Global Ecology: Abiotic Factors and Biome Distribution
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Ecology
Study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment.
Abiotic Factors
Non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems.
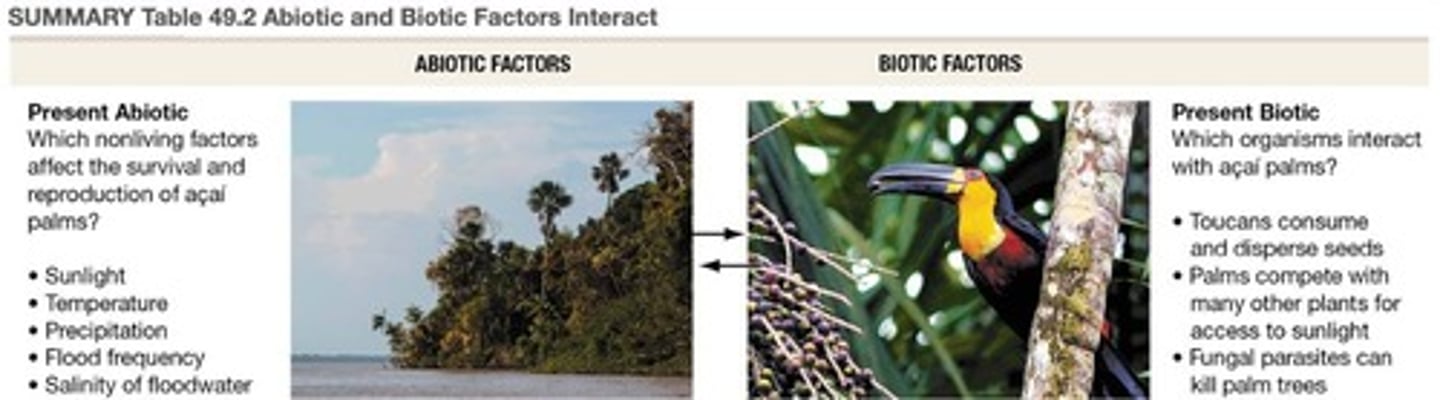

Sunlight
Amount of sunlight affects daylength and sunlight intensity, which influences photosynthesis.
Temperature
Enzymes only work in a specific range and it affects access to water.
Moisture
Uneven solar heating causes atmospheric circulation and predictable precipitation patterns.
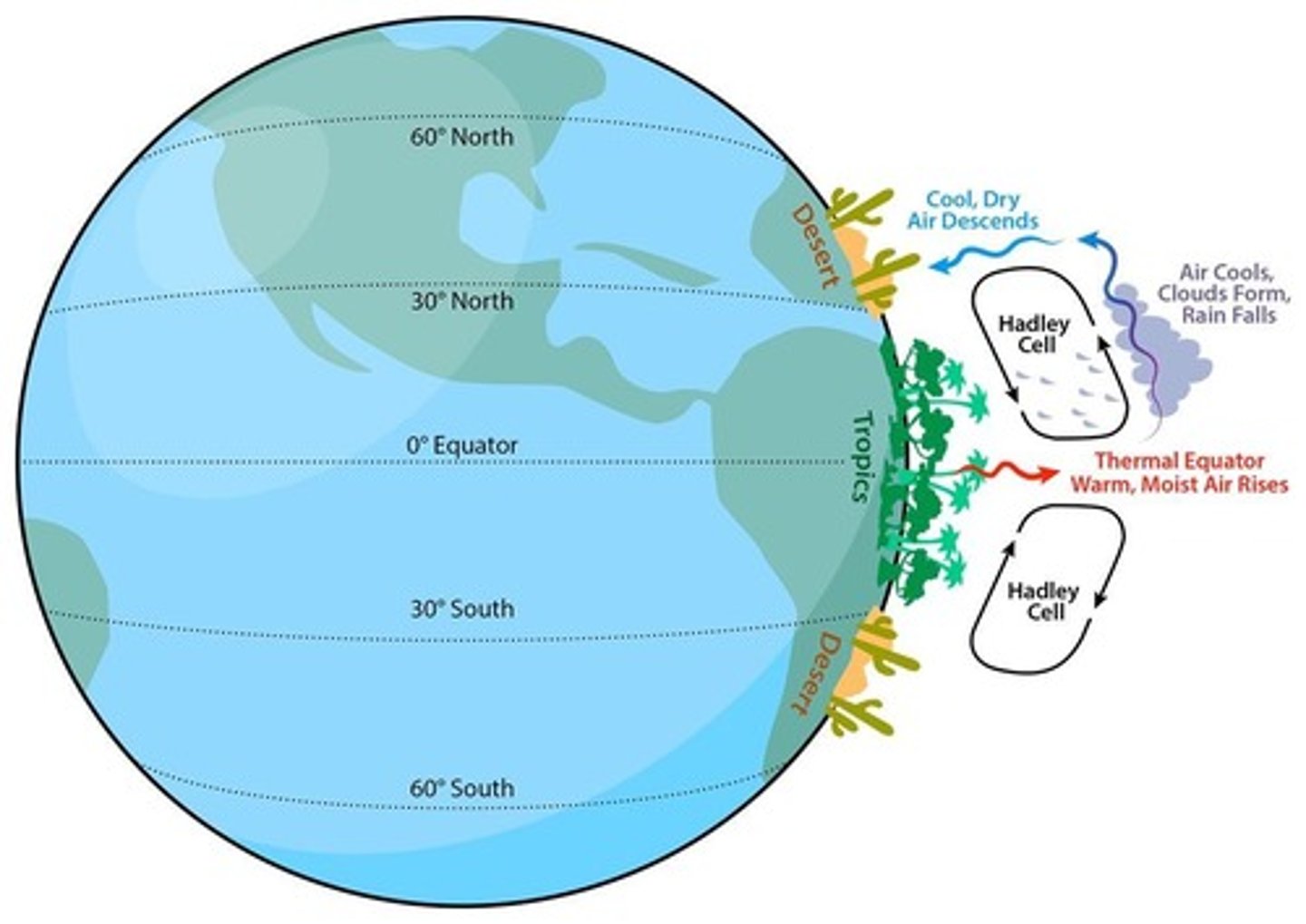
Hadley Cells
Hot rising air at the equator creates these cells, which generate predictable areas of precipitation.
Seasons
Caused by the tilt of the earth, creating variation in daylength over time and space.
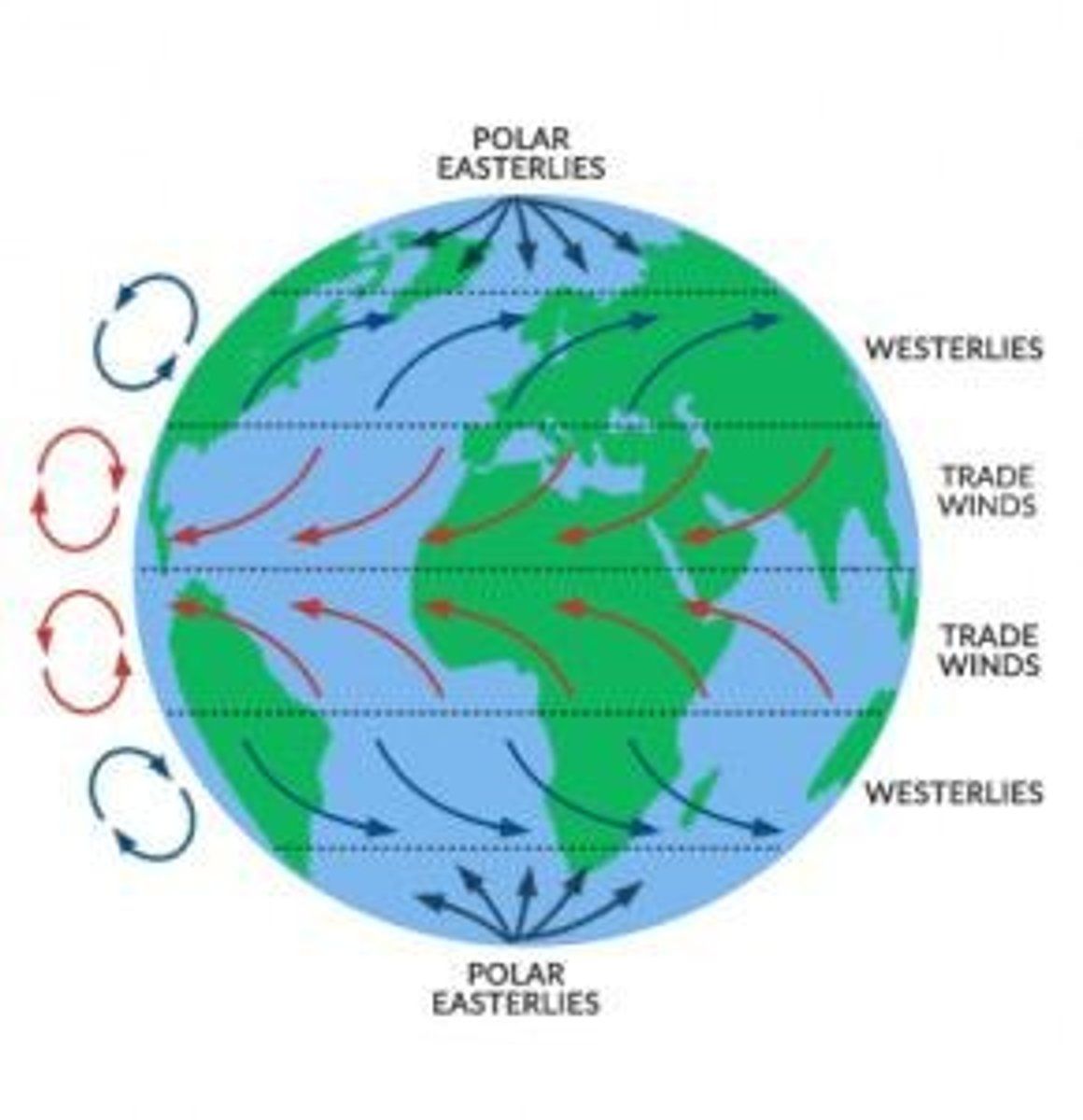
Global Patterns of Water Circulation
Influenced by uneven heating of the Earth's surface.
Biomes
Major types of ecosystems characterized by specific climate conditions, flora, and fauna.
Latitude
