Varices, Esophagitis, Toxic ingestion, GERD
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Portal Hypertension
An increase in portal venous pressure above 10 mmHg (considered clinically significant at 12+)
Portal vein thrombosis, splenic vein thrombosis, schistosomiasis
What are some pre-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
cirrhosis (most common), schistomoiasis, congenital hepatic fibrosis
What are some intra-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
Budd-Chiari (obstruction of hepatic veins), right side HF, constrictive pericarditis
What are some post-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
Collateral circulation development to relieve congestion, splanchnic vasodilation increased portal blood inflow
What are some consequences of portal hypertension
splenomegaly, esophageal/gastric varices, caput medusae, ascites, hepatic enceptalopathy, thrombocytopenia (splenic sequestration)
Clinical features of Portal HTN
doppler U/s, CT, MRI, endoscopy identifies varices, Measurement of HVPG (hepatic venous pressure gradient)
How do you diagnose portal hypertension (in addition to hx and physical)?
GI bleeds (variceal hemorrhage), ascites, bacterial peritonitis, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome
Complications of portal hypertension
non-selective beta blockers, endoscopic variceal ligation
Management plan for portal HTN → primary prophylaxis
Octreotide, endoscopic band ligation, balloon tamponade
Management plan for portal HTN → variceal bleeding
sodium restriction, diuretics, para
Management plan for portal HTN → ascites
TIPS, Liver transplantation
Management plan for portal HTN → definitive
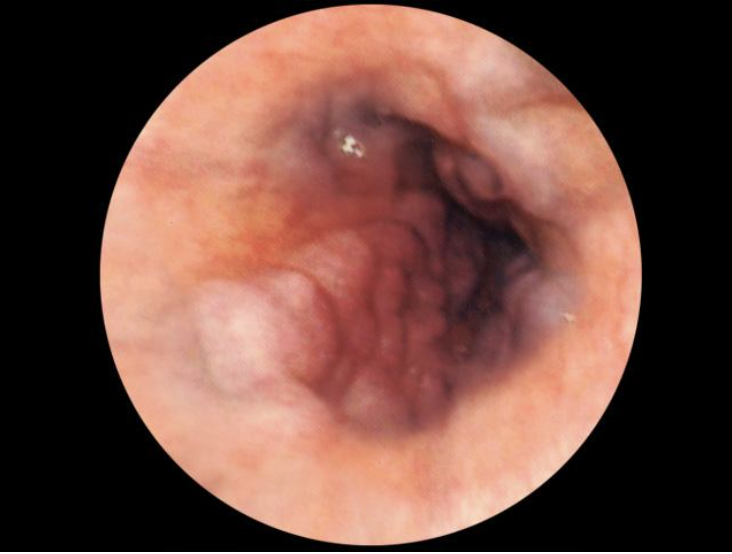
Esophageal varices
Dilated blood vessels that develop as a direct result of portal HTN as an attempt to bypass congestion with collateral flow that become dilated and can lead to upper GI Bleeds (usually asymptomatic until then)
EtOH, Cirrhosis (50%), Hepatitis (35.1%)
Risk factors for Esophageal varices
Lower extremity swelling, jaundice, easy bruising, hemorrhoids, spider nevi, ascites, splenomegaly
Red flags for portal congestion or liver disease that may also present with Esophageal varices → physical exam is usually low yield
Upper endoscopy (screen for varices when diagnosing cirrhosis)
What is the gold standard for diagnosing Esophageal varices
prophylactic non-selective beta blockers (propanolol), EVL (usually via bands), TIPS,
Treatment plan for chronic liver disease with Esophageal varices
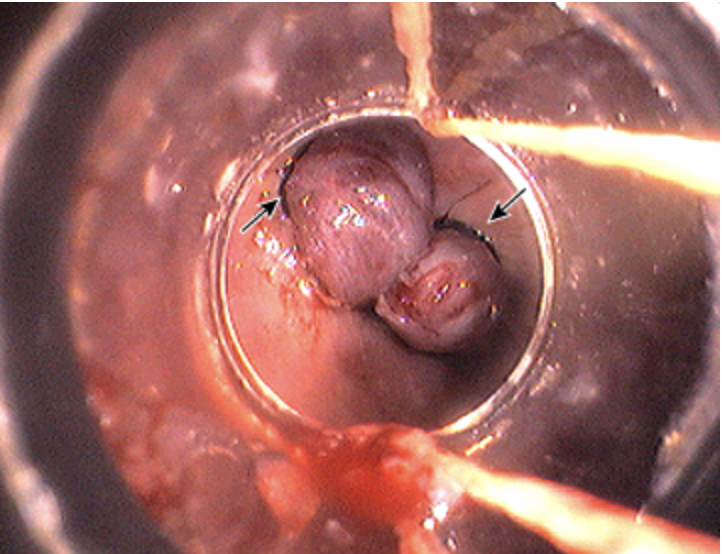
AIRWAY (protect with intubation)!! Balloon tube tamponade (hemorrhage control), Ceftriaxone prophylaxis, Octreotide/somatostatin to constrict splenic vessels, Anti-emetics (do not disrupt the clot), emergent endoscopy (definitive treatment banding/ligation)
Okay so if the varices start bleeding what is the gameplan?

