CH 13 - Instrumentation
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gamma Camera: Basic Principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
radionuclide imaging
what is the most important application of radioactivity in nuclear medicine
distribution of a radioactively labeled substance within the body after administration
the purpose of radionuclide imaging is to obtain a picture of the:
by recording the emissions from the radioactivity with external radiation detectors placed at different locations outside the patient
how is obtaining an image of the distribution of radioactivity with the body accomplished
50-500 keV
what is the preferred energy range of radiation for a gamma camera?
they are ideal to penetrate the body but not powerful enough to pass through the scintillator material
why is 50-500 keV the preferred range of radionuclide energy?
detection effiency
imaging system detectors must have good _____ for gamma ray
energy discrimination
an installed system should also have _____, so that gamma rays that have lost positional information (energy) by compton scattering within the body can be rejected based on their reduced energy
NaI(Tl)
what kind of detector provides both good detection efficiency and energy discrimination for gamma cameras?
8-300 keV
what is the range of gamma ray energies typically detected by NaI(Tl) detectors.
low penetrating power
why are alpha and beta particles of little use to imaging?
late 1940s
first attempts of radionuclide imaging occurred when?
an array of detectors around the head
how was early imaging performed in the 1940s
the incredible mathematical load
why was advancements of nuclear medicine a slow process?
rectilinear scanner
what did Benedict Cassen invent
Benedict Cassen
who invented the rectilinear scanner
1950s
when was the rectilinear scanner invented
raster like pattern
with the rectilinear scanner, the detector was scanned mechanically in a ________ over the area of interest
rectilinear scanner
the image was a pattern of dots imprinted on a sheet of paper by a mechanical printer that followed the scanning motion of the detector was the process of what instrument?
real time
in a rectilinear scanner, dots were added to the image in ______ as the gamma rays were detected
long imaging time due to needing several measurements at different angles around the organ of interest
the primary disadvantage of a rectilinear scanner
Hal Anger
who invented the first gamma ray camera
1953
when was the first gamma ray camera invented?
gamma ray camera
what did Hal Anger invent?
gamma ray camera
this instrument was capable of recording at all points of the images
pinhole aperture embedded in a sheet of lead
what allowed Hal Anger’s gamma camera to record at all points on the image
collimator
Hal Anger’s pinhole aperture in a sheet of lead is essentially a modern day ______
crystals
Hal Angers lead sheet was later changed to _____ to allow for faster imaging times as well as lower the administered doses
Anger scintillation/gamma camera
the introduction of crystal instead of lead in Anger’s gamma camera lead to the development of
light
radiation interacts with the NaI(Tl) scintillator and releases _____
electrical current
light released by the scintillation crystal is then converted and recorded as ____
titanium oxide (TiO2)
the NaI(Tl) crystal is surrounded by reflective material such as _____
maximize light output
titanium oxide is used to:
hermetically
how is the TiO2 sealed inside of a thin aluminum casing?
vacuum sealed or air tight
what does hermetically mean?
