Embryology of Heart Development: Week-by-Week Cardiac Formation and Fetal Circulation
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the primitive heart tube?
The initial structure of the heart formed by the fusion of two heart tubes during embryonic development.
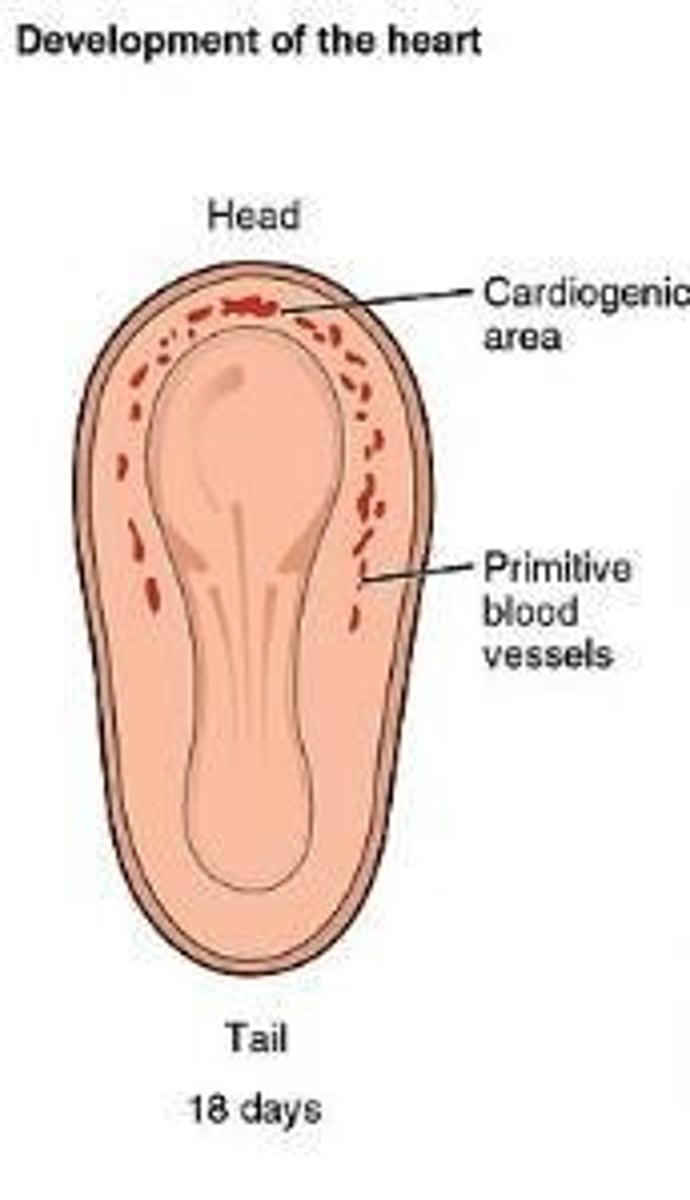
What are the key stages of heart development from fertilization to week 3?
Week 1: Fertilization and formation of blastomeres, morula, and blastocyst.
Week 2: Formation of bilaminar disk and implantation. Week 3: Gastrulation and formation of three germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm).
What are the three germ layers formed during gastrulation?
Endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm.
What structures does the endoderm give rise to?
Epithelial lining of digestive and respiratory tracts, lining of urethra, bladder, reproductive system, liver, and pancreas.
What structures does the mesoderm develop into?
Notochord, musculoskeletal system, muscular layer of stomach and intestine, and the circulatory system.
What does the ectoderm develop into?
Epidermis of skin, cornea and lens of eye, and the nervous system.
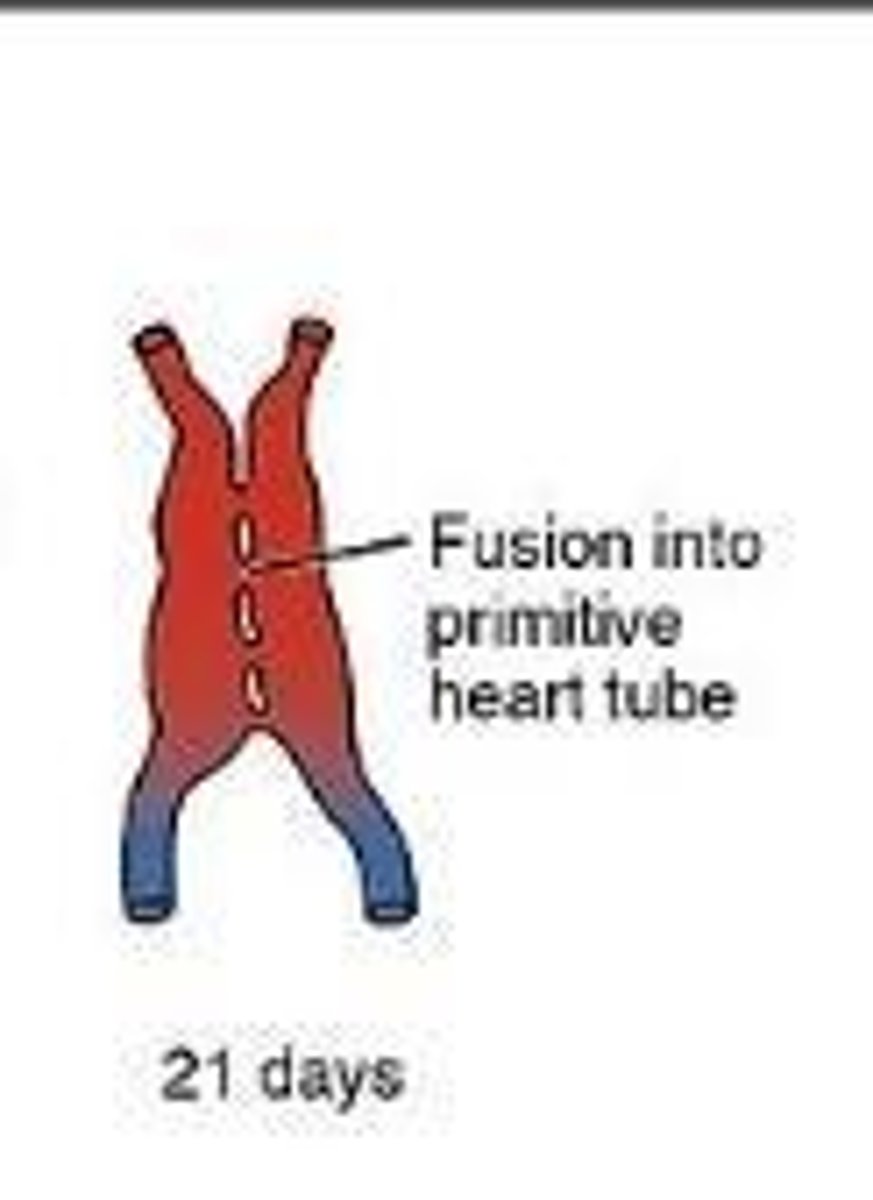
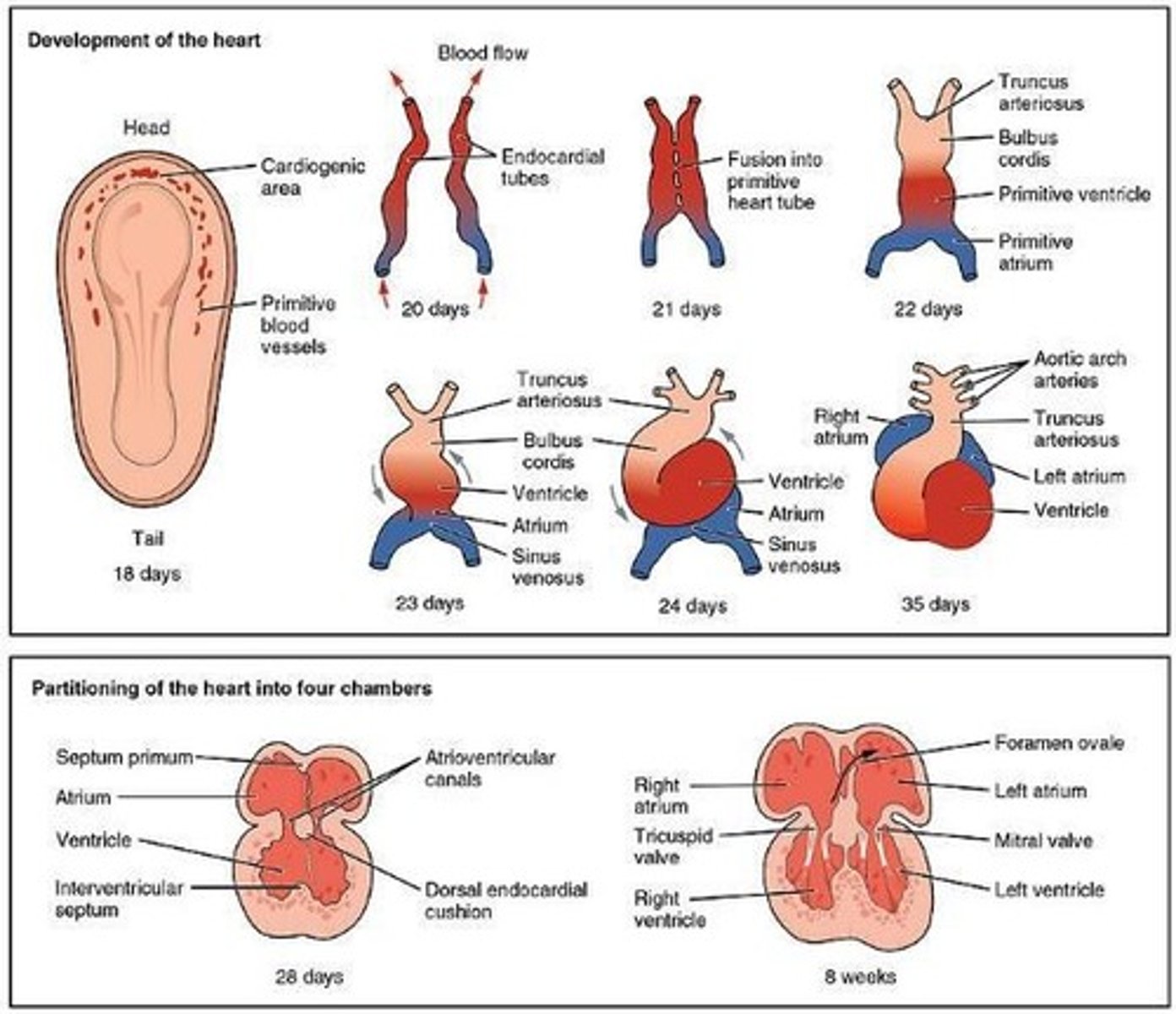
What happens to the heart tubes by week 3 of development?