Peptic ulcer disease, mallory-weiss tear, Boerhaave syndrome, caustic esophagitis, erosive gastritis, esophageal mechanical injury
DDX for bleeding Esophageal varices
Esophagitis
Any inflammation, injury, or infection of the esophagus usually due to candia, HSV, or CMV
GERD, pill induced, ingestion of chemicals
Caustic causes of esophagitis
New/nonstandard food, chemicals, medications, bedridden patients, immunocompromise, systemic antibiotics, systemic immunosuppressants, MDI/nebulized immunosuppressant
Risk factors of esophagitis
Odynophgia (HALLMARK), dyspepsia/heartburn, dysphagia, chest pain
Symptoms of esophagitis
EGD (sensitivity 90%, specificity 100%)
Gold standard for odynophagia
AIDS/HIV, Medications, radiation, antibiotics, DM
Risk factors for infectious esophagitis → usually opportunistic in immunocompromised peeps but can occur in immunocompetent peeps as well
Endoscopy with biopsies, KOH prep/gram stain
Patient presents to the clinic for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient reports that he is taking corticosteroids for his RA. He also reports pain at the angles of his lips. On a physical exam you note white, scrapable plaques in the mouth. What do you want to order?
oral fluconazole (7-14 days)
Patient presents to the clinic for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient reports that he is taking corticosteroids for his RA. He also reports pain at the angles of his lips. On a physical exam you note white, scrapable plaques in the mouth. See endoscopy. KOH prep shows budding yeast. Let’s say we’re treating him outpatient, what meds?
IV fluconazole, then oral (14-21 days)
Patient presents to the clinic for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient reports that he is taking corticosteroids for his RA. He also reports pain at the angles of his lips. On a physical exam you note white, scrapable plaques in the mouth. See endoscopy. KOH prep shows budding yeast. Let’s say we’re treating him inpatient, what meds?
EGD, viral PCR, culture
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient also reports fatigue and body aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.6 temp. On a physical exam you note shallow oral lesions. What do you want to order?
Supportive care
