BIOL 2460 chapter 7
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Macronutrients
The six key elements that organisms need in relatively large amounts: Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur
• 99% of cell dry weight
• 4 most common: H, C, O, N
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals needed in small amounts. : Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium, Zinc, Iron, Calcium, Molybdenum, Copper, Cobalt, Manganese, Vanadium
Organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon.
• Mostly larger and more complex
• Form cell structures
• Held together by covalent bonds
Inorganic molecules
no carbon
• Simpler and smaller
• Do not form cell structure
Carbon Skeletons
Framework of carbon atoms in organic molecules. Arrangements can be chain, branched, or cyclic
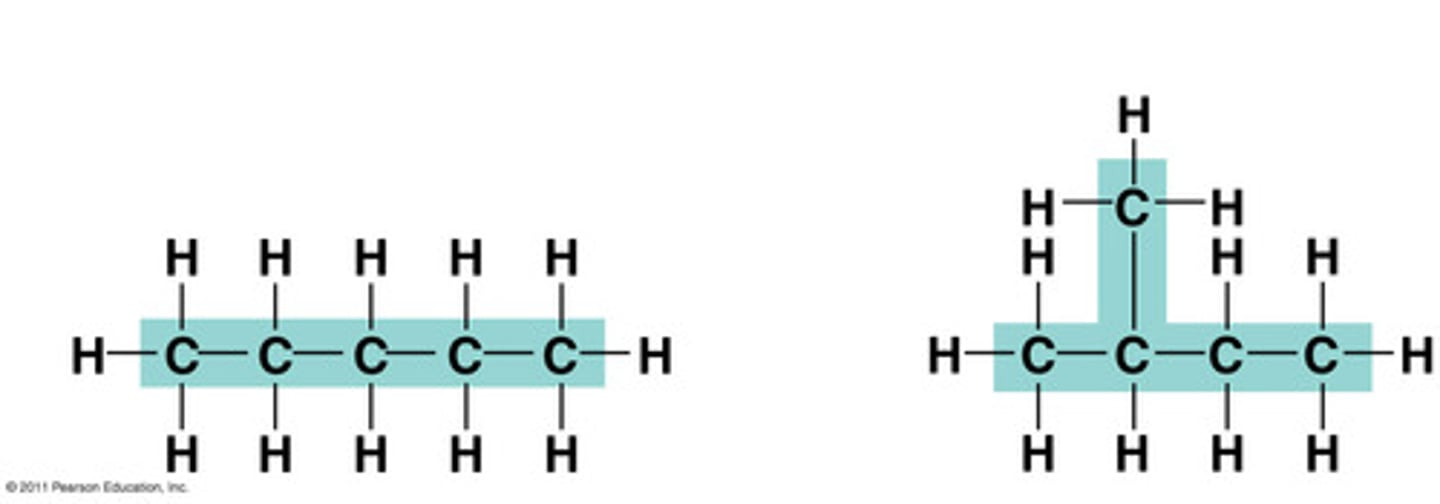
Structural isomers
carbon molecules with the same formula but different arrangement
Stereoisomers
same sequence, same structure, but different 3D shape
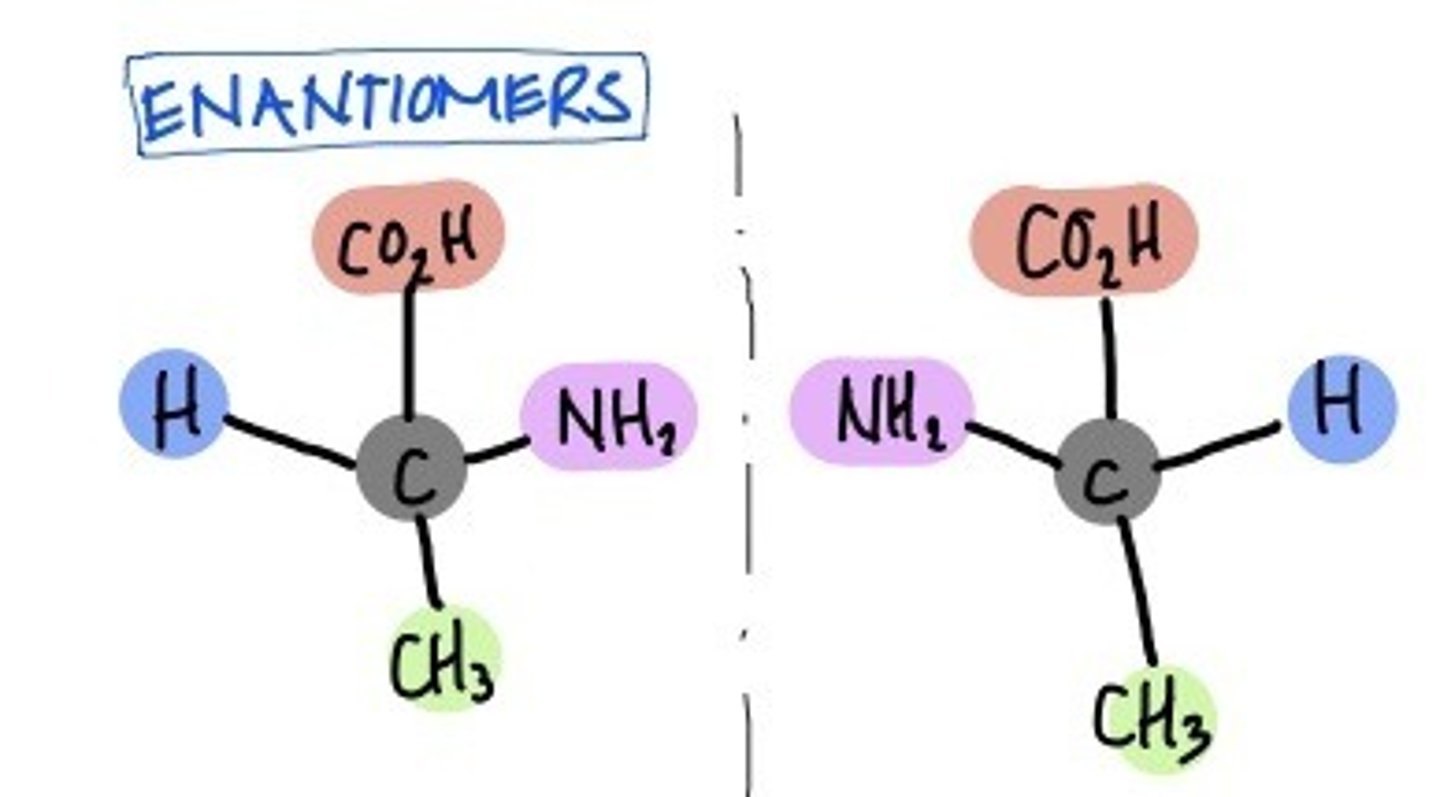
Enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