The two heart tubes fuse into a single endocardial heart tube.
What are the components of the heart tube by week 3?
Sinus venosus, primitive atrium, atrioventricular sulcus, primitive ventricle, interventricular sulcus, bulbus cordis, and aortic sac.
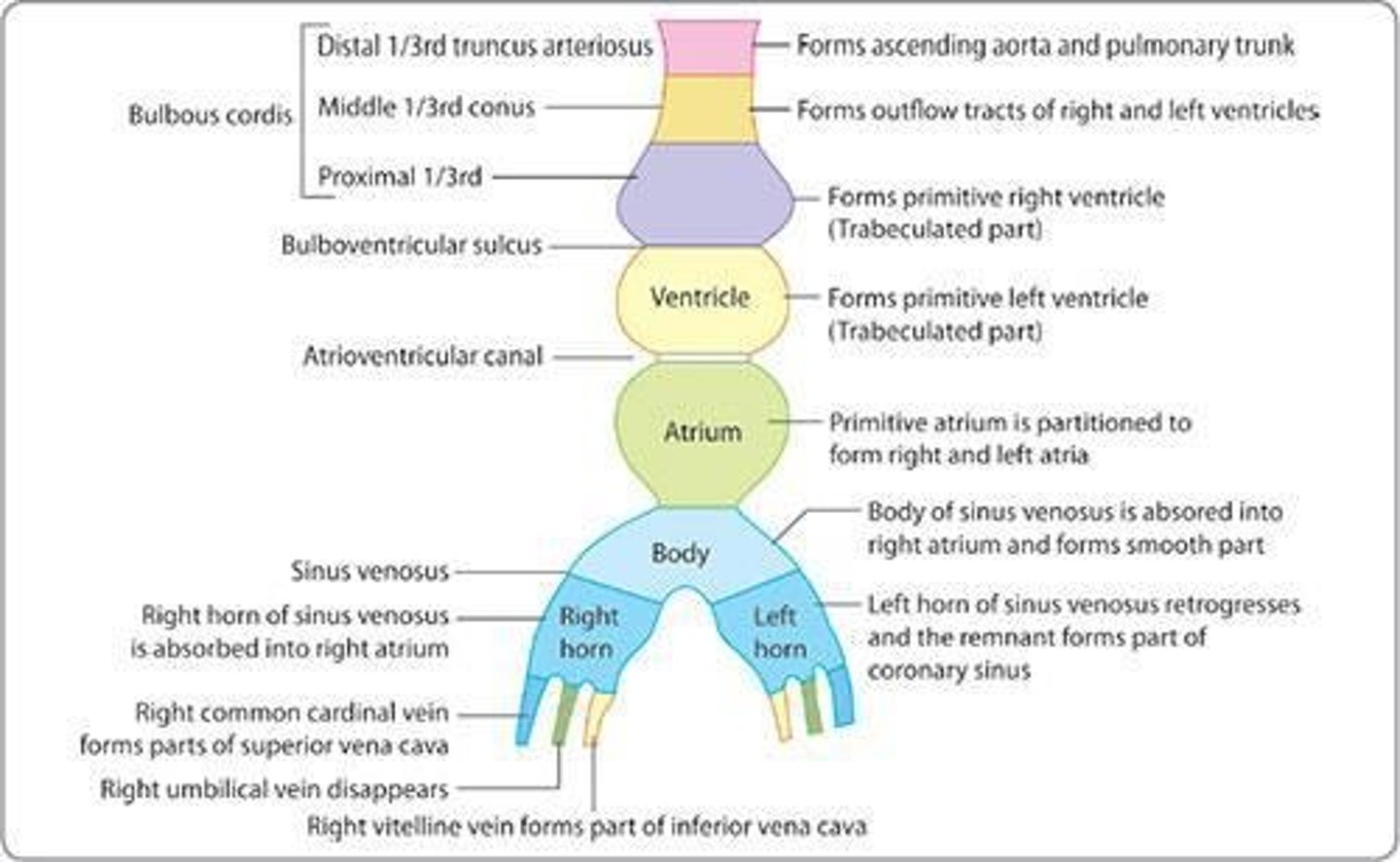
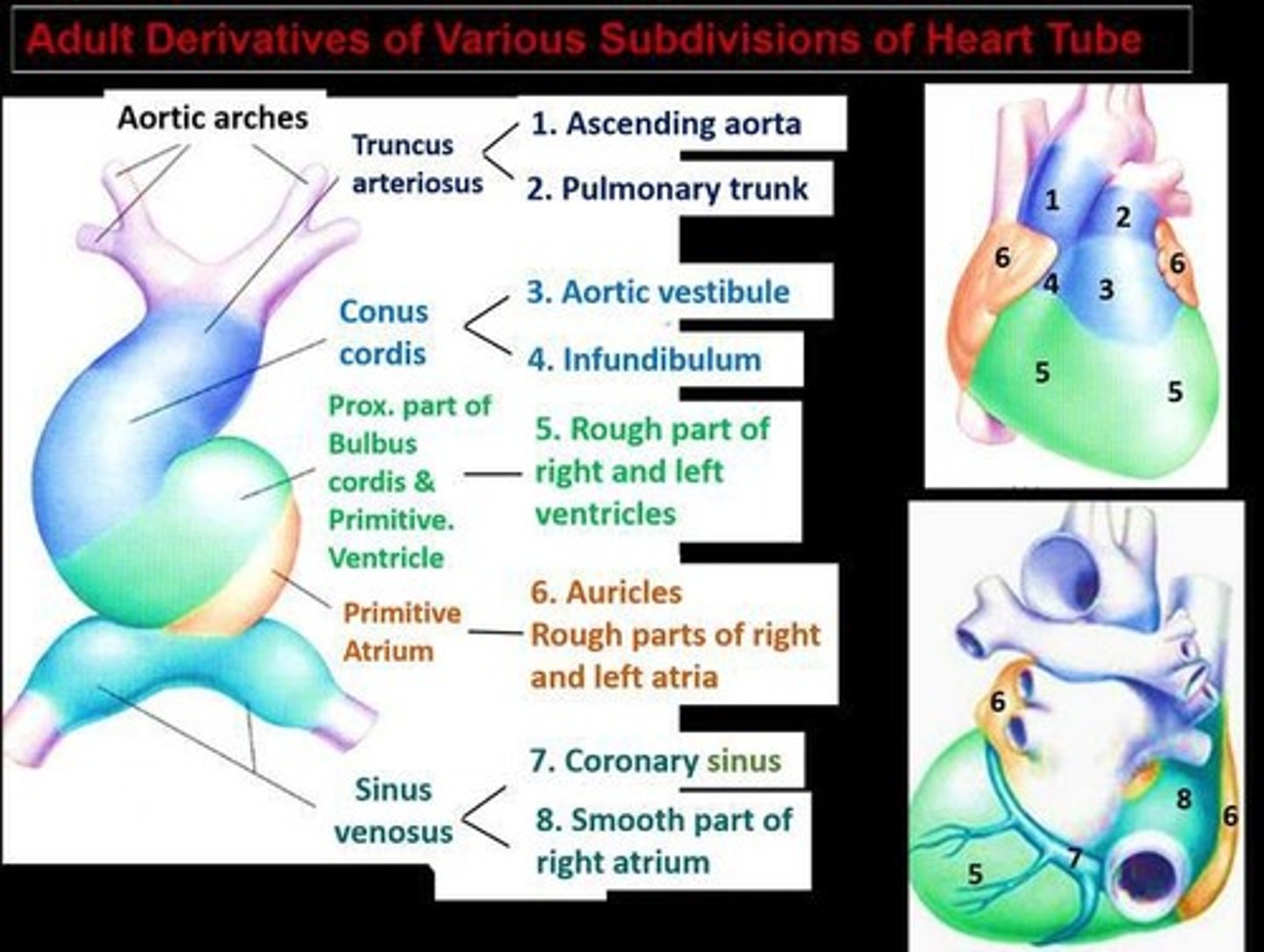