Geographical coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface.
Rainfall
Precipitation that varies across different biomes and is influenced by moisture and temperature.
Distribution of Life
Refers to how different species are spread out across the planet.
Abundance of Life
Refers to the number of individuals of a species present in a given area.
Ecosystem Ecology
Focuses on the interactions between organisms and their environment as a system.

Community Ecology
Study of how different species interact within a community.
Population Ecology
Study of how populations of species interact with their environment.
Organismal Ecology
Study of individual organisms and their interactions with the environment.
Solar Radiation
Energy from the sun that affects temperature patterns on Earth.
Curvature of the Earth
Dictates variation in temperature over space.
Daylength
The duration of time in a day during which sunlight is present.
Photosynthesis
Process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
Seasonal Variation
Changes in environmental conditions and biological processes that occur at different times of the year.
Moisture
Hot rising air at the equator creates Hadley cells, which generate predictable areas of precipitation (e.g. deserts).
Coriolis effect
A phenomenon that causes fluids, like water and air, to curve as they travel across or above Earth's surface.
Abiotic factors
Four main abiotic factors fundamentally affect the distribution and abundance of life on earth (ecology): Sunlight, Temperature, Moisture, Wind.
Sunlight
Amount of sunlight affects daylength; the tilt of the earth creates variation in daylength over time & space.
Temperature
Curvature of the earth dictates variation in temperature over space.
Wind
Wind is due to temperature differences and earth rotation.
Biotic interactions
Interactions among organisms, including predation, competition, mating, and parasitism.
Ecology
Ecology is defined as the study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment; its main outcome is understanding the distribution and abundance of organisms on the planet.
Seasonality in weather
Caused by Earth's spherical shape and its tilt on its axis by 23.5 degrees.
