histology- respiratory system
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
pseudostratified columnar with cilia or simple columnar-cuboidal,
goblet cells
describe respiratory epithelium
transitional to pseudostratified columnar
what is the epithelium of the nasal vestibule?
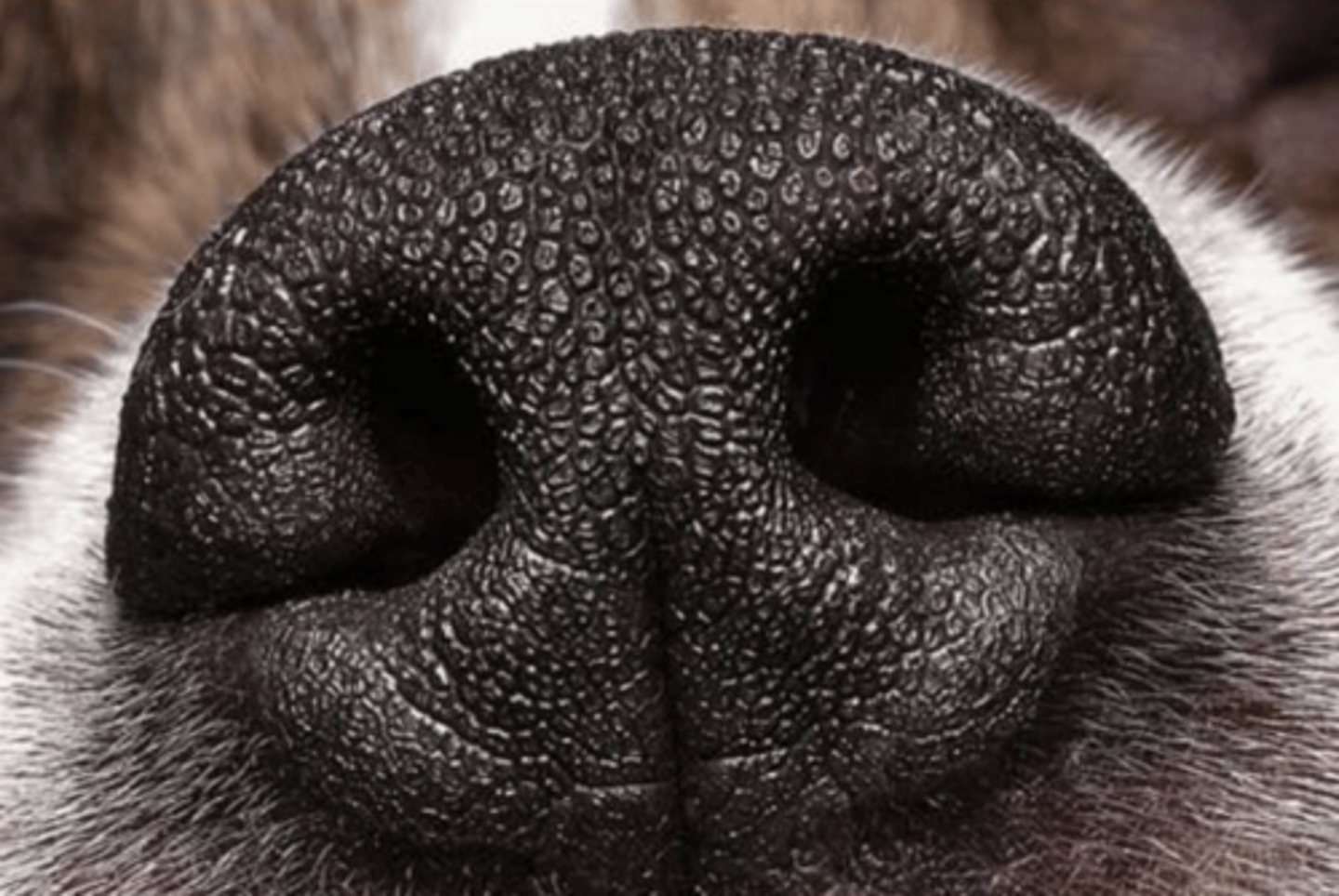

no
does the nasal vestibule epithelium have cilia?

goblet cells
what are these?
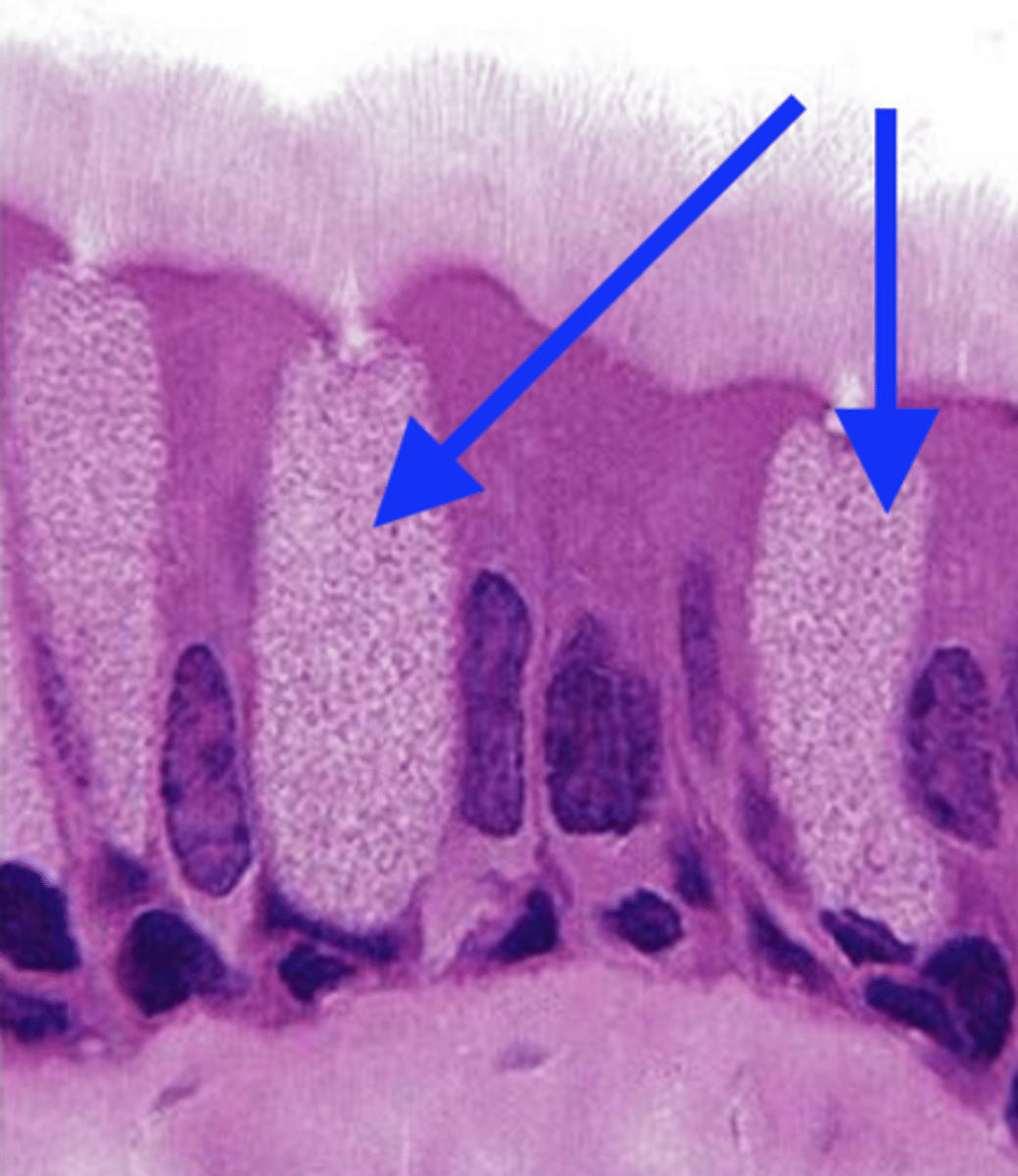
simple columnar, with goblet cells and cilia
what type of epithelium is this?
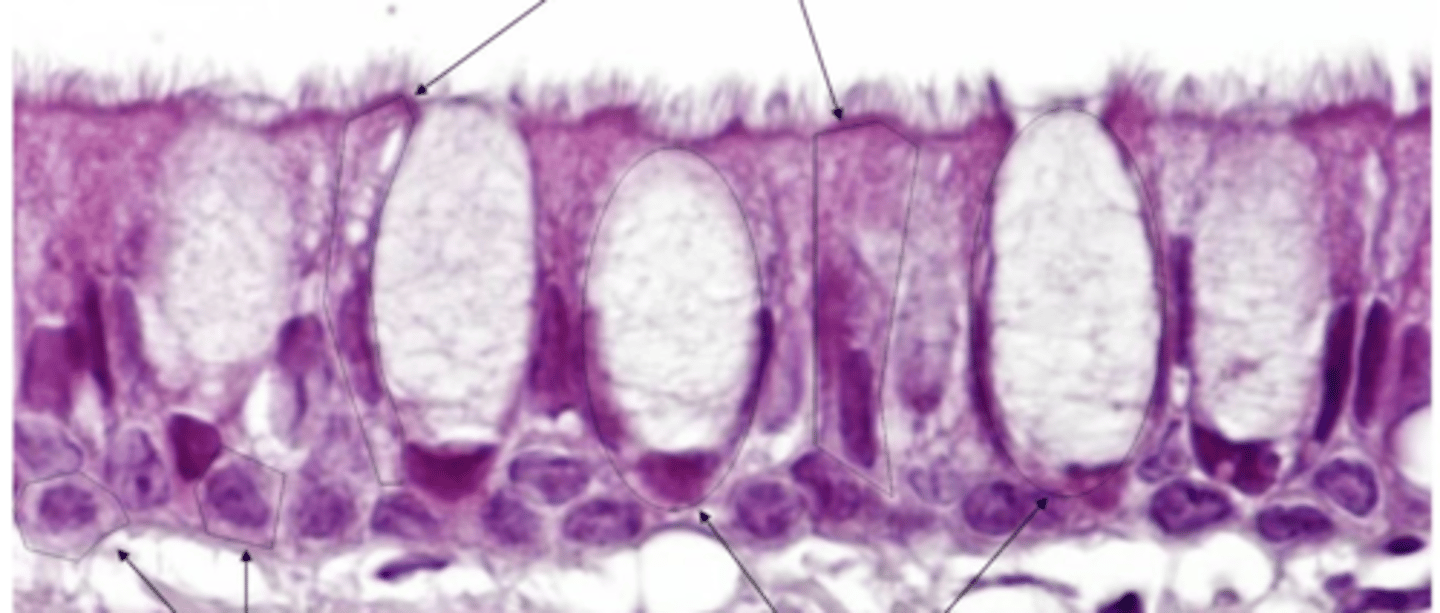
dense CT (for extra protection), defense cells, serous glands, vessels
what is the lamina propria of the nasal vestibule like?
