MCAT Physics: Light and Quantum Mechanics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
light is what kind of wave
transverse wave composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propgates WITHOUT A MEDIUM
transverse wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels
speed of light
c = 3.00 x 10^8 m/s
intensity of light is proportional to
The square of the wave amplitude (strength of the electric field)
when light encounters the interface between two media
light will reflect and refract
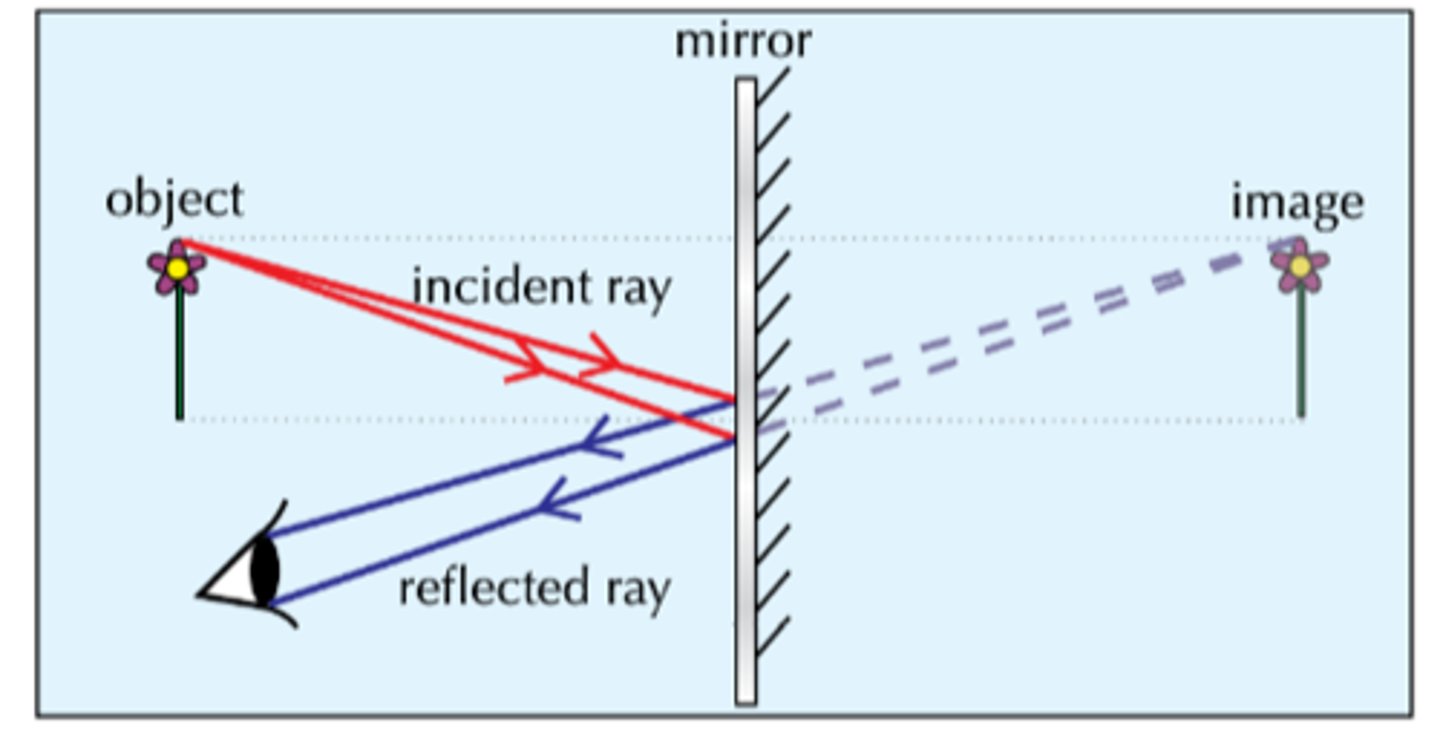
reflection equation
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
in reference to the surface normal
refraction definition
bending of light as it is transmitted from one medium to another
index of refraction
how much slower light travels through a medium than through a vaccuum
index of refraction equation
n = c / v
c: speed of light in a vacuum
v: speed of light in the medium
index of refraction of air
1
snells law
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
when light is transmitting to a medium of lower refractive index
θ2 will increase, bending away from the surface normal
when light is transmitted to medium of higher refractive idex
θ2 will decrease, bending towards the surface normal
critical angle definition
the angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90 degrees
critical angle equation
sin(c) = ( n2 / n1 )
total internal reflection
any incidence angle greater than the critical angle will have the light completely reflected and NOT refracted
diffraction
the spreading out of waves when they encounter an obstacle or aperture about the same size as their wavelength; instead of continuing along a linear path, they spread out as though emerging from a new point source
dispersion
Higher frequencies generally have slightly higher indexes of refraction (bend more) than lower frequencies, allowing prisms to split up white light into its component colors
polarization
occurs when one direction of oscillation is privileged, whether by reflection or transmission through a special material or filter. Only transverse waves can be polarized
plane polarization
removal of all electric field oscillations except from those along one plane parallel to the direction of propagation
circular polarization
Two perpendicular electric field components oscillate 90 degrees out of phase with each other --> superposition of these components creates a field that rotates in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation
optics equation
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
f: focal length
o: object distance from mirror
i: distnace from lens that an image is formed
focal length
intrinsic property of lens/mirror; equal to half of the radius of curvature
When is the focal length positive
converging optics: a concave mirror or convex lens
when is focal length negative
diverging optics: convex mirror, concave optic
when is image distance positive
where the image is formed, where the light actually travels: behind a lens and in front of a mirror
magnification equation
m = -i/o
magnification definition
the size of the image compared to the object
real image
Light rays converge, and the image is formed where the light is supposed to go (positive image distance).
positive magnification
upright and virtual image
negative magnification
inverted real image
virtual image
Seems like the light rays converge to an observer, even though they do not actually (negative image distance)
myopia
Nearsighted, the focal length of the eye lens system is too short (light converges before the retina). Needs a diverging lens to form an image at the retina
lens power
P = 1/f
hyperopia
farsightedness, the focal length of the eye's lens system is too long (light doesn't converge), and needs a converging lens to correct.
photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
energy of a photon
E = hf = hc/λ
energy of a photoelectron
KEmax = hf - phi
phi is the work function
work function
binding energy of the metal target
brightness of the light is proportional to
the number of photons
stopping potential
The minimum potential difference required to stop the highest kinetic energy electrons from leaving the metal plate (no current) in the photoelectric effect.
stopping potential equation
-eVstop = KE(max)
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
∆x∆p≥h/2π