What is the significance of the bulbus cordis in heart development?
It divides into three parts that contribute to the right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta, and main pulmonary artery.
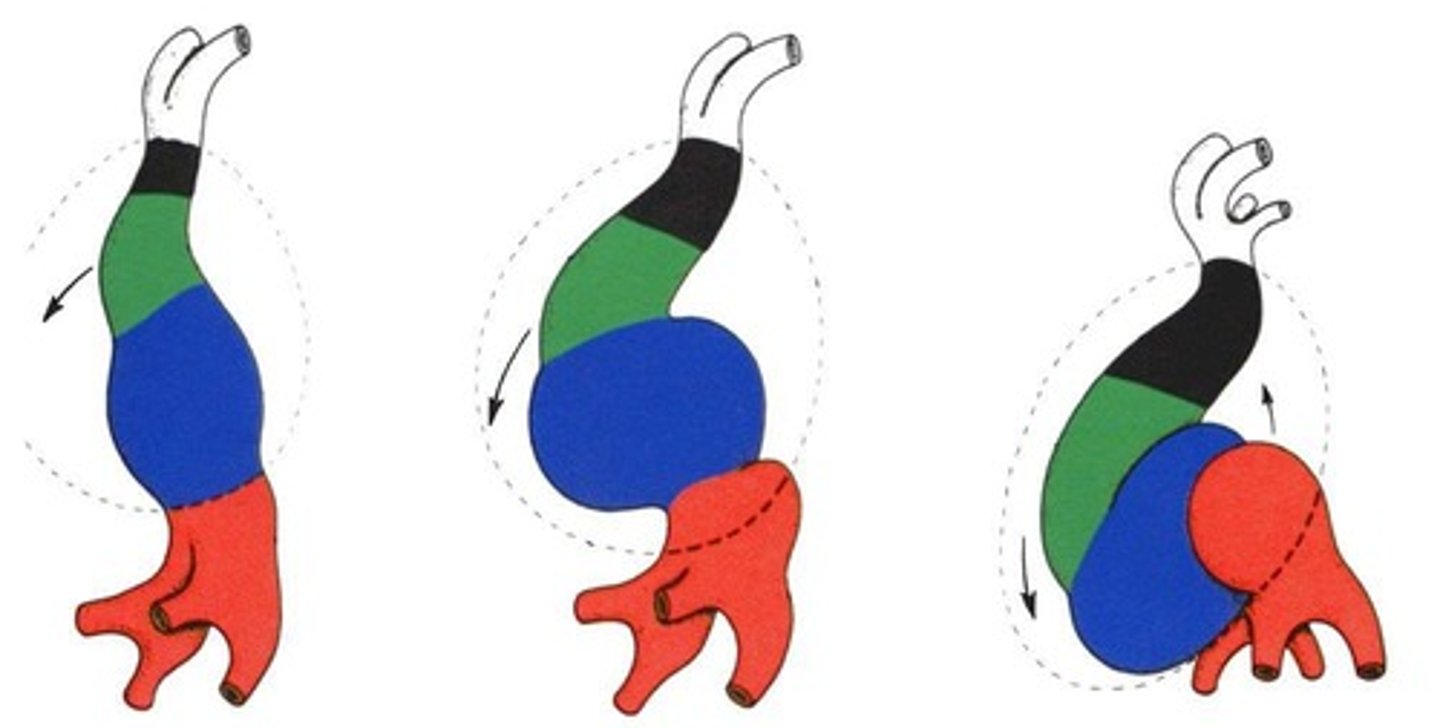
What occurs in week 4 of heart development?