Variation in temperature with latitude
Caused by Earth's spherical shape and its tilt on its axis by 23.5 degrees.
Areas at 30° North and South latitude
Most likely to be subjected to falling air currents and desert conditions.
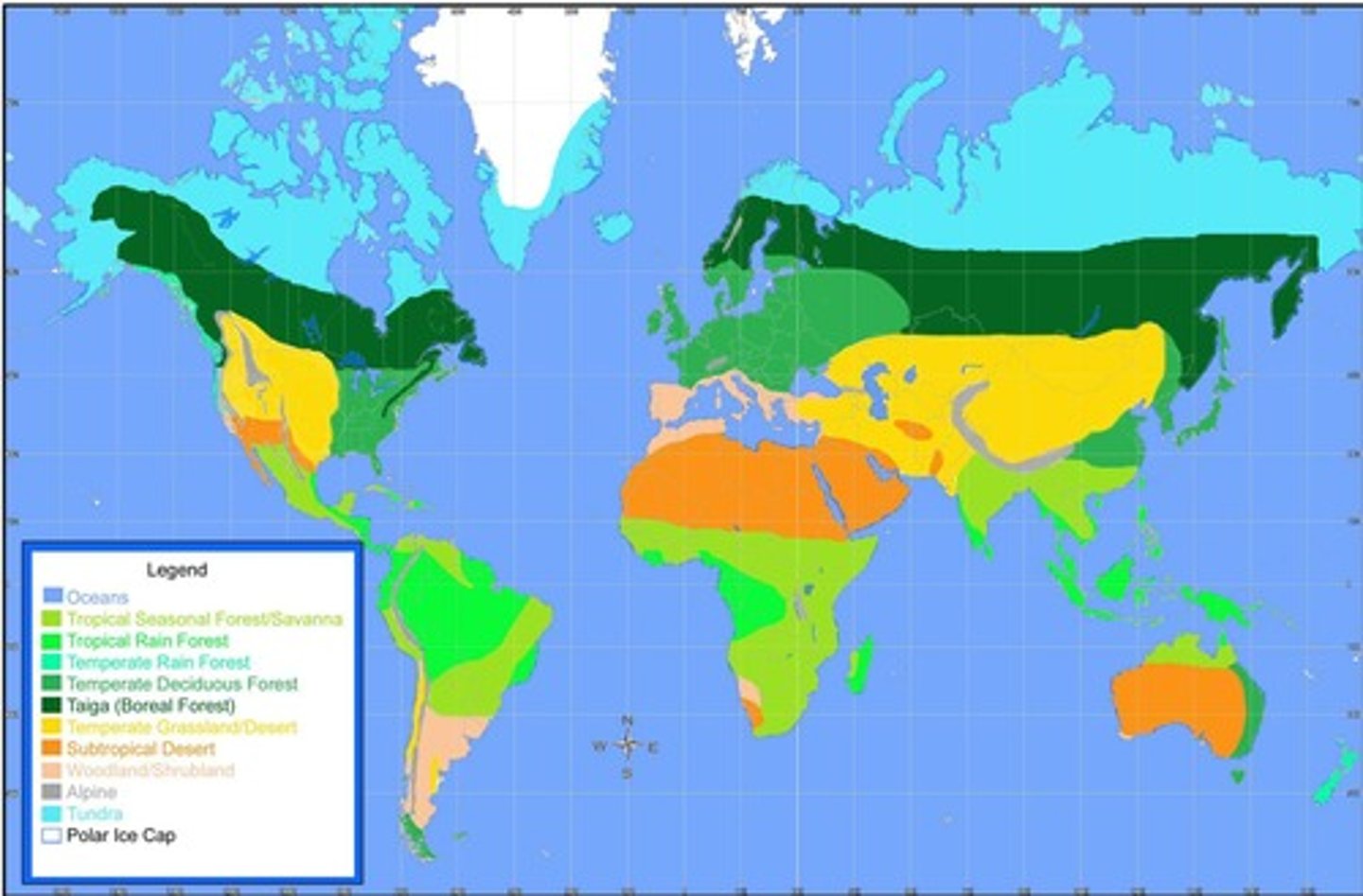
Biomes
Broad scale patterns of distribution of plant and animal 'types'.
