Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What will happen to the scale of output in the long-run
Its long-run average total costs will initially decrease due to the benefits it receives.
These benefits are called economies of scale
During this period the firm is enjoying increasing returns to scale
What will happen when a firm increases its scale of output in the long-run
Its LRATC will start to increase at some point
The reasons for the increase in the LRATC are called diseconomies of scale
During this period the firm is facing decreasing returns to scale
Economies of scale
Financial economies
Managerial economies
Marketing economies
Purchasing economies
Technical economies
Diseconomies of scale
Management diseconomies
Communication diseconomies
Geographical diseconomies
Cultural diseconomies
Financial economies
Large firms often recieve lower interest rates on loans than smaller firms as they are percieved as less risky. A cheaper loan lowers the AC
Managerial economies

Marketing economies

Purchasing economies

Technical economies

Risk-bearing economies

Management diseconomies

Communication diseconomies

Geographical diseconomies

Cultural diseconomies

Minimum efficient scale
The minimum efficient scale is the lowest cost point on a long-run average total cost (LRATC) curve
It represents the lowest possible cost per unit that a firm in the industry can achieve in the long run.
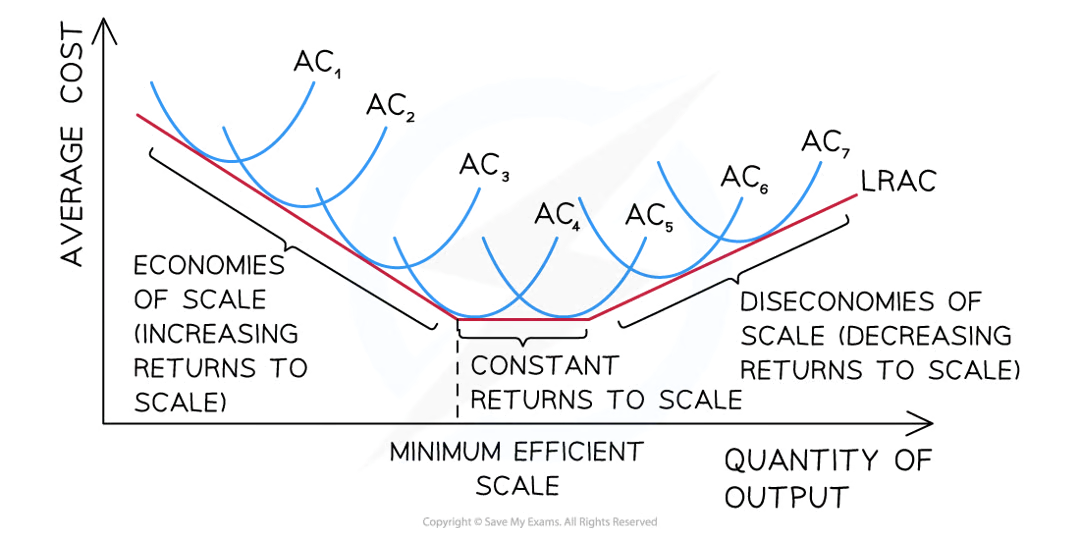
Diagram analysis
Each subsequent short-run average cost (SRAC) curve represents growth and an increase in size
Output increases with each period of growth
Initially firms experience increasing returns to scale as a result of the economies of scale
At a certain level of output, the firm will reach the minimum efficient scale where it experiences constant returns to scale
If it continues to grow beyond that level of output the firm will experience decreasing returns to scale as diseconomies of scale occur
When do external economies of scale occur
External economies of scale occur when there is an increase in the size of the industry in which the firm operates
The firm is able to benefit from lower LRATC generated by factors outside of the firm
Source and explanation
