Ecology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Last updated 6:23 PM on 1/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Geosphere/Lithosphere
rocks,minerals,earths crust
2
New cards
Atmosphere
Air,gases
3
New cards
Hydrosphere
water
4
New cards
biosphere
plants,animals,living things
5
New cards
biotic
Are living or once were
6
New cards
abiotic
Non-living things that influence an ecosystem
7
New cards
herbivore
organism that only eats plants
8
New cards
carnivore
organism that eats mostly/only meat
9
New cards
omnivore
organism that eats both plants and animals
10
New cards
detrivore
organisms that eat deccaying organic material
11
New cards
decomposer
organism that breaks down decaying material into nutrients
12
New cards
producer
organisms that produce their own food
13
New cards
food chain
feeding relationships between organisms
14
New cards
food web
over lapping and interconnecting food chains
15
New cards
primary conumers
first to consume on the trophic level
16
New cards
secondary consumer
second to consume on the trophic level
17
New cards
teritary consumer
third to consume on a trophic level
18
New cards
photosynthesis
the process in which plant produce oxygen and glucose
19
New cards
cellular respiration
the process in which animals produce carbon dioxide and water
20
New cards
Primary Succesion
Newly exposed or newly exposed rock is colonized by living things for the first time
21
New cards
Secondary succesion
An area that has been disrupted (flood,eruption) but recolinizes after
22
New cards
Dissolved oxygen
The amount of oxygen available to aquatic organisms
23
New cards
Biological oxygen demand
The amount of oxygen needed by decomposers in an aquatic ecosystem to break up waste
24
New cards
Eutrophication
Inorganic enrichment of natural waters, leading to an increased production of algae and macrophytes
25
New cards
Oligotrophic
Healthy lake
26
New cards
Keystone species
typically an apex predator that regulates the population of lower trophic levels, therefore keeping ecosystems in equilibrium. Part of the food web would die off without them
27
New cards
Biodiversity
the number of different types of organisms (species) within an ecosystem
28
New cards
Carrying capacity
The carrying capacity is the maximum population size (number of individuals of the same species) that an ecosystem can maintain over a period of time
29
New cards
Dynamic Equillibrium
when the forward and reverse processes occur at the same rate, resulting in no observable change in the system.
30
New cards
Limiting factor
anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing.
31
New cards
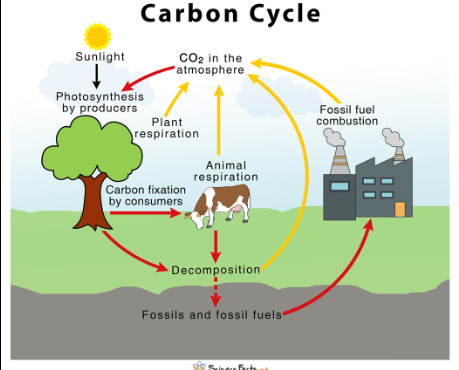
Carbon cycle
nature's way of reusing carbon atoms, which travel from the atmosphere into organisms in the Earth and then back into the atmosphere over and over again
32
New cards
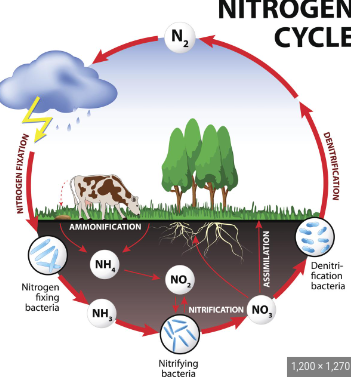
Nitrogen cycle
a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere
33
New cards
autotroph
producer
34
New cards
heterotroph
consumer