moisture
the aluminum casing and hermetic seal protects the crystal from:
silicone based adhesive or grease
an array of PM tubes is coupled optically to the back face of the crystal with a:
plastic light guides or guides grafted directly onto the crystal
what is used in a PM tube to help shuttle light into the PM tube
coordinates
once counts are sent to the circuits, data is assigned _____ in a graph
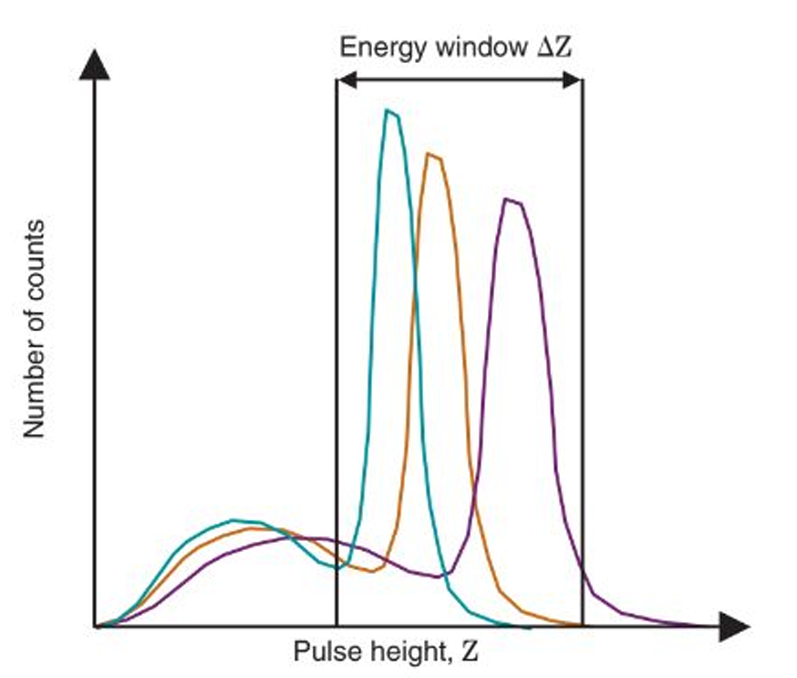
uses simple energy discrimination for falling into the energy window
describe this approach
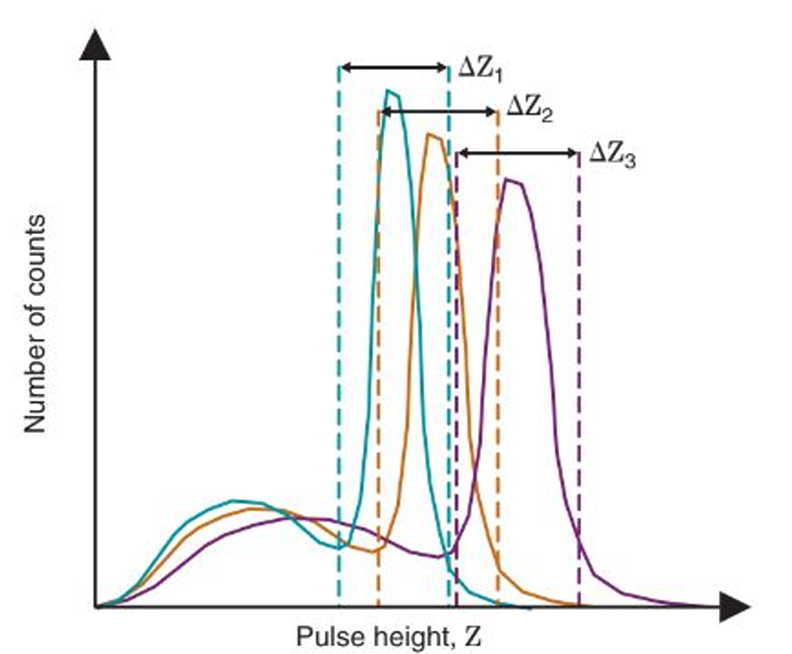
photopeak positions and discriminator levels are set and stored in the computer. it has to be an exact match to known values saved or it is ignored from processing
describe this approach
9-10% at 140 keV
a modern gamma camera has a energy resolution of about
14% or 20 keV
