b1.1 - carbohydrates and lipids
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
4 classes of macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Why is life described as carbon-based?
All carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids contain carbon.
How does carbon form bonds?
It shares its outer shell electrons to form covalent bonds.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form and with which elements?
Four covalent bonds, often with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus.
What are common functional groups in biochemistry?
Hydroxyl (-OH), Amino (-NH₂), Carboxyl (-COOH), and Phosphate (H₂PO₄).
What reaction links monomers to form polymers?
Condensation reactions.
What are macromolecules made of?
Smaller molecules called monomers.
What breaks macromolecules into monomers?
Hydrolysis reactions, which break covalent bonds.
What happens during hydrolysis?
Water is split into two components and becomes part of the two smaller molecules.
What are digestive enzymes classified as?
hydrolyzing enzymes
Give an example of a hydrolysis reaction involving lactose.
Lactose → galactose + glucose.
What happens after digestion of monomers?
They are rebuilt into macromolecules by condensation reactions.
What is formed during condensation reactions?
A water molecule.
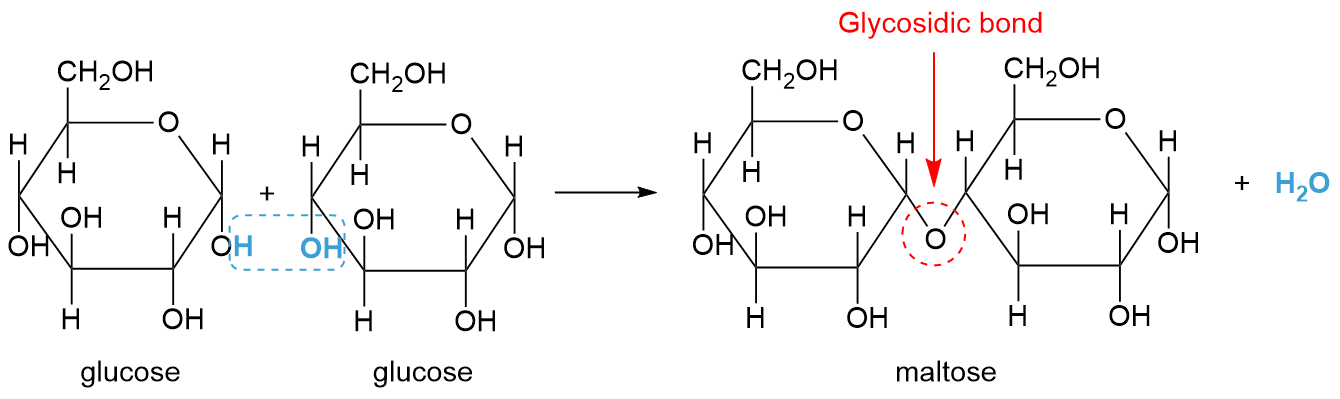
Glucose + galactose
lactose + water
Glucose + many glucose
starch + many water
Many amino acids
protein + many water
Phosphate group + pentose sugar + base
nucleotide + 2 water.
What is the covalent bond between two amino acids called?
A peptide bond.
What makes up overall metabolism?
The sum of condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
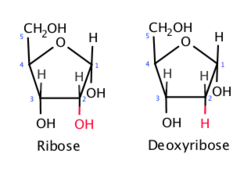
What type of sugar is ribose?
A pentose monosaccharide.
What type of sugar is glucose?
A hexose monosaccharide.
Why is glucose important?
It is used in respiration and photosynthesis.
What are key properties of glucose?
It is polar, stable, soluble in water, easily transportable, and releases a lot of chemical energy during oxidation.
How do plants store glucose?
As starch, a polysaccharide.
What forms amylose and what is its structure?
Carbon 1 bonded to carbon 4, forming a linear helix shape.
What forms amylopectin and what is its structure?
Links between carbon 1 and 6, forming branching structures.
Why are starch and glycogen good for storage?
they are insoluble in water
What is glycogen?
The animal equivalent of amylopectin, stored in liver and muscle tissue.
What type of glucose does cellulose use?
beta glucose
What structure does cellulose form and why?
A grid structure due to beta-1,4 bonds.