Frederic Clements
Noted for his work on biomes and the relationship between vegetation types and their associated animals.
Tundra
A type of biome characterized by cold temperatures and minimal vegetation.
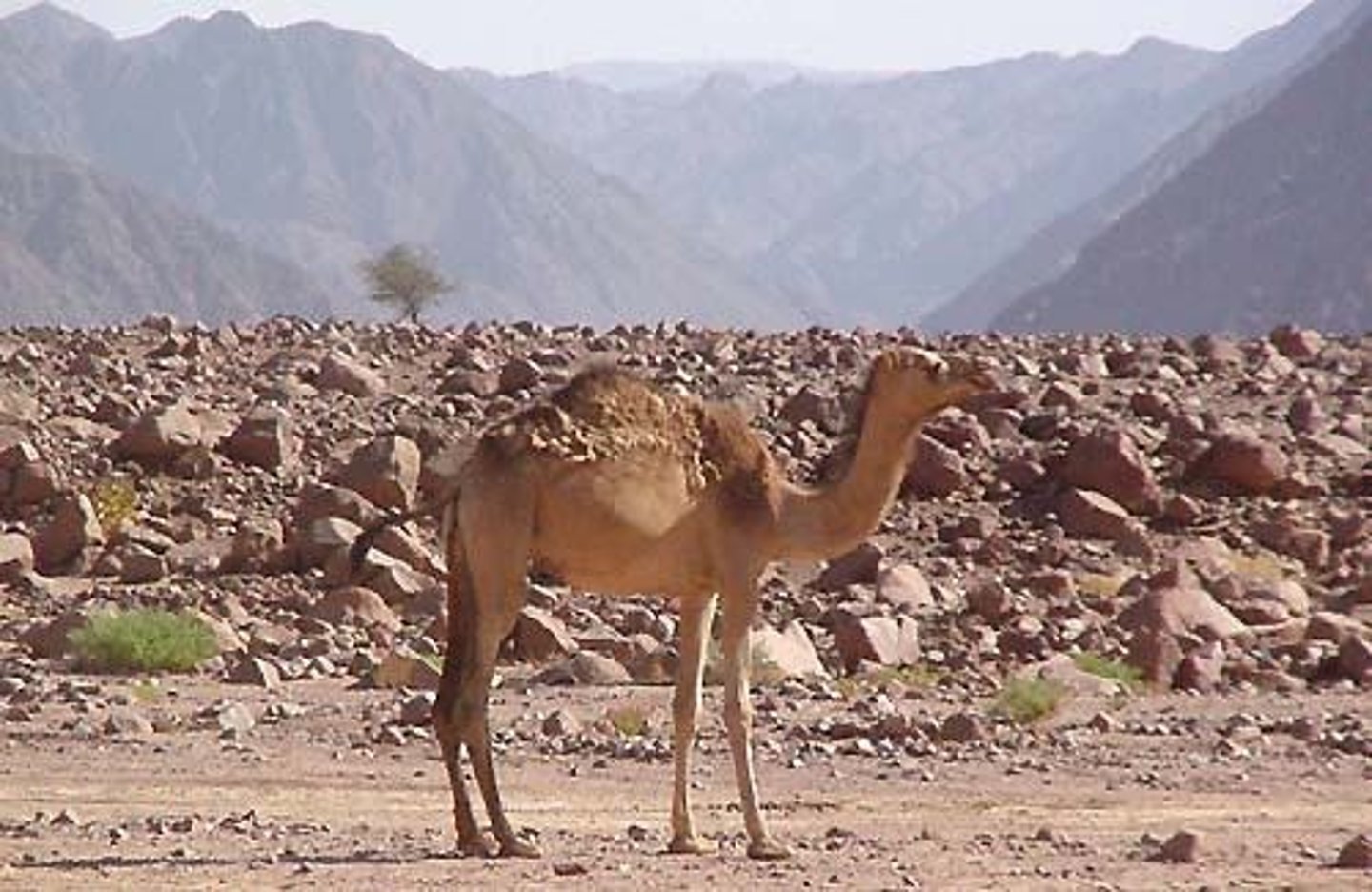
Desert
A biome characterized by low precipitation and extreme temperatures.

