The Autonomic/Somatic Nervous system
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Two pathways for autonomic nervous system
preganglionic - myelinated; CNS → autonomic ganglion
postganglionic - unmyelinated; unmyelinated axon → effector
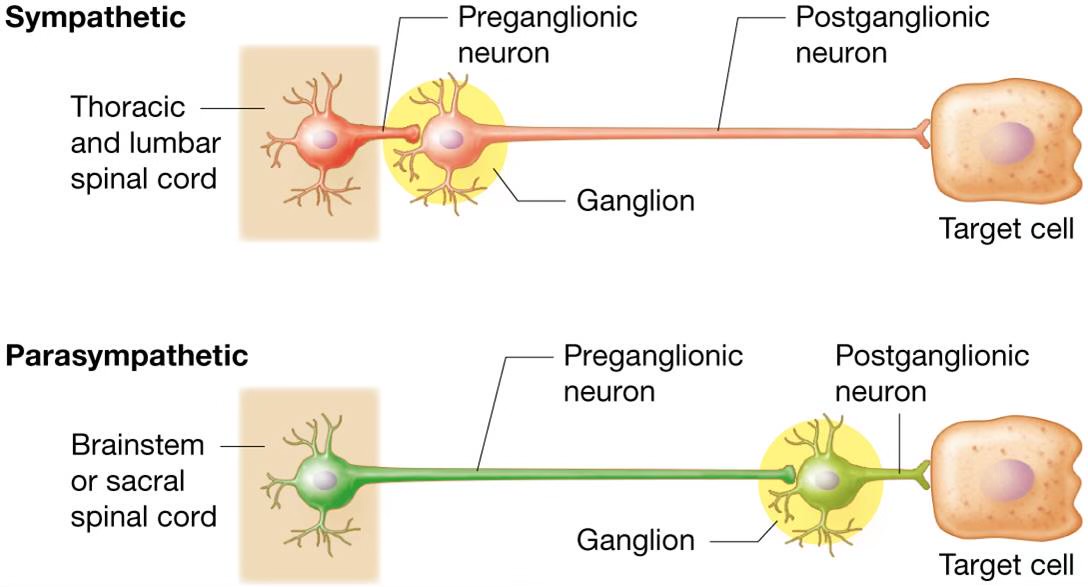
Sympathetic division pre/post
preganglionc - short
postganglionic - long
thoracolumbar
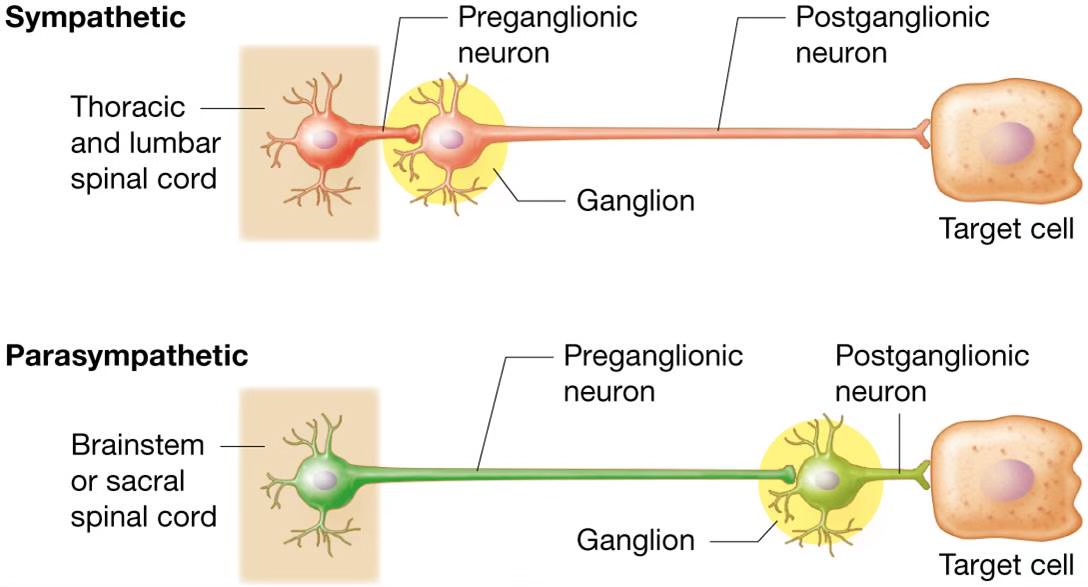
Parasympathetic pre/post
preganglion - long
postganglionic - short
craniosacral
Sympathetic receptor classes
Adrenergic receptors
bind to epinephrine and norepinephrine
Major types of adrenergic receptors
Alpha
alpha 1
alpha 2
beta adrenergic
beta 1
beta 2
beta 3
Cholinergic receptors
bind to ACh
muscarinic
nicotinic
Beta 1 function
cardiac muscle cells, certain kidney cells, and adipose cells
Beta 2 function
SKM cells lining airways of respiratory tract, and in wall of urinary bladder, skeletal muscle fibers, cells in liver, pancreas, salivary glands
Beta 3 function
primarily in adipose tissue cells, and SM cells in walls of digestive tract
Muscarinic function
on sweat glands of skin
Nicotinic function
in plasma mb of all postganglionic neurons
w/i sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medullae
Classification of sensory receptors
general senses: somatic and visceral
somatic - tactile
visceral - info about conditions
Free nerve endings
nociceptors, thermoreceptors
encapsulated nerve endings
pacinian corpuscles, meissner’s corpuscle
What are exteroreceptors?
at/near body surface
What are interoreceptors?
inside body, includes blood vessels, viscera, nervous system
What are proprioceptors
muscles, tendons, joints, inner ear
What is sensory receptor adaptation?
decrease in potentials during a maintained, constant stimulus
What is a rapidly adapting receptor?
receptors that detect pressure, smell, and touch
What are slowly adapting receptors?
receptors that detect pain, body position, and chemical composition of the blood
What are the four somatic sensations?
tactile
thermal
pain
proprioceptive
What is referred pain?
pain is felt in or just deep to the skin that overlies the stimulated organ or in a surface area far from the stimulated organ
What are prorpioceptive sensations?
name of receptors in name
slow adaptation
weight discrimination
Three types of proprioceptive sensations
muscle spindles
tendon organs
joint kinesthetic
What are first order neurons?
impulses from somatic receptors to the brain stem or spinal cord
What are second order neurons
impulses from the brain stem and spinal cord to thalamus
What are third order neurons
thalamus → somatosensory area cortex on same side
Three main somatic sensory pathways
posterior column-medial lemniscus
anterolateral (spinothalamic) pathway
trigeminothalamic pathway
Nerves that extend out of the brainstem and spinal cord are called what?
low motor neurons (LMNs)
Four somatic motor pathways circuits
local circuit - located close to LMNs in the brainstem and spinal cord
upper motor neurons (UMNs) - input to both lower circuit and neurons and LMNs
basal nuclei neurons - assist movement by indirectly providing input to UMNs
Cerebellar neurons - assist movement via control of activity of UMNs
Two somatic sensory pathways
Direct motor pathways: signals to LMNs from cerebral cortex
Indirect pathwaysL signals to LMNs from motor centers in the basal nuclei, cerebellum and cerebral cortex