The heart begins to beat, and the bulboventricular loop forms.
What is the heart rate at the beginning of week 4?
60-70 beats per minute.
What is the role of the septum primum during heart development?
It grows from the dorsal wall of the primitive atrium toward the endocardial cushions, contributing to atrial septation.
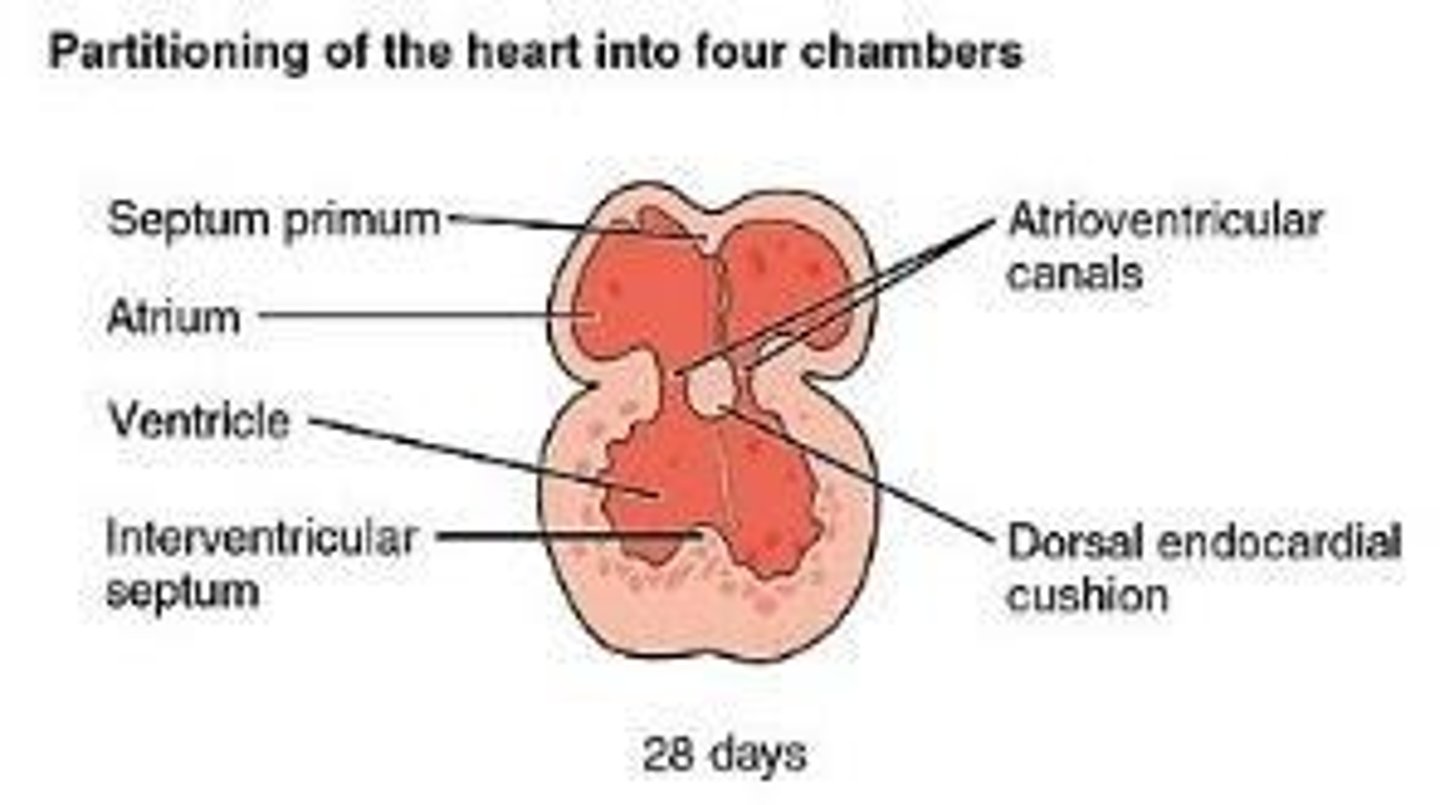
What happens in week 5 regarding the septum primum?
The septum primum reaches the endocardial cushions and gets perforated to form the ostium secundum.
What is the function of the endocardial cushions?
They serve as primitive valves within the atrioventricular canal.
