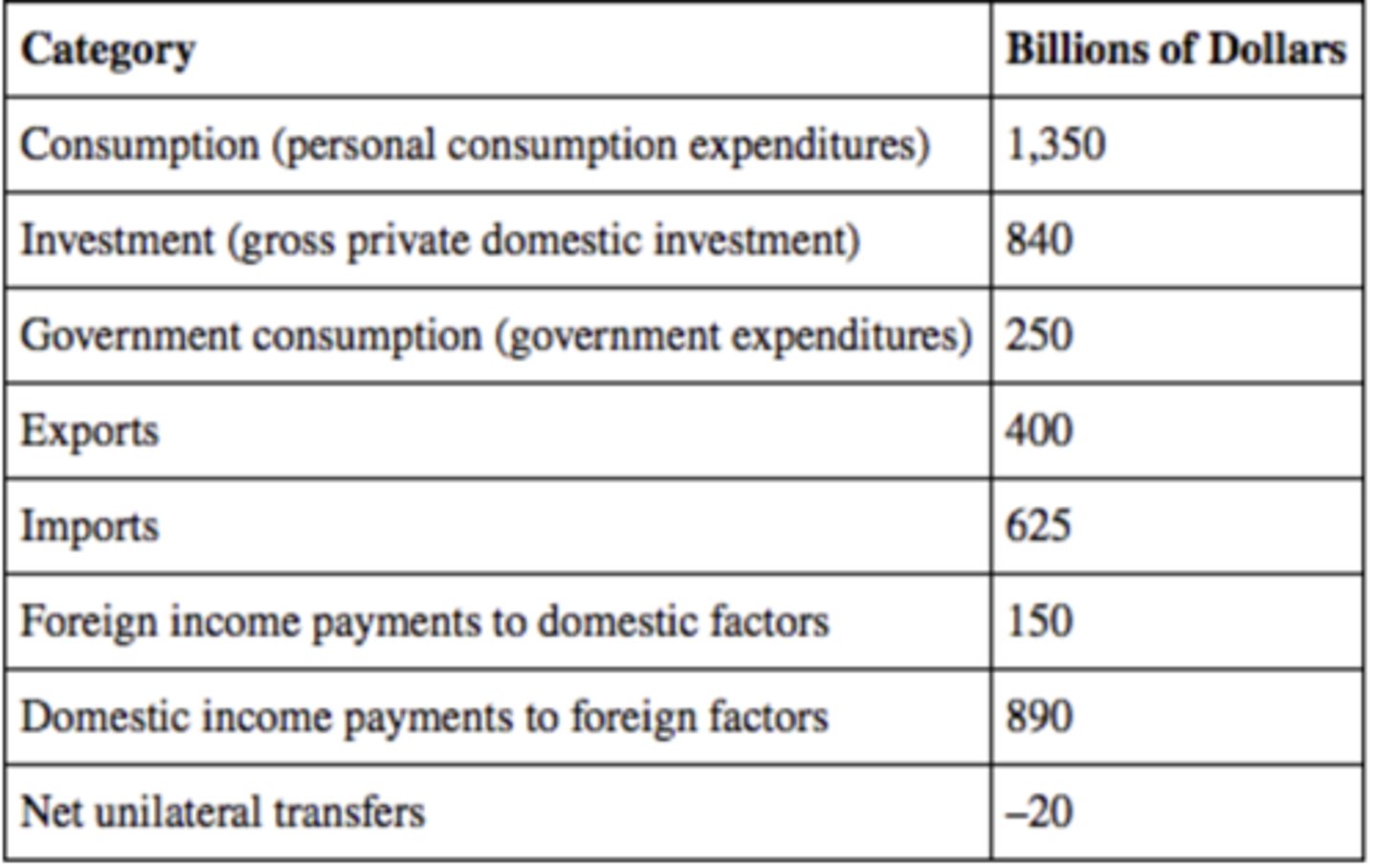
Based on the table, the GNE is
$12,150 billion.