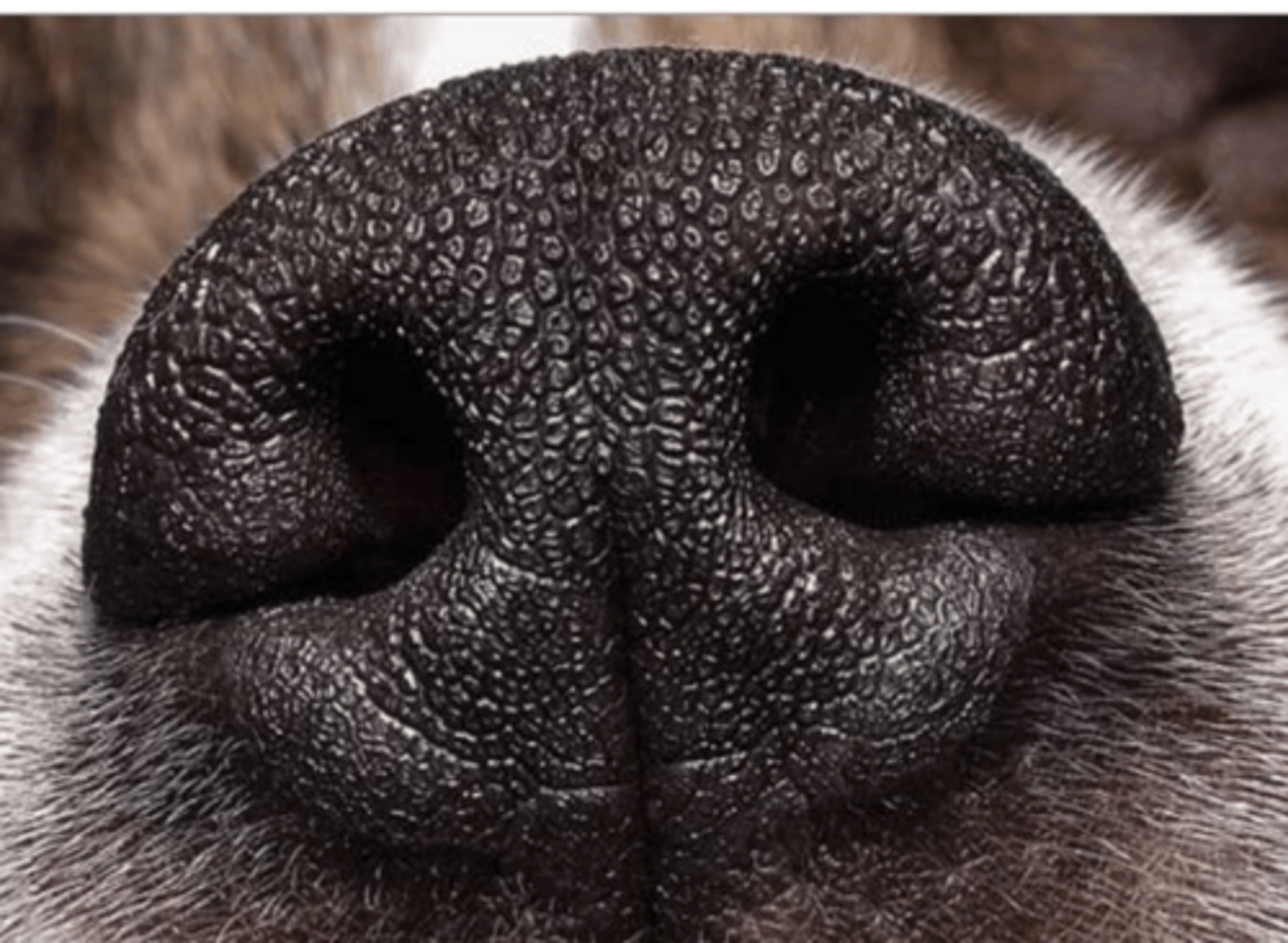

hyaline
what type of cartilage does the nasal vestibule have?
yes, serous glands
does the nasal vestibule have glands?
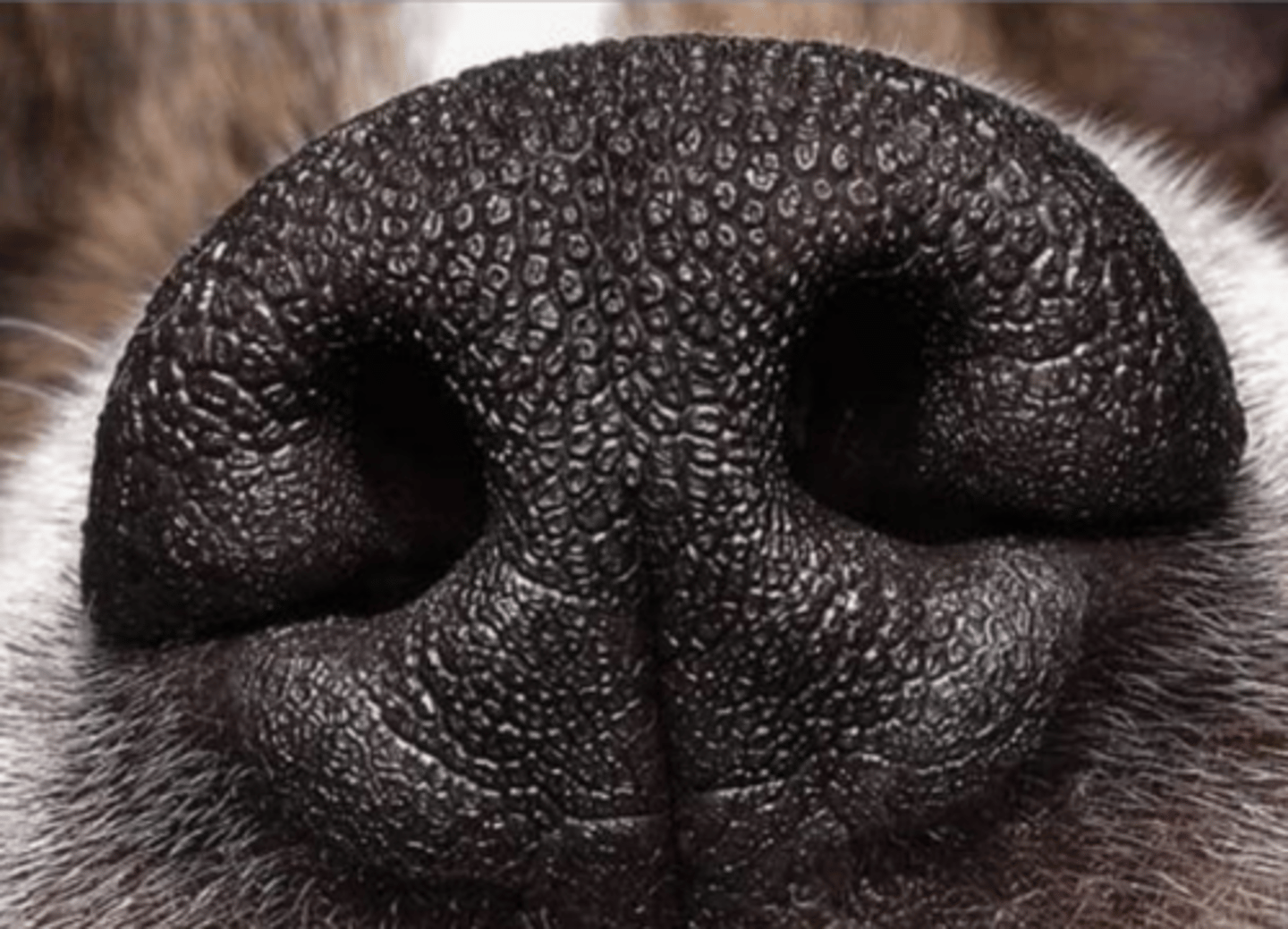
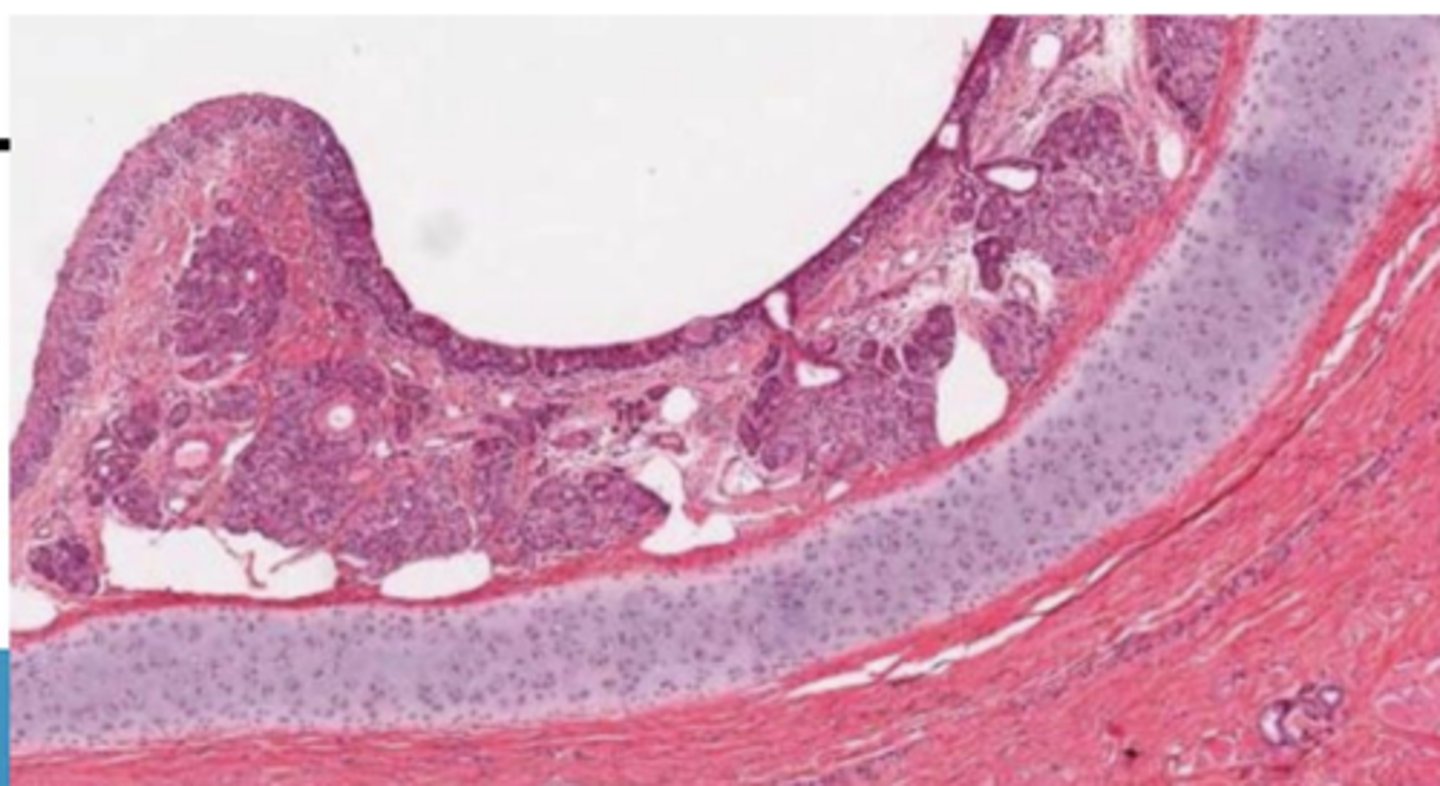