the energy window on a modern gamma camera is normally set to ____ around 140 keV
pinhole
what kind of collimator is this
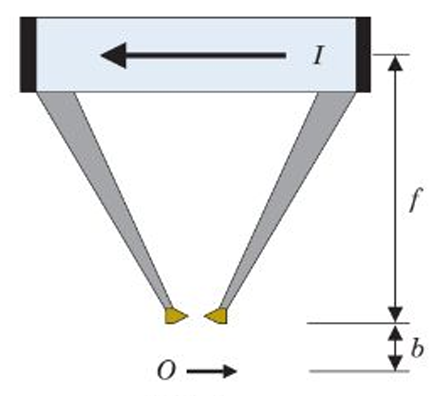
parallel hole
what kind of collimator is this
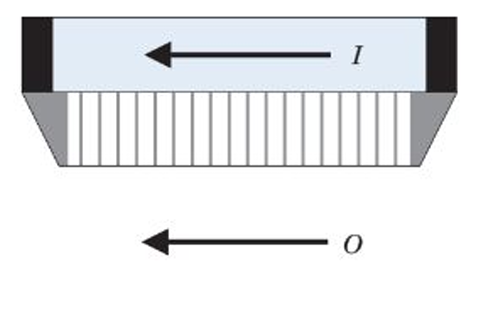
converging
what kind of collimator is this
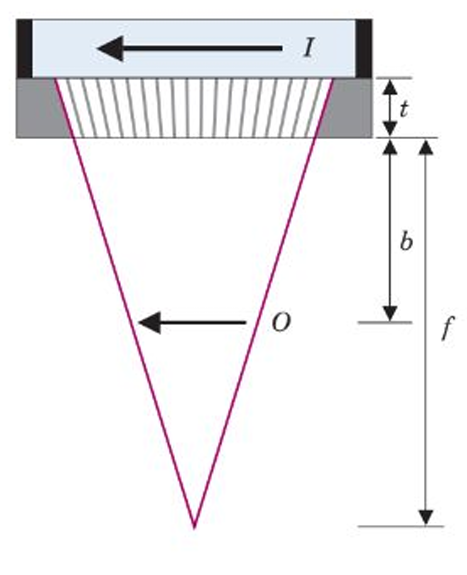
diverging
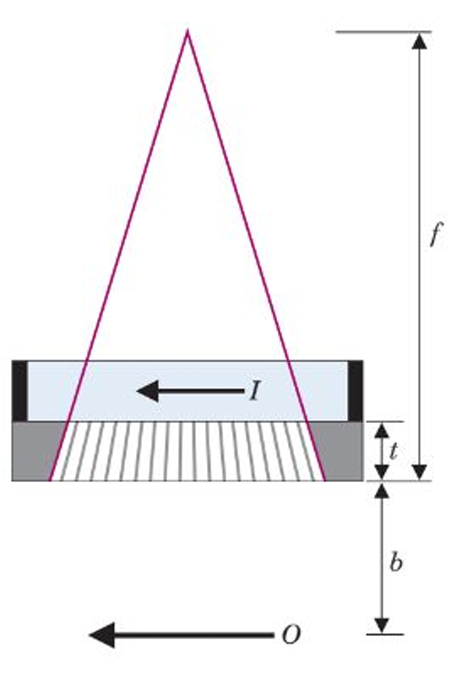
what kind of collimator is this
no
can gamma cameras have normal lens to focus the radiation?
absorptive collimation
gamma cameras utilize what type of collimation for image formation
absorptive collimation
this projects an image of the source distributions to travel through to the detector only from the desired plane to the projector and blocks unwanted radiation from other angles.
they are absorbed by the collimator
what happens to projections that are not traveling in the proper direction?