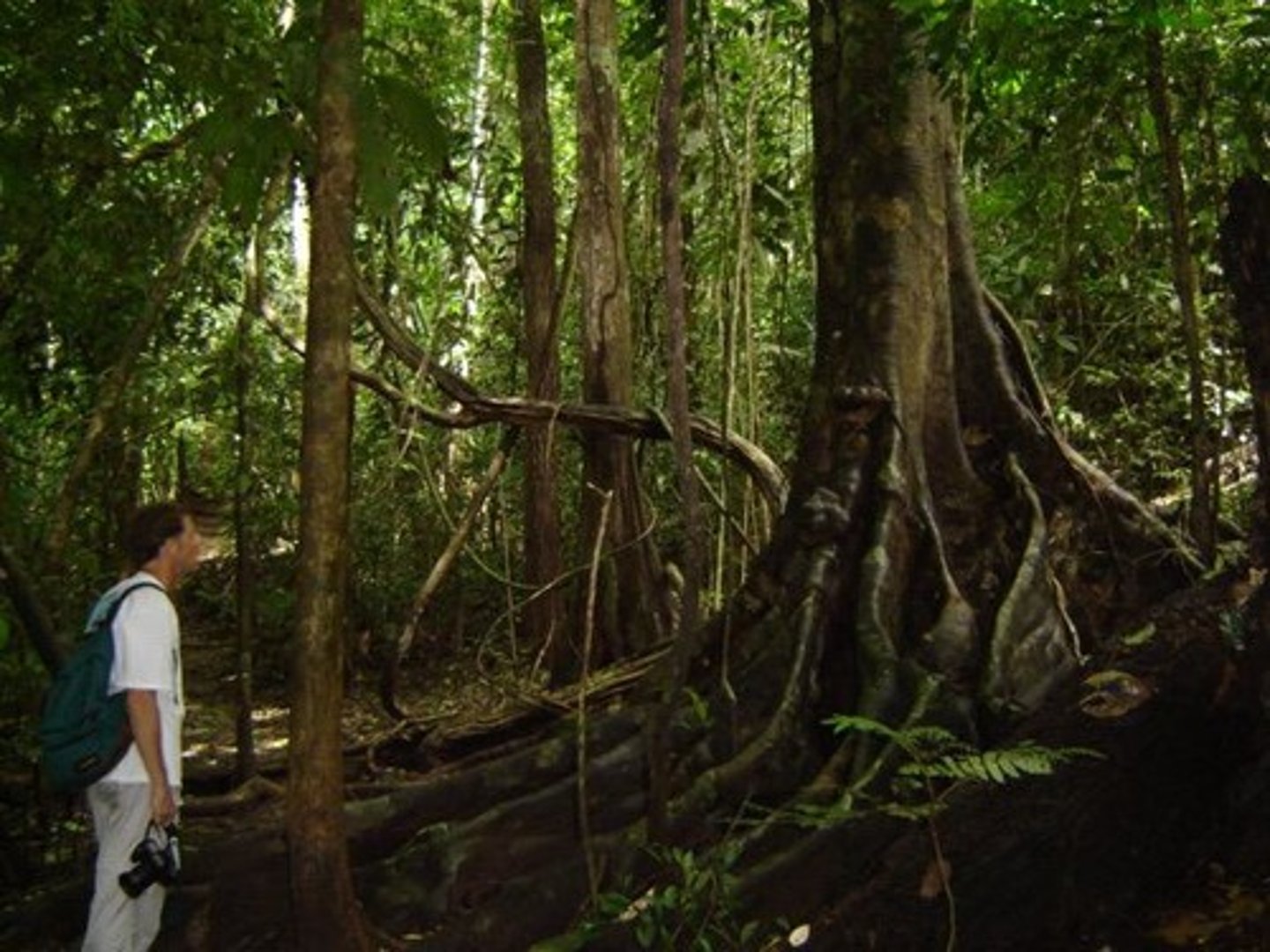
Tropical Rainforest
A biome characterized by high rainfall and diverse plant and animal life.