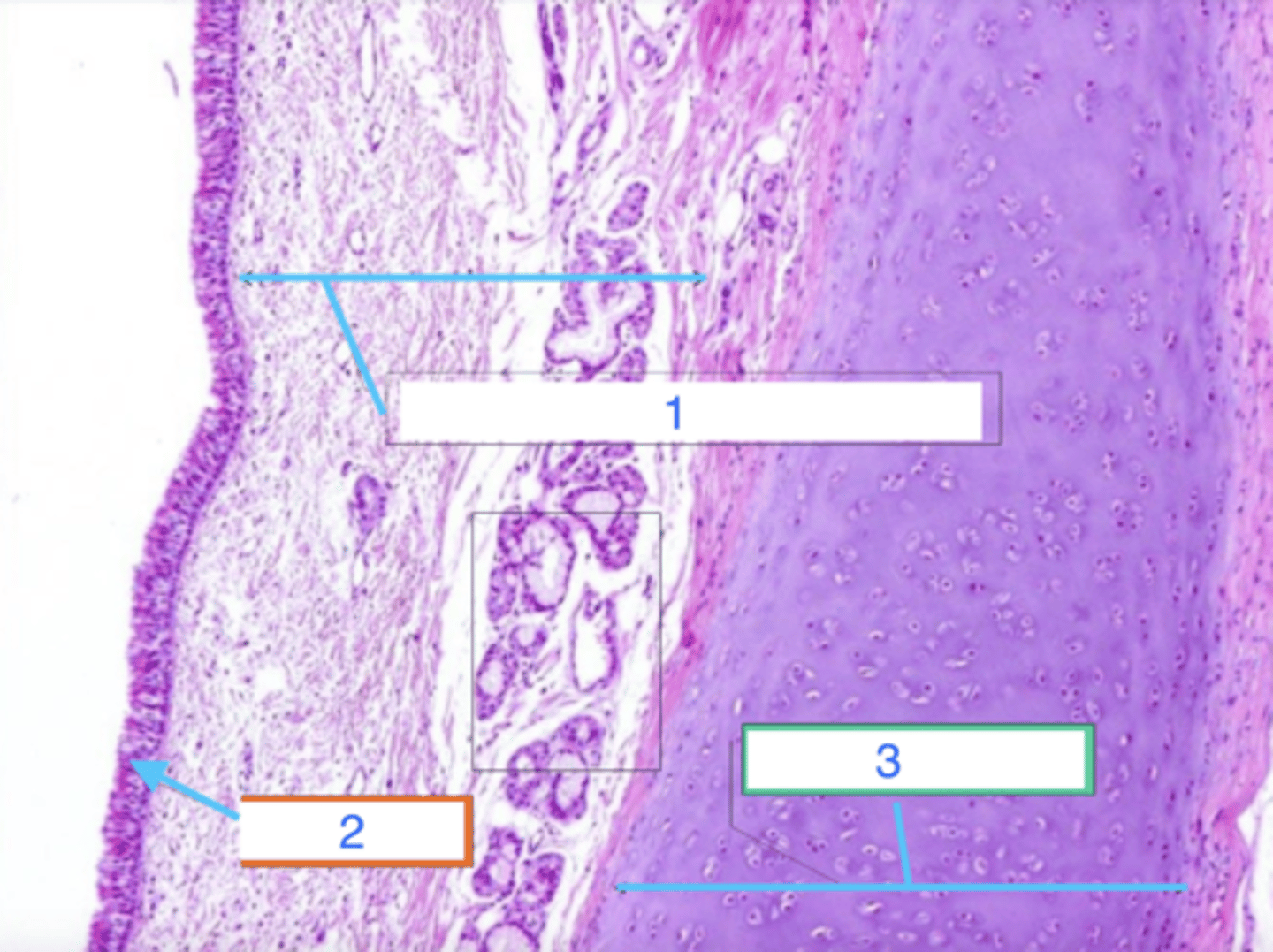
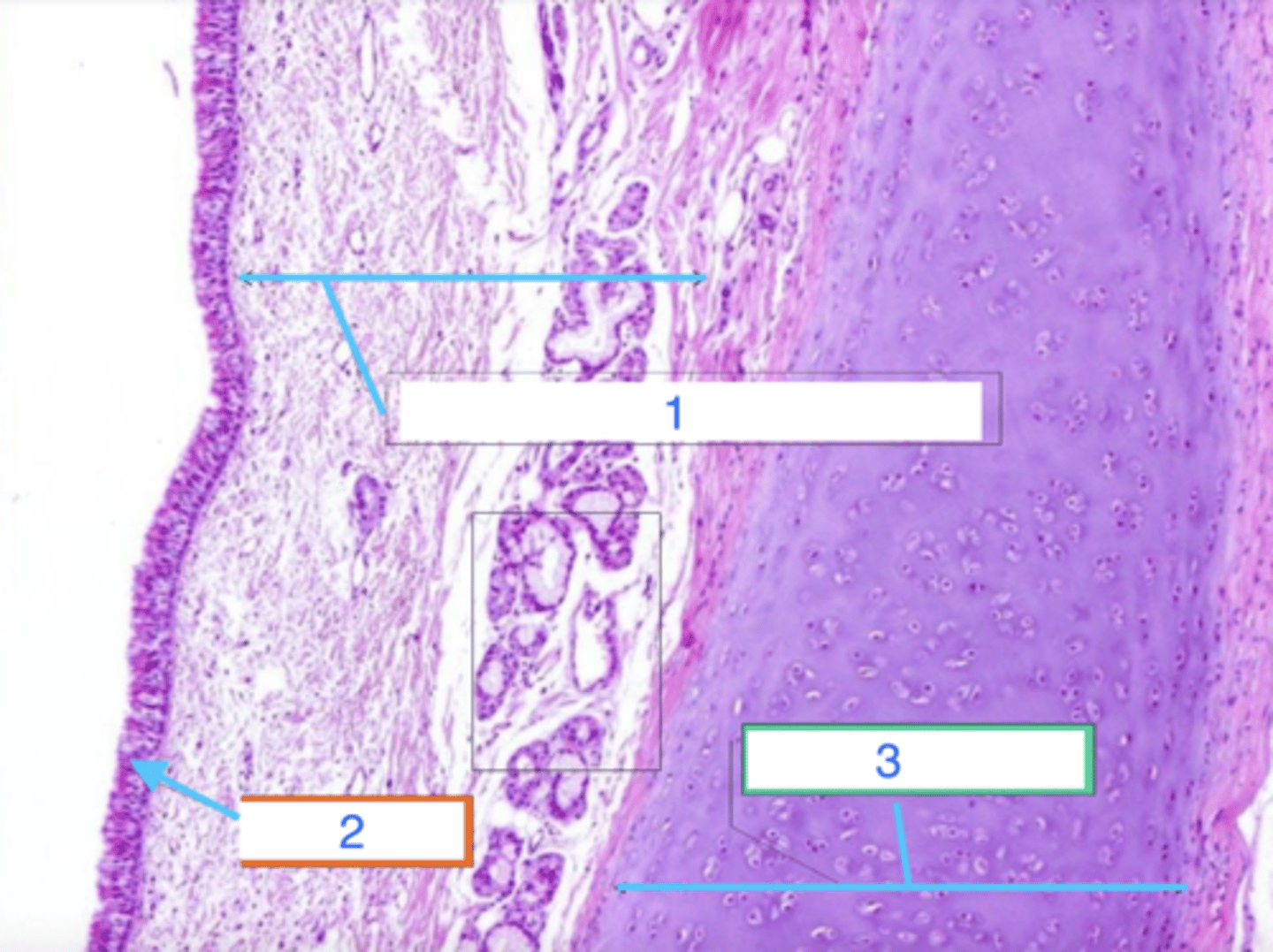
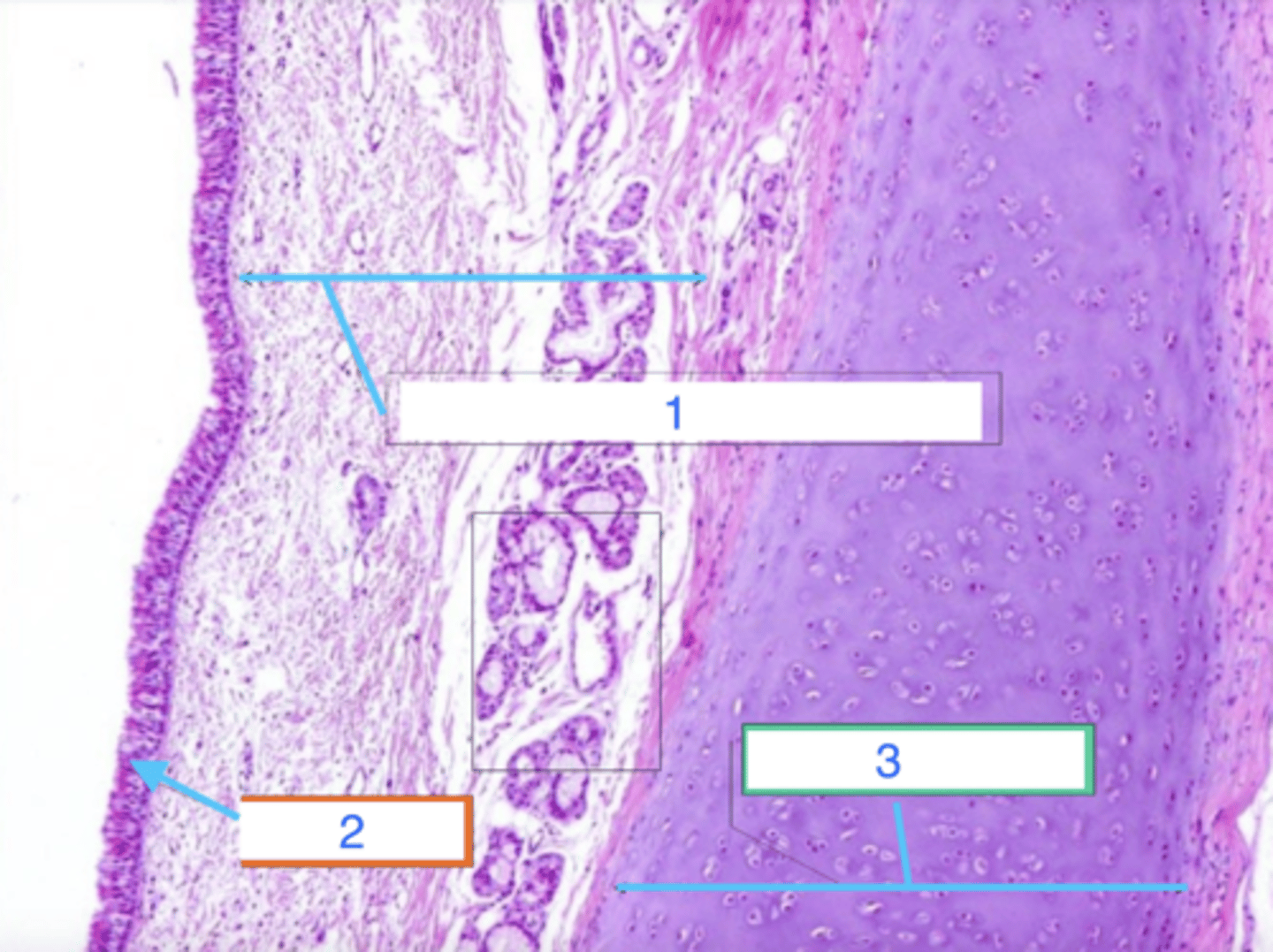
nasal vestibule
what is this?
transitional/pseudostratified columnar epithelium
what is 1?
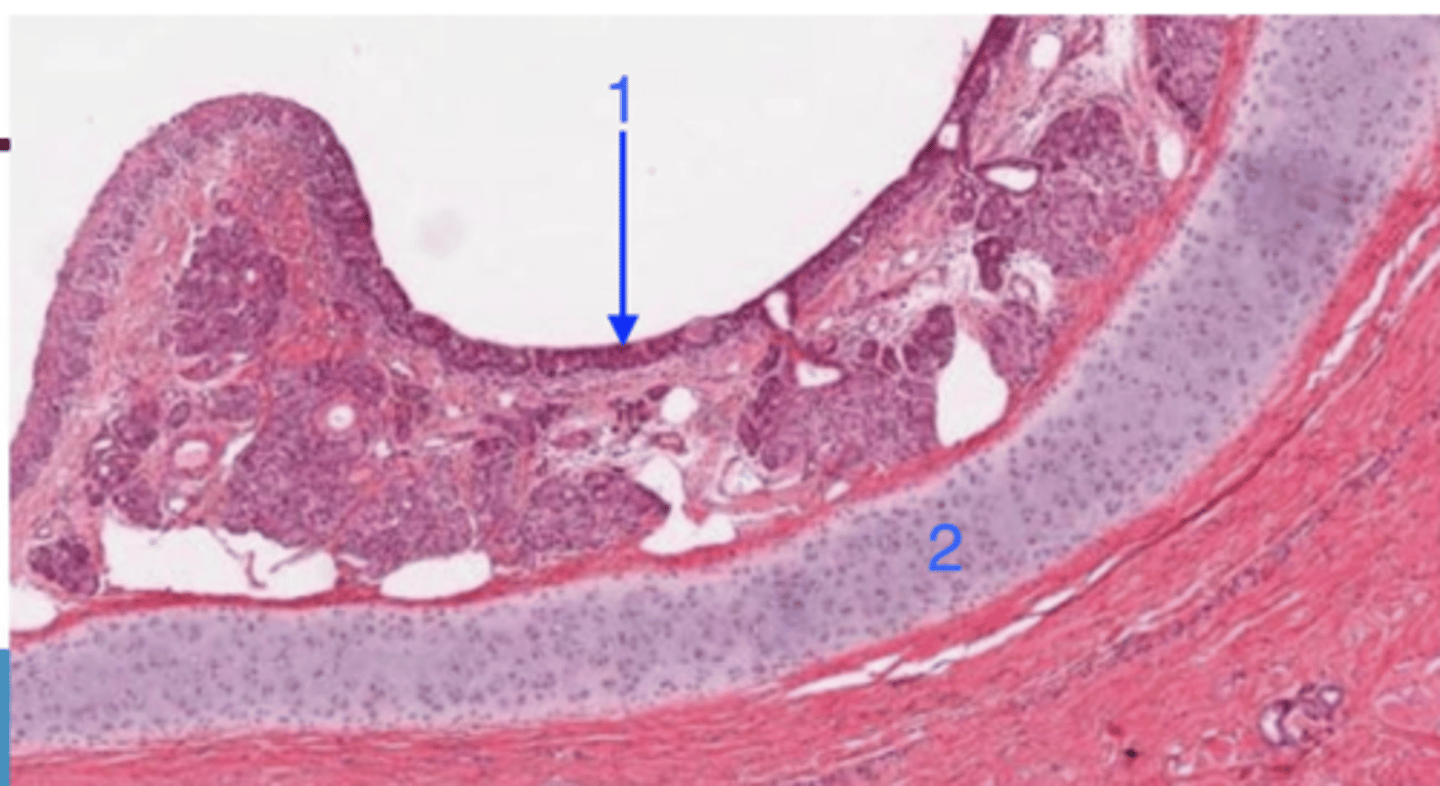
hyaline cartilage
what is 2?