• Organisms may only want one type of enantiomer
• Can give drugs different therapeutic effects
Biological Functional Groups
Groups of atoms with a specific chemical composition attached to a carbon chain, branching, or cyclic formation
Monomers
building blocks of (most) macromolecules
Polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.. Forms some polymers.
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Carbohydrates
Most abundant macromolecule. Serves as a food source, a structure, and a transmitter of genetic information. Provides energy in the form of starch and glycogen.
Monosaccharides
simplest building block of carbohydrates (monomer): glucose, fructose, galactose
•Classified on carbonyl group placement (C=O)
and the number of carbons
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides. polymer chain of monosaccharides.
• Bonded with a glycosidic bond
• Examples: agar, cellulose, starch, chitin, peptidoglycan
Disaccharides
chain of two monosaccharides
•Bonded with a glycosidic bond
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Nutrients and energy storage, structure for membranes and hormones. : Fatty acids, phospholipids, Isoprenoids/Sterols
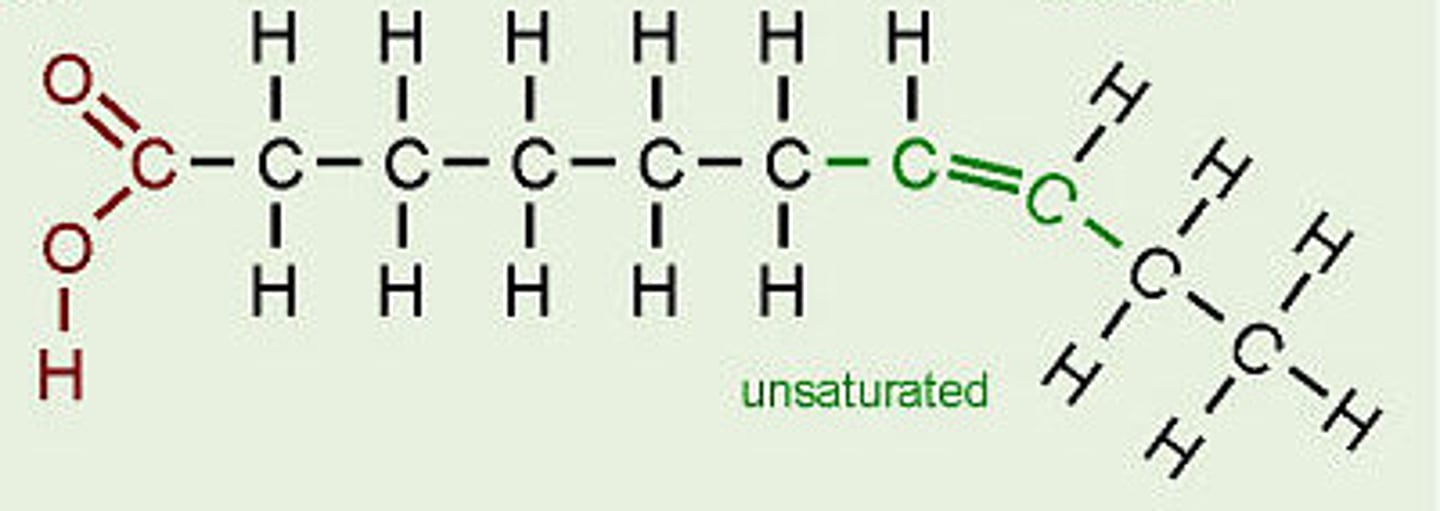
Fatty acids
Long-chain hydrocarbons with terminal
carboxylic acid
•Hydrophobic/non-polar
•Saturated or unsaturated groups
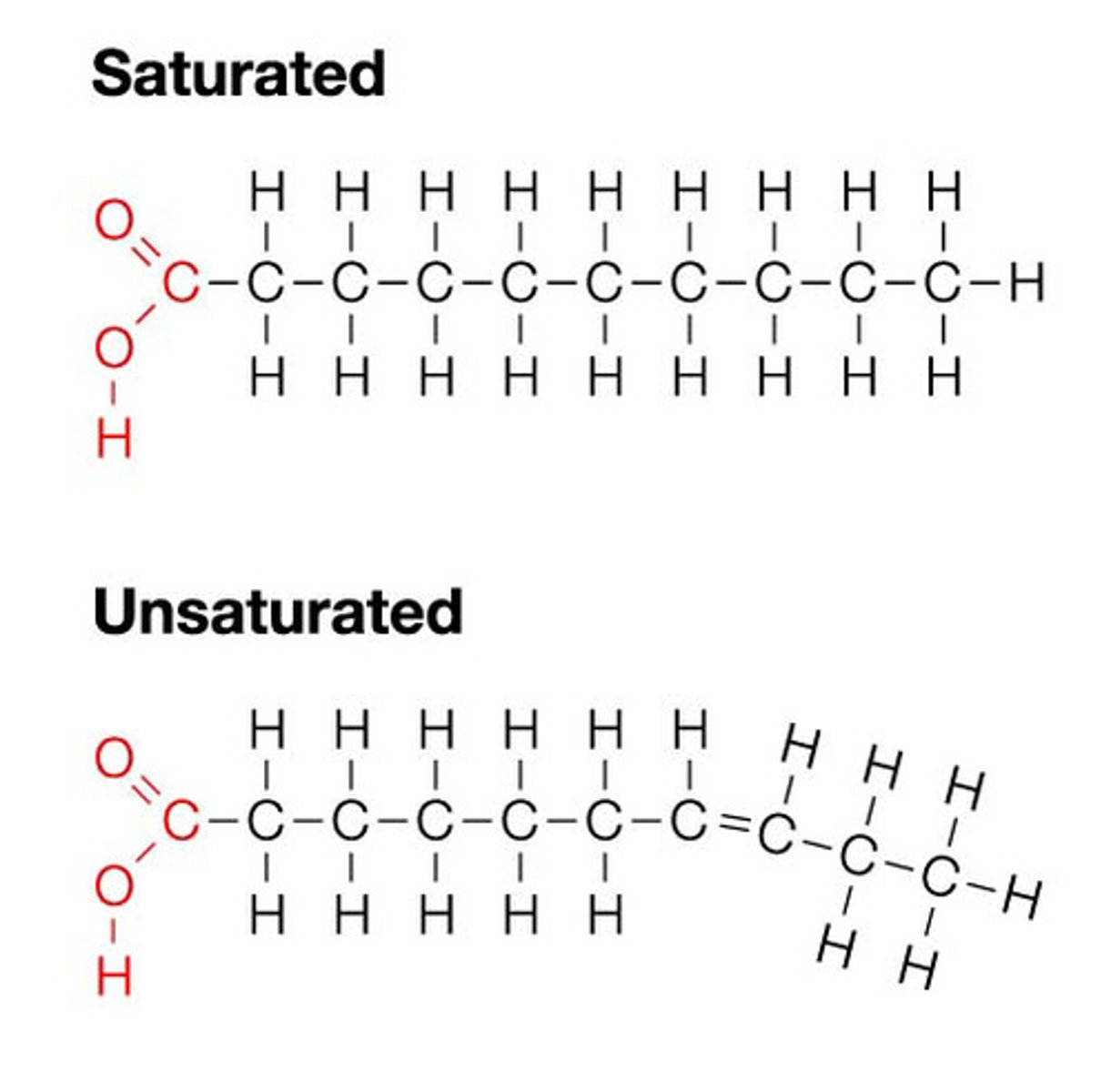
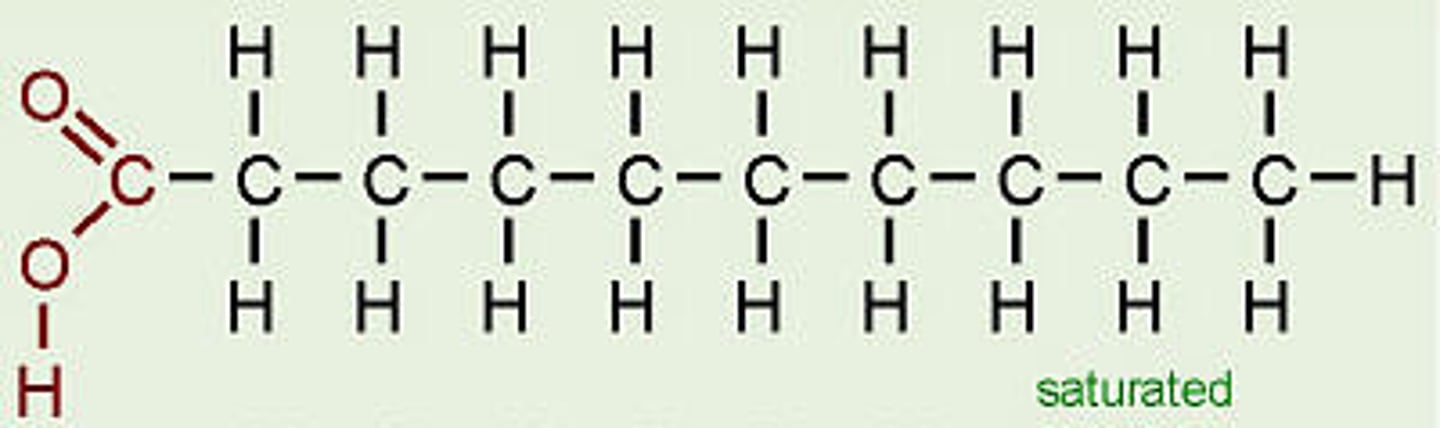
Saturated fatty acids
no double bonds. Liquid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
have one or more double bonds. Solid at room temperature
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids + glycerol molecule
•Common to adipose tissue & sebum oil
•Three fatty acid chains are bound to glycerol by dehydration synthesis
Phospholipids
lipids with a phosphate group
•Chains may be saturated or not
•Amphipathic allows for various formations
Micelles
tiny spherical complexes of emulsified fat that arise during digestion; most contain bile salts and the products of lipid digestion
Isoprenoids
branched lipids (aka terpenoids)
• Uses: pharmaceuticals, pigments, fragrances
•Found in many hydrophobic oils & waxes
•Many bacteria rely on isoprenoids
Ex. Propionibacterium acnes
Steroids
Rigid structure in membranes(especially when no wall is present)
•Fungi & protozoa - ergosterol
•Bacteria - hopene
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids
Amino acids
H atom + carboxyl + amino + side chain
Polymerization
Joining monomers to form a polymer occurs via a peptide bond & dehydration synthesis.
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary protein structure
coiling or folding of a polypeptide due to H-bonding between amino acids. ⍺ helix & β sheets
tertiary protein structure
3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
quaternary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain. combined subunits
MALDI-TOF
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionizationtime-of-flight mass spectrometry
FAME
fatty acid methyl ester analysis
PLFA
phospholipid-derived fatty acids analysis
Proteomic analysis
the study of all accumulated proteins of an organism; can also be used for bacterial identification
Carbohydrate analysis
Isolate and identify sugars in a sample