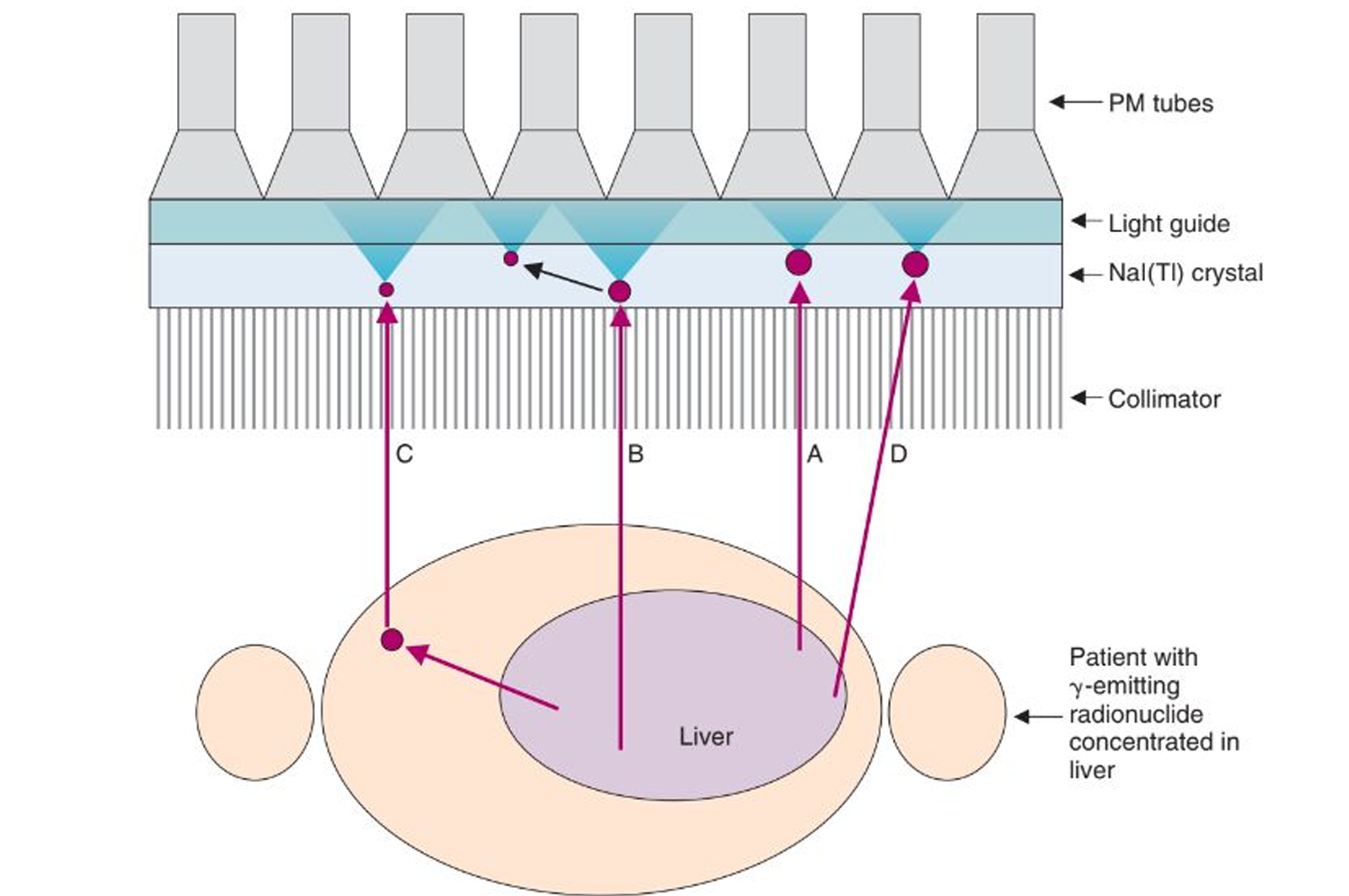
valid event
a gamma ray is emitted parallel to the collimator, depositing all of its radiation at a single location
detector scatter event
a gamma ray is emitted parallel to the collimator holes, passing through and causing compton scattering in the NaI(Tl) crystals. this causes the scatter to either interact with the crystal or keep scattering.
object scatter event
the gamma ray is not emitted toward the collimator, instead it scatters through the body until it is emitted toward the detector
septal penetration
this occurs if the gamma ray is emitted toward the detector, but not straight on and it contains enough energy to move through the lead collimation
I-131 energy
what kind of energy can cause septal penetration for the camera?