3 multiple choice options
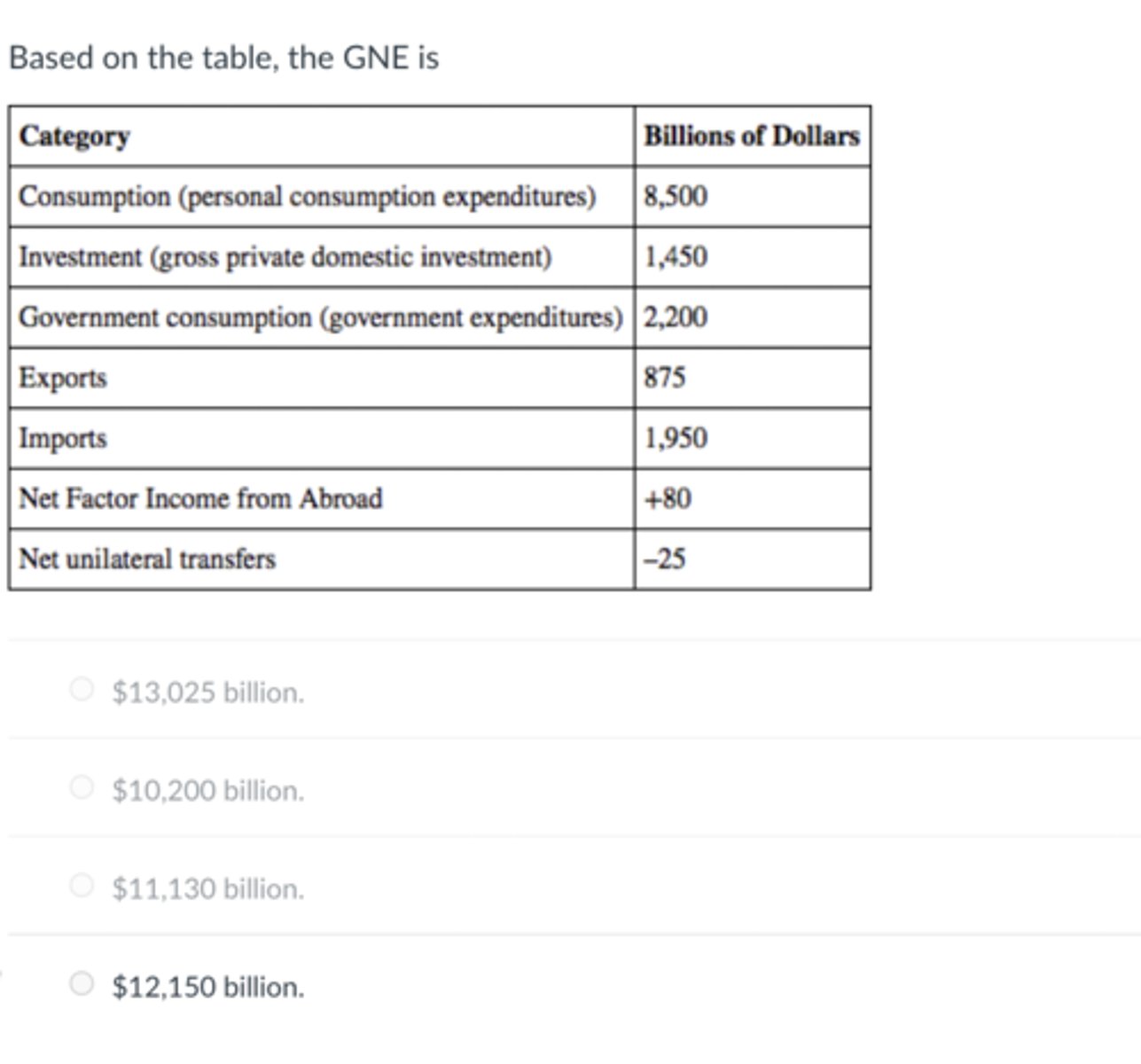
Based on the table, the trade balance for the economy is
-$1,075 billion.
3 multiple choice options
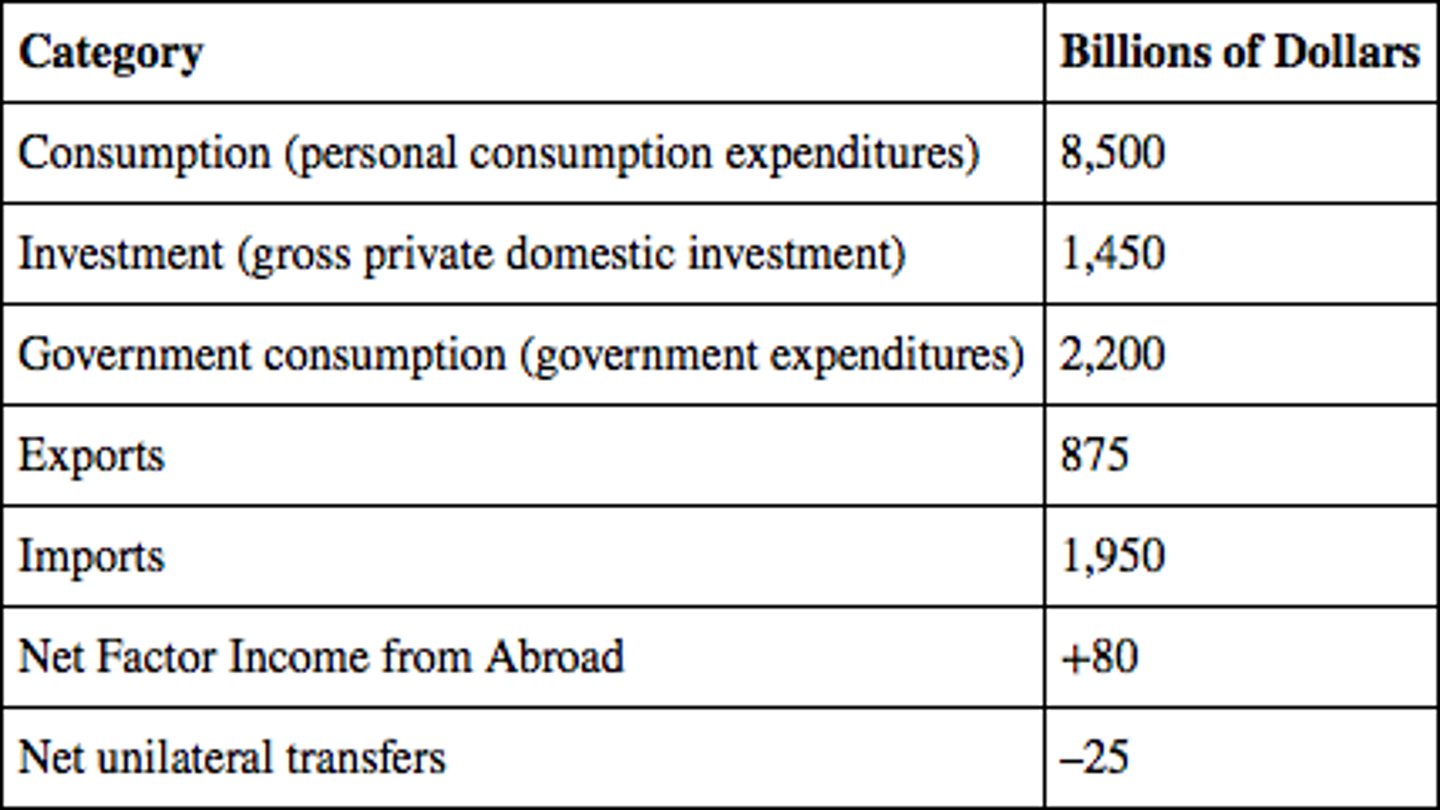
The GNI for this economy is
$1,475 billion.
3 multiple choice options
Private savings deficits plus government budget deficits contribute to higher current account deficits. Some economists refer to the Ricardian equivalence theory to assert that
the public will offset its future tax liability to some degree by increasing saving.
3 multiple choice options
The GDP for this economy is
$780 billion.
1 multiple choice option
The example in the text about Ireland demonstrates that
a nation's GDP is not a good measure of income paid to domestic factors when payments to foreign factors are large.
3 multiple choice options
The Irish example indicates that GDP per capita and GNI per capita
can be quite different.
3 multiple choice options
When measuring GNDI in an open economy, one must recognize not only net transfer payments to factors of production but also
net unilateral transfers, which include official aid and private charitable gifts.
3 multiple choice options
The GNDI for this economy is
$10,615 billion.
3 multiple choice options
When a national entity receives investment from abroad, economists call it a(n)
external liability.
3 multiple choice options
Suppose that a Canadian farmer buys a Japanese tractor with cash. For Canada, this counts as a
current account debit, financial account credit.
3 multiple choice options
The U.S. current account deficit, which has persisted for over 20 years, has resulted in a(n)
financial account surplus.
1 multiple choice option
The balance on the financial account consists of
the change in external liabilities minus the change in external assets.
