5.1 Electron structure
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Atomic orbitals
A region around the nucleus where a pair of electrons with opposite spins exist
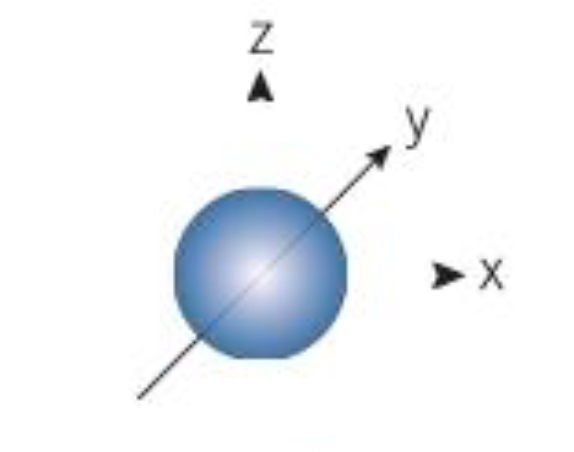
What orbital is shown here
S orbital
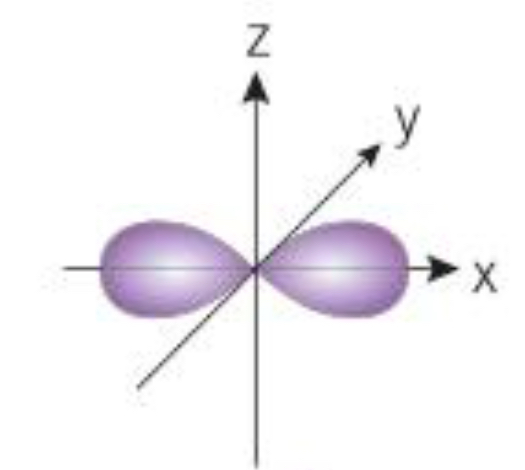
What orbital is shown here
P orbital
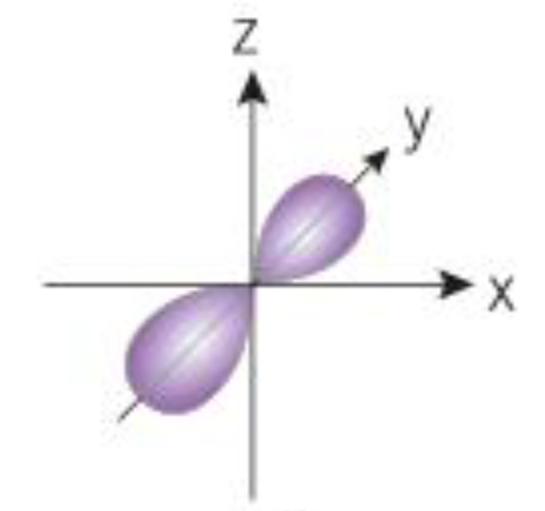
What orbital is shown here
P orbital
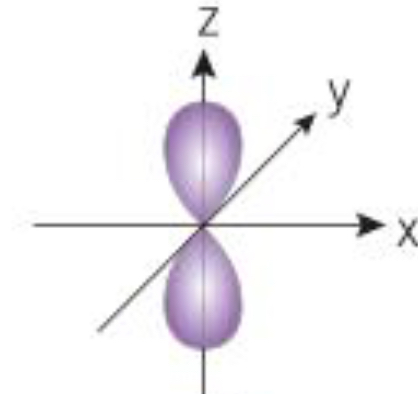
What orbital is shown here
P orbital
How many electrons are there in a full d orbital
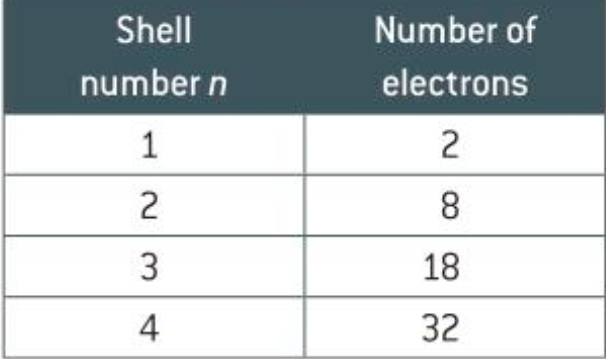
What is a shell
A shell can also be known as the energy level of an atom. The shell number (principal quantum number n) can tell us how many electrons there are
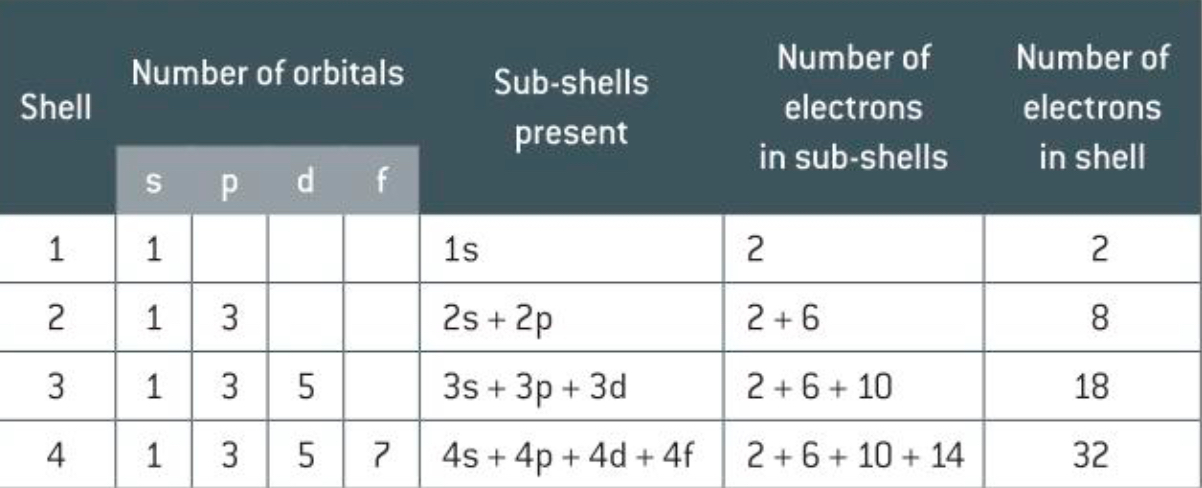