What is cellulose good for?
Providing stability, like in plant cell walls.
What molecules are included under lipids?
Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids.
Why are lipids hydrophobic?
They have many non-polar carbon and hydrogen bonds, making them insoluble in water.
How do lipids sometimes become soluble?
by conjugating with another molecule
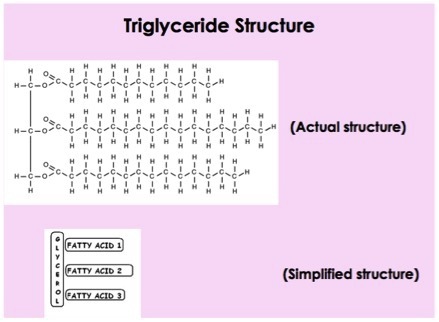
How is a triglyceride formed?
Glycerol links to three fatty acid chains by condensation reactions.
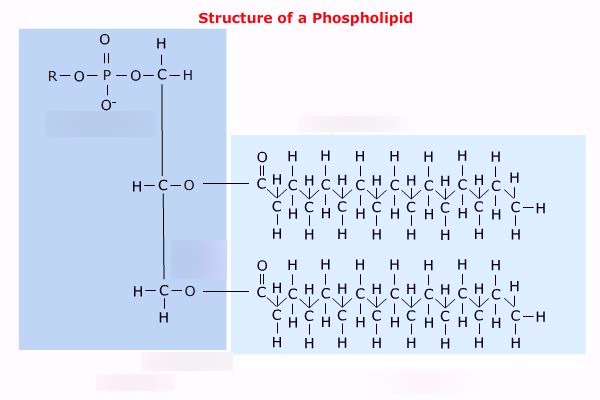
How is a phospholipid formed?