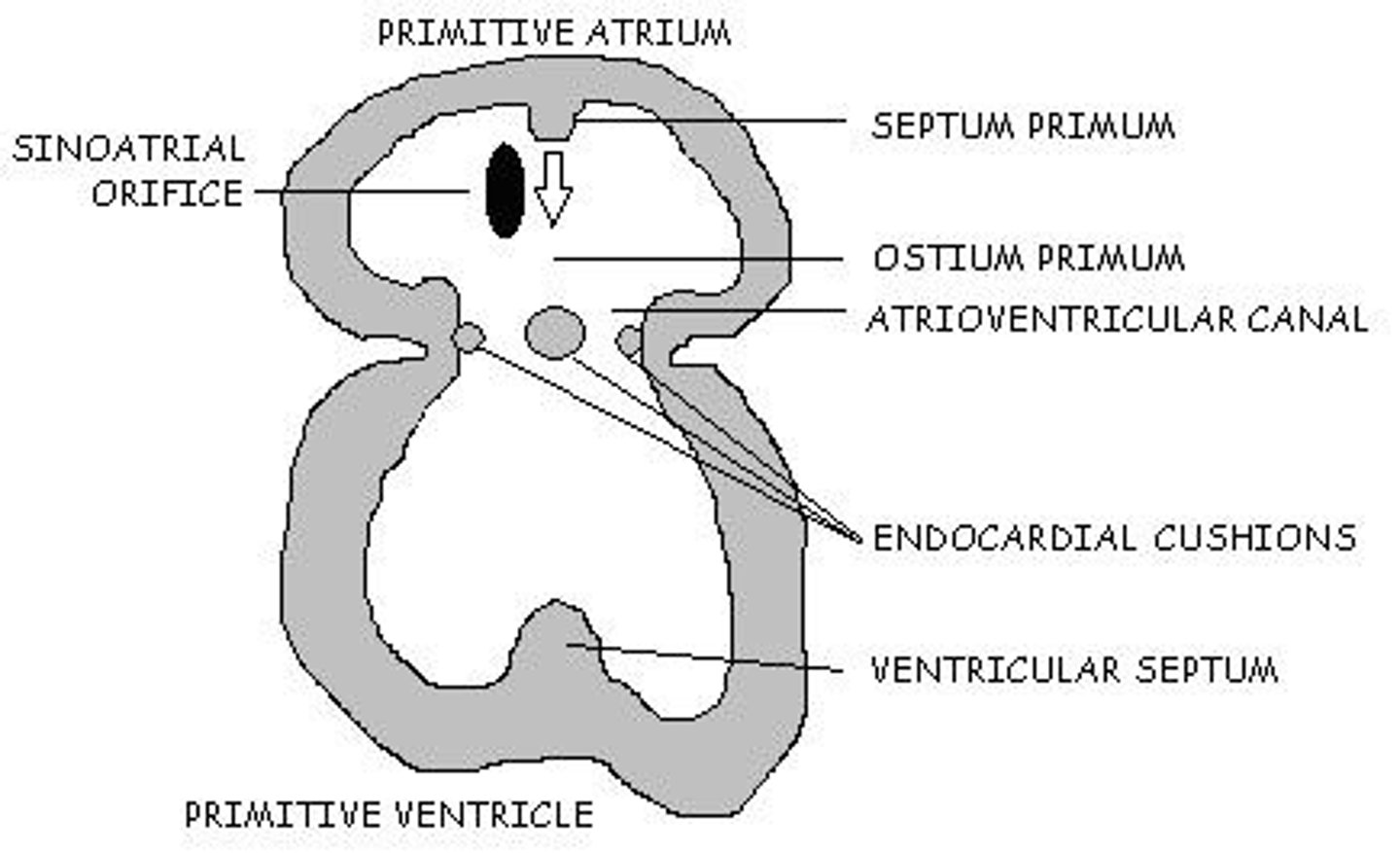
What is the significance of the interventricular sulcus?
It externally separates the ventricles and indicates the internal division of the heart.
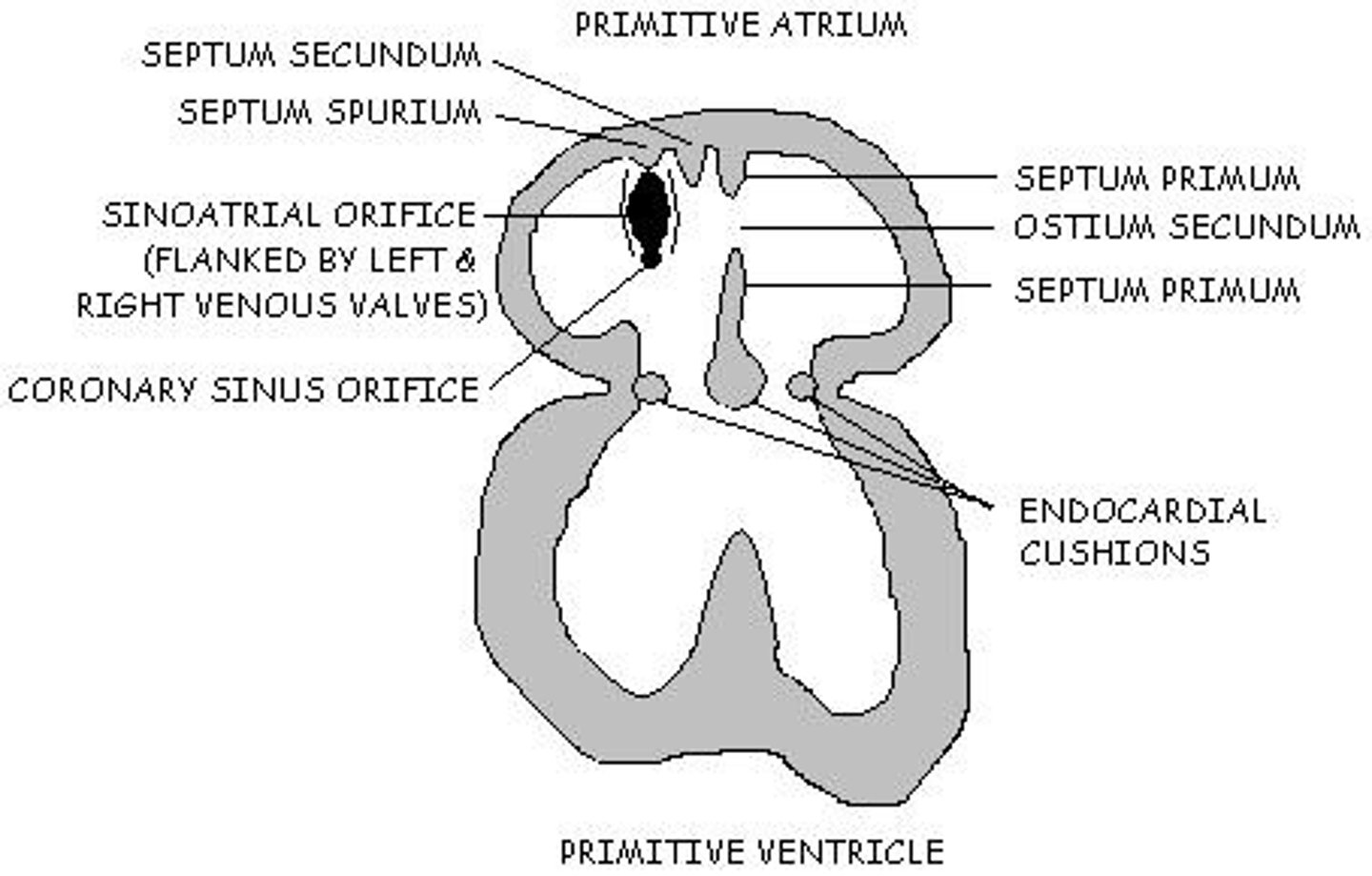
