anatomy and physiology honors chapter 1
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
anatomy
the study of the structure of body parts (morphology)
physiology
the study of the function of body parts
list in order from least to most complex the levels of structural organization
atoms→ molecules → cells → tissues → organ → organ system → organism
examples of each level
atoms - hydrogen, lithium, etc.
molecules - H2O, CO2
cells - osteocytes (bone cells), myocytes (muscle cells), cardiocytes (heart cells)
tissues - Muscular, Epithelial, Nervous, Connective (MENC)
organs - liver, heart, lungs, etc.
organ systems - digestive, cardiovascular, nervous, etc.
organism - humans
CCT-OSO
Chemical (atoms and molecules) , Cells, Tissues, Organ, Organ System, Organism
4 types of tissues and examples of each
MENC
muscular - helps with movement; ex. cardiac, skeletal, smooth
epithelial - lines body cavities; ex. blood vessels, glands
nervous - sends and receives information about stimuli; ex. neurons, neuroglia
connective - most dominant; ex. blood and bone (solid), cartilage and adipose (loose)
11 organ systems
Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous, Endocrine, Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, Male/Female Reproductive
Integumentary System function and major organs
encloses internal body structures
site of many sensory receptors
hair, skin, nails
Skeletal System function and major organs
supports the body and enables movement (with muscular system)
bones, cartilage, joints
Muscular System function and major organs
enables movement (with skeletal system) and helps maintain body temperature
skeletal muscles, tendons
Nervous System function and major organs
detects and processes sensory information
activates bodily responses
brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
Endocrine System function and major organs
secretes hormones and regulates bodily temperatures
pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, testes/ovaries
Cardiovascular System function and major organs
delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues
equalizes temperature in the body
heart, blood vessels
Lymphatic System function and major organs
returns fluid to blood and defends against pathogens
thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, lymphatic vessels
Respiratory System function and major organs
removes carbon dioxide from the body and delivers oxygen to the blood
nasal passage, trachea, lungs
Digestive System function and major organs
processes food for use by the body
removes wastes from undigested food
stomach, liver, gall bladder, large/small intestine
Urinary System function and major organs
controls water balance in the body
removes wastes from blood and excretes them
kidneys, urinary bladder
Male Reproductive System function and major organs
produces sex hormones and gametes
delivers gametes to female
epididymis, testes
Female Reproductive System function and major organs
produces sex hormones and gametes