valid event
A
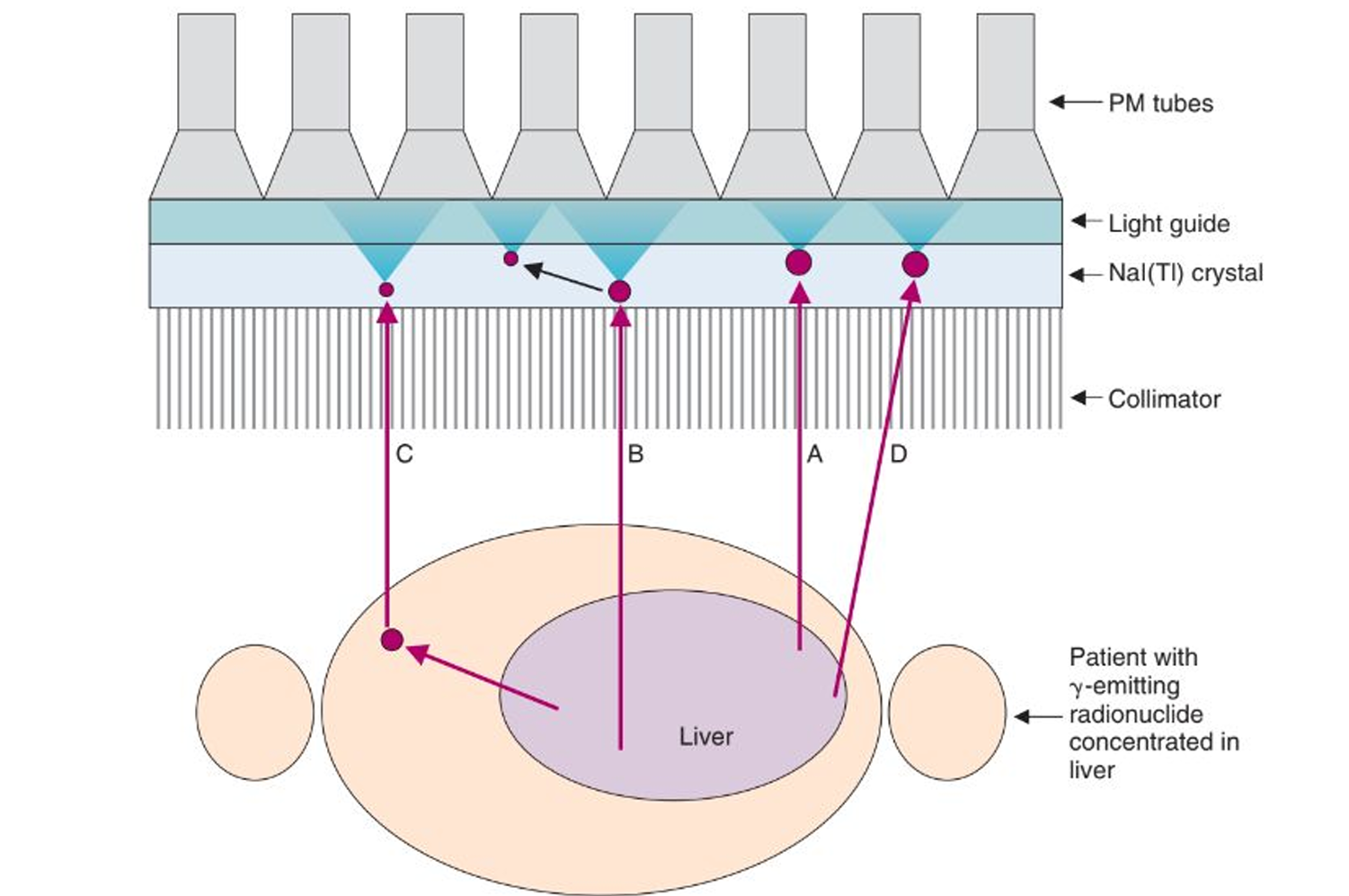
detector scatter event