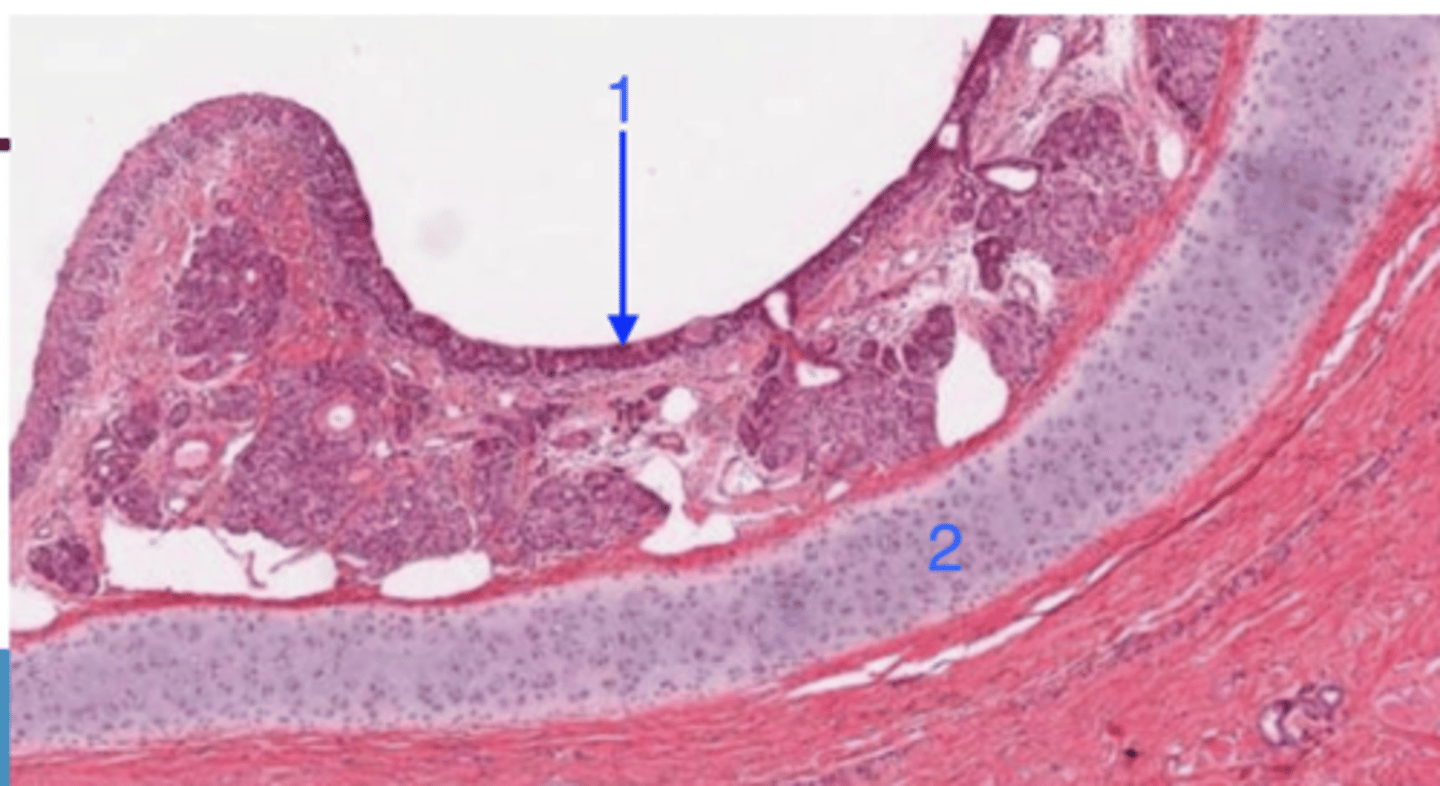
nasal cavity
where are turbinate bones found?
bipolar neurons, microvilli on columnar cells
what special structures does the respiratory epithelium of the olfactory region have?
cavities covered by respiratory epithelium
what are paranasal sinuses?
respiratory epithelium, nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
the nasopharynx/soft palate consists of what?
olfactory region
where in the respiratory system would you find bipolar neurons?
nasopharynx and epiglottis
where in the respiratory system would you find nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
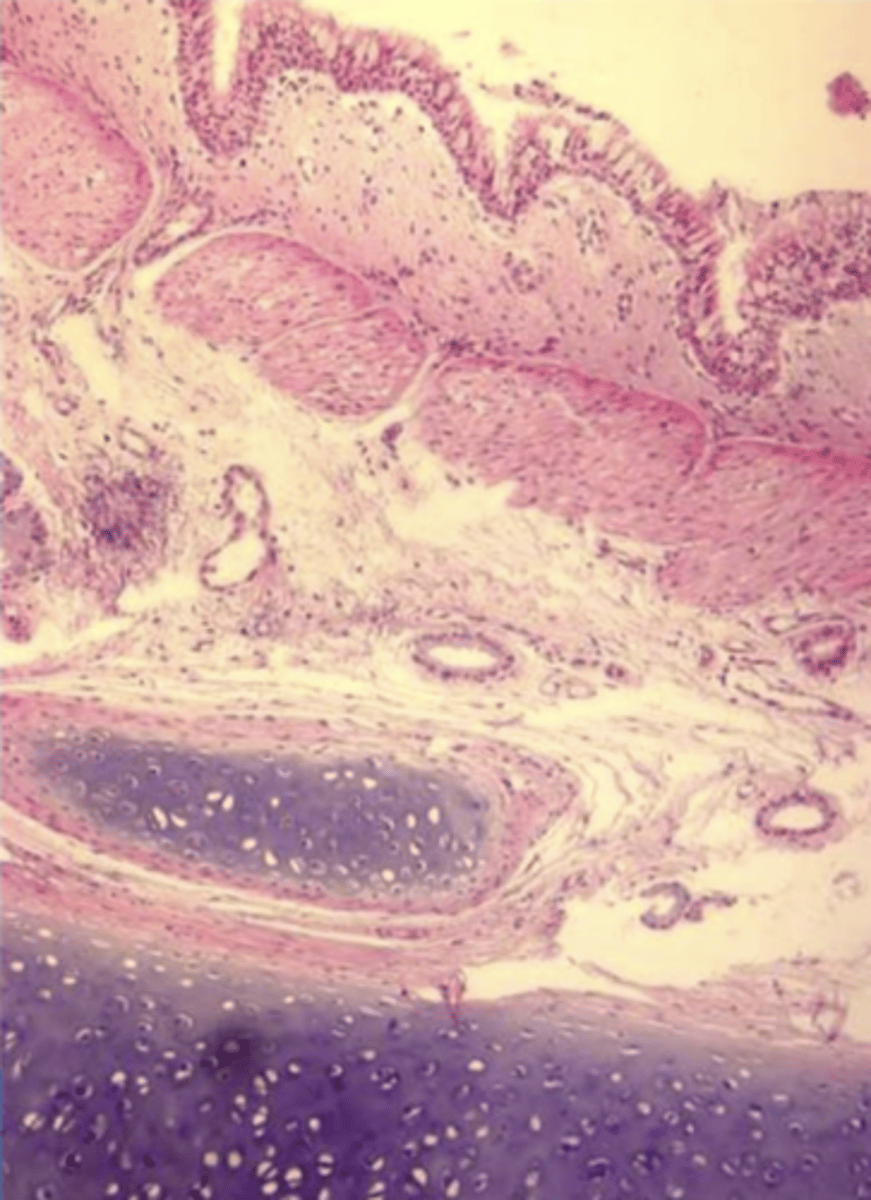
cartilage covered by mucosa
the larynx is composed of..
hyaline- thyroid and cricoid
elastic- epiglottis and arytenoids
what type of cartilage makes up the larynx?
elastic
what type of cartilage composes the epiglottis?
elastic
what cartilage composes the arytenoids?
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the epithelium of the epiglottis like?
respiratory epithelium
most of the larynx (- the epiglottis) has what type of epithelium?
defense cells and mucous glands
what do you find in the lamina propria of the larynx?
hyaline cartilage
what is this?
thyroid and cricoid cartilages
in what parts of the larynx would you find this?
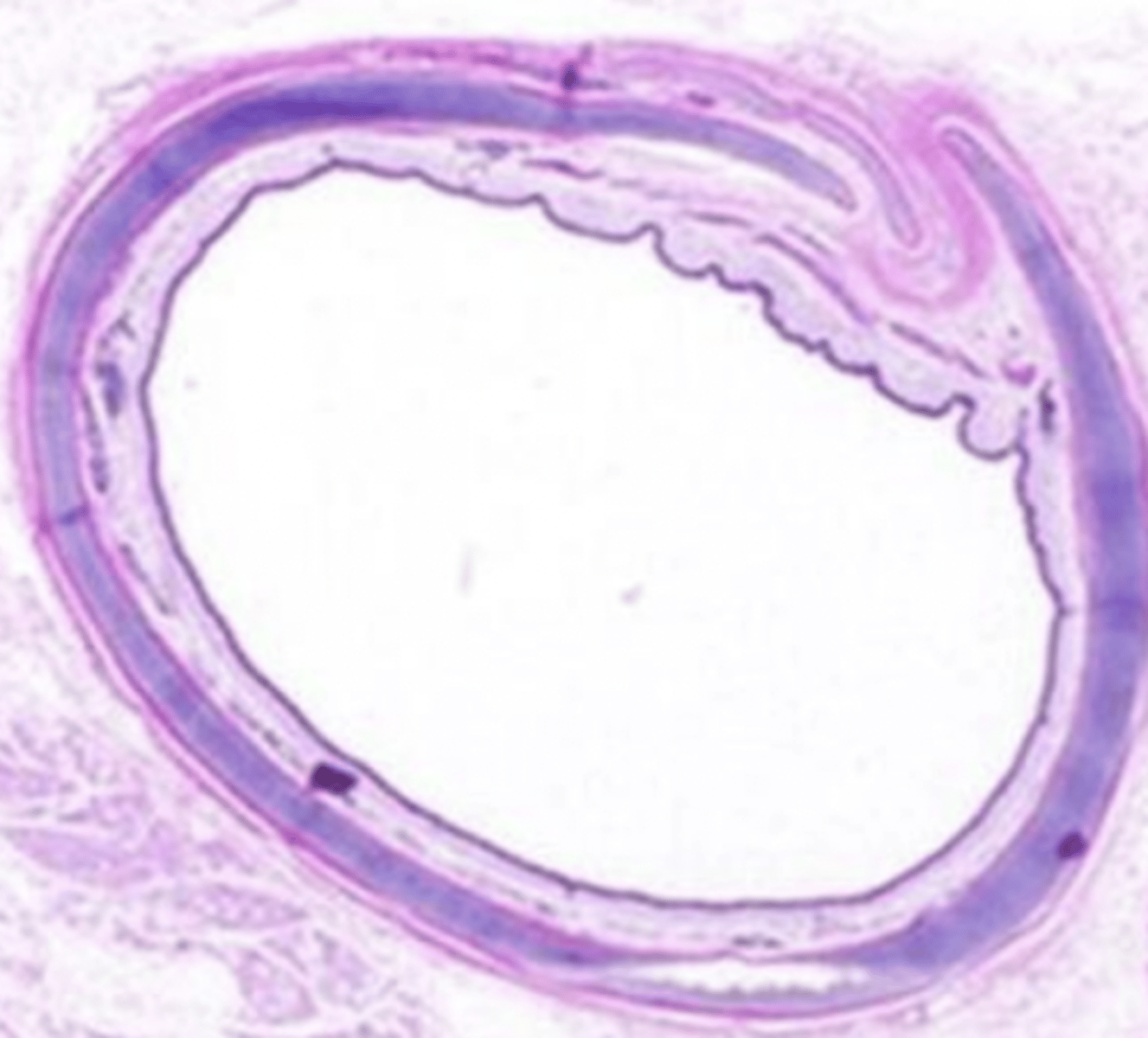
respiratory epithelium (with goblet cells, basal cells, and columnar ciliated epithelium)
what type of epithelium is in the trachea?
yes
can you find cilia in the trachea?
yes
can you find goblet cells in the tracea?
trachea
which organ has no barrier between the lamina propria of the mucosa and the submucosa?
loose CT, tracheal (seromucous) glands, lymphoid tissue, nerve ganglia
describe the contents of the lamina propria/submucosa of the trachea
C-shaped, gap filled by smooth muscle
describe the cartilage of the trachea
trachea
what organ is this?
lumen
what is 1?