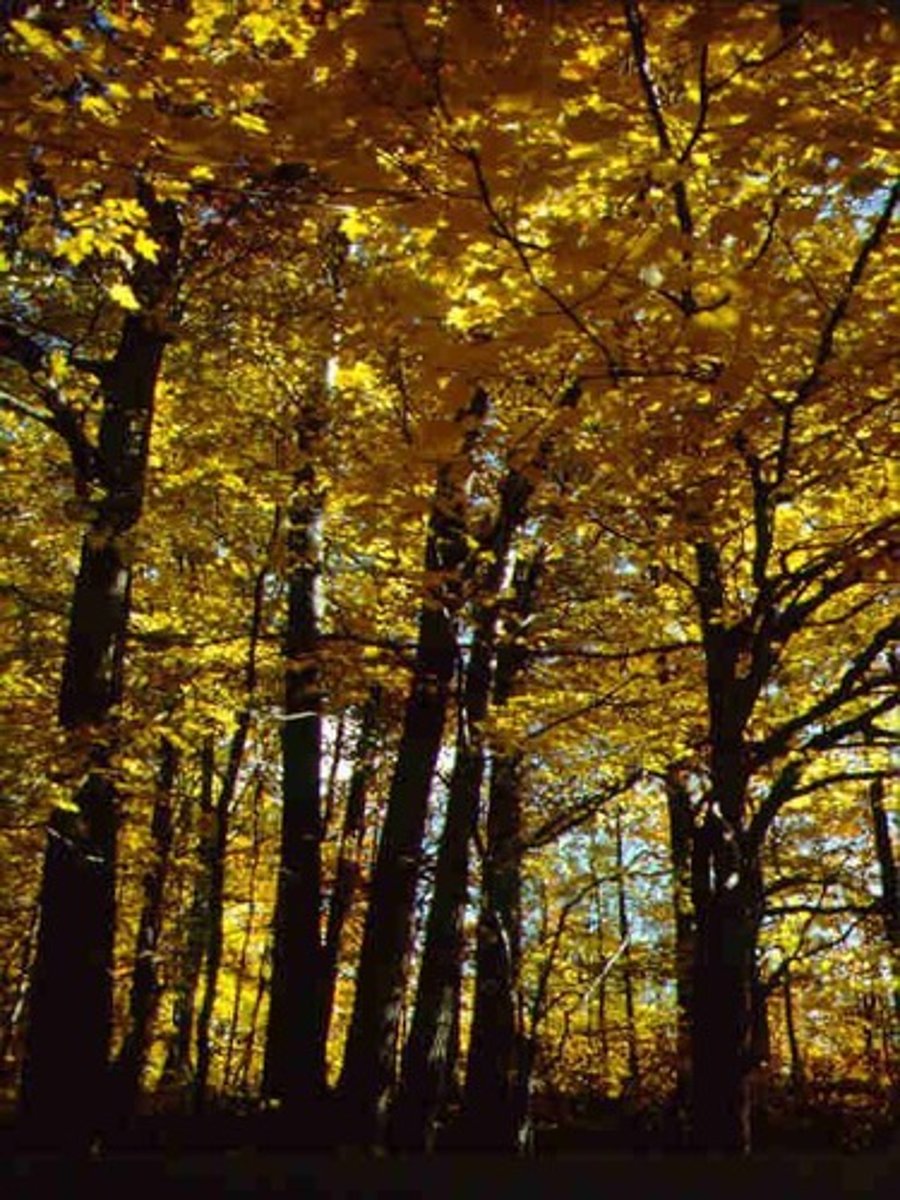
Temperate Deciduous Forest
A biome characterized by four distinct seasons and trees that shed leaves in winter.

Grassland
A biome characterized by vast open spaces dominated by grasses.