Glycerol links to two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group by condensation reactions.
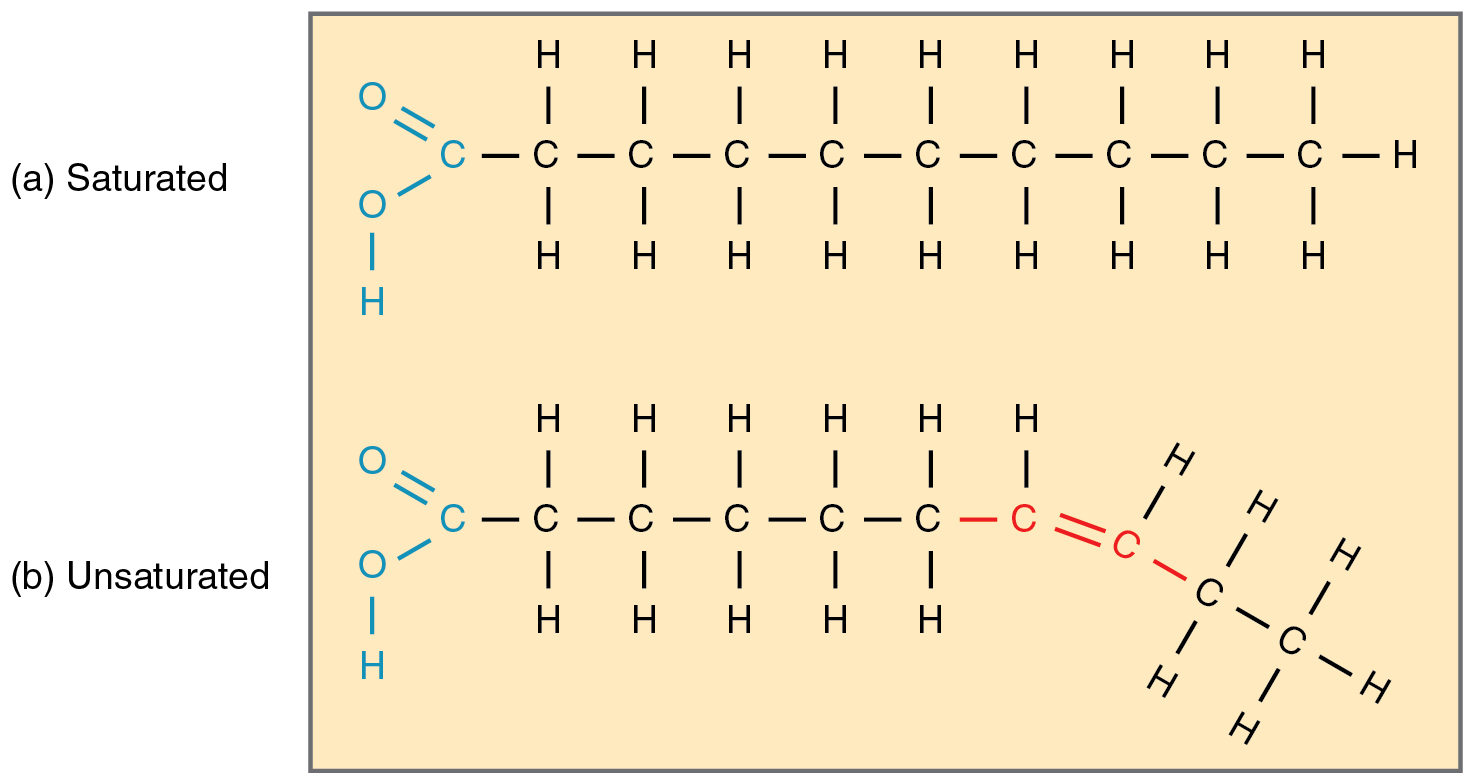
What are saturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with single bonds between carbons, fully saturated with hydrogen; solid at room temperature (e.g., animal meats, butter).
What are monounsaturated fatty acids?
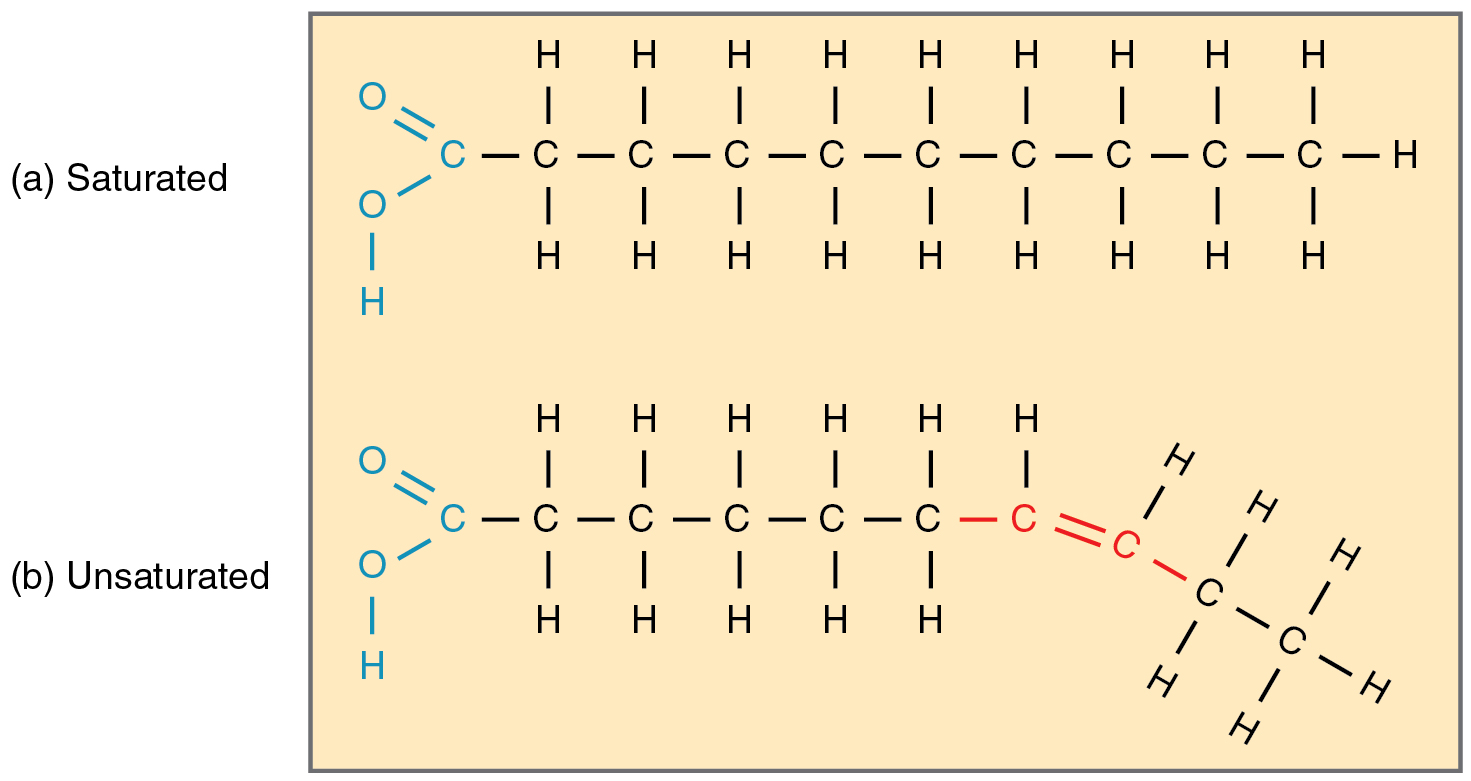
Fatty acids with one double bond between carbons; liquid at room temperature, used for energy storage by some animals and plants.