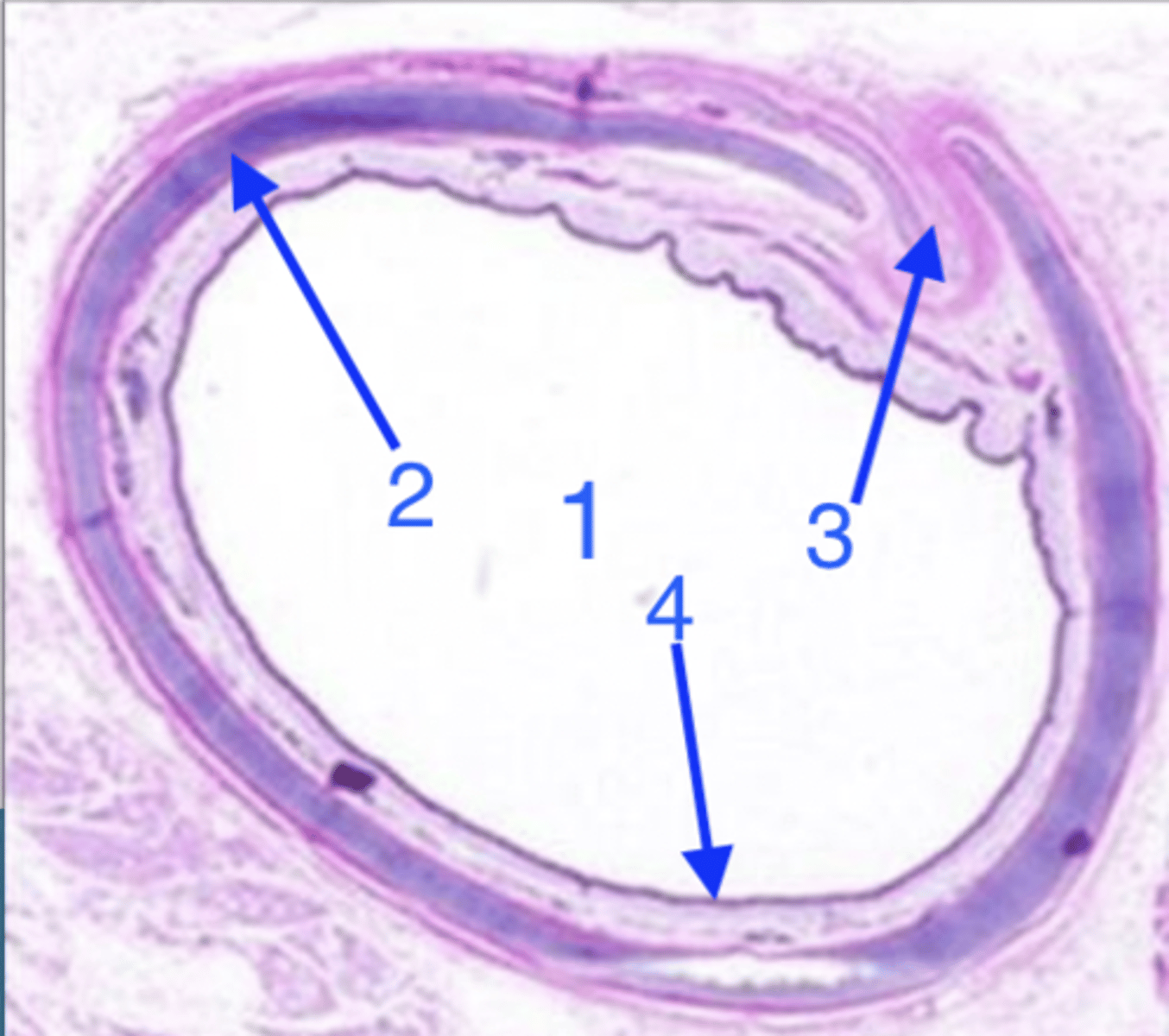
hyaline cartilage
what is 2?
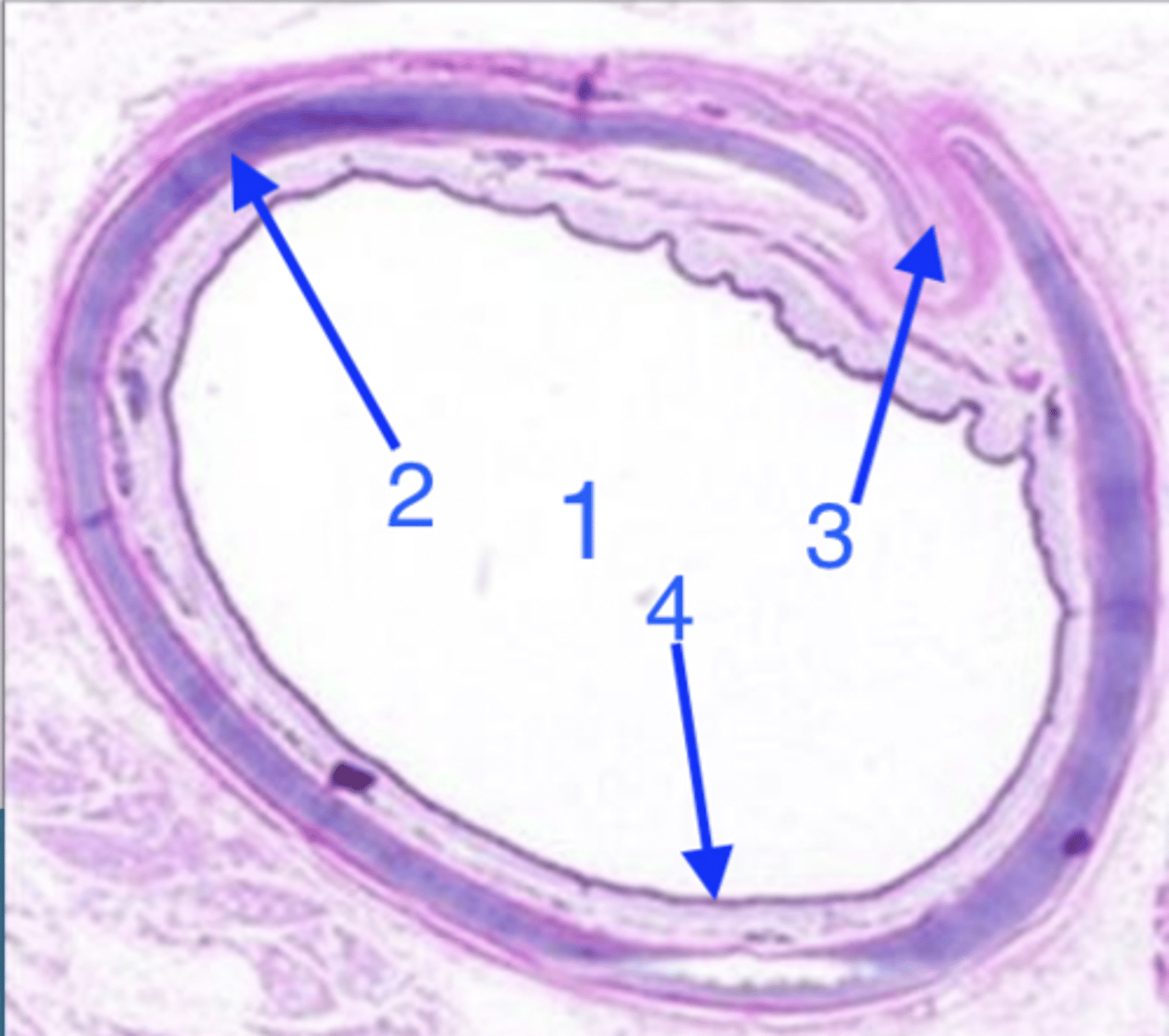
smooth muscle
what is 3?
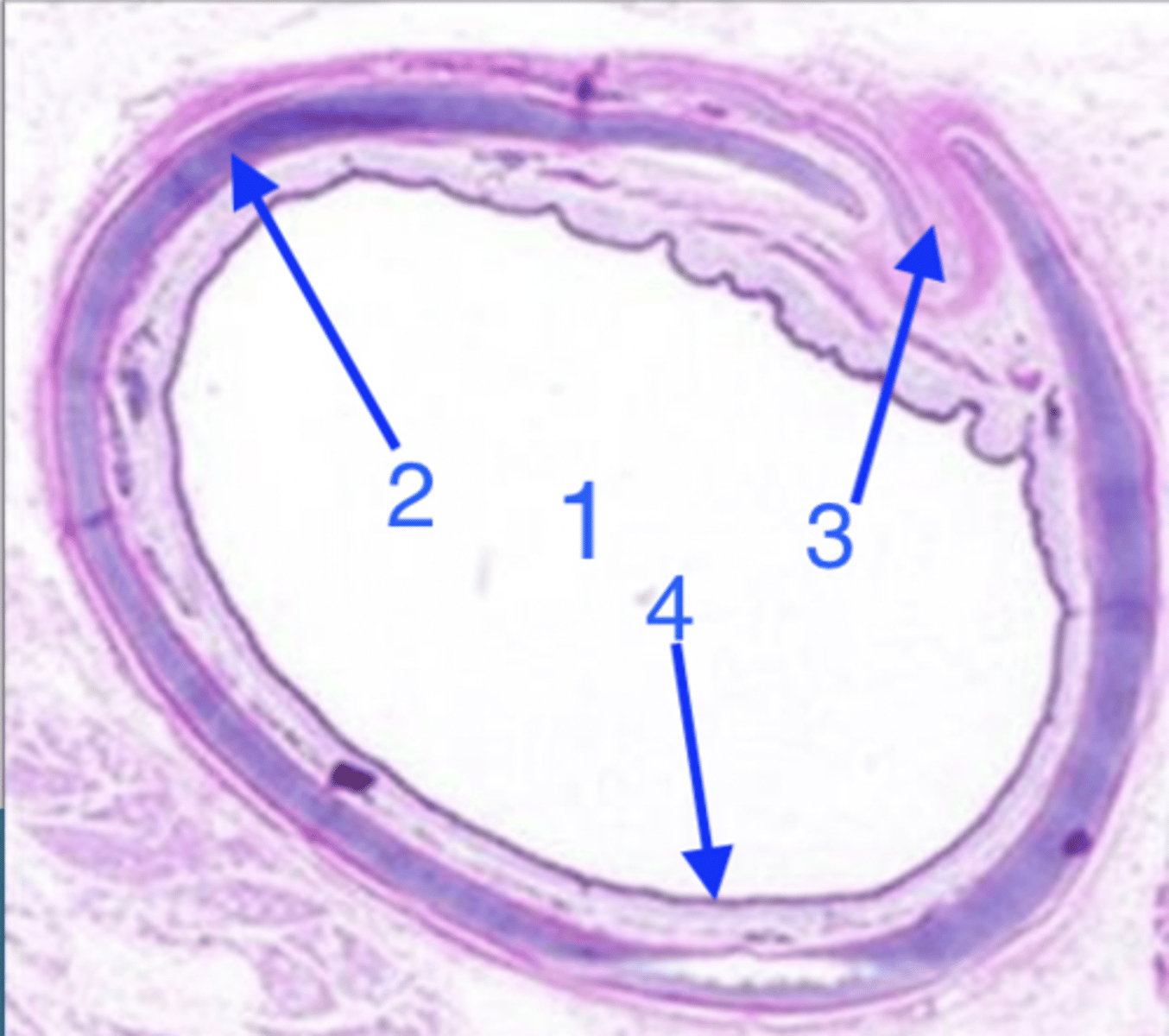
epithelium and lamina propria/submucosa
what is 4?