supports embryo/fetus until birth
produces milk for infant
mammary glands, ovaries, uterus
Disease
more specific term for illness characterized by a recognizable set of signs and symptoms
Disorder
any disturbance of structure and/or function
Diagnosis
identification of the nature of an illness or other problem by examination of the symptoms
Sign vs. Symptom
Sign - objective changes that can be observed
Symptom - objective changes in body functions that are not apparent to the observer
Homeostasis
the body’s maintenance of a stable environment
3 parts of negative/positive feedback loops:
receptors detect a change
brain (control center) compares the change to the set point
effectors respond to correct the change
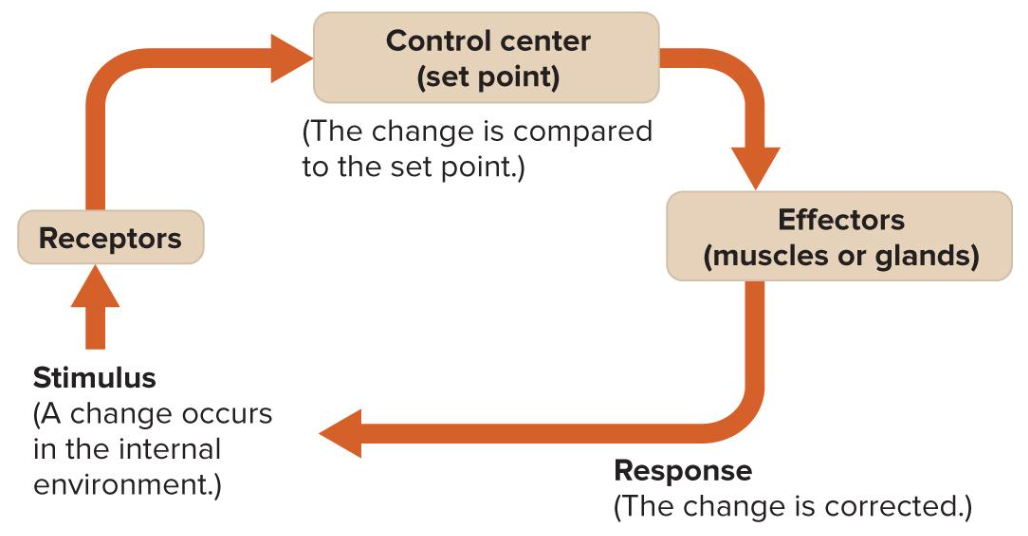
positive feedback
encourages something that needs to be done (reinforces)
ex. blood clotting
negative feedback
reverses changes
ex. if body temperature increases, we sweat to reverse the change and decrease body temperature
anatomical position
standing up straight, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward
directional term for above
superior
directional term for below
inferior
directional term for toward the front
anterior or ventral
directional term for toward the back
posterior or dorsal
directional term for closer to the sides
lateral
directional term for closer to the midline
medial
directional term for same side
ipsilateral
directional term for opposite side
contralateral
directional term for closer to the point of attachment
proximal
directional term for farther from the point of attachment
distal
directional term for closer to the surface
superficial or peripheral
directional term for more internal
deep
term for lying on the back
supine
term for lying on the stomach
prone
major body sections (cuts/planes)
sagittal - divides left/right
transverse or horizontal - divides superior/inferior
coronal or frontal - divides anterior/posterior
cross-section - a cut across a cylindrical organ
oblique section - an angular cut across a cylindrical organ
longitudinal section - a lengthwise cut
midsagittal plane - divides body/organ into left/right down the middle
5 major human body cavities
Thoracic, Abdominal, Pelvic, Cranial, Vertebral (Spinal)
thoracic cavity organs
lungs, heart, trachea, esophagus, thymus gland
abdominal cavity organs
stomach, liver, spleen, gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas
pelvic cavity organs
terminal end of the large intestine, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs
cranial cavity organs
brain
vertebral/spinal cavity organs
spinal cord
diaphragm muscle
divides the thoracic and abdominal cavity
9 regions of the abdominal area
Right Hypochondriac, Epigastric, Left Hypochondriac
Right Lumbar, Umbilical, Left Lumbar
Right Iliac, Hypogastric, Left Iliac
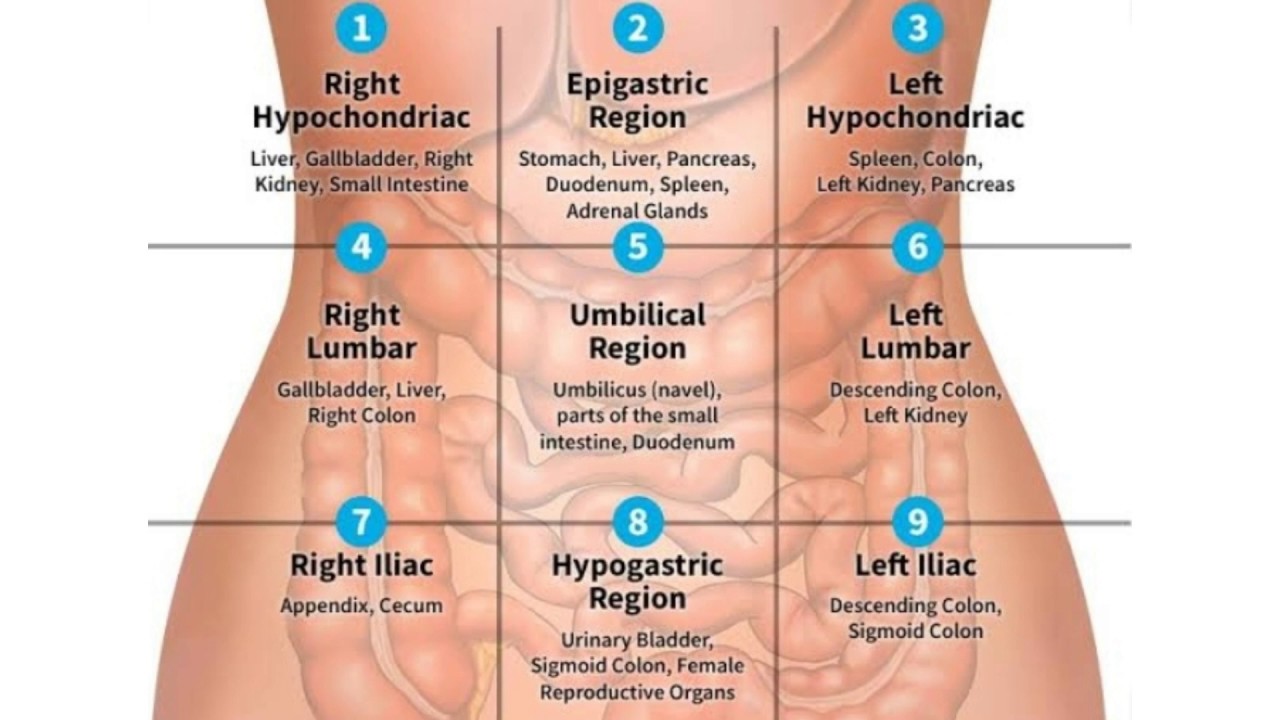
right hypochondriac region organs
liver, gall bladder, right kidney, small intestine
epigastric region organs