B
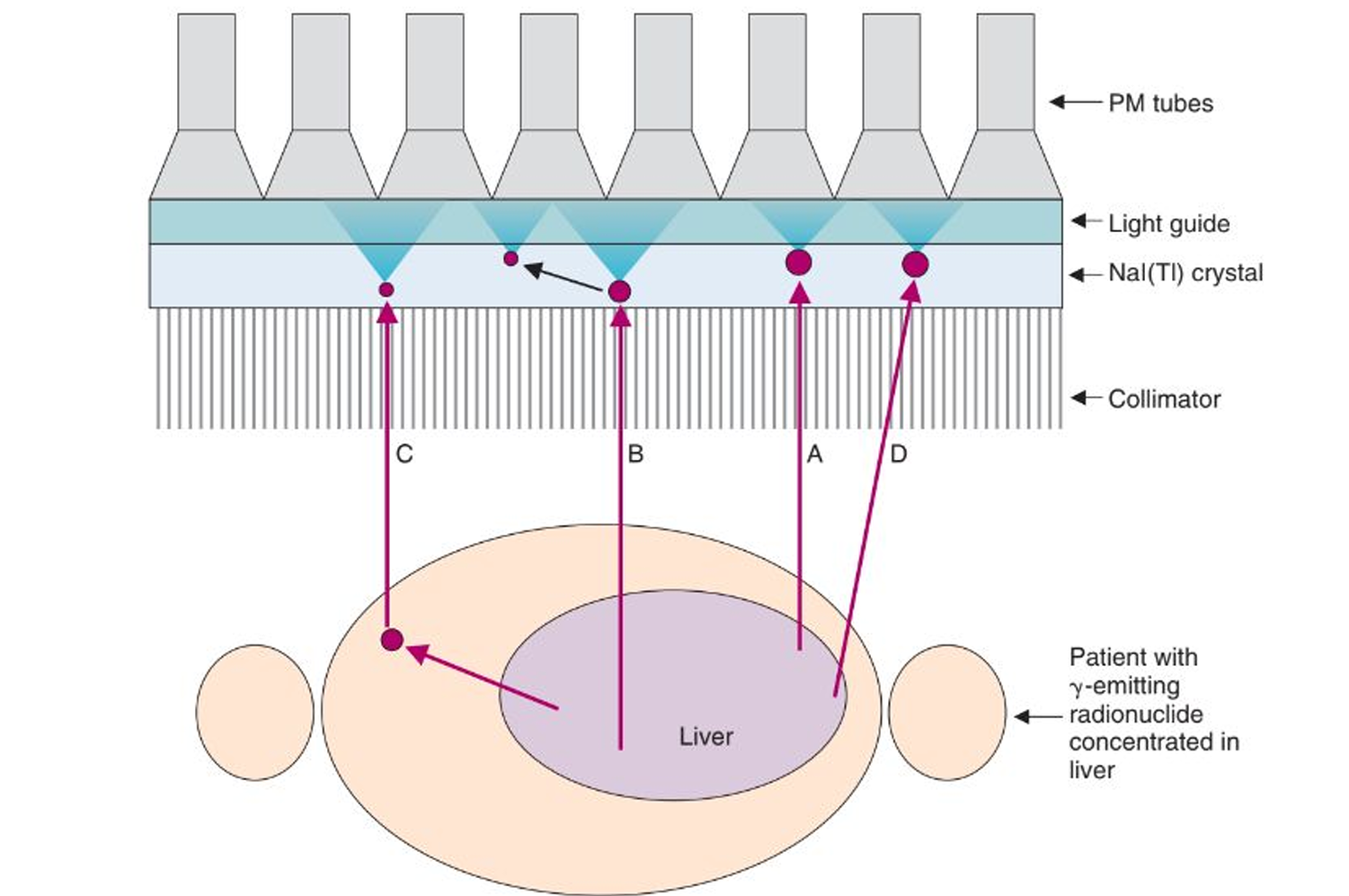
object scatter event