3 multiple choice options
During the period in which a nation has a current account surplus, it is a net ____, and whenever it has a current account deficit, it is a net ____.
lender; borrower
3 multiple choice options
Suppose that a German trades a mug of beer for a glass of wine with a Frenchman. For France, this counts as a
current account credit, current account debit.
3 multiple choice options
Suppose that an Austrian buys a car from Germany with cash. For Germany, this counts as a
current account credit, financial account debit.
3 multiple choice options
The primary driving force behind changes in external wealth is
an imbalance between a nation's total income and its total spending.
3 multiple choice options
When calculating the balance of payments, credit (or [+] entries) are made, except whenever which of the following occurs?
A domestic firm signs a contract to buy half of a foreign company headquartered overseas.
3 multiple choice options
The balance on the current account equals the negative of the balance on the financial account, plus
the negative of the balance on the capital account.
3 multiple choice options
When a domestic investor sells a domestic asset to a foreigner, the financial account
rises
1 multiple choice option
Which of the following would cause a financial account (FA) surplus?
the purchase of stock in a U.S. corporation by a foreign buyer
3 multiple choice options
Developing nations may have a rather large capital account surplus compared with developed nations because of
nonmarket debt forgiveness.
3 multiple choice options
The capital account is now used mainly for
debt forgiveness, confiscation of assets, and nonfinancial assets such as copyrights and franchises.
3 multiple choice options