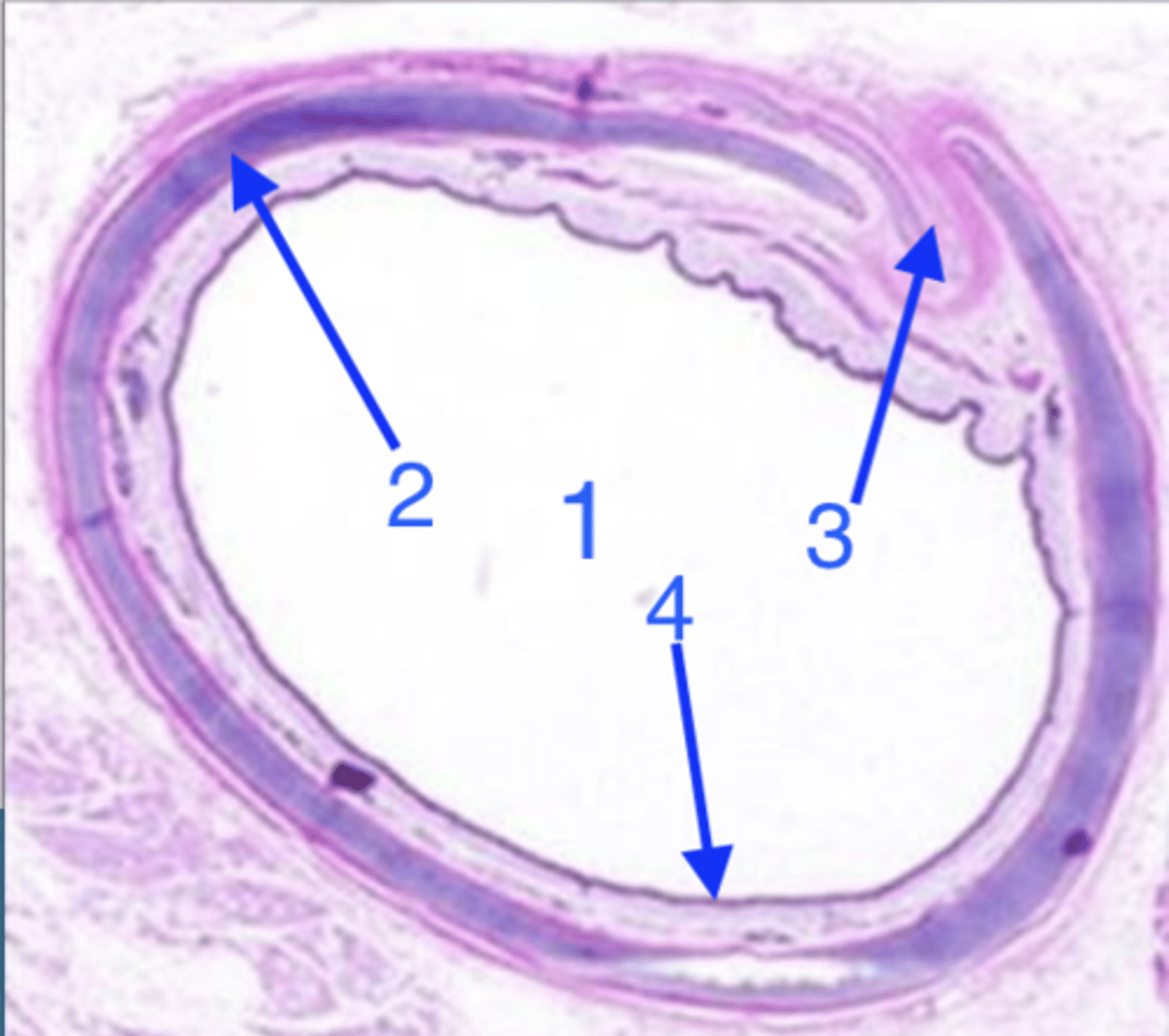
lamina propria and submucosa
what is 1?
respiratory epithelium
what is 2?
hyaline cartilage
what is 3?
the trachea has C-shaped cartilage rings, and the bronchus has incomplete cartilage plates (less cartilage)
how can you differentiate the trachea from the bronchus?
it begins to disappear
as you go deeper into the respiratory system, approaching the lungs, what happens to the cartilage?
more elastic fibers
what is special about the mucosa of bronchi?
bronchus- random hyaline cartilage plates, respiratory epithelium with goblet cells
what is this? why?
yes
do bronchi have goblet cells?
bronchus: no blood in lumen, columnar epithelium, cartilage
vessel: usually blood in lumen, squamous epithelium
how can you distinguish bronchus from a vessel?
no
do the bronchioles have goblet cells?
bronchus- hyaline plates, respiratory (columnar) epithelium
blood in lumen is abnormal
what is this? why?
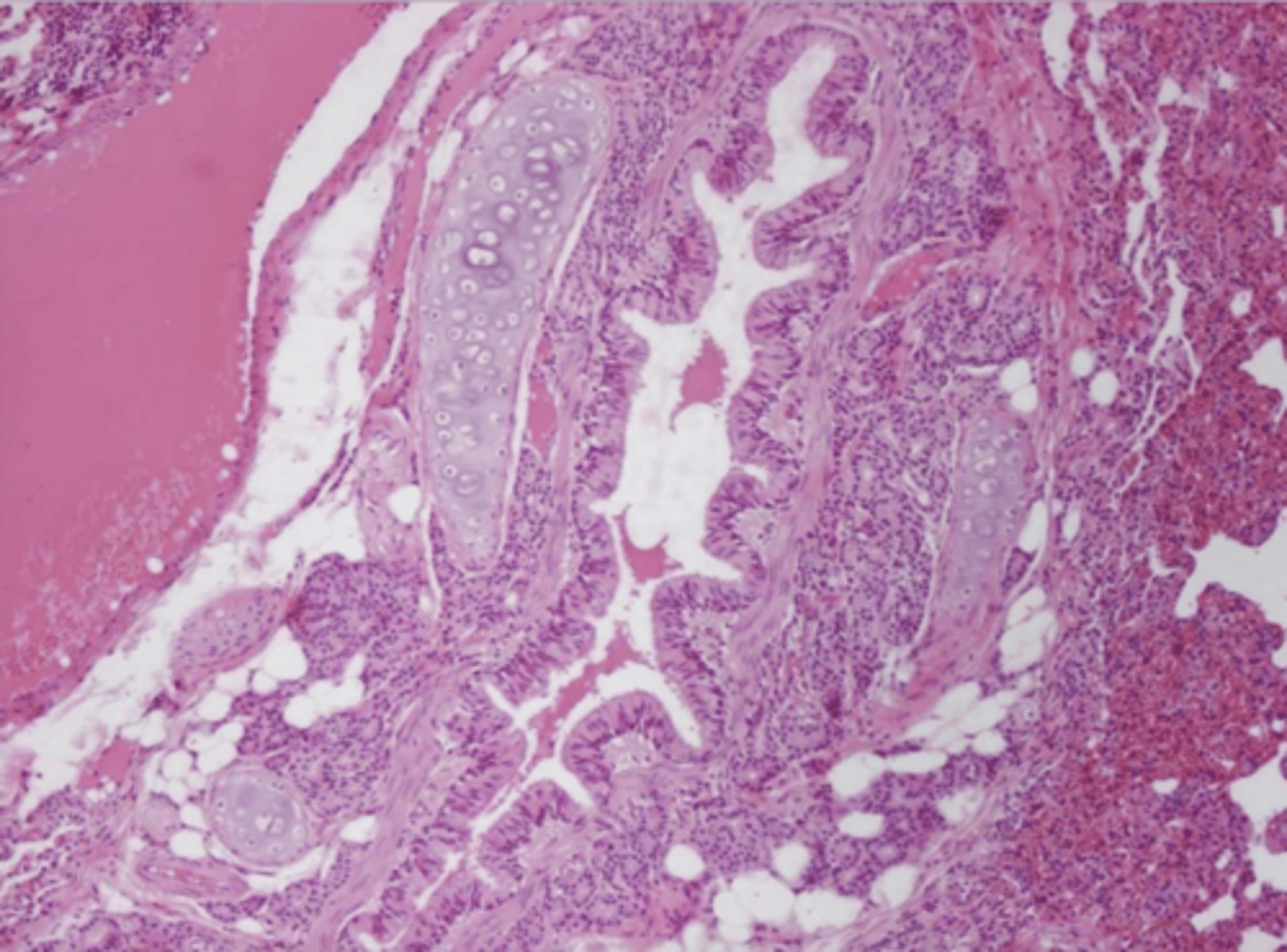
no
do bronchioles have glands?
no
do bronchioles have cartilage?
yes, a lot
do bronchioles have muscle?
yes, but it is scarce
do bronchioles have lamina propria?
cuboidal to columnar
what is the epithelium of a bronchiole?
bronchus- cartilage, goblet cells
bronchiole- no cartilage, no glands, thin walls
how can you distinguish a bronchus and a bronchiole?
bronchus- hyaline plates, respiratory (columnar) epithelium
what is this? why?
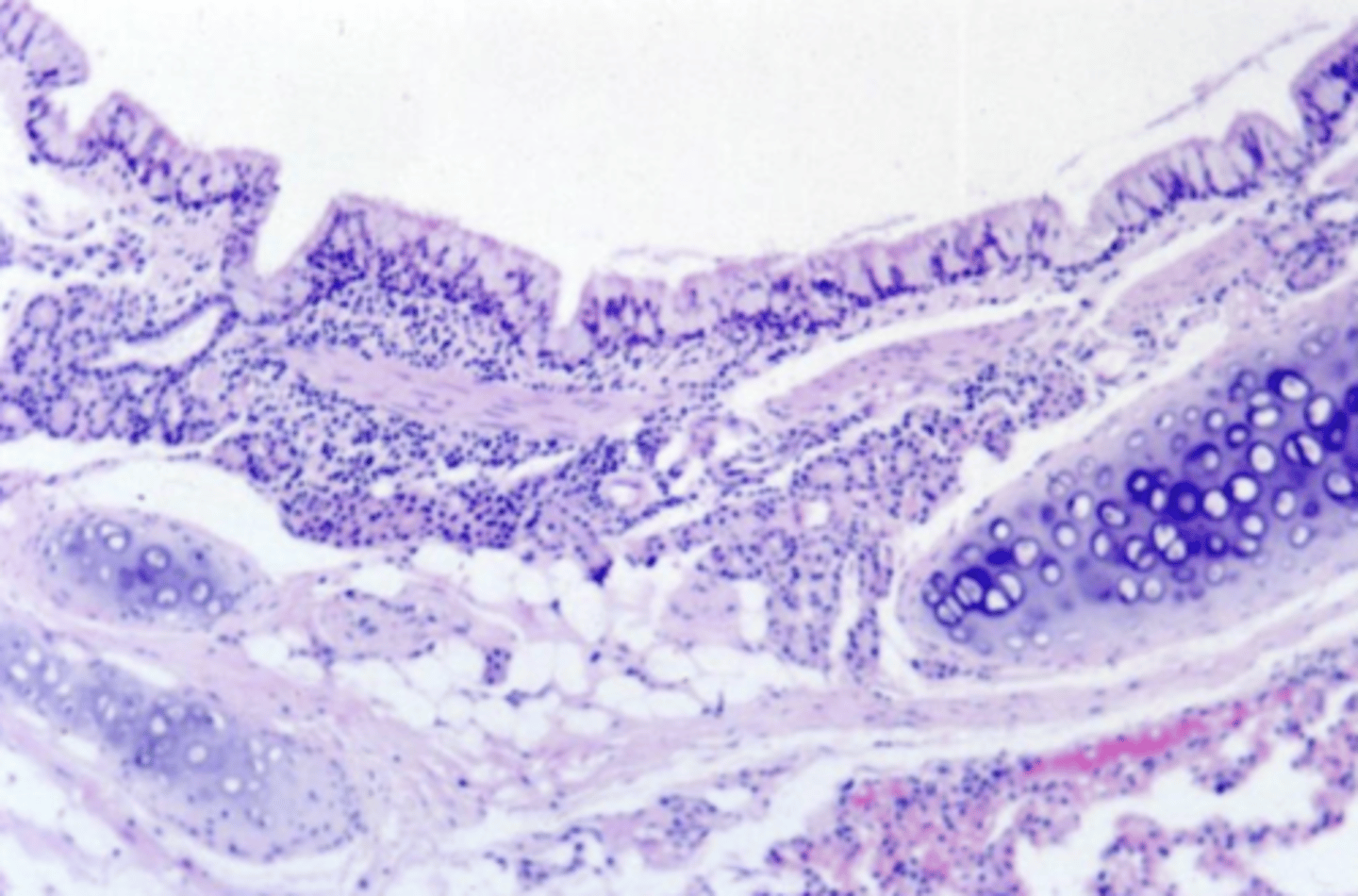
bronchus- hyaline plates, respiratory epithelium
what is this? why?