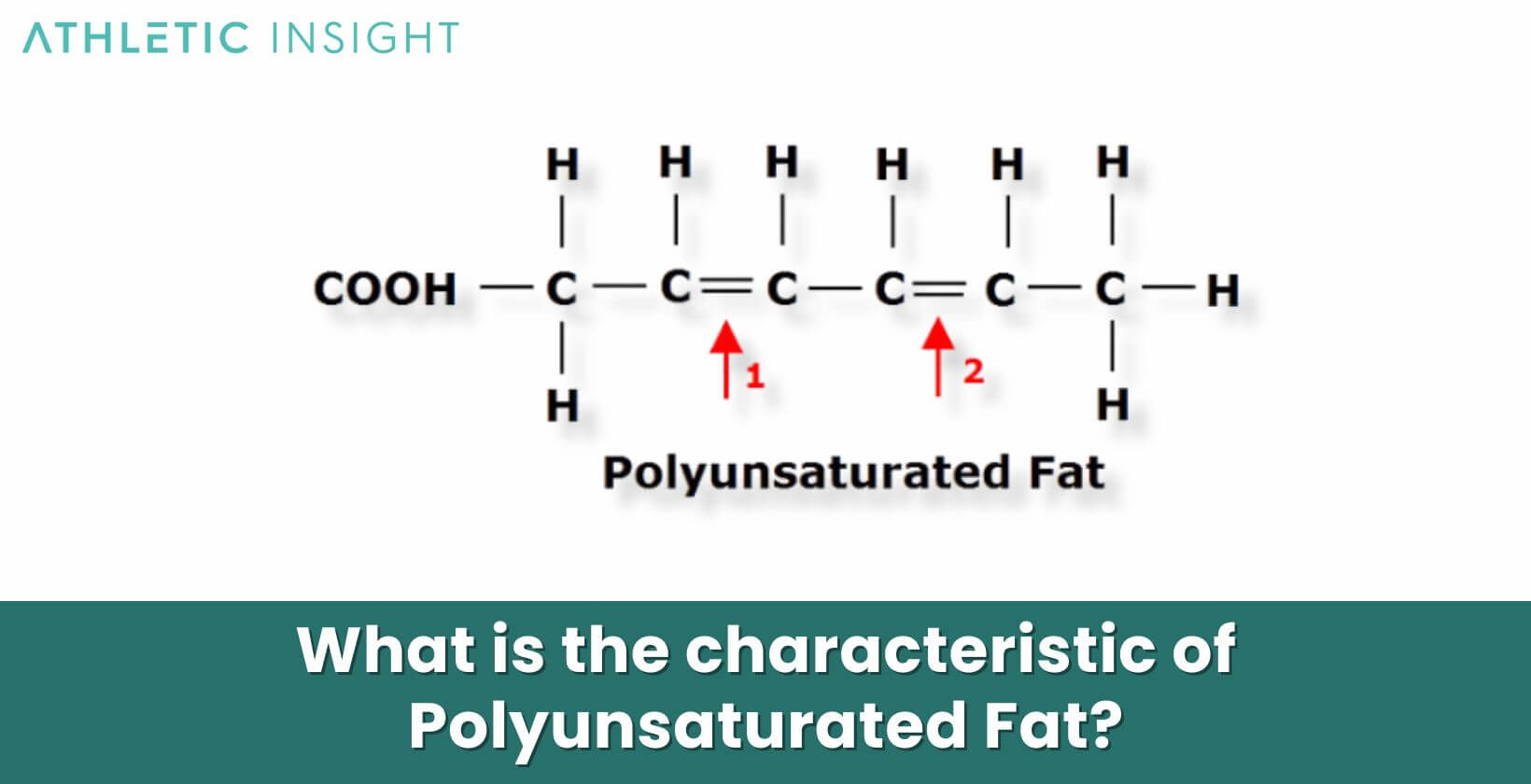
What are polyunsaturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with more than one double bond; liquid at room temperature, used for energy storage by some plants.