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient also reports fatigue and body aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.6 temp. On a physical exam you note shallow oral lesions. Endoscopy shows multiple, small, deep ulcerations. Let’s say he’s not immunocompromised and symptoms are improving → medication game plan
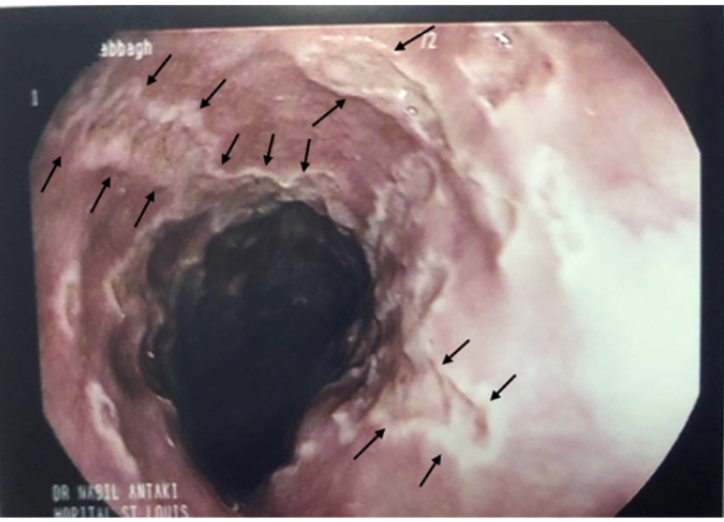
Oral acyclovir (5-7 days)
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient also reports fatigue and body aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.6 temp. On a physical exam you note shallow oral lesions.. Endoscopy shows multiple, small, deep ulcerations. Let’s say he’s not immunocompromised → medication game plan
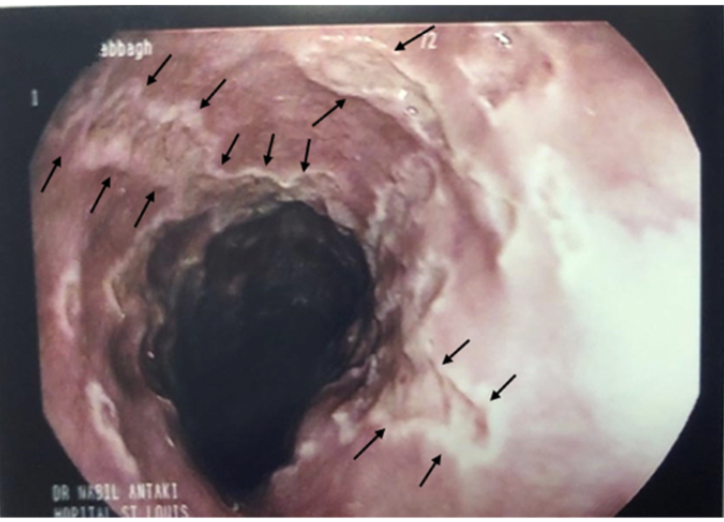
Oral Acyclovir (14-21 days)
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient also reports fatigue and body aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.6 temp. On a physical exam you note shallow oral lesions.. Endoscopy shows multiple, small, deep ulcerations. Let’s say he’s immunocompromised and can stay outpatient → medication game plan
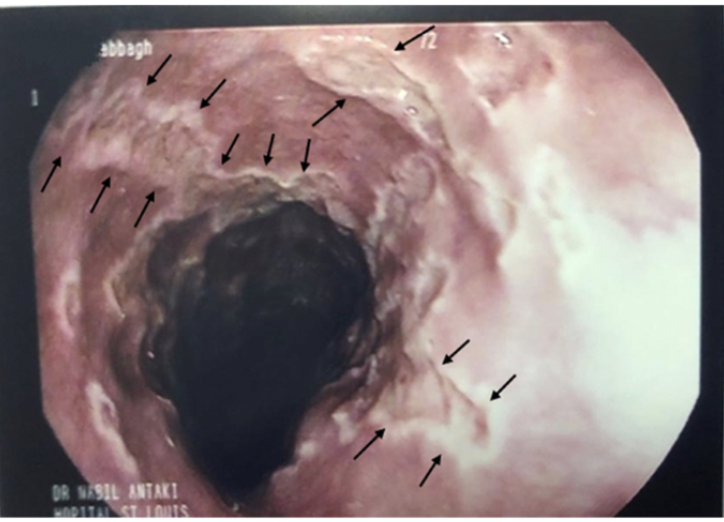
IV Acyclovir then oral (14-21 days)
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. Patient also reports fatigue and body aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.6 temp. On a physical exam you note shallow oral lesions.. Endoscopy shows multiple, small, deep ulcerations. Let’s say he’s immunocompromised and is inpatient → medication game plan
Endoscopy with biopsy, CBC (he has AIDs get a white count)
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. PMHx is positive for AIDs. Patient also reports stomach pain and nausea. Vitals are stable with the exception of 99.9. On a physical exam you note abdominal tenderness, oral ulcers, and signs of malnutrition. What do you want to order?
IV ganciclovir, re-initiation, alteration, or initiation of HAART, may require long-term immunosuppression
Patient presents to the ER for difficult and painful swallowing. PMHx is positive for AIDs. Patient also reports stomach pain and nausea. Vitals are stable with the exception of 99.9. On a physical exam you note abdominal tenderness, oral ulcers, and signs of malnutrition. Endoscopy shows several large, superficial, ulcerations. What is your treatment gameplan?