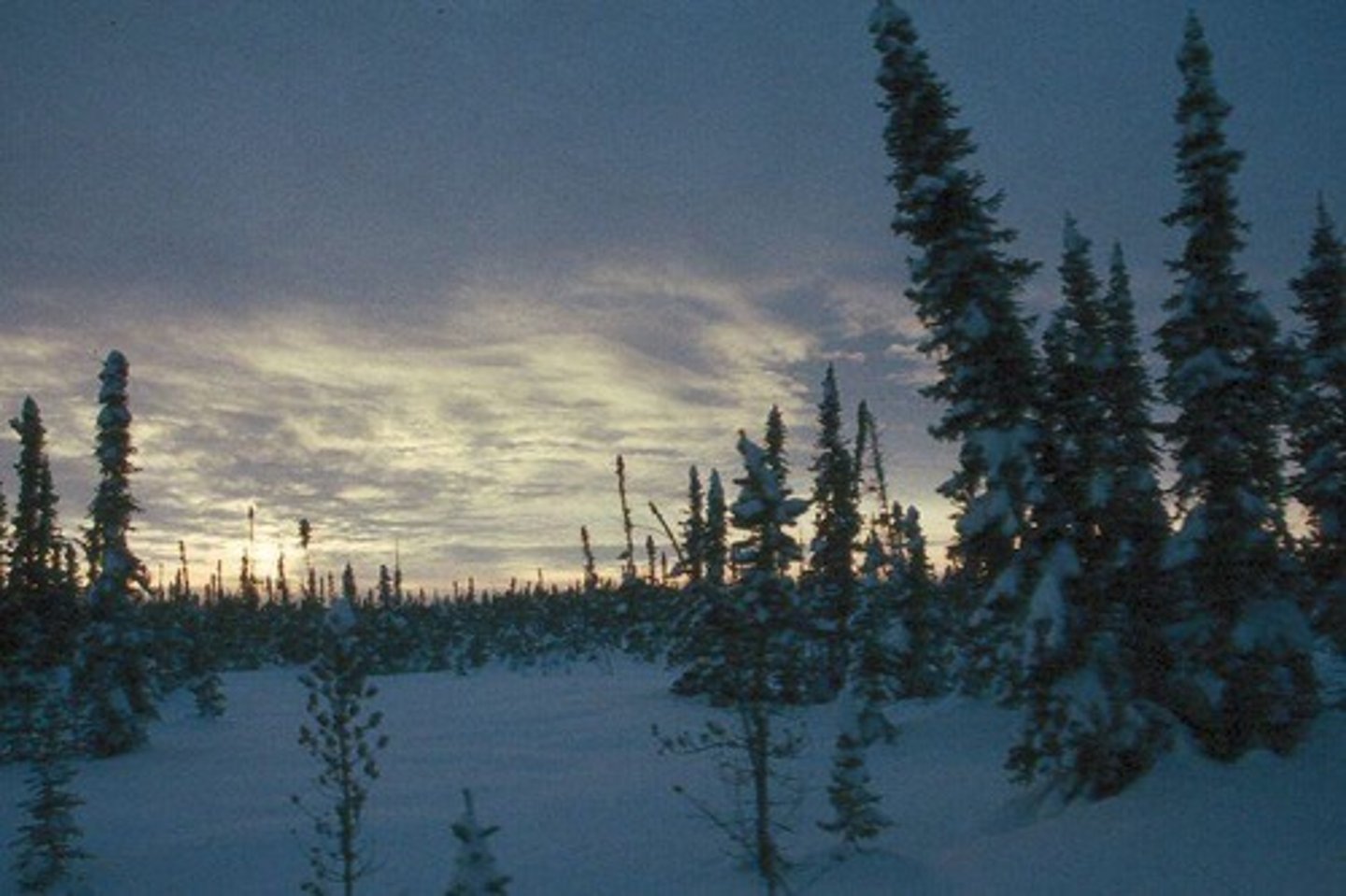
Taiga/Boreal Forest
A biome characterized by coniferous forests and cold climates.

Dominant Plant Life Forms
Trees, grasses, shrubs, and low trees reflect adaptations to different climatic environments.
Climograph
A graphical representation of the climate of a region, showing temperature and precipitation patterns.