C
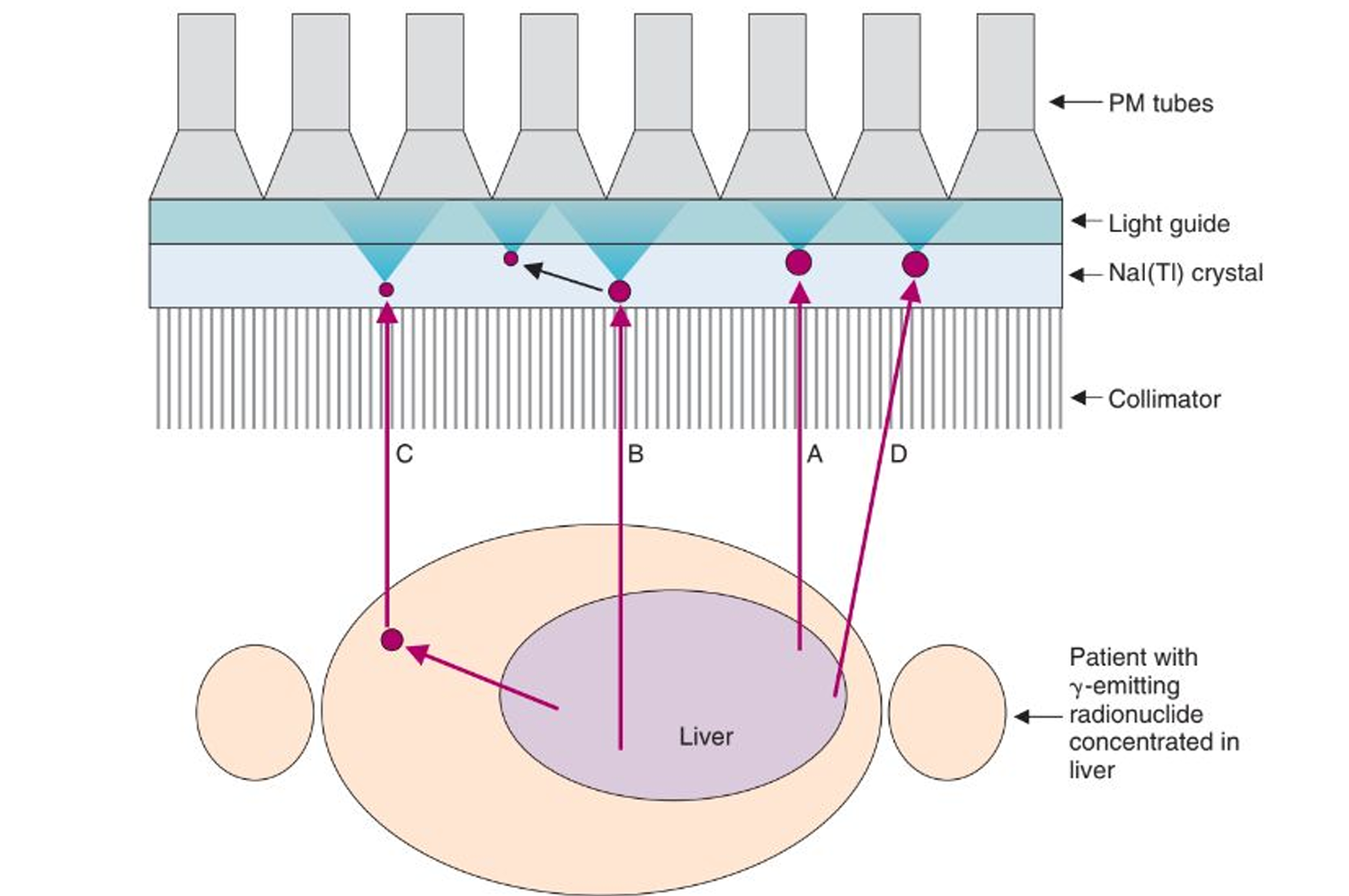
septal penetration
D