How does the atrioventricular canal change during development?
It transitions from a common orifice to two orifices, eventually forming the mitral and tricuspid valves.
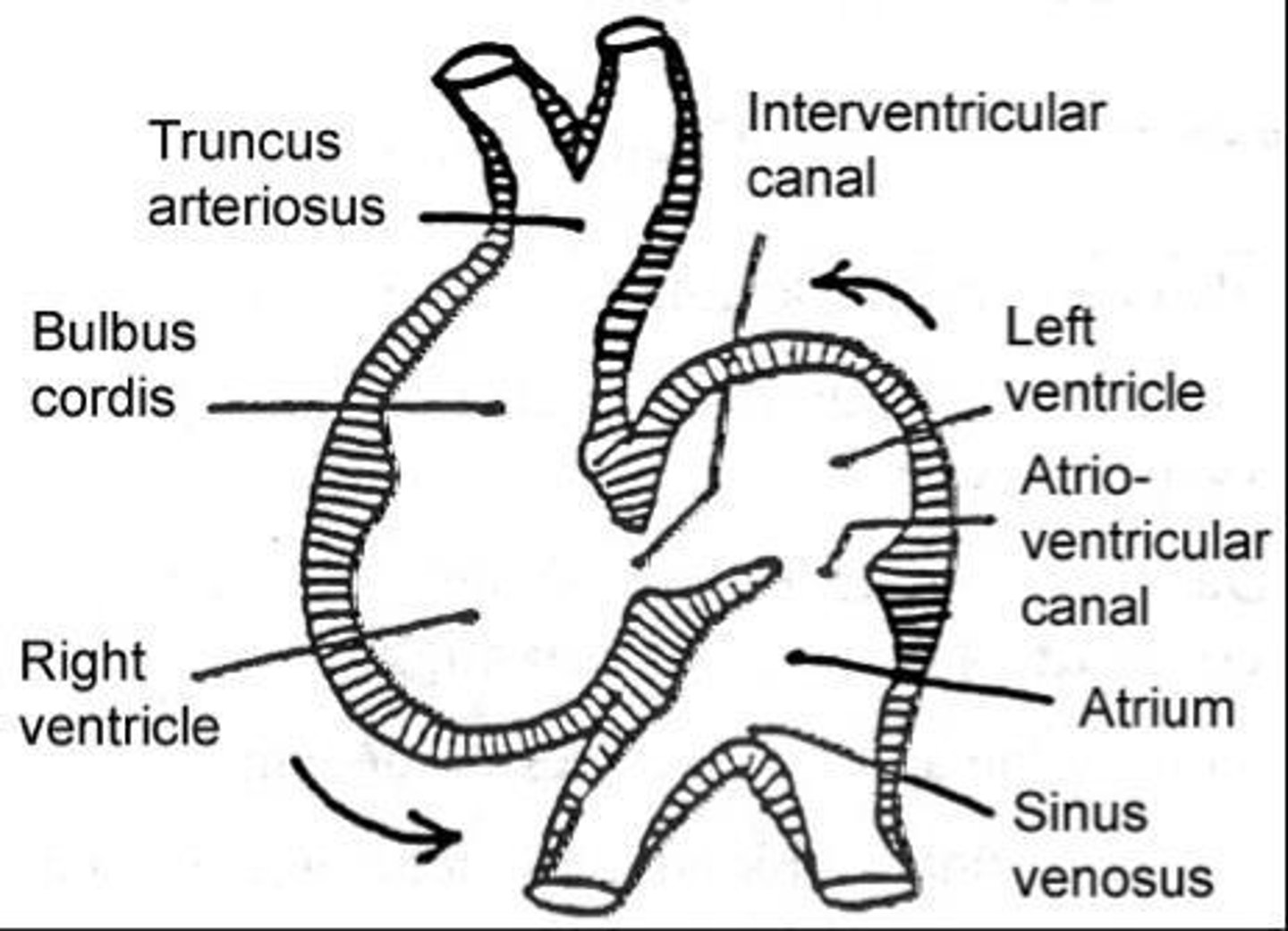
What is the role of the truncus arteriosus?