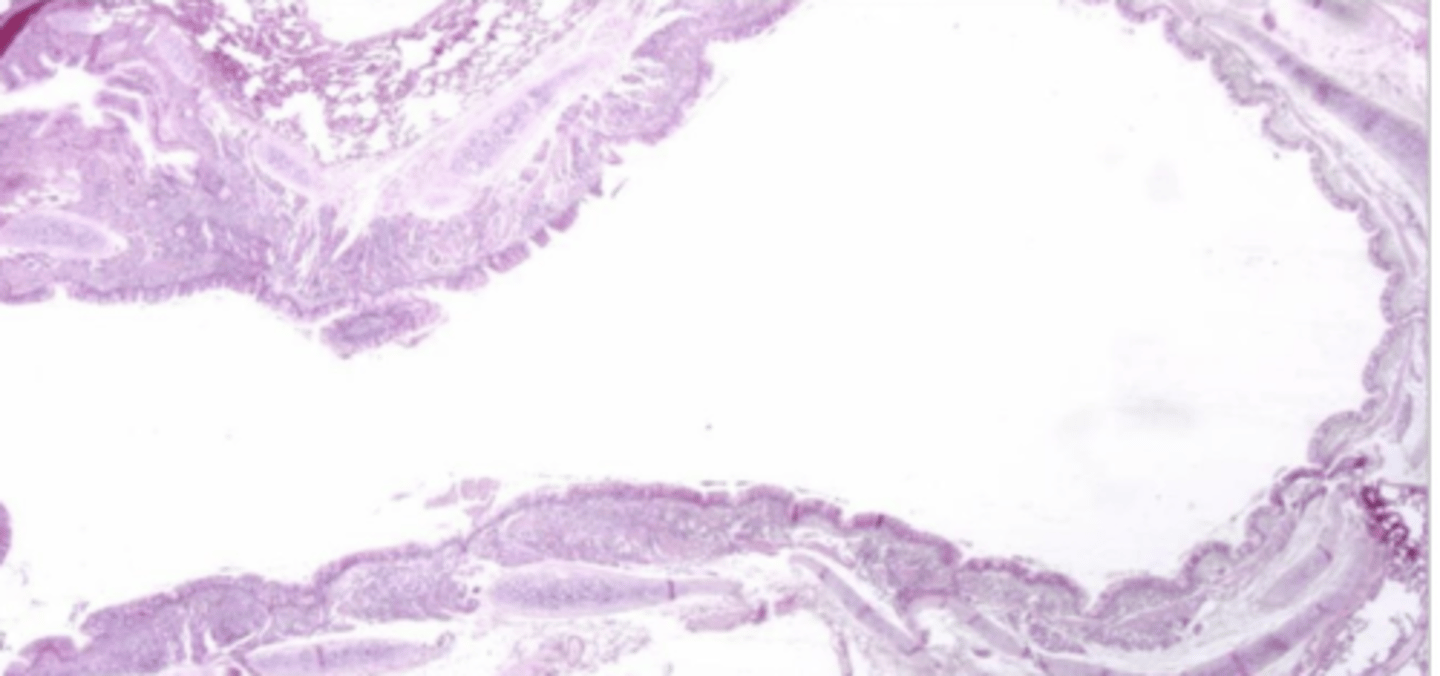
bronchioles- no cartilage or glands, right next to vessel
what are the 2 circles?
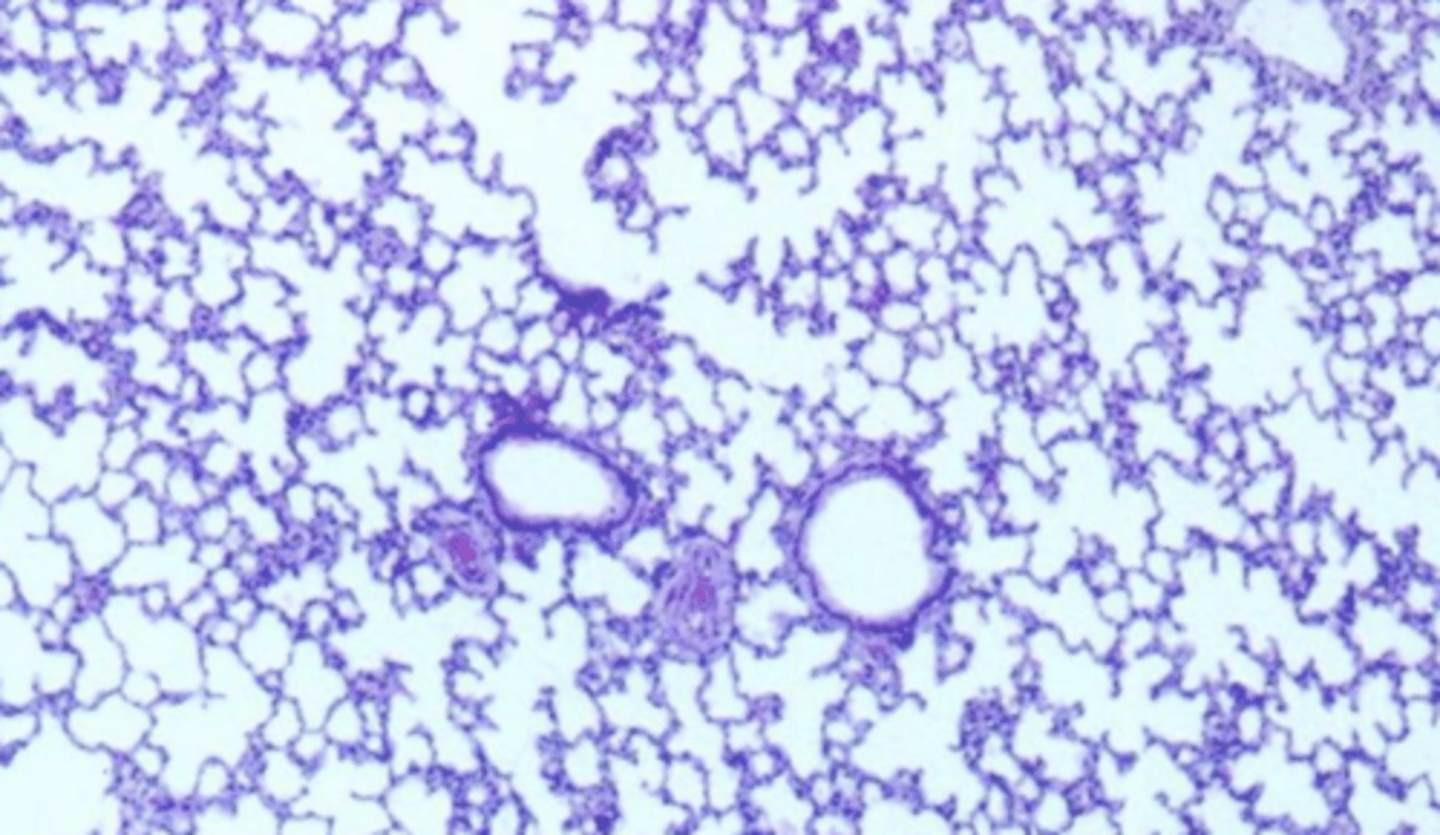
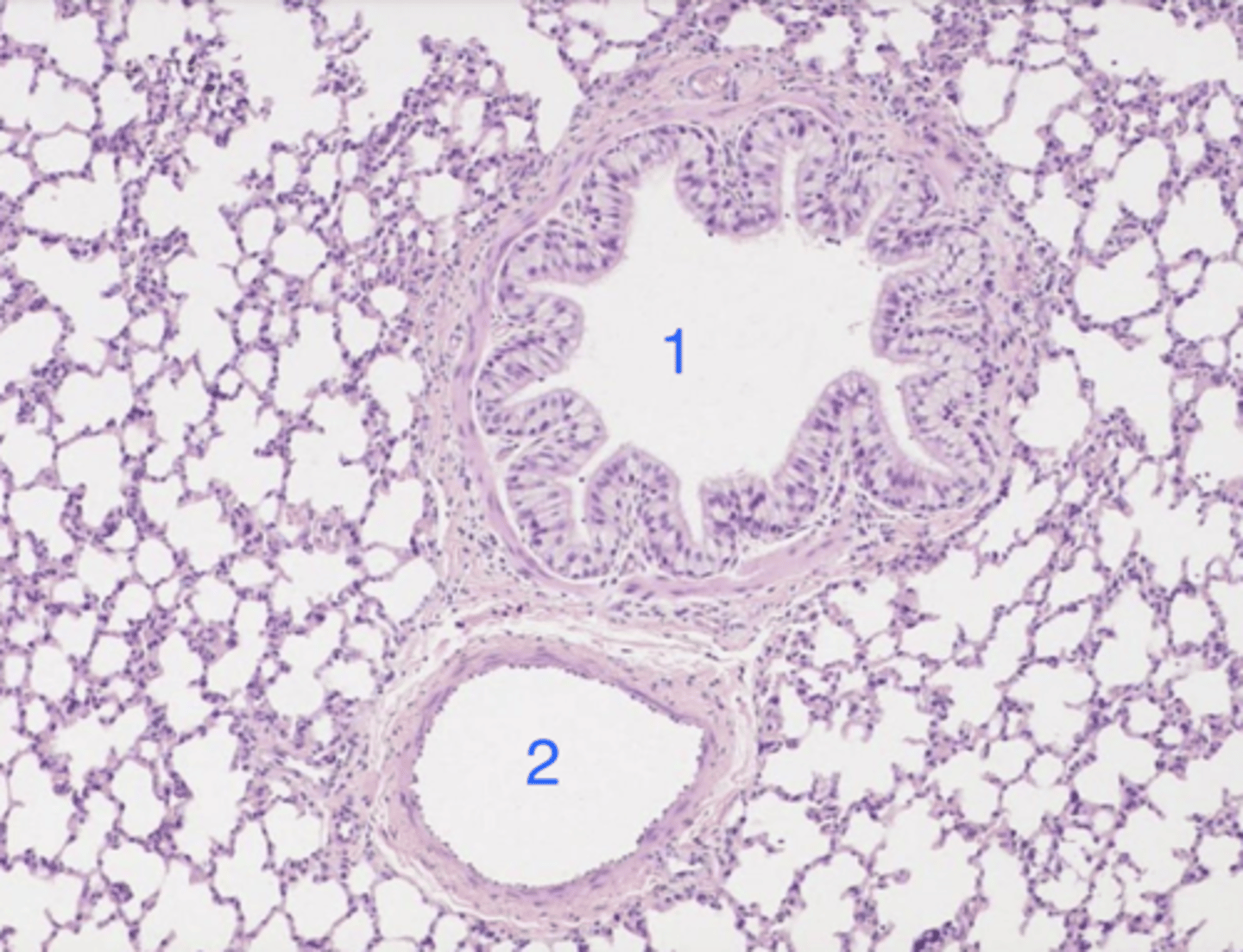
bronchiole- no cartilage or glands, but muscle and columnar epithelium
what is 1? why?
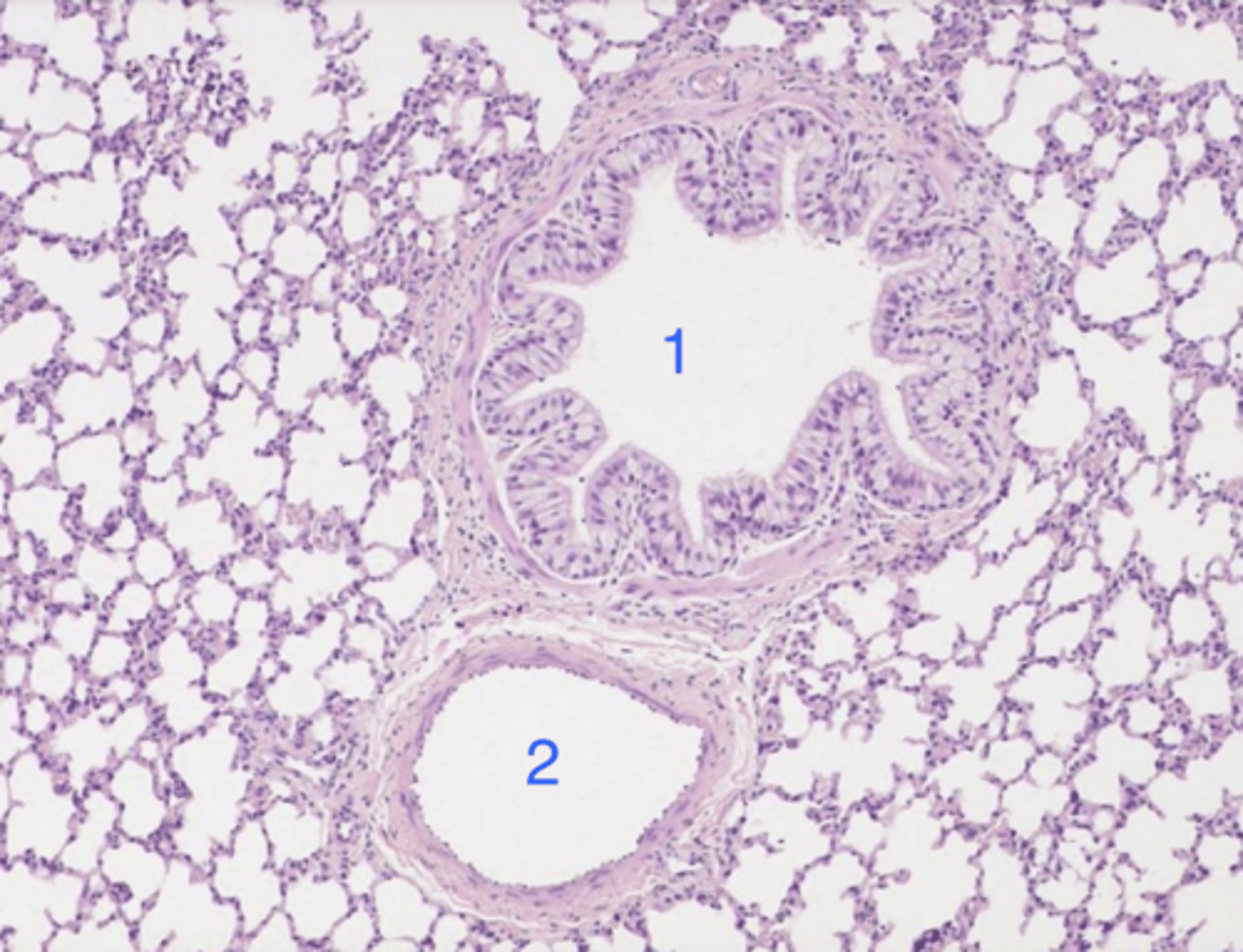
artery- simple squamous epithelium
what is 2? why?