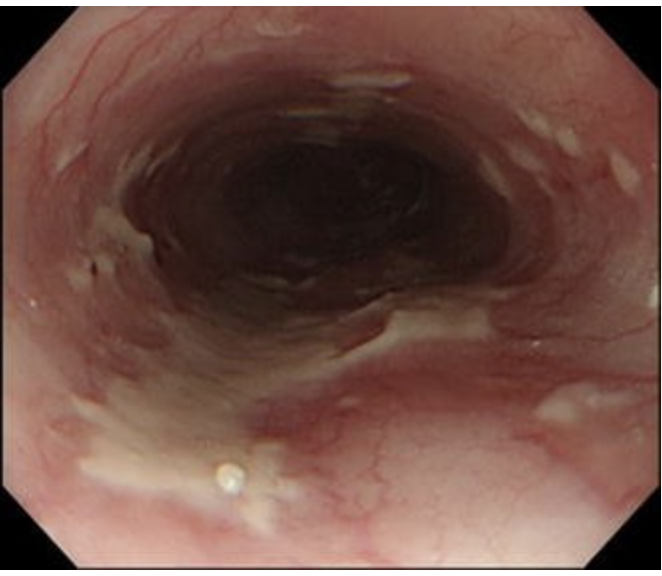
thug it out (supportive care - its self limited)
In a immunocompetent patient with CMV esophogitis, what is the gameplan

Pill-induced esophagitis
Medication taken improperly (supine, no water) allows the pills to adhere to esophageal mucosa disrupting the normal protective mechanisms leading to pressure necrosis and chemical irritation → watch your bed bound peeps
NSAIDs, Alendronate, K-supplements, Fe, vitamin C, Doxy, Tetracycline, Clindamycin, TMP-SMX
Meds that can cause esophagitis
Stop the NSAIDs or take them correctly, should heal within 48-72
Patient presents to the ER for odynphagia and dysphagia. He notes that he recently started taking NSAIDs before he goes to bed. Physical exam is negative. Endoscopy shows ulceration and biopsy is negative. What is your treatment plan?
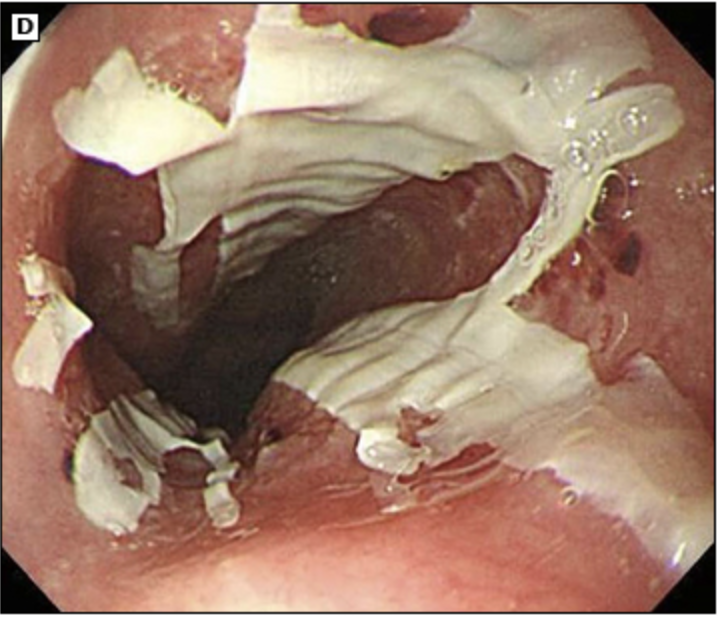
Ingestion related esophagitis
Intentional or accidental ingestion of irritants that damage the esophagus - damage is related to time in contact and pH
bleach, drain cleaner, detergents, batteries
Common irritants of ingestion-related esophagitis
Depression, SI, previous Suicide attempt, missing time in parent Hx of events, report accidental ingestion and intentional ingestion
Risk factors for TI
Odynophagia, dysphagia, N/V, abd pain and tenderness, hematemesis, coffee-ground emesis, hematochezia, melena, airway damage, respiratory difficulty, AMS
Signs and symptoms for TI depend on damage - what are some examples
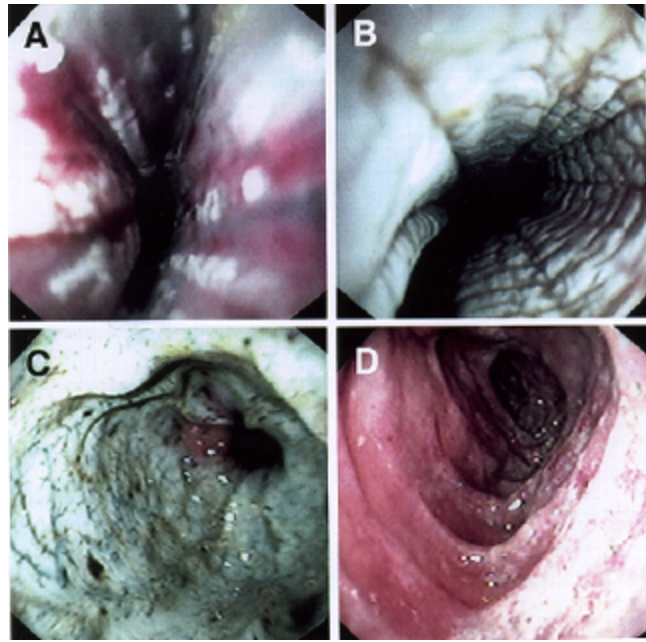
CXR (respiratory issues), Abdominal Xray (r/o perforation, battery vs. coin ingestion), Upper endoscopy if perforation is r/o (determines injury severity and follow up complications)