It is the only great vessel leaving the heart during early development.
What is the difference between fetal and neonatal circulation?
Fetal circulation involves shunts like the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus, which close at birth to establish neonatal circulation.
What are the main differences between the primitive atrium and the adult atria?
The primitive atrium communicates directly with the left ventricle, while in the adult heart, it communicates with both ventricles via the atrioventricular valves.
What is the fate of the right and left venous valves during heart development?
They develop to help separate the right and left atria and facilitate proper blood flow.
What is the significance of the aortic sac in heart development?
It gives rise to the definitive aortic arch and contributes to the formation of great vessels.
What is the role of the sinus venosus in the developing heart?
It is formed by the union of three pairs of veins and contributes to the formation of the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and pulmonary veins.
What happens to the heart's structure by the end of week 7?
The heart has developed into four chambers with atrioventricular and semilunar valves.
What is the heart rate at birth?
130-150 beats per minute.
Where is the inlet IVS located?
At the level of the atrioventricular canal.
Where is the outlet IVS located?
At the level of the ventricular outflow tract.
What happens to the septum secundum during week 6 of cardiac development?
It ceases to grow and forms the foramen ovale.
What occurs during week 6 in terms of atrial communication?
The right atrium communicates with the right ventricle, and the left atrium communicates with the left ventricle.
What is the role of the remnant of the septum primum during week 7?
It acts as a flap at the foramen ovale, controlling blood flow between the two atria.
What major structures are formed by the end of week 7 in cardiac development?
The coronary sinus is formed, and the secondary interventricular foramen is obliterated by the membranous septum.
What is the significance of the bulbar ridges in the truncus arteriosus?
They grow toward each other and fuse, dividing the truncus arteriosus into the aorta and main pulmonary artery.
By the end of the 7th week, what is the status of heart development?
The major development of the heart is complete, and fetal circulation is in place.
What does the sinus venosus receive blood from?
It receives blood from the common cardinal vein, umbilical vein, and vitelline vein.
What does the right horn of the sinus venosus contribute to?
It contributes to the formation of the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus, and posterior wall of the right atrium.
What forms the internal jugular vein?
The anterior cardinal vein (distal).
What is the fate of the left common cardinal vein?
It forms the coronary sinus.
What does the right anterior cardinal vein form?
It forms the right brachiocephalic vein (innominate vein).
What happens to the ductus arteriosus after birth?
It closes almost immediately due to muscular contraction, becoming the ligamentum arteriosum.
What is the primary role of the placenta in fetal circulation?
It is responsible for delivering vital oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products.
How does blood flow from the placenta to the fetus?
Oxygen-rich blood travels from the placenta through a single umbilical vein.
What is the difference in blood oxygen saturation between the left and right heart in a fetus?
The left heart has a high O2 saturation (approximately 98%), while the right heart has a low O2 saturation (approximately 75%).
What happens to the foramen ovale at birth?
It closes due to increased left atrial pressure, becoming the fossa ovalis.
What is the normal fetal heart rate range?
Between 110 and 160 beats per minute (bpm) throughout pregnancy.
What occurs to the umbilical arteries shortly after birth?
They close shortly after birth due to smooth muscle contraction.
What does the left arch of the fourth aortic arch form?
It forms part of the arch of the aorta.
What does the right arch of the sixth aortic arch form?
It forms the right pulmonary artery.
What is the outcome of the fifth aortic arch?
It either never forms or forms incompletely and regresses.
What is the role of the ductus venosus in fetal circulation?
It allows a portion of enriched blood to bypass the liver and flow directly into the inferior vena cava.
What happens to the umbilical vein after birth?
It closes and becomes the ligamentum venosum.
What is the primary function of the lungs in adult circulation?
They are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What does the truncus arteriosus become?
Ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk.
What congenital defects result from failed neural crest migration in the truncus arteriosus?
Transposition of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot.
What does the bulbus cordis form?
Right ventricle and smooth parts of the left ventricle.
What does the primitive atria give rise to?
Trabeculated parts of the left and right atria.
What does the primitive ventricle develop into?
Majority of the left ventricle.
What does the left horn of the sinus venosus become?
Coronary sinus.
What does the right horn of the sinus venosus form?
Smooth part of the right atrium
What does the right common cardinal vein + right anterior cardinal vein form?
Superior vena cava.
What does the foramen ovale become after birth?
Fossa ovalis
What does the umbilical artery become?
Medial umbilical ligaments.
What does the umbilical vein become?
Ligamentum teres hepatis (within the falciform ligament).
What does the ductus arteriosus form?
Ligamentum arteriosum.
What does the ductus venosus become?
Ligamentum venosum.
What structure does the allantois give rise to?
Urachus (→ median umbilical ligament in adults).