stomach, liver, pancreas, duodenum, spleen, adrenal glands
left hypochondriac region organs
spleen, colon, left kidney, pancreas
right lumbar region organs
gall bladder, liver, right colon
umbilical region organs
umbilicus (navel), parts of small intestine
left lumbar region organs
descending colon, left kidney
right iliac region organs
appendix, cecum, right ovaries
hypogastric region organs
urinary bladder, sigmoid colon, female reproductive organs
left iliac region organs
descending colon, sigmoid colon, left ovaries
serous membranes
double layered membranes
two types: parietal and visceral
purposes - protects organs, prevents diseases from spreading, prevents friction between organs
parietal serous membranes
lines the cavities
3 types:
parietal pleura - lines the thoracic cavity
parietal pericardium - lines the heart cavity
parietal peritoneum - lines the abdominal cavity
visceral serous membranes
viscera = organ
covers the organs
3 types:
visceral pleura - covers the right/left lungs
visceral pericardial - covers the heart
visceral peritoneum - covers each organ in the abdominal cavity
which system does this apply to: body movement of the trunk and limbs; provides structure and support
muscular
which system does this apply to: eliminates wastes; maintains water and chemical balance
urinary
which system does this apply to: defends and protects the body against infection and disease
lymphatic
which system does this apply to: maintains homeostasis by secreting hormones
endocrine
which system does this apply to: produces sperm and eggs; produces offspring
reproductive
which system does this apply to: delivers oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from the blood
respiratory
which system does this apply to: makes food soluble and passes nutrients to the blood
digestive
which system does this apply to: regulates most body systems with impulses transmitted by neurons
nervous
which system does this apply to: allows for support, protection, attachment of muscles, stores nutrients and produces blood
skeletal
which system does this apply to: protects against pathogens and water loss; contains sensory receptors
integumentary
which system does this apply to: transports oxygen carbon dioxide, and nutrients to and from all body tissues
cardiovascular
which system does this apply to: returns tissue fluid to the blood and destroys pathogens that enter the body
lymphatic
term for forehead
frontal
term for cheek
buccal
term for nose
nasal
term for mouth
oral
term for face
facial
term for eye
orbital
term for ear
otic
term for neck
cervical
term for chin
mental
term for chest
thoracic
term for armpit
axillary
term for arm
brachial
term for elbow
antecubital
term for forearm
antebrachial
term for wrist
carpal
term for thumb
pollex
term for palm
palmar
term for fingers
digital
term for leg
crural
term for kneecap
patellar
term for ankle
tarsal
term for calf
sural
term for thigh
femoral
term for toes
digital
term for foot
pedal
term for sole of the foot
plantar