TI diagnostics
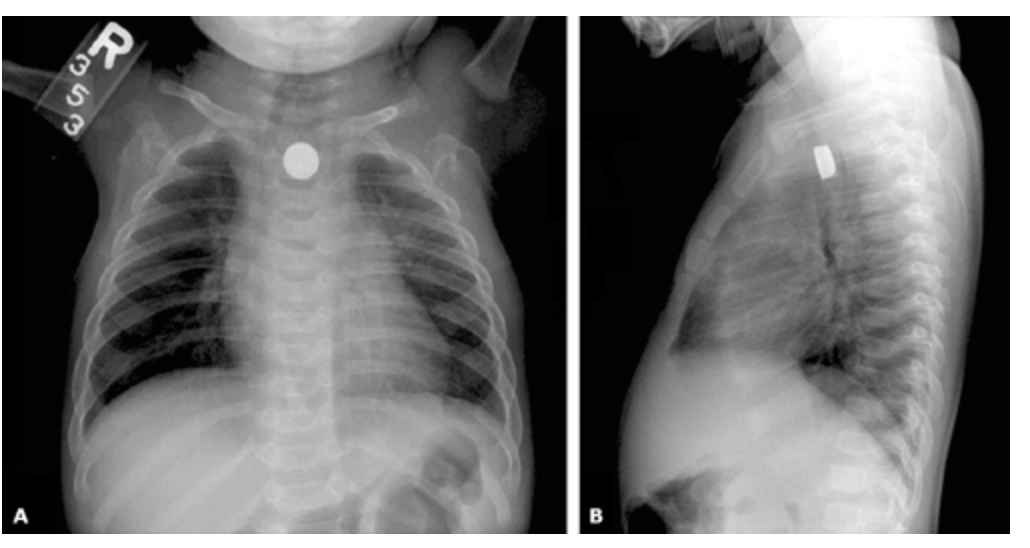
AIRWAY!!, Remove battery via endoscopy (A$AP no rocky), If its a liquid use neutralizing agents (NO VOMIT)
Treatment plan for TI
esophageal stricture formations, esophageal cancer
Ingestion related esophagitis increases the risk of
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
A condition that develops when stomach contents reflux into the esophagus resulting in symptoms and esophageal tissue damages
Some is normal, Large amounts override the body’s ability to neutralize, related to gastric over-filling and transient relaxation of the LES, Hypotensive LES, Hiatal hernia
Etiology of GERD
LES constriction → additional diaphragmatic external pressure around the LES → salivary bicarb neutralizes a small amount → esophageal peristalsis moves reflux back into the stomach
Normal deterrents to excessive reflux
large meals, lying down shortly after, truncal obesity, EtOH, smoking, diet, medications, decreased saliva production, delayed gastric emptying
Risk factors for GERD
heartburn, acid regurgitation
Classic symptoms of _________ and _________________ help establish the diagnosis, but their absence does not rule out GERD
Dyspepsia, regurgitation, sour/metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, chest pain, hypersalivation, hoarseness, sore throat, sleep disturbances, black stools, dysphagia, odynophagia, cough, Asthma adult onset
GERD S/S
Inflammation and erythema or oropharynx, lung wheezing, laryngitis
GERD physical findings (note: not many non-invasive findings)
Ambulatory 24-hr esophageal pH monitoring (standard), Patient trial of GER medication, Upper endoscopy (gold standard for the complications!)