What is adipose tissue composed of?
Cells that store fat in triglyceride form.
Where are thicker layers of adipose tissue commonly found?
In cold habitats, known as blubber.
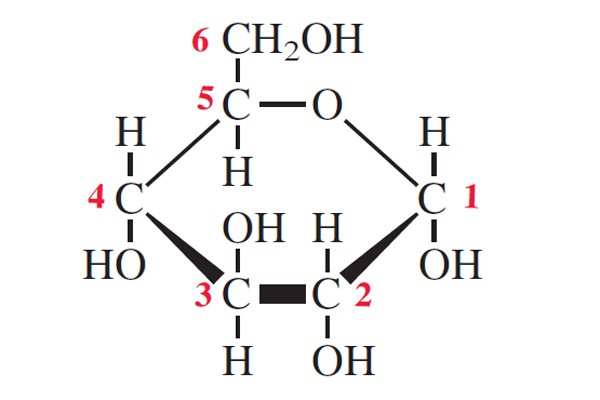
draw an alpha glucose
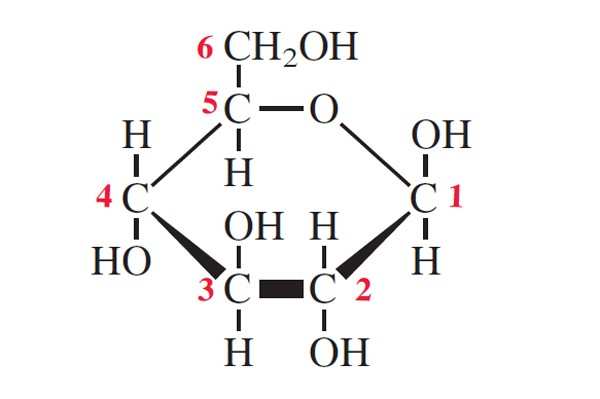
draw a beta glucose
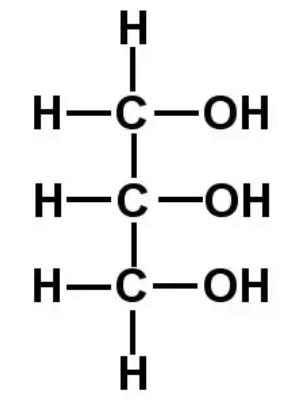
draw glycerol
draw a triglyceride
draw a phospholipid
draw a saturated fatty acid
draw a monounsaturated fatty acid
draw a polyunsaturated fatty acid
draw a ribose sugar
pentose monosaccharide
draw condensation reaction
Carbohydrate + Protein
glycoprotein
Lipid + Protein
lipoprotein
Carbohydrate + Lipid
glycoprotein
Functions of Conjugated carbon molecules
cell signaling (cell to cell communication)
transport
adhesion
catalysis
recognition of self and non-self
long carbon chain length (lipids)
high melting point
few number of double bonds
high melting point
short carbon chain length
low melting point
many double bonds
low melting point
Steroid Hormones
made by gonadal tissue
Molecules produced by glands (variety) in the body. One group of hormones are called steroids. They are made up from a type of lipid: cholesterol. They regulate a wide variety of processes in the body