WJEC AS LEVEL BIOLOGY UNIT 1.2 Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells.
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is Eukaryotic cell?
A type of cell that contains a true nucleus along with membrane bound organelles
What is a prokaryotic cell?
A cell that contains no true nucleus or any membrane bound organelles
What is a virus?
A non-living microorganisms that consists of genetic material surrounded by a protein husk
What is the function of the nucleus?
Coordinate cell activity
Contains DNA coiled around chromatin into chromosomes
What is chromatin?
A DNA-protein moles found in eukaryotic cells
Describe the structure and function of the flagella in prokaryotic cells.
Long whip-like protrusion made of flagellum
Rotates to propel the organism
Sensory organ
How is genetic information stored in prokaryotes
Plasmids - small rings of DNA that carry non-essential genes, exchanged between bacterial cells via conjugation.
Loop of DNA - Circular DNA stored in the nucleoid region of the cell
Describe the function and structure of pili in prokaryotic cells.
Hair like microfibres made if pilin that extend through the cell wall.
Enable the attachment of bacteria to each other and to other surfaces.
What is the function of the capsule in prokaryotic cells?
protective, slimy layer
Helps the cell to retain moisture and adhere to other surfaces.
Which organelles are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
cell membrane
Cytoplasm, with a from of cytoskeleton (cytoskeleton is more significant in eukaryotes.)
Ribosomes
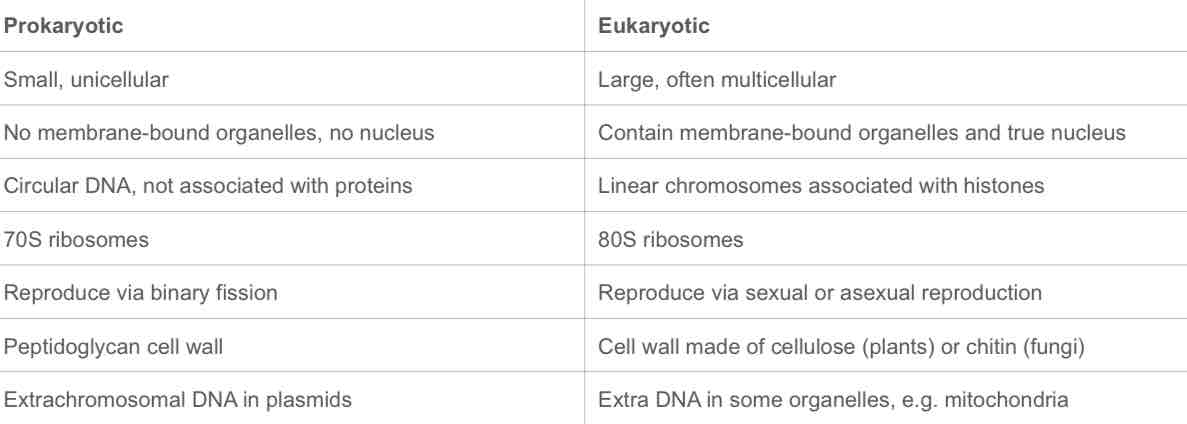
Contrast between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Contrast eukaryotic PLANT cells and ANIMAL cells

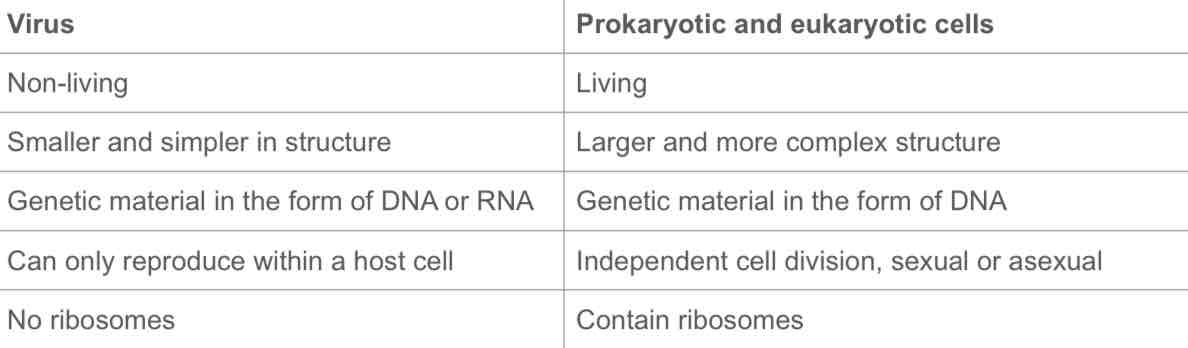
How do viruses differ from prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Define Tissue
A group of cells working together to carry out a specific function
Define organ
A group of tissue working together to carry out specific function
Define a organ system
A group of organs working together to carry out a specific function