Diagnostic test for GERD → there is NO gold standard
avoid the foods and medications that worsen symptoms, sleep with head elevated, eat smaller meals, weight loss
Lifestyle changes for GERD
Famotidine (H2), PPI (usually preferred initial treatment is 4-8 weeks, then may D/c)
Pharm treatment for GERD
Surgical fundoplication (healthy patients withe severe symptoms, noncompliant patients, large hiatal hernias)
Surgical treatments for GERD → may increase dysphagia, bloating, flatulence
Onset of symptoms 50+, dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, positive fecal occult blood test, melena, bloody emesis, anemia, PPI failure, GI cancer in 1st degree relative
GERD Red Flags that mean we need to get a IMMEDIATE Upper endoscopy and start PPIs
esophagitis, peptic ulcer disease, cardiac, esophageal spasm/motility disorder, achalasia, esophageal trauma, referred pain from abdomen, PE, globus pharyngeus
DDX of GERD
Erosive esophagitis, esophageal stricture, Barrett esophagus, esophageal cancer
Complications of GERD
Barrett esophagus
A complication that occurs in 10% of patients with chronic GERD that is characterized by the replacement of squamous epithelial cells by goblet and columnar cells 1 cm proximal to the gastroesophageal junction
Upper endoscopy with biopsy
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for the 1st time in 40 years for a checkup. While collecting a history he states that he use to have really bad heartburn but recently its gotten a lot better. What do you want to order?
GERD for 5-10 years, age 50+, hiatal hernia, obesity, nocturnal reflux, tobacco use, 1st degree relative with it or adenocarcinoma
Risk factors for Barrett Esophagus
Long term PPI (reduce cancer risk, does not cause regression), surveillance every 3-5 yr with EGD
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for the 1st time in 40 years for a checkup. While collecting a history he states that he use to have really bad heartburn but recently its gotten a lot better. Endoscopy shows orange, gastric type epithelium that extend upwards from the stomach. NO Dysplasia noted. What is your treatment plan?
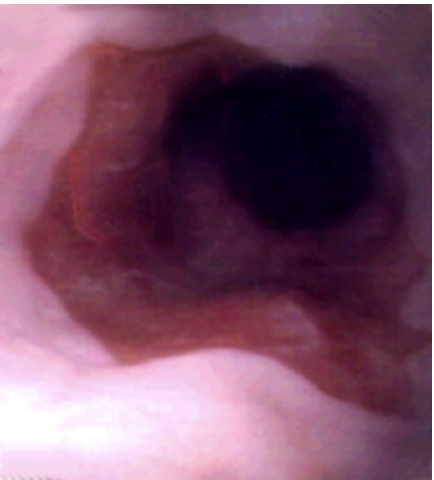
Optimize PPI, repeat EGD in 2-6 months
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for the 1st time in 40 years for a checkup. While collecting a history he states that he use to have really bad heartburn but recently its gotten a lot better. Endoscopy shows orange, gastric type epithelium that extend upwards from the stomach. NO Dysplasia noted, but its definitively not normal. What is your treatment plan?
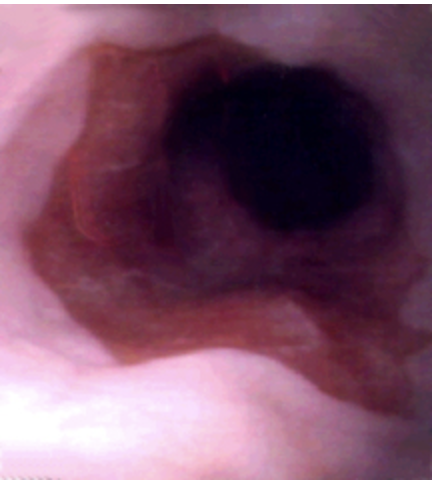
PPI, Endoscopic ablation, resection
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for the 1st time in 40 years for a checkup. While collecting a history he states that he use to have really bad heartburn but recently its gotten a lot better. Endoscopy shows orange, gastric type epithelium that extend upwards from the stomach. Dysplasia noted. What is your treatment plan?
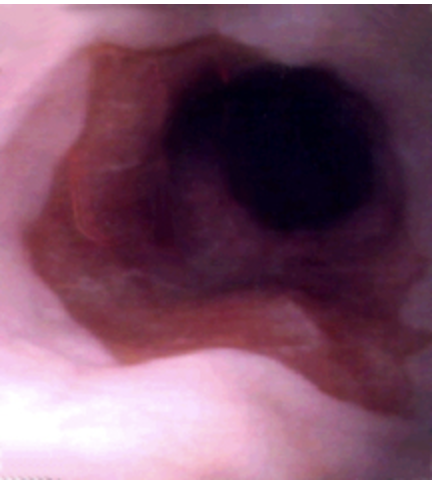
0.33%/yr (7-19% with high grade dysplasia)
What is the risk that Barrett esophagus progresses to adenocarcinoma
high dose PPI with radiofrequency ablation
What treatment combination resulted in 90% of patients experiencing complete resolution of Barretts esophagus