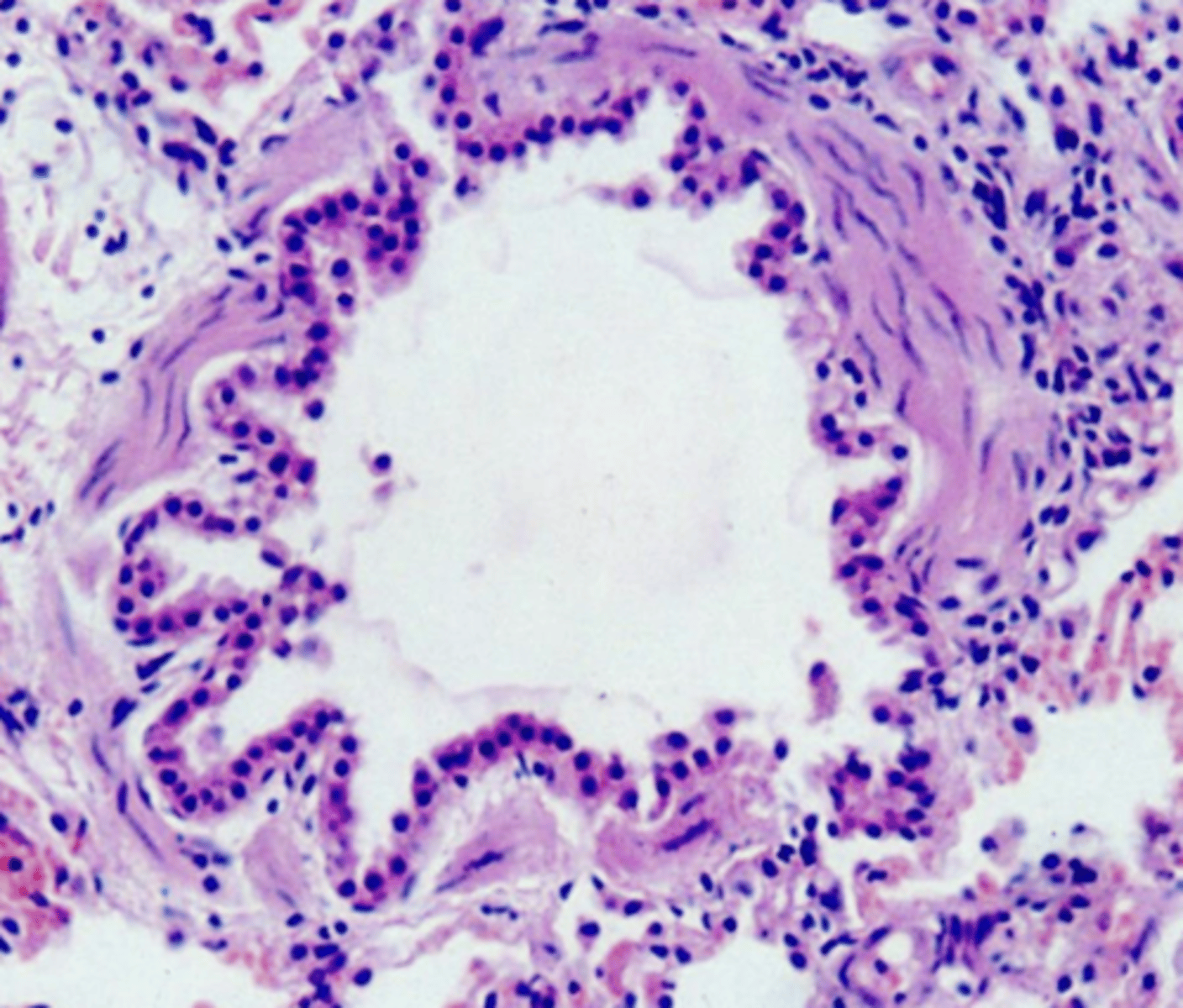
bronchiole- cuboidal epithelium, no cartilage, no cilia, no glands
what is this? why?
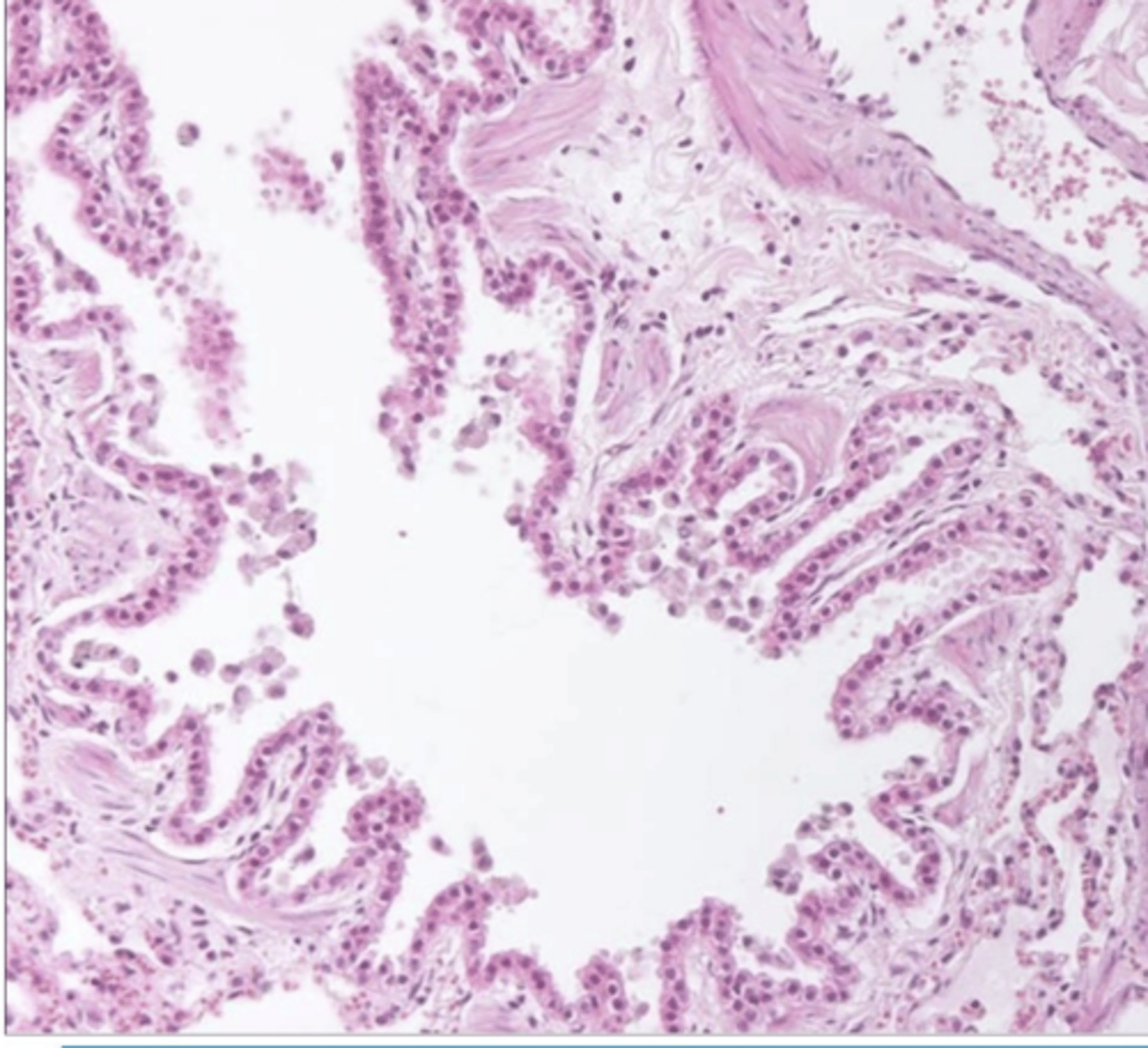
bronchiole- cuboidal epithelium, no cartilage, no cilia, no glands
what is this? why?
groups of alveoli
what are alveolar sacs?
cuboidal epithelium, smooth muscle in openings
what is the composition of alveolar ducts?
neumocytes
what special cells are in alveoli?
connective tissue and blood vessels
what is in the interalveolar space?
alveoli
what are all of these?
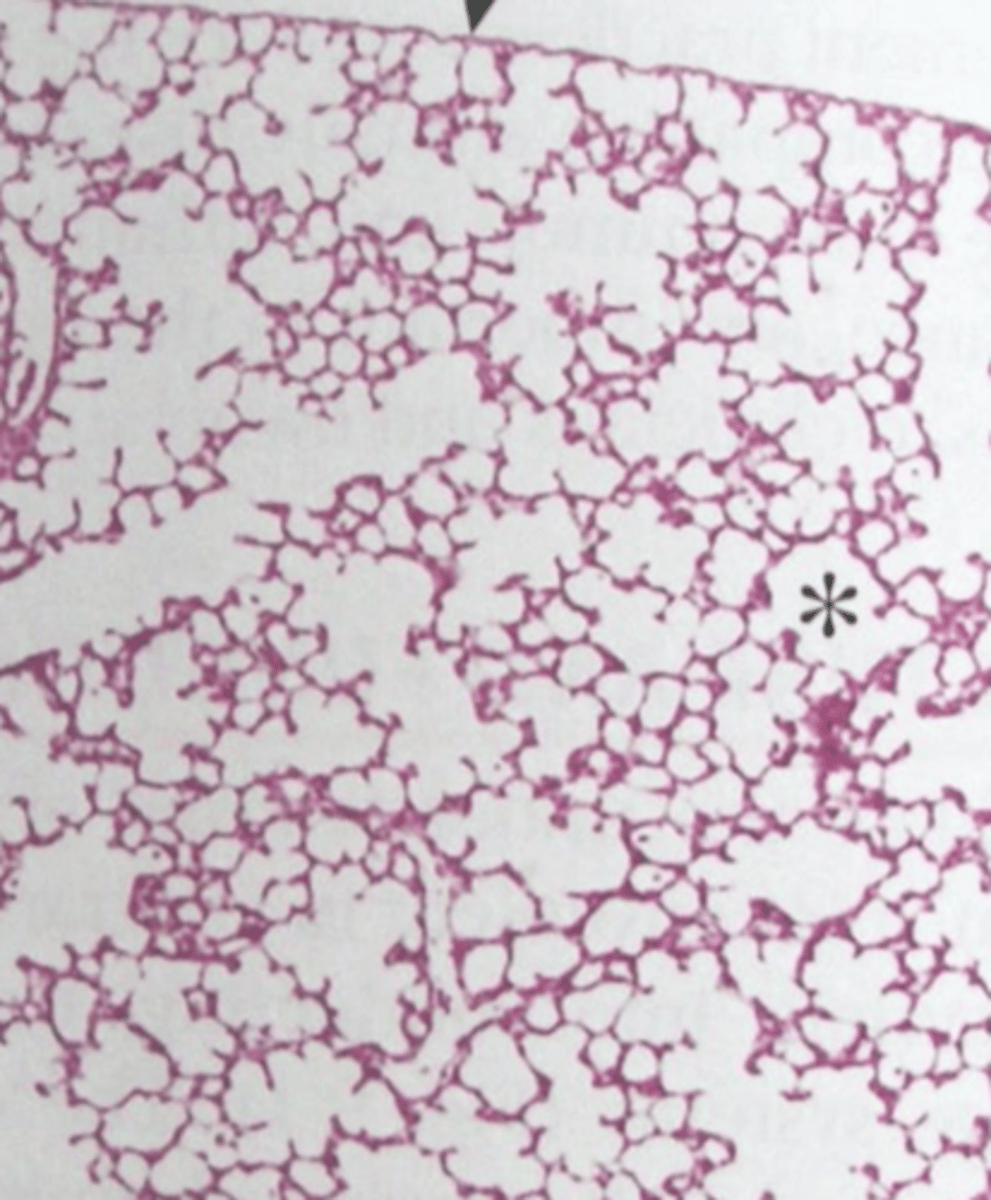
in the epithelium of alveoli
where do you find neumocytes?
fibroelastic connective tissue and mesothelium
what is the visceral pleura of the lungs composed of?
no
does the pleural cavity have fluid?