Computer Networks Question 5 Subnetting etc.
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Explain Function of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Explain what info is stored in an ARP table on a host, (5 marks)
Maps IP addresses to MAC addresses within a LAN.
If host doesn't know the MAC for an IP, it sends a broadcast ARP request.
The device with that IP replies with its MAC address.
ARP table stores the IP address, corresponding MAC address, and interface.
Helps the host send data directly without repeating the request.
Explain role of subnet mask value (ie 255.255.192.0), which is required when setting an IP address on a host.
Explain how its used to calculate the network address.
Separates IP address into network and host portions. To find network address, a host performs a bitwise AND between IP address and subnet mask.
This gives the first address in the subnet (the network address). Mask also helps devices decide if a destination is local or remote. E.g, a /18 mask gives larger networks than a /24.
Explain role of Domain Name System (DNS). Use example to give details of the operation. (5 marks)
DNS translates domain names e.g www.cisco.com into IP addresses so users don’t have to remember numbers.
When a browser sends a DNS request, it gets back the correct IP. DNS usually uses UDP port 53. E.g, www.google.com might resolve to 142.250.74.196. Device can then contact the server using that IP.
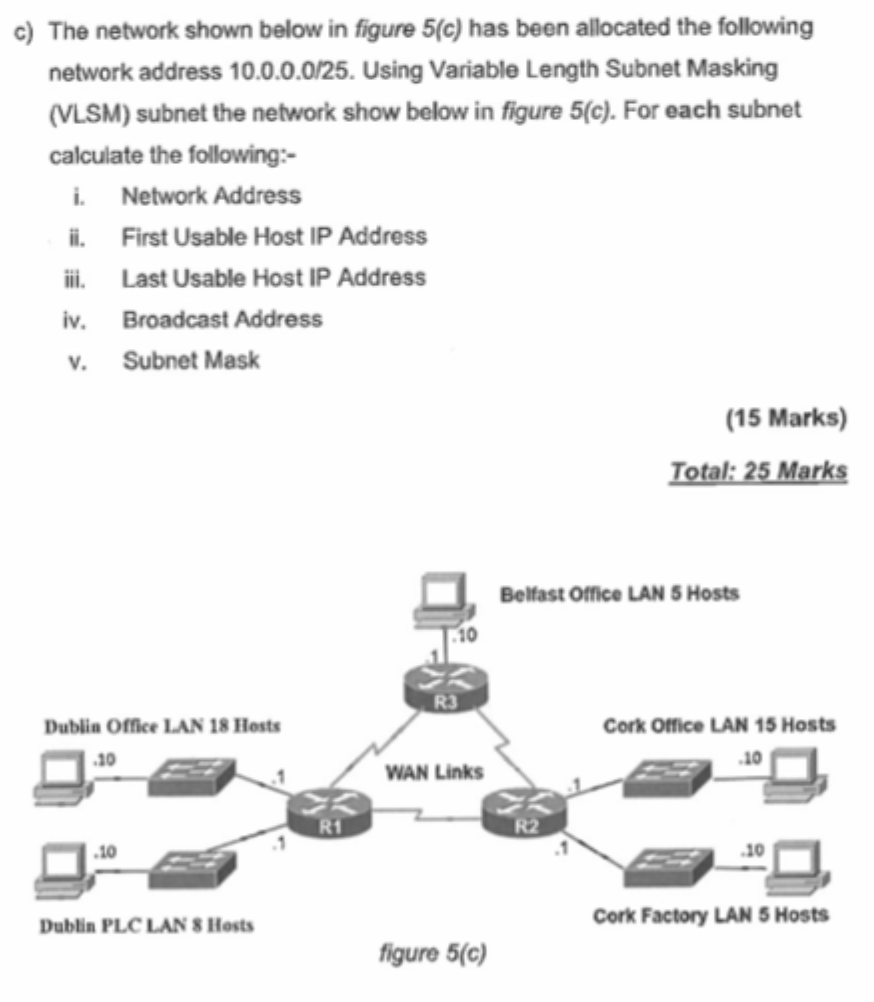
Sort Host Requirements By Size.
Total IPs= Required+2 (for Network and Broadcast).
Block size= Nearest 2n to get total IPs
Subnet Mask= 32-n from the previous part.
i) Network Address= First IP 10.0.10.0 (or last groups broadcast+1)
ii) First Usable= Network+1
iii) Last Usable= Broadcast-1
iv) Broadcast= Network Address+(Block size-1)
DONT FORGET WANs: 3x in this question
Same process but smaller
Total IPs= Always 2 IP addresses per link + 2 (Broadcast and Network)
Block size = 2²= 4-32= 30 Use /30 subnets (255.255.255.252)
next WAN block = current + 4
Describe Unicast Communication. Give an example where it would be used. (2 marks)
Sends data from one device to one specific destination (e.g. a PC sending a file to another PC).
Differ from others by how many receivers get the message + how it travels across network.
Reasons for Subnetting a Network (3 Marks)
Reduces network congestion, improves performance.
Enhances security by splitting one big network into smaller parts.
Helps efficiently assign IP addresses and simplifies routing.
Benefits of Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) (3 marks)
Allows subnets of different sizes, so no IPs are wasted.
Larger subnets can go to offices needing many devices, and smaller ones to links or small sites.
This makes the network more scalable and efficient.
Describe Broadcast Communication. Give an example where it would be used. (2 marks)
Sends data to all devices in the local network (e.g. ARP requests).
Differ from others by how many receivers get the message + how it travels across network.
Describe Multicast Communication. Give an example where it would be used. (2 marks)
Sends data to a group of devices that have joined a multicast group (e.g. streaming a live lecture to many users).
Differ from others by how many receivers get the message + how it travels across network.