What is a sub shell
A sub shell tells us how the electrons within a shell maps out. When n = 1 the sub shell is 1s2 meaning that number of electrons is 2
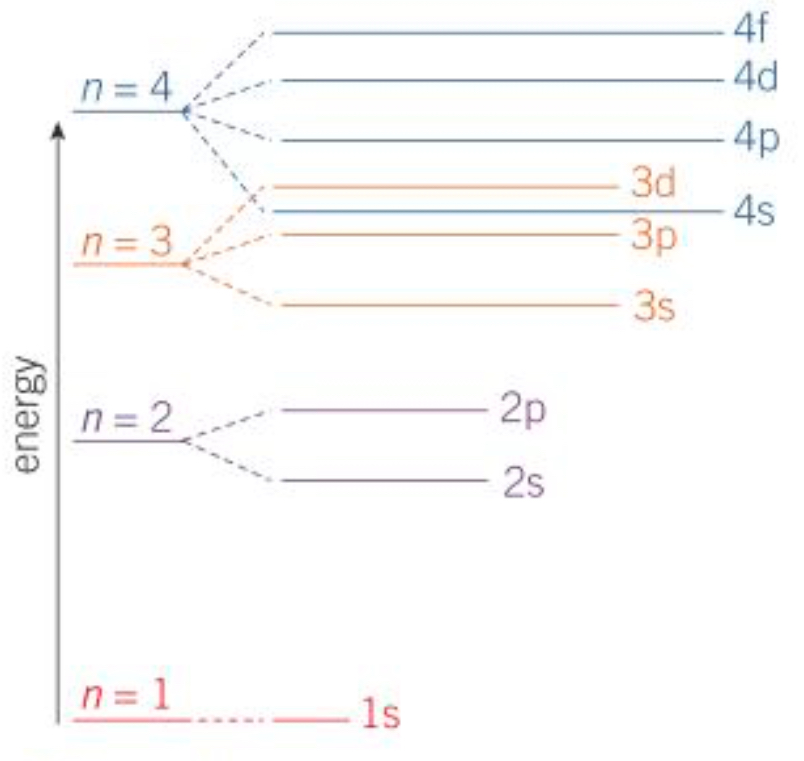
Describe how energy levels affect the order in which sub shells are filled
Sub shells are filled based on their energy levels. Lower energy levelled sub shells are filled first because they’re easier to fill out. This means that 4s is filled before the 3d shell
What are the rules for filling up shells
Electrons should fill up all the orbitals within a sub shell before pairing up. Paired up electrons must have opposite spins to reduce repelling each other.
Rules for writing out electron configuration
Write them out in shell order
4